Psychopathology: Week 3
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Effects of loci
Large number of contributing loci, each locus effects is small and approximately equal, effects add up over loci
Biometric tradition
Can estimate genetic and environmental effects even when individual loci, genes, environments are unknown
How is the diathesis/gene- stress/environment modeled mathematically?
Biometrical decomposition
What’s the biometrical decomposition equation?
P = G + E (GxE)
P= phenotype
G= genes
E= environemnt
GxE= gene-environment interaction
Usually simplified as P= G + E
What are the expanded terms of rthe biometrical decomposition equation?
P= (A + D + I) + (CE + NE + ME)
A: Additive genetic effects
D: Dominance genetic effects
I: Epistasis genetic effects
CE: Shared environment
NE: nonshared environment
ME: measurement error
What is the additive genetic effect?
A: effects of alleles taken singly aggregated across loci
What do shared environements mean in the biometrical decomposition?
CE: environemtn that contributes to sibling similarities
What do non-shared environments mean in the biometrical decomposition?
NE: environment that contributes to sibling differences
Measurement error in the biometrical decomposition equation
ME: errors in measuring the phenotype as well as short-term temporal instability
What does “e” mean in the biometrical decomposition equation?
It is the non-shared environment and the measurement error added together
Phenotypic variance model (original, expanded, and simplified to equal 1)
Original:
VP= VG + VE
Variance of G is how different genes are, variance of E is how different enviornments are
Expanded:
VP= VA + VCE + VNE +VME
Adds up to 1:
1= a² + c² + e²
a²=heritability
c²= shared environment
e²= non-shared environment
What is heritability?
It is:
The proportion of phenotypic variance that is attributable to genetic variance in the sample
an index of the extent to which genetic factors currently predict phenotypic differences in the sample of individuals under study
It is not:
an index of whether a phenotype is genetically fixed or determined
Hans Eusenck and Arthur Goldberer on heritability
Eusenck: social policies aren’t necessary if things are genetically determined (such as an individual’s earning capacity)
Goldberger: Just because things are heritable don’t mean you shouldn’t do anything about it (ex: eyeglasses)
What are examples of heritable traits?
Height is highly heritable
not fixed though, also impacted by nutrition, medicine, etc.
Reading ability
a² effect is high and c² effect is low when receiving the same reading instruction
What is the equation for familial resemblance for a quantitative phenotype?
cor(P1, P2) = raa² + rcc²
ra= probability that 2 relatives share a randomly selected allele at a randomly selected locus identical by descent
ra=(1/2)n
n= degree of relationship (1st degree, 2nd degree)
rc= usually specified as 1 for reared-together relative and 0 otherwise (this is open to interpretation)
What are the familial resemblances for quantitative phenotypes based on degrees of relationship?
MZ twins reared together, apart, DZ twins, Parent-offspring, half siblings
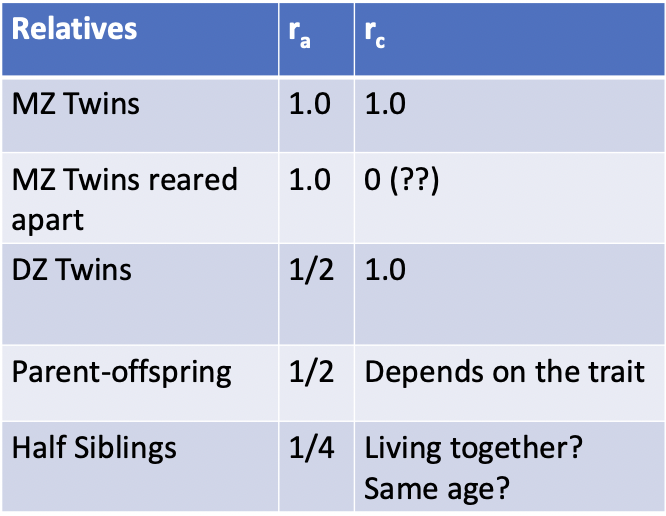
What is the principal of additivity?
There are 5 sources of variance (a2, d2, i2, c2, e2) but only 3 are usually used in practice (a2, c2, e2) to approximate the major sources of phenotypic variance
Can a precise determination of heritability (a) be found? Why or why not?
What about c and e?
Approximate estimates of heritability can be found, but not precise determinations, this is because:
heritability is not a fixed constant
assumtion are needed to calculate heritability
Additivity of genetic effects
Nature of environmental transmission
No GxE interaction
No G-E correlation
The same issues can apply to c and e