Chapter 7 AICE biology Topic 1 Structure of stems, roots, leaves, xylem and phloem
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
We better pass bro.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
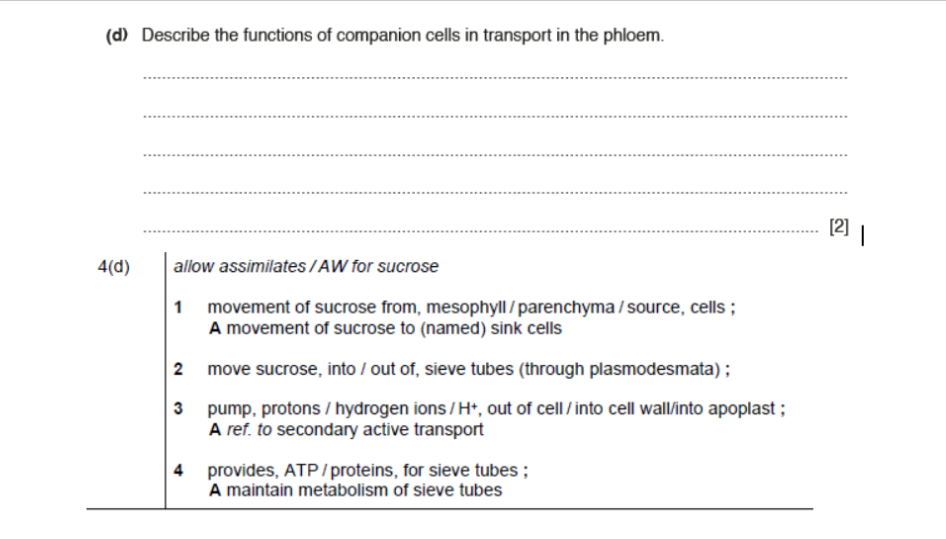
Where is the xylem found (in leaves)?
the upper side of the vascular bundle (closest to the upper epidermis)
In stems what are the bundles in which the xylem and phloem are found in?
Vascular bundles
In a stem, how are the vascular bundles arranged?
In a ring! (Xylem in the stem is towards the inside and phloem towards the outside.)
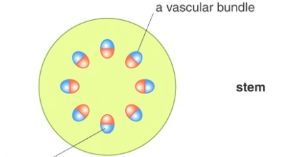
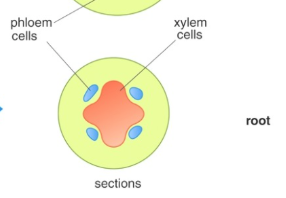
Where is the xylem in roots?
the center, and the phloem is between ‘arms’ of xylem
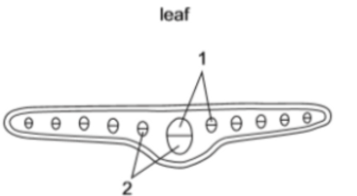
Label 1 and 2
1 is the xylem and 2 is the phloem
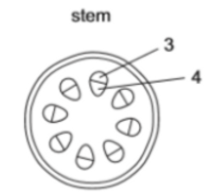
Label 3 and 4
3 is the phloem and 4 is the xylem
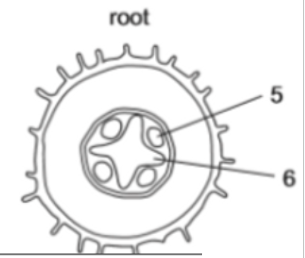
Label 5 and 6
5 is phloem and 6 is xylem
What is the xylem responsible for?
the transport of water and mineral salts (and support but mostly the other one)
The phloem is a tissue containing?
Sieve tubes
What is the phloem responsible for?
transport through the plant of organic solutes (like sucrose)
Functions of parenchyma (thinner)
metabolically active
food storage
support
play an important role in the movement of water and food products in the xylem and phloem
Collenchyma functions (thicker because of extra cellulose)
Provide extra support (in midrib of leaves and at the corners of square stems)
What is the epidermis
the outer layer of cells covering the body of a plant or animal
function of epidermis?
covered with a cuticle which provides additional protection against loss of water and disease
Characteristic of a monocot leaf is?
parallel veins
Characteristic of a monocot stem?
vascular bundles are scattered
Characteristic of a monocot root?
many spread out roots

Characteristic of a dicot leaf?
Branched veins

Characteristic of a dicot stem?
Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring
Characteristic of a dicot root?
One main root

what are the main organs involved in transport within plants?
Stems
Roots
Leaves
How many transport tissues do plants have and what are they called
2 transport tissues
Xylem
Phloem
What does the xylem transport
water and inorganic ions (mineral salts) from roots to the parts above ground.
True or false:
Can xylem move in more than on direction?
False, xylem can move in only one direction, from roots to the rest of the plant (flow is always upwards)
What does the phloem carry?
substances made by photosynthesis from the leaves to other areas of the plant.
True or false:
Can phloem move phloem sap in more than on direction?
True! upwards in some sieve tubes and downwards in others
function of xylem vessel elements
Transport of minerals and water
support
phloem sieve tube function is?
transport of sucrose / organic solutes
phloem companion cell function?
loading / unloading of sucrose into or out of phloem sieve element
forms a functional unit with sieve element
how thick is the endo and epidermis?
1 cell thick
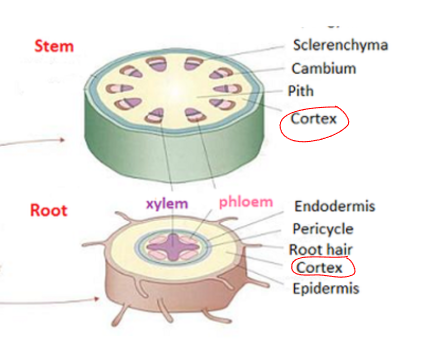
What is the outer region of stem and roots called
the cortex (and it is mainly made of parenchyma.)
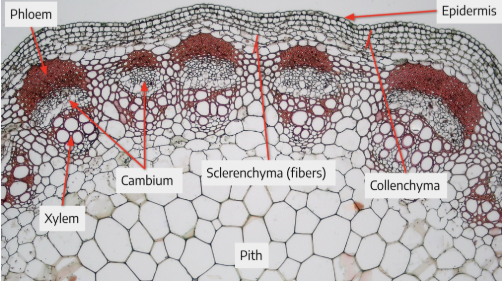
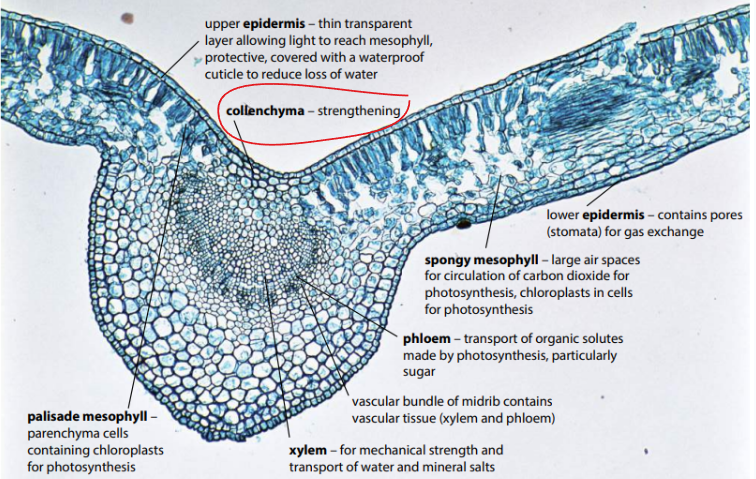
Collenchyma cells are?
parenchyma cells with thicker walls for more support found around the outside of stems just below the epidermis and in the midrib of leaves
Sclerenchyma cells are? (cap of fibers on vascular bundles)
parenchyma cells with the thickest cell walls
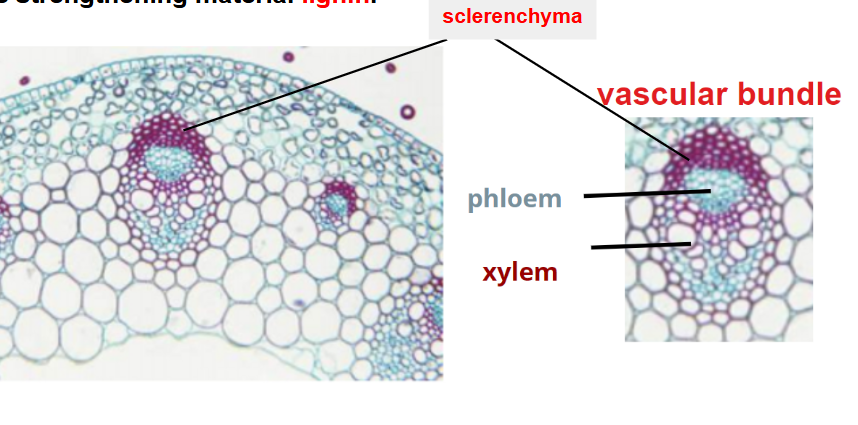
Like xylem, sclerenchyma?
walls contain the strengthening material lignin.
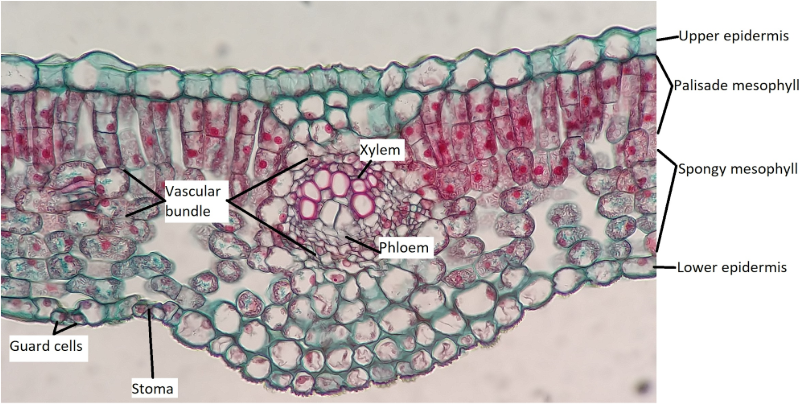
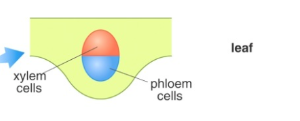
dicot leaf (this card is just to examine the photos)
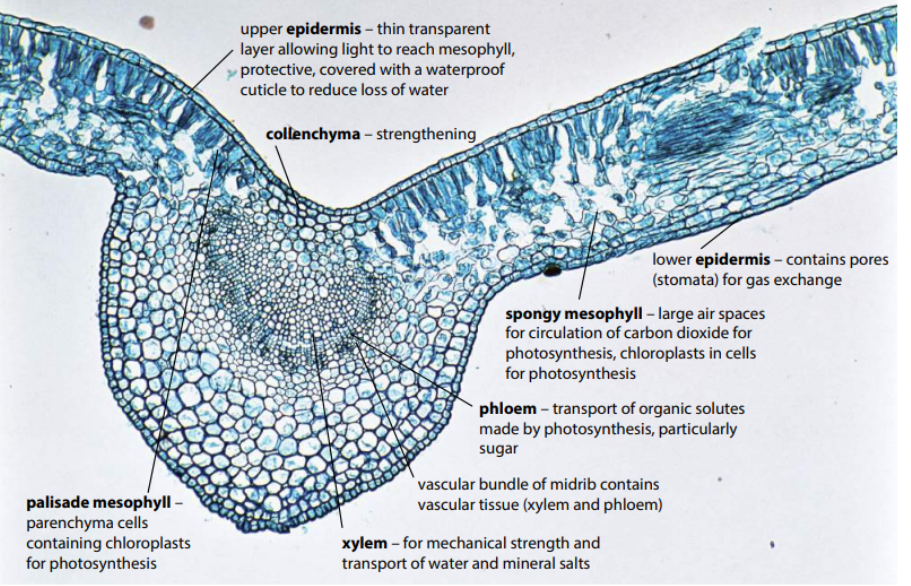
what does the outside of a vascular bundle contain
caps made of sclerenchyma fibers.
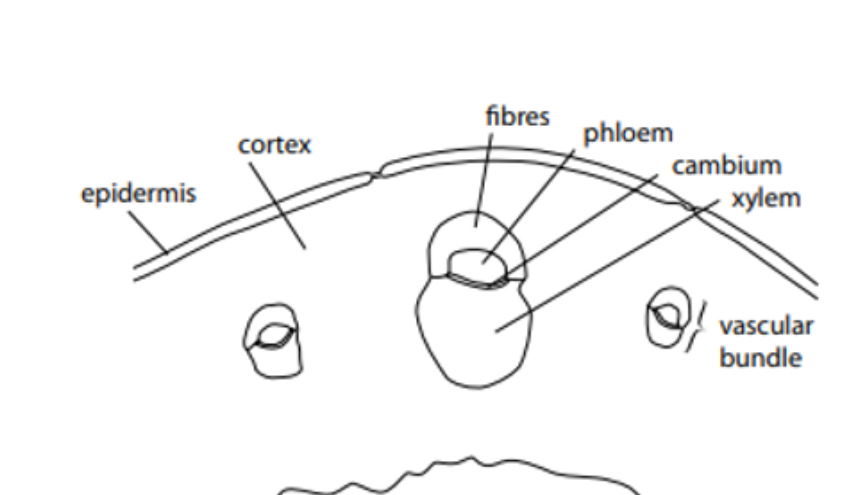
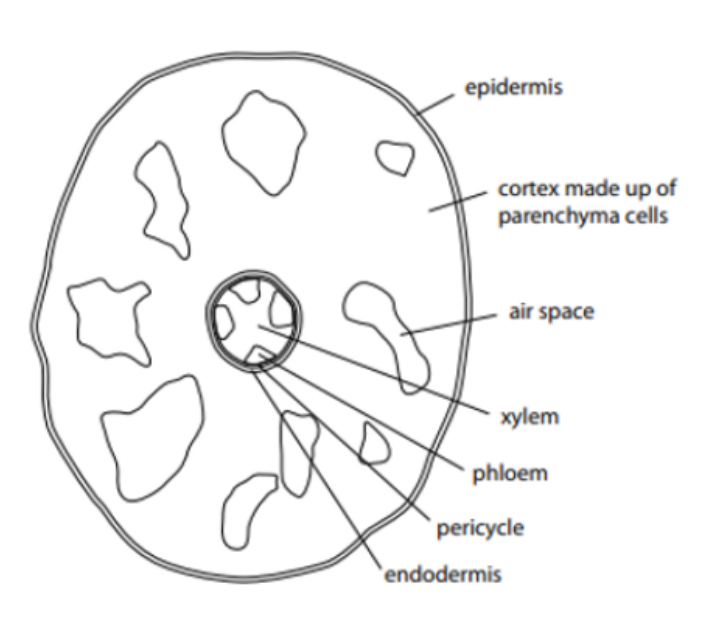
nothing here just examine the photo
features of Sclerenchyma fibres
Sclerenchyma fibres are elongated cells with lignified walls that help to support the plant.
They are dead cells
they have no living contents at all.
Parenchyma is made up of:
thin-walled cells used as packing tissue
The cells are very metabolically active and may be used for storage of foods like starch.
Support the plant, preventing wilting.
Air spaces between the cells allow gas exchange.
Parenchyma forms the cortex in roots and stems, and the pith in stems.
Parenchyma contains chloroplasts in leaves, where it is modified to form the palisade and spongy mesophyll.
Collenchyma
modified form of parenchyma with extra cellulose deposited at the corners of the cells.
provides extra strength.
the midrib of leaves contains collenchyma
Mesophyll
They are specialized for photosynthesis and contain chloroplasts
What are xylem vessels made out of?
elongated cells with no end walls (xylem vessel elements)
True or False:
The cells in the xylem structure are alive
false, they r ded fr like me rn michelle - 1:50 am
The lack of cell contents in xylem allows for? (and lack of end wall)
uninterrupted pathway for water to flow
(Still talking ab xylem) The wider the diameter?
the ore water that can be moved up the xylem vessel
The lignified walls in the xylem provide
support, preventing the vessels from collapsing inwards
The cells are elongated cells joined end to end to form tubes for?
transport
no end walls
so minimal resistance to the flow of water
hollow , no cytoplasm, no contents
more space for greater volume to flow with minimal resistance to flow of water
lignified (walls) / walls contain(s) lignin A thickened walls R lined with lignin so prevents
collapsing preventing it from bursting
True or false:
Is lignin permeable in water?
False, it is impermeable and does not ddissolve
High-power detail diagram of xylem
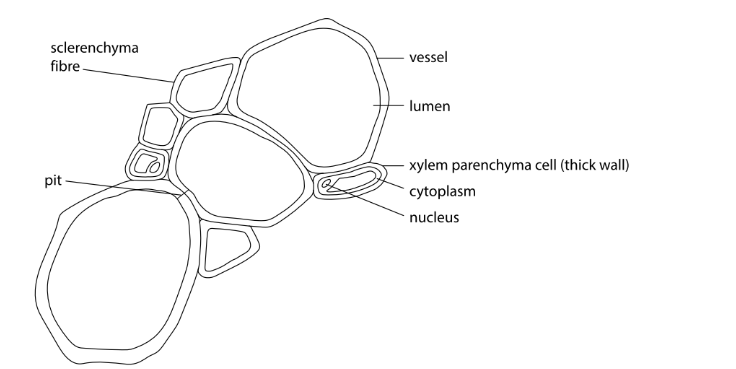
Phloem is made up of? (living)
sieve tubes made from cells called sieve tube elements
features of sieve tube element
a cell found in phloem tissue
is a living cell
NO NUCLEUS
No ribosomes
Contains endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
No vacuoles no tonoplast
very little cytoplasm
Non lignified walls
Sieve tubes have only a thin layer of cytoplasm and no nuclei this?
reduces resistance to flow
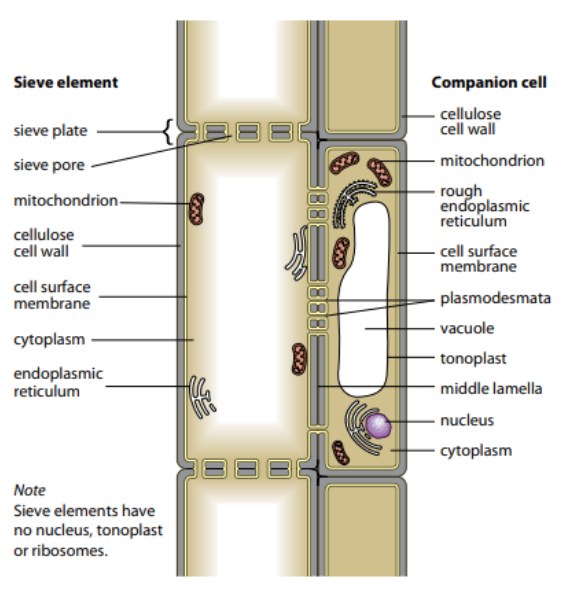
Relate the structure of phloem sieve tube elements to their function
elongated cells joined end to end to form long tubes
very little cytoplasm, no nucleus, fewer organelles to reduce resistance to flow
sieve plates have pores, so it is easy for phloem sap to pass from cell to cell
sieve plates support the sieve tube elements
plasmodesmata between sieve tube and companion cell for easy loading and unloading of sucrose
features of a companion cell
a cell with an Un thickened cellulose wall and dense cytoplasm
Nucleus present
large number of mitochondria and ribosomes
metabolically very active
found in close association with a phloem sieve element to which it is directly linked via many plasmodesmata
Relate the structure of phloem companion cell to their function
Allow the movement of sucrose from mesophyll cells/ source cells
Many plasmodesmata between companion cell and sieve tube to move sucrose into and out of sieve tubes
Proton pumps in its cell surface membrane pump hydrogen ions out of cell into cell wall to move sucrose against its concentration into the companion cell
large number of mitochondria and ribosomes to provide ATP and proteins for sieve tubes