ESS Unit 1
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
DDT
synthetic pesticide used to control insects. DDT was used to battle malaria Its effects include thinning of eggshells, bioaccumulation in food chains, and potential harm to wildlife and humans.
ecocentrist
places nature and the environment at the center of their values and decision-making, prioritizing ecological well-being over human interests.
technocentrist
believes in the central role of technology in society, often prioritizing technological solutions over other factors. Environmental issues can be solved by development (e.g. trump)
A silent spring
Niche
how an organism makes a living
ecoystem
where plants, animals and other organisms as well as weather work together to form a bubble of life
ecology
study of organisms and their interactions
habitat
environment in which a species normally lives
species
a group of organisms that share common characteristics, that can interbreed and create fertile offspring
biotic
living factors that affect an ecosystem(plants, animals, bacteria)
abiotic
non-living factors that affect an ecosystem(weather, humidity, soil, proximity to water)
carrying capacity
the maximum population that an environment can sustainably support
population density
average amount of organisms within an area (e.g. m²)
population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time
Realised Niche
actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic reactions
fundamental niche
full range of conditions which a sepcies could live in(basic needs)
spatial niche partitioning
differebt species occupy different spaces in a habitat
dietary niche partitioning
different species eat different things
Niche partitioning by resource height
Species occupy same habitat but have access to resources at different heights
Temporal niche partitioning
species share a habitat but feed at differebt times(times of day, seasons, environmental conditions)
Positive Feedback
a cycle that amplifies change within an environment.
Negative feedback
steady-state equilibrium. Cycle that stabilizes itself and always returns to its original state
Limiting factors
factors that slow population growth.
Biotic limiting factors
Density dependent. food, competition, parasitation
Abiotic limiting factors
Density independent. Rainfall, sunlight, temperature
Autotrophs
use energy from the sun to photosynthethise and grow
Mutualism
two species benefit from eachother
Parasitism
one benefits at the expense of the other
Predator and prey
one feeds off of the other
Pathogen
causes a disease
decomposers
break down dead organisms
detritivores
feed by consuming dead matter or faeces
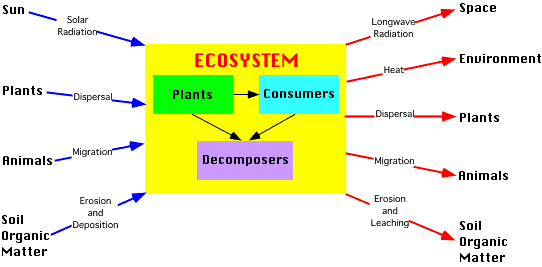
system
shows inputs, outputs and stores of an ecosystem
open system
can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings
closed system
no matter is lost, energy can be transferred
isolated system
doesn’t excange matter or energy
daisy planet
an environmental model that shows how negative feedback loops affect the temperature of earth
first law of thermodynamics
energy in an isolated system cannot be created or destroyed
second law of thermodynamics
entropy of a system is always increasing
entropy
the dispersal of energy through work: evaporation, waste, respiration
resillience
the ability of a system to return to its initial state after a disturbance
bioaccumulation
build-up of chemicals in an individual organism over time
biomagnification
build-up of pollutants over several trophic levels, the top predator consumes the highrst concentration as they have to eat several small polluted creatures
primary pollutants
are emmited directly from one source
secondary polllutants
form in the atmospherethrough cheical reactions