WGU.D316.L4 Comparing Local Network Hardware complete questions with expert solutions + rationales
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Uses radios and antennas for transmission and reception based on IEEE 802.11
Wireless Lan (WLAN)
Network spanning multiple geographic locations, for Internet
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A company dedicated to facilitating access to the Internet from local networks is called an
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Area equivalent to city or firm w/ multiple connected networks within the same metro area—larger than LAN but smaller than WAN
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Dedicated Site provisioning server resources supporting IT enterprise service offerings at scale
Data Center
Isolated network typically only accessible by servers, providing access to a configurable pool of storage devices that can be used by application servers
Storage Area Network (SAN)
SANs use connectivity technologies such as
Fiber-Channel and Internet SCSI (iSCSI)
wireless connectivity to connect to devices at a range of a few meters
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A MAC address consists of
48 binary digits, making it six bytes in size
MACs are typically represented as
12-digit hexadecimal value
ach frame of Ethernet data identifies ____________ in the frame header
Source and Destination MACs
Modern PC motherboards have this network adapter capability
1000BASE-T compatible adapter
Some NICs have multiple ports of same type (forex 2/41000BASE-T) and can be bonded to create a...
High-speed bonded link. 4 1-GB Eth ports bonded for nominal 4 Gbps
cables running terminated to insulation displacement connector (IDC) punch-down blocks on the panel frame each with RJ45 port
Patch Panel
Centralized networking device b-cast transmission from a node across all other ports so all nodes seem to be attached to same cable sometimes resulting in reduced efficacy due to collisions
Hub (obsolete)
ZERO hubs are compatible with _____________
GIGABIT ETH
First provided by inserting ___________ between hubs to break up collision domains.
Ethernet bridges
Decode incoming frame to ID source/dest MAC, tracking MAC to port and forwards it appropriate dest MAC port
Eth Switch
In a switched environment, what does full duplex mean?
Node can send/receive simultaneously at full line speed
On a switch each port is full duplex and a separate _________________
collision domain
switch performs its function without requiring any sort of configuration. You just power it on and connect some hosts to it, and it establishes Ethernet connectivity between the network interfaces without any more intervention
Unmanaged Switch
A ___________ is unmanaged OOB, but access via mgmt port, for advanced function and uplink ports allowing connect to other gear
Managed Switch
Gear provides PS and fast-comm backplane to interconnect multiple units and enables provisioning at scale via single compact footprint
Enterprise modular switch
Configuring a managed switch can be performed over either ________________
a web or command line interface.
used to intercept the signals passing over a cable and send them to a packet or protocol analyzer.
Network tap or TAP
Most popular type of network cable
UTP cable
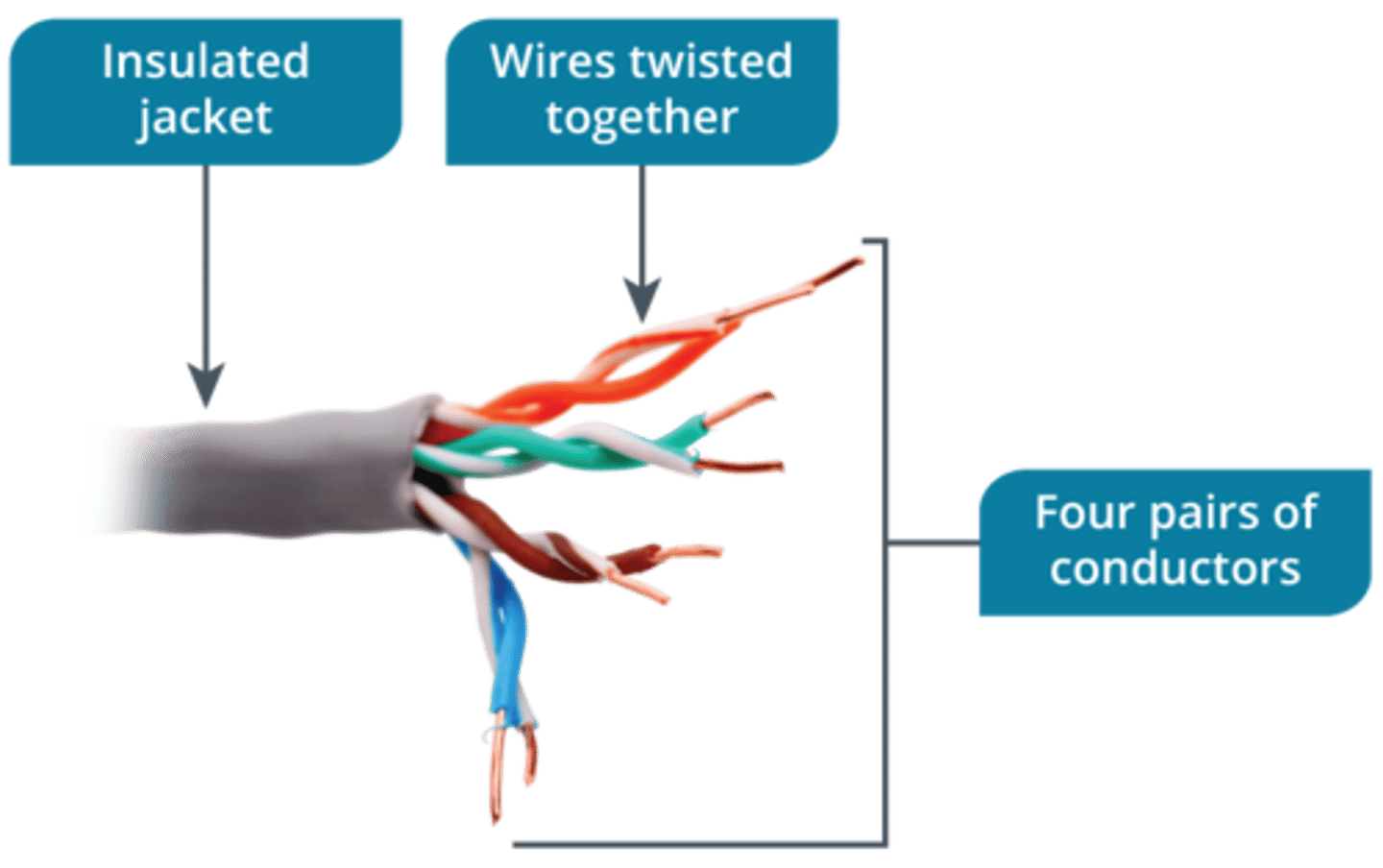
extra protection against interference. Shielded cable is often used for 10G Ethernet and higher within datacenter networks because it is more reliable than UTP
STP cable
Eth cabling standard
TIA/EIA-568 standard

pin 1 is wired to green/white, pin 2 is wired to green, pin 3 is wired to orange/white, and pin 6 is wired to orange
TIA/EIA-568 - T568A

orange terminates to 1 and 2 and green to 3 and 6
TIA/EIA-568 - T568B

MAC address of the AP's radio is the
Basic Service Set ID (BSSID)
Most Wi-Fi networks are configured in what is technically referred to as
Infrastructure Mode
Infrastructure mode means each client device is configured to network using ________________
Access Point (AP)
APs establish WIFI net but can also be a
bridge between WIFI devices and wired net.
5GHz devices must implement to prevent interference for radar and satellite installations
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS)

lower data rates at longest range, lower channels interference w/other wireless and appliances, best propagation
2.4GHz
higher data rates at shorter ranges, more channels less interference, but less penetration
5 GHz
Standard using 5 GHz only
IEEE 802.11a 54 Mbps rate
Standard using 2 GHz only
IEEE 802.11b 54 Mbps
Standard upgrade from 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g 54 Mbps rate
Works dual-band, with optional channel bonding for increased bandwidth
IEEE 802.11n 72 Mbps
802.11n (2x 20MHz => 40 MHz channel)
Channel bonding 150 Mbps
802.11n reliability/bandwidth increase using signal multiplexing multiple antennas (2-3)
Multiple In/Multiple Out (MIMO)
802.11n APs are classed using Nxxx designations, where xxx is the
Nominal bandwidth
2 bonded channel w/ 300 Mbps rate, on both 2.4 and 5 GHz
N600 2x2 AP where 600 Mbps is bandwidth
Designed for only 5GHz allows ~8 streams (80 MHz at 433 Mbps) although most is 4x4
802.11ac (WIFI5) / AC5300
Per-stream data rate over 80 MHz to 600 Mbp
802.11ax (WIFI6) / AX6000
WIFI5/6, allows AP to use multiple antennas to send data to up to 4 clients simultaneously
Multiuser MIMO and DL MU-MIMO
Works w/ MU-MIMO to improve client density—sustaining high data rates when more stations are connected to same AP
WIFI6 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA).
Wireless signal strength is measured in
decibel (dB)
Signal strength is represented as the ratio of a measurement to 1 milliwatt (mW), where 1 mW is equal to
0 dBM
Comparative data signal strength to background noise
Signal to Noise (SNR)
regulation of the radio spectrum means that the transmitters required to cover long distances must be carefully configured. These solutions are referred to as
LR Fixed Wireless (LRFW)
NetOps has exclusive right to use a frequency band within a given geographical area from authoritative regulator
Licensed LRFW
Ops uses public band, 900M, 2.4 and 5 GHz where interference is risk and power output is limited by regulatory requirements
Unlicensed LRFW
DSL (sym, asym) data rate
DLR 24 Mbps and ULR 1.25-2.5 Mbps
Data over Cable Service Interface Spec (DOCSIS) data rate
DLR 38 Mbps (NA) or 50 Mbps (EU) and ULR 27 Mbps
Use a SIM card to use an unlocked handset with chosen network provider
Global System Mobile Communication (GSM)
handset is directly managed by the provider and there is no removable SIM card.
Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
Converged standards supported by both GSM and CDMA providers where SIM card issued by provider
4G LTE
Rather single large antenna serving a cell, has many smaller antenna arrays for multipath and beamforming to overcome propagation limitations - Massive MIMO
5G