AP Bio: chapters 12 - 13
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Anchorage dependence
the requirement that a cell must be attached to a substratum in order to initiate cell division
Autosomes
chromosomes other than sex chromosomes
One chromosome from a pair comes from the mother and the other from the father
Sex chromosomes
the x and y chromosomes that determine an individual’s sex
Xy = male (only small parts are homologous)
Xx = female (homologous pair)
Cell cycle
G0 phase - cells that remain in G0 will not divide as they cannot pass the G1 checkpoint, these cells can leave G0 when necessary
Examples include: neurons, liver cells
G1 phase - first gap of the cell cycle, where the cell is able to grow to reach division, phase is the most variable in length spending on types of cells or other conditions, it is the part of the cycle in which the cell is performing it's typical function
G1 checkpoint - the point in the cell cycle where cells reach a point of no return, once they pass the checkpoint they must divide or die off, assesses four things
Growth signal - TSH, GH, ECF, assess whether the cell has enough signal that is telling it to divide
Size - the cell must be large enough to divide, this means that the cells are older and have not divided recently
Density dependence - if the cell does not have enough room to grow the necessary materials for division, it cannot divide
Anchorage dependence - checking that the cell is attached to a substratum
S phase - synthesis of materials necessary for division in the cell occurs, chromosomes are copied (DNA and chromosomes are continued to be duplicated into the G2 cycle) and the cell continues to grow, occupies ½ of the cell cycle
G2 phase - DNA is continued to be copied as well as organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplast which cannot be duplicated through organismal DNA in the nucleus, the cytoskeleton will begin to break down to provide material for the mitotic spindle and for the cell to change shape, the centromeres are duplicated to complete the duplication of DNA, it's usually the shortest of interphase
G2 checkpoint - performs checks to decide if the MPF gene has been turned on and thus the cell has grown enough to complete the G2 phase and move on to the M phase to complete division
M phase - mitosis
Cell plate
structure that forms in the center of dividing plant cells that forms of vesicles containing cellulose that will eventually form a cell wall between the two new nuclei to finally divide a plant cell
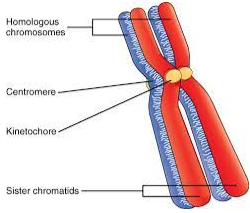
Centromere
a region of the chromosoma
DNA where the chromatid is attached most closely to its sister chromatid, mediated by proteins bound to the centromeric DNA
Checkpoints (when and what)
G1 checkpoint - the point in the cell cycle where cells reach a point of no return, once they pass the checkpoint they must divide or die off, assesses four things
Growth signal - TSH, GH, ECF, assess whether the cell has enough signal that is telling it to divide
Size - the cell must be large enough to divide, this means that the cells are older and have not divided recently
Density dependence - if the cell does not have enough room to grow the necessary materials for division, it cannot divide
Anchorage dependence - checking that the cell is attached to a substratum
G2 checkpoint - performs checks to decide if the MPF gene has been turned on and thus the cell has grown enough to complete the G2 phase and move on to the M phase to complete division
M checkpoint - The cell examines whether all sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle microtubules that separate them. If not, the cell pauses mitosis until all sister chromatids have been attached in the right way.
Chiasmata
x shaped regions where crossovers have occurred in each homologous pair
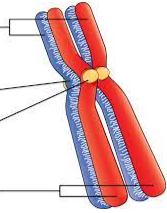
Chromosome anatomy
Cleavage furrow
a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate, first sign of cleavage
Occurs through a ring of actin filaments that interact with the protein myosin and thus contract to close of the cell membrane, creating two cells eventually
Crossing over
the DNA molecules of non-sister chromatid are broken and rejoined to each other
Allows for more diversity and the combination of genes that may be more beneficial
Cyclins
a cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration, activate commonly inactive kinases that drive the cell cycle
Cytokinesis
final phase of mitosis, the final division of the cytoplasm to create to entirely different cells
Density dependent inhibition
a phenomenon in which crowded cells stop dividing to prevent an excess
An example of the effect of an external physical factor on cell division
Diploid
any cell with two sets of chromosomes
Has a diploid number of 2n
Haploid
cells that contain a single set of chromosomes, gametes
1n
Genes
hereditary units with coded information endowed to offspring by there parents
Account for familial resemblances
Program the specific traits that emerge as we develop from fertilized eggs to adults
Alleles
one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome
Homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs with the same length, centromere position and staining pattern
Independent assortment
in metaphase of meiosis I, the orientation of pairs of homologs is random, different chromatids will create unique crossovers and combine in meiosis II
Karyotype
a display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape
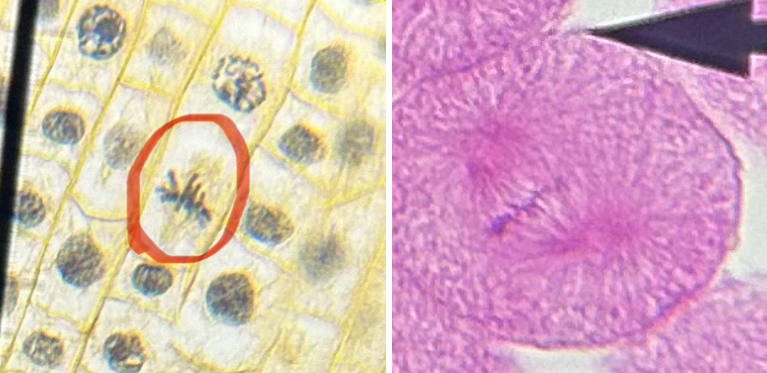
What phase is the fish and onion cell in?
metaphase
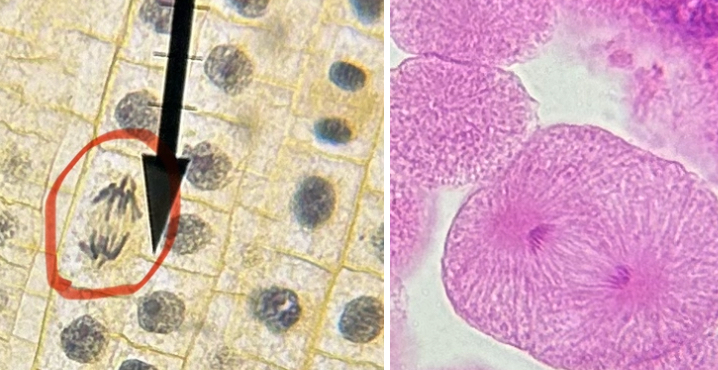
What phase is the fish and onion cell in?
anaphase
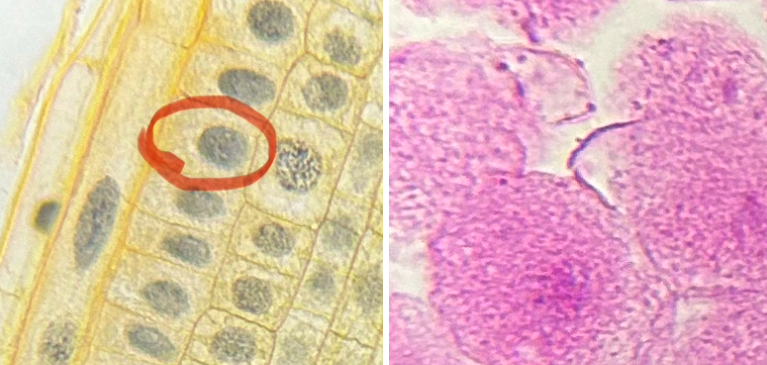
What phase is the fish and onion cell in?
interphase
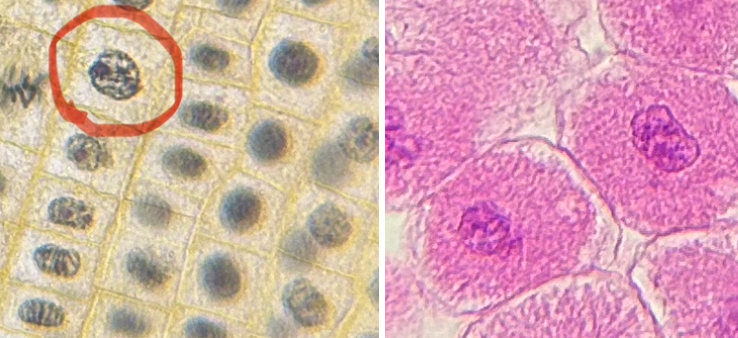
What phase is the fish and onion cell in?
prophase
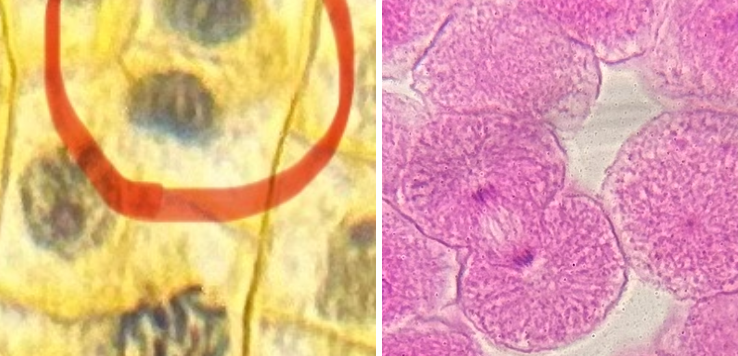
What phase is the fish and onion cell in?
telophase
Meiosis I
called reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes from diploid to haploid
first stage
Three events unique to meiosis (in meiosis I) -
Synapsis and crossing over - in prophase I, duplicated homologs pair up and crossing over occurs
Homologous pairs at the metaphase plate - at metaphase I, chromosomes are positioned at the metaphase plate as pairs of homologs, in mitosis they are paired with chromatids
Separation of homologs - in anaphase I, the duplicated chromosomes of each homologous pairs move toward opposite poles, sister chromatid are still connected, in mitosis sister chromatid will by pulled to opposite poles but they stay together in meiosis due to cohesion that is mediated cohesion proteins
Meiosis II
occurs as mitosis does, creates a total of four haploid daughter cells from the separation of sister chromatids, called the equational division
after telophase
Meiosis
Meiosis I - called reductional division because it reduces the number of chromosomes from diploid to haploid
Prophase I -
Longest stage, processes in prophase of mitosis occur
Duplicated homologous chromosomes pair to create tetras (synapsis) and crossing over occurs
Metaphase I -
Tetras or homologous pairs line up on the metaphase plate after being pulled by kinetochore fibers (like in metaphase of mitosis)
Chromosomes are attached as a whole to one kinetochore fiber (sister chromatid are attached together and to the same pole)
Anaphase I -
Each tetra separates and chromosomes move to opposite poles as a unit
Telophase I and cytokinesis -
Two haploid cells form, each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids
Meiosis II - occurs as mitosis does, creates a total of four haploid daughter cells from the separation of sister chromatids, called the equational division
Mitosis
Prophase -
Chromosomes begin to condense
Nuclear membrane dissociates and joins other membranes (plasma, Golgi, etc)
Nucleolus dissociates
Sister chromatids are formed
Mitotic spindle begins to form and centrosomes move away from each other towards opposite poles through polar fibers pulling them
Prometaphase -
Chromosomes continue to condense
Kinetochore fibers begin to pull the chromosomes to the metaphase plate
Centrosomes are almost at poles
Metaphase -
Chromosomes are lined on the metaphase plate which each sister chromatid attached to a polar fiber from an opposite pole
Centrosomes reach opposite poles and are secured with aster fibers
M checkpoint - required for the cell to reach anaphase, ensures that the cell has duplicated centromeres, chromosomes are the most condensed and all chromosomes are accounted for
Anaphase -
Kinetochore fibers tug on the sister chromatid, eventually separating them and pulling the sister chromatid to the pole from which the kinetochore extends from
Chromosomes start to unwind slightly
Telophase -
Nuclei are reassembled with the nuclear envelope and nucleolus
Cytoskeleton is also reformed
Cytokinesis -
The cells are fully divided once the cytoplasm has split
Meiosis vs. Mitosis
In mitosis bonds between sister chromatids are broken at the end of metaphase by enzymes, where in meiosis, cohesins are released first in anaphase I and again in anaphase II
Property | Mitosis (diploid or haploid) | Meiosis (diploid only) |
DNA replication | Occurs during interphase, before the start of mitosis | Occurs during interphase, before meiosis I begins and not before meiosis II |
Number of divisions | 1, including PPMAT | 2, including PMAT |
Number of daughter cells and genetic composition | 2 daughter cells which are each genetically identical to the parent cell with the same number of chromosomes, haploid if haploid parent cell, diploid if diploid | 4 daughter cells which are each genetically different from the parent cell and from other sibling cells, cells will have a haploid number of chromosomes compared to the diploid |
Role in the animal or plant body | - Allows multicellular organisms of animal or plant (gametophyte or sporophyte) to arise from a single cell - Produces cells for growth, repair and asexual reproduction in some species - Produces gametes in the gametophyte plant | - Produces gametes in animals or spores (in the sporophyte plant) - Reduces number of chromosome sets by half - Introduces genetic variability among the gametes or spores |
Mitotic spindle (KF, PF, aster)
structure that begins to form in the cytoplasm during prophase
Made up of fibers made out of microtubules and associated proteins
Microtubules come from the partial disassembly of the cytoskeleton
Spindle microtubules polymerize (elongate) by adding more subunits of the protein tubulin
Nonkinetochore/polar fibers (PF) - connect centrosomes and push them toward opposite poles, stretch out the cell to make it larger, part of the mitotic spindle
Kinetochore fibers (KF) - fibers extending from the centrosomes that attach them to a kinetochore protein attached to each sister chromatid to allow the centrosome to move the chromatid/chromosome, part of the mitotic spindle
Aster - short microtubules that extend from each centrosome and attach the centrosome to either pole in the cell, part of the mitotic spindle
MPF
maturation promoting factor, the first discovered cyclin-cdk complex
Triggers the cell’s passage to the m-phase past the G2 checkpoint because as pathways are complete in G2 such as duplication of mitochondria, they begin to turn on the gene to produce MPF so, once enough pathways have been complete the MPF gene will be turned on and the cell can proceed into mitosis
Three Life Cycles
All
only if fertilization occurs, then the diploid is allowed to grow
common themes are fertilization and meiosis
Most fungi and some protists
majority of life is in the state of a haploid
Plants in some algae
half time spent as diploid, while the other half the haploid
Animals
while they are gametes they are haploid
majority of life is in the state of a diploid
biological benefit of two copies of each gene (so if one is mutated than the other can still function)
Prophase
The chromatin fibers become more tightly coiled, condensing into discrete chromosomes observable with a light microscope.
The nucleoli disappear.
Each duplicated chromosome appears as two identical sister chromatids joined at their centromeres and, in some species, all along their arms by cohesins (sister chromatid cohesion).
The mitotic spindle (named for its shape) begins to form. It is composed of the centrosomes and the microtubules that extend from them. The radial arrays of shorter microtubules that extend from the centrosomes are called asters ("stars").
The centrosomes move away from each other, propelled partly by the lengthening microtubules between them.
Prometaphase
The nuclear envelope fragments.
The microtubules extending from each centrosome can now invade the nuclear area.
The chromosomes have become even more condensed. Each of the two chromatids of each chromosome now has a kinetochore, a specialized protein structure at the centromere.
Some of the microtubules attach to the kinetochores, becoming "kinetochore microtubules," which jerk the chromosomes back and forth.
Nonkinetochore microtubules interact with those from the opposite pole of the spindle.
Metaphase
The centrosomes are now at opposite poles of the cell.
The chromosomes have all arrived at the metaphase plate, a plane that is equidistant between the spindle's two poles.
The chromosomes' centromeres lie at the metaphase plate.
For each chromosome, the kinetochores of the sister chromatids are attached to kinetochore microtubules coming from opposite poles.
Anaphase
Anaphase is the shortest stage of mitosis, often lasting only a few minutes.
Anaphase begins when the cohesin proteins are cleaved. This allows the two sister chromatids of each pair to part suddenly. Each chromatid thus becomes a full fledged chromosomes.
The two liberated daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell as their kinetochore microtubules shorten. Because these microtubules are attached at the centromere region, the chromosomes move centromere first (at about 1 um/min).
The cell elongates as the nonkinetochore microtubules lengthen.
By the end of anaphase, the two ends of the cell have equivalent—and complete collections of chromosomes.
Telophase
Two daughter nuclei forms in the cell.
Nuclear envelopes arise from the fragments of the parent cell's nuclear envelope and other portions of the endomembrane system.
Nucleoli reappear.
The chromosomes become less condensed.
Any remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized.
Mitosis, the division of one nucleus into two genetically identical nuclei, is now complete.
Random fertilization
any sperm could come to any egg, gametes produce 223 possible chromosome combinations which is doubled when fused to another gamete in fertilization
Random mating
any person can chose to mate with anyone else, creates infinite combinations of possibilities to combine genes
Recombination
produces a huge amount of variation
Recombinant chromosomes - products of recombination, individual chromosomes that carry genes derived from two parents
Produce chromosomes with new combinations of maternal and paternal alleles which creates versatility
Somatic cell
all of the cells of the body except gametes and their precursors
Diploids (2n)
In human somatic cells, there are 46 chromosomes (2 sets of 23)
Germline cell
cells that follow a specialized line to produce gametes; they undergo mitosis to become gametes
Gamete
reproductive cells in plants and animal cells that transmit genes from one generation to the next (sperm and egg)
Haploid (1n)
In human gametes, there are 23 chromosomes (1 set of 23)
Syngamy
the process of the union of two gametes for the generation of one zygote (the fusion of their nuclei in reproduction)
Tetrads
two duplicated homologous chromosomes (4 chromatids) bound together by chiasmata in Prophase I
Tetrads form during synapsis and are held in precise positions by a protein lattice/structure called synaptonemal complex
Tumor (malignant/benign)
Benign tumor - a tumor that remains at the original site because it has too few genetic and cellular changes to survive at another site, they usually do not cause serious problems to the host organism
Malignant tumor - a tumor in which the cells have undergone enough transformation that they can spread to new tissues and impair function in one or more organs
Sexual reproduction
1 sperm + 1 egg = 1 zygote
meiosis
Asexual reproduction
organism reproduces with itself
mitosis and meiosis
Diversity
good
mutations are the initial source of all diversity
source of all variation, but cause of least variation
crossing promotes diversity
recombination
allele / genes that were linked to other genes
independent assortment
changes pair of male and female
alignment of homologous
recombination
mate choice
random fertilization
Problems in cell cycle
cancer
uncontrolled division
Regulation of cell cycle
checkpoints
2n to 1n ...HOW .... WHY
diploid to haploid
through meiosis
want to copies of the genes, so if one doesn’t work than than the organism still has functionality
Recombination... HOW ... WHY
crossing over
non sister chromosomes exchange parts
chiamata where the cross over occurs
it can be used to help repair broken DNA
to create more diversity as a result
ID of mitotic/meiotic phases
meiosis is essentially mitosis double
the chromosomes are affected differently
nuclear membrane reforms in telophase for mitosis, while it reforms in telophase 2 for meiosis