AQA Psychology - Biopsychology
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:06 AM on 9/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
1
New cards
nervous system
What is the complex system of nerve cells that carry messages to and from the brain?
2
New cards
central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What is the nervous system made up of? Include both full name and abbreviation.
3
New cards
somatic nervous system (SNS) and autonomic nervous system (ANS)
What two systems made up the PNS?
4
New cards
brain and spinal cord
What does the CNS consist of?
5
New cards
reflex actions
What is the spinal cord responsible for?
6
New cards
somatic nervous system / SNS
Which system controls voluntary movements and passes information from sensory and motor neurons to and from the CNS?
7
New cards
autonomic nervous system / ANS
Which system controls involuntary actions and transmits motor information to and from the CNS?
8
New cards
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
What are the two systems that made up the ANS?
9
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
Which system increases bodily activities and triggers the fight-or-flight reaction?
10
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
Which system maintains or decreases bodily activities, returning the body to the rest state?
11
New cards
specialised cells that carry information throughout the body using chemical and electrical signals
What are neurons?
12
New cards
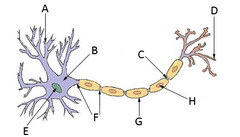
B
Which part is the control center of a neuron (soma)?
13
New cards
A
Which letter represents dendrites?
14
New cards
receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors
What is the role of dendrites?
15
New cards
myelin sheath
Which part protects the axon?
16
New cards
carries impulses away from the cell body
What is the role of the axon?
17
New cards
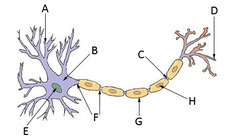
nodes of Ranvier
What are the gaps between cells in the axon called?
18
New cards
axon terminal
Which part of the neuron allows for communication with the next neuron across the synapse?
19
New cards
sensory (neurons), relay (neurons), motor (neurons)
What are the three types of neurons?
20
New cards
sensory neuron
Which type of neuron carries messages from the PNS to the CNS?
21
New cards
relay neurons
Which type of neuron carries messages from one part of the CNS to another?
22
New cards
motor neurons
Which type of neuron carries messages from the CNS to effectors?
23
New cards
relay and motor neurons
What are two types of neurons that are multipolar?
24
New cards
synapse
What is the gap between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of the adjacent neuron called?
25
New cards
one-way transmission
Is synaptic transmission one-way or two-way transmission?
26
New cards
neurotransmitters
What is the chemical message that is packaged into synaptic vesicles and released into the synapse when triggered called?
27
New cards
serotonin
Which neurotransmitter can caused inhibitory effect?
28
New cards
acetylcholine / adrenaline / dopamine
Which neurotransmitter can caused an excitatory effect?
29
New cards
until reuptake
How long will effects of the neurotransmitter last?
30
New cards
summation
What is the process that determines whether the neuron will fire after totaling the excitatory and inhibitory input?
31
New cards
acetylcholine / ACh
What is the neurotransmitter that caused muscles to contract?
32
New cards
endocrine system
What is the name of a chemical system of communication that instructs glands to release hormones directly into the bloodstream?
33
New cards
target organs
Where are hormones carried towards?
34
New cards
glands
What are the organs that secrete hormones called?
35
New cards
pituitary gland
What is the 'master gland' called?
36
New cards
hormones
Do effects of hormones or effects of neurotransmitters last longer?
37
New cards
fight-or-flight response
Which response is activated by the sympathetic nervous system when we are in high-arousal or stressful situtations?
38
New cards
acute stressor
Which event triggers the hypothalamus?
39
New cards
adrenaline
Name the hormone that triggers the fight-or-flight response.
40
New cards
increased heart rate / increased blood pressure / pupils dilate
State an example of an emergency reaction caused by fight-or-flight.
41
New cards
suppressed digestion / dry mouth / contracted rectum
State an example of a non-emergency reaction caused by fight-or-flight.
42
New cards
localisation of function
What is the idea that specific functions have specific locations within the brain called?
43
New cards
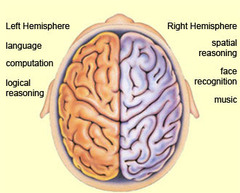
hemispheric lateralisation
What is the idea that the two hemispheres of the brain are functionally different and are responsible for different behaviours?
44
New cards
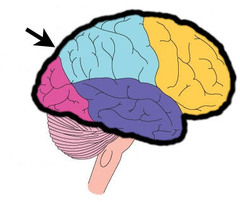
cerebral cortex
What is the outer layer of both brain hemispheres called?
45
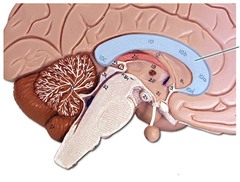
New cards
corpus callosum
What is the 'bridge' that connects the two brain hemispheres, allowing communication between the two halves called?
46
New cards
right hemisphere
Which hemisphere is dominant in recognising emotions?
47
New cards
left hemisphere
Which hemisphere is responsible for language processing?
48
New cards
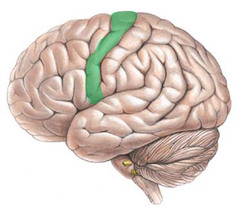
motor cortex
Which part of the brain sends messages to the muscles and is responsible for generating voluntary motor movements?
49
New cards
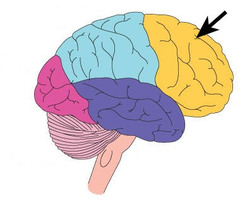
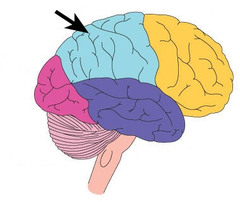
frontal lobe
Where is the motor cortex located?
50
New cards
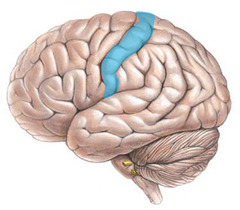
somatosensory cortex/area
Which is the area of the brain that processes sensory information?
51
New cards
parietal lobe
Where is the somatosensory cortex located?
52
New cards
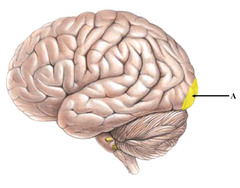
visual area/cortex
Which part of the receives and processes visual information?
53
New cards
occipital lobe
Where is the visual area located in the brain?
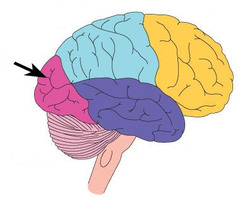
54
New cards
auditory area/cortex
Which part of the brain is concerned with the analysis of speech-based information?
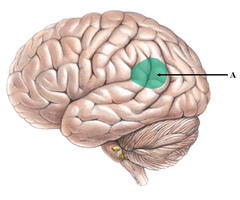
55
New cards
temporal lobe
Where is the auditory area located?
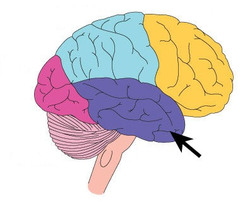
56
New cards
speech production
What is Broca's area responsible for?
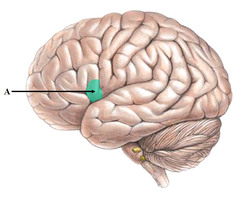
57
New cards
left frontal lobe
Where is the Broca's area located in the brain?
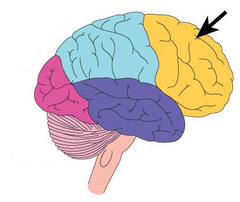
58
New cards
Wernicke's area
Which area of the brain (B) is responsible for language comprehension?
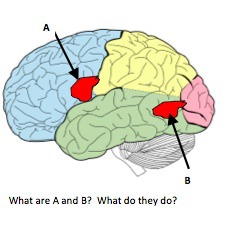
59
New cards
temporal lobe in the left hemisphere (encircling the auditory cortex)
Where is the Wernicke's area located?
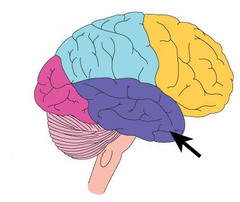
60
New cards
Broca's aphasia
Which condition is characterised by speech that is slow, laborious and lacking fluency?
61
New cards
Wernicke's aphasia
Which condition is characterised by neologisms (nonsense words)?
62
New cards
case studies of brain damaged patients / brain scan
Where does evidence to support localisation of functions come from?
63
New cards
Paterson et al (1988)
Who used brain scans to demonstrate how Wernicke's area was active during a listening task and Broca's area was active during a reading task?
64
New cards
too simplistic
What is the main point of criticisms for the localisation theories?
65
New cards
split-brain research
What is the research conducted by Sperry to help understand hemispheric lateralisation?
66
New cards
11 patients that had their corpus callosum removed
What was the sample in Sperry's study?
67
New cards
to remove severe epileptic seizures
Why do the patients had their corpus callosum removed?
68
New cards
If the image is shown to the right visual field, they can describe it; but if it is shown to the left visual field, they report that there is nothing there
What were the results when participants were asked to describe what they see in Sperry’s research?
69
New cards
the patient select the object that was most closely associated with the object presented to the left visual field
What is the results when the patients are asked to select an object using their left hand?
70
New cards
left hemisphere
Which hemisphere processes the right visual field (RVF)?
71
New cards
low population validity
What is a problem with the small sample size in Sperry's study?
72
New cards
lowers internal validity
What if the patients were taking drugs in the split-brain research?
73
New cards
JW
Name a case study that contradicts Sperry's research from Gazzaniga (1998). The case study can speak using their right hemisphere
74
New cards
well-controlled
What was a strength of the split-brain research?
75
New cards
Szflarski (2006)
Who suggests that lateralisation may be further complicated by age?
76
New cards
neural plasticity
What is the term used to describe the ability of the brain to change in response to experience?
77
New cards
spontaneous recovery
What is the term used to describe the idea that recovery occurred quickly after trauma and then slows down?
78
New cards
synaptic pruning
What is the process that can occur at any stage of life in which rarely used connections are eliminated and frequently used connections are strengthened?
79
New cards
secondary neural pathways
What is unmasked or activated to enable functioning of the brain to continue? This "pathway" would not normally be used to carry out certain functions
80
New cards
axonal sprouting
What is the growth of new nerve ending which connect with other undamaged nerve cells to form new neuronal pathways?
81
New cards
axonal sprouting / reformation of blood vessels / recruitment of similar areas on the opposite side of the brain
Name a structural change in the brain that supports the unmasking of secondary neural pathways
82
New cards
age / gender
Name a factor that affects the recovery of the brain after trauma
83
New cards
Maguire et al (2000)
Who used an MRI scanner to scan the brains of London taxi drivers and found that they had significantly more volume of grey matter in the posterior hippocampus?
84
New cards
Kempermann et al (1998)
Who found that rats placed in complex environments had an increased number of new neurons that rats housed in laboratory cages?
85
New cards
neurorehabiliation
What practical application has plasticity contributed to?
86
New cards
Ramachandran and Hirstein (1998)
Who found that 60-80% of amputees have been known to develop phantom limb syndrome, which caused an unpleasant feeling that the missing limb is still there?
87
New cards
functional magnetic resonance imaging
What does fMRI stand for?
88
New cards
electronencephalogram
What does EEG stand for?
89
New cards
event-related potentials
What does ERPs stand for?
90
New cards
Haemodynamic response
What happens when a brain area is more active, consumes more oxygen and to meet this increased demand, blood flow is directed to the active area?
91
New cards
3D images
Which type of image does fMRI produce?
92
New cards
5 seconds
What is the time-lagged between the image produced and brain activity in fMRI scans?
93
New cards
detect activity in deeper regions / records specific brain activity for localisation
Name a strength of fMRI
94
New cards
expensive / ignores communication between areas / low temporal resolution
Name a weakness of fMRI
95
New cards
EEG
Which method of studying the brain measures electrical activity within the brain via electrodes on a skull cap?
96
New cards
high temporal resolution / cheap / has practical application / takes into account communication between areas
What is a strength of using EEG?
97
New cards
cannot detect image from deeper brain regions (hypothalamus)
What is a weakness of using EEG scans
98
New cards
statistical analysis
What does ERPs use to filter out specific types of brainwaves that relate to a specific function?
99
New cards
lack of standardisation in which statistical test to use
What is a weakness of using ERPs that is not a weakness of EEG?
100
New cards
post-mortem examinations
What is the analysis of a person's brain following their death?