theme 2.1 measures of economic performance
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
economic growth
this refers to the percentage change in GDP in real time
GDP
gross domestic profit - total uk output, total value of goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time
nominal GDP
total market value of the goods and services produced in an economy over a given period, not adjusted for inflation
Real GDP
total market value of the goods and services produced in an economy over a given period, is adjusted for inflation
recession
occurs when an economy has 2 consecutive quarters of negative growth
how to calculate real GDP
nominal GDP x (price level previous year/price level current year)
GDP per capita
the average income of one person in an economy
how to calculate GDP per capita
Total GDP/population level
what does a higher GDP per capita mean
higher average income - higher standard of living
what can GDP per capita be expressed as
Volume and value
volume
quality and untis produced
value
market value and items produced
other ways to measure national income
GNI
National happiness
GNI
gross national income- total value of goods and services produced in an economy plus income from overseas(e.g remittances)
national happiness
this measure focuses on wellbeing of the people in an economy
what does national happiness include measures of
social justice
sustainability
social connectedness
health and education
why would national hapiness reduce even if average GDP is rising
income inequality can happen and reduce happiness therefore a rise in income may not rise national happiness
how is national happiness normally measured
surveys
why are surveys limited in meaasuring national happiness
limited by subjectivity
purchasing power parities
an exchange rate from one currency to another which compares how much a typical basket of goods costs in one country compared to another
why is ppp useful for comparing countries
takes account of the cost of living and so usefull measure to compare living standards
Big Mac index
PPP, compares the cost of big Mac around the world
limitations of using GDP to measure living standards
shadow economy - unrecorded transactions e.g drugs
non-financial factors - wellbeing and happiness
distribution of income
less reliable if not adjusted for PPP i.e cost of living
negative externalities - higher GDP - higher activity - higher pollution and congestions which decrease living standards
non-marketed output - DIY,voluntary work,favours,childcare
inflation
a general and sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in economy overtime
deflation
a general and sustained decrease in general price level of goods and services in economy overtime
disinflation
occurs when rate of inflation declines but inflation is still positive( price levels increasing at a slower rate)
CPI
consumer price index - average level of prices at a point in time
how to measure inflation
percentage change in CPI
how to measure CPI
finding the average basket of goods and services in a typical uk houshold and measures the average price level depending on spending
found out using surveys
why is CPI a weighted average
because goods and services have different affect on a persons e.g petrol has a higher weighting because it takes up a higher proportion of icome therfore an increas in petrol price will have a bigger impact on the rate of inflation
limits of using CPI
does not include all goods and services
updated annually therefore not comparing the same 2 goods every year
unlikely to represent an individual houshold
no account on improvements in products, just price changes
RPI
another measure of inflation, calculated same way as CPI but includes mortgage payments
why is RPI sometime more usefull than CPI
because mortgage payments are a huge expense in the cost of living but is less useful for thos without mortgage payments
RPI is also more volatile and affected by interest rate changes
2 types of inflation
demand pull - excess demand outsrips supply causing prices to rise
cost push - when an increase in production costs causes business to put prices up
effects of inflation
menu costs
search costs
uncompetitive exports
fiscal drag
uncertainty
policy response
menu costs
rapid price increases, cost of updating menus,marketing, leaflets, website increases
search costs
increase cost in terms of time + money in researtching latest prices
uncompetitive exports
if UK has a high inflation it implies increase in costs for business causing increase in prices - reducing exports
fiscal drag
when inflation leads to increase in nominal wages which puts people in a higher tax bracket but there is no increase in real wages therefore the people are losing out.
uncertainty
rapidly increasing inflation makes it hard to plan ahead which reduces business and consumer confidence
policy response
when inflation is above target - policy response is to increase interest rates.
unemployment
those of working age that who are seeking work but unable to find employment
economically inactive
those of working age who are neither employed or unemployed i.e not seeking work
2 measures of unemployment
claimant count
labour force survey
claimant count
the amount of people receiving job seekers allowancel
labour force survey
this surver records all those who are looking for a job but can’t find one
useful for comparing unemployment between countries because countries use the same methodology
underemployment
when those in work want to but can’t work more hours or are able to fully utilize their skills
form of hidden unemployment
affect of increase employment
increase income - increase living standards
increase tax - increase investment
increase skills and workforce
structural unemployment
occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the requirements of the job
cyclical unemployment
unemploymenmt tie directly to the economic cycle, high when recession
seasonal unemployment
occurs when unemployment is dependant on the seasons
e.g. tourism
frictional unemployment
temporary unemployment when people are in between jobs or entering the workforce
i.e people that work from contract to contract
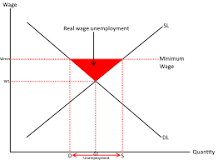
real wage inflexibility
Fixing wages above the equilibrium rate (minimum wage) can result in the supply of labour being more than the demand for labour.
migration
flow of people into and out of a country
how does immigration impact the labour market
reduce or increase unemployment
increase tax revenue
effects of unemployment
long term - de-skilling
reduce tax + increase G - worsen fiscal position
health
income inequality
poverty
balance of payments
all of the financial transactions in a country with the rest of the world
current account
capital account
financial account
current account
record payment for trade in goods and services and net flow of primary and secondary income
capital account
records the international transfer of non-financial assets with a country with the rest of the world
financial accounts
a record of transactions involving financial assets and liabilities, either held by individuals/businesses with other countries
FDI
components of current account
net balance of trade of goods
net balance of trade of services
primary income
secondary income
primary income
net flow of income a country receives and pays on its investments and assets, along with compensation of employees
secondary income
transfer in which one receives something without giving something of same economic value back