cobalt
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
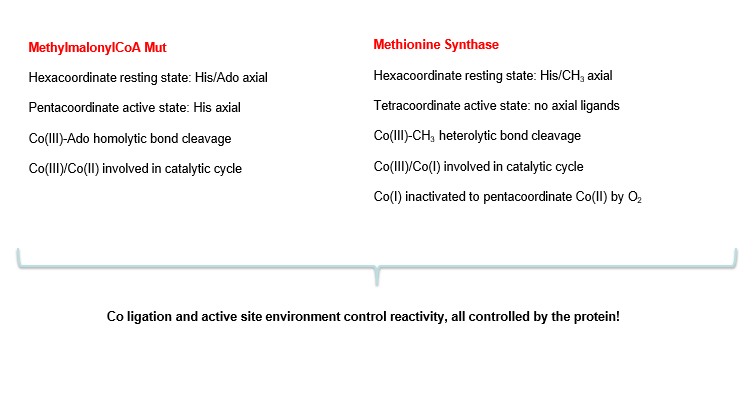
why is cobalt an essential element in humans?
three oxidation states
cobalt (II) can perform radical reactions which other metals like Ni and Fe are too unstable for
vitamin B12 is a cobalamin. describe what cobalamins are
Cobalt in centre, always low spin. 3+ easily reduced to 2+ and even +
equatorial ‘corrin’ ligand forms 4 bonds with this cobalt
axial 5th ligand is DMB
axial 6th ligand varies: methyl group or Ado (deoxyadenosyl). can have unnatural ligands too like OH-
what are the different outcomes of enzymes binding AdoB12 vs MeB12?
adoB12: homolytic fission of C-Co bond, allowing radical chemistry
MeB12: heterolytic fission of Me-Co bond, making methyl carbocation
the C-Co bond is relatively weak, and enzymes binding make it even weaker, allowing for bond fission
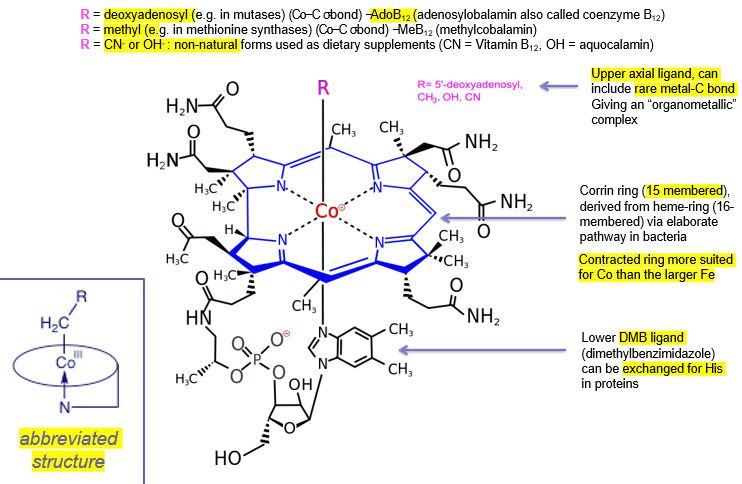
compare how B12 (cobalamin) is during the 3 oxidation states of Co
Co(III): 6 ligands, resting state of b12. base-on
Co(II) 5 ligands, performs radical chemistry. base-on
Co(I) 4 ligands, now square planar, acts as a strong nucleophile since it has 2 electrons paired in high energy orbital. base off
base on/off determines coordination number of cobalt
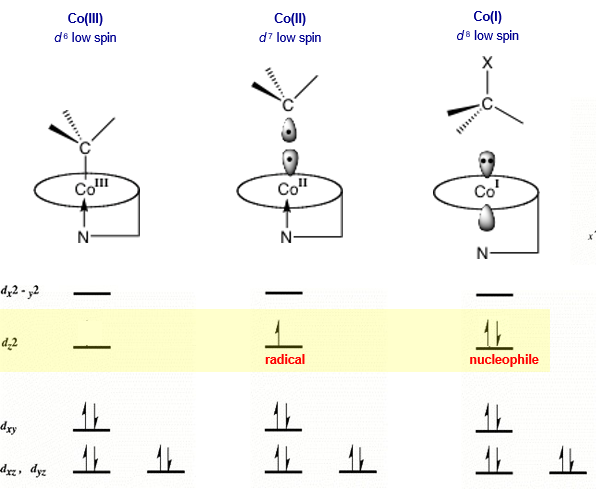
describe how radical mutases become active
substrate enters, shifts enzyme orientation, causing homolytic fission of weak C-Co bond
results in Co 2+ radical and Ado radical, which is trapped in the active site
dependence on substrate ensures radicals are only formed when needed
describe how radical mutases, once active, perform their action of making branched substrates linear
the radical Ado in the active site abstracts a H atom from the branch of the substrate
substrate then rearranges into a linear radical
linear radical substrate takes a H atom back from Ado, reforming stable Ado radical
methylmalonyl CoA mutase is an example of a radical mutase. what is the importance of this enzyme?
methylmalonylCoA is made from catabolism of key amino/ fatty acids
its mutase enzyme makes it into linear succinyl CoA, which can be used in citric acid cycle for energy
describe the use of MeB12 in methionine synthase
Me-H4 folate enters enzyme
MeB12 has C-Co bond broken heterolytically, making strong nucleophilic Co(I)
Cobalt attacks methyl group of Me-H4 folate, making H4 folate and reforming MeB12
another substrate, homocysteine, attacks MeB12, taking the methyl group and becoming methionine
remember, heterolytic fission=uneven bond breaking=no radical
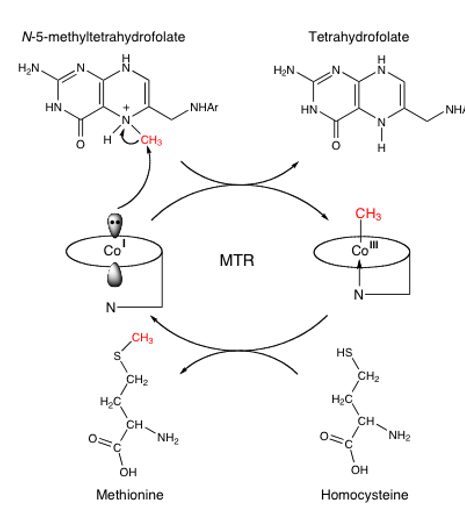
explain what happens to that cycle when O2 is introduced to Co(I)
O2 hijacks the cycle if it reacts with Co(I)
MSRred recovers the cycle by making Co(I) again
SAM (aka AdoMet) reforms MeB12 by giving its methyl group via nucleophilic attack.
compare the two B12 cycles