Ochem Lab Final: Aspirin and Other Experiments
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
What statements are always true about limiting reactants?
The limiting reactant is completely used up in the reaction
The limiting reactant dictates the amount of product
There will be an excess of other reactants at the end of the reaction
Identify the medical applications of aspirin
Pain killer, fever reducer, anti-inflammatory agent
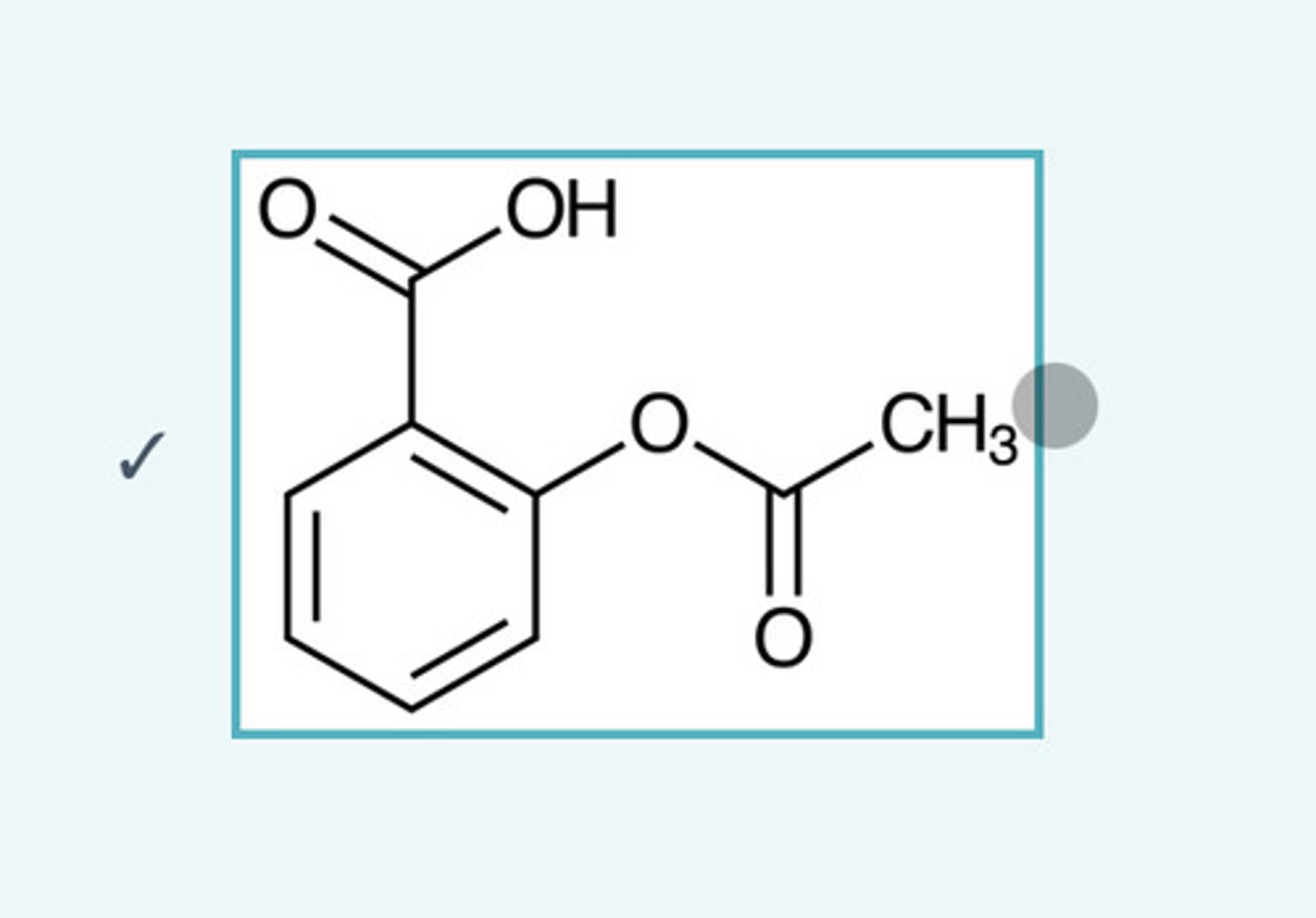
What is this?
Aspirin
Why do you need to support a vacuum filtration apparatus with a clamp?
The filter funnel makes the apparatus top-heavy
When using vacuum filtration to separate a dissolved solid from an undissolved solid, what techniques should you use to ensure a quantitative separation?
Carefully rinse the flask into the filter funnel with a small amount of water
Wet the filter paper before pouring the mixture into the filter funnel
Wash the solid on the filter paper with a small amount of water
Dry the solid on the filter paper after the separation
Iron(III) chloride can be used to assess the purity of aspirin synthesized from salicylic acid. Iron(III) chloride **** react with aspirin because the reaction requires a *** which is present in ****.
does not, phenolic functional group, salicylic acid but not aspirin
Once the vacuum filtration set-up is complete, start by **** in the filter funnel. Then, *** the mixture ****.
adding a small amount of water, slowly decant, into the middle of the filter paper
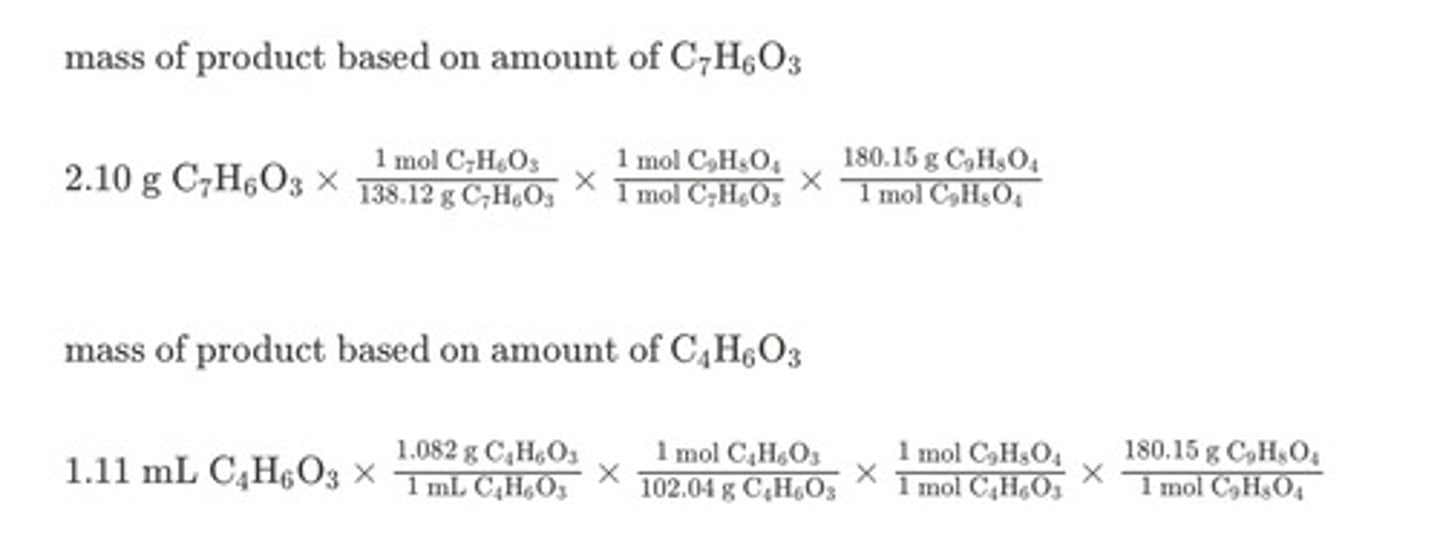
Aspirin can be prepared from salicylic acid (C7H6O3), which has a molar mass of 138.12 g/mol, and acetic anhydride (C4H6O3), which has a molar mass of 102.04 g/mol. The density of acetic anhydride is 1.082 g/mL. C7H6O3 + C4H6O3 ⟶ C9H8O4 + C2H4O2
What is the yield, in grams, of aspirin (C9H8O4), which has a molar mass of 180.15 g/mol, possible when reacting 2.10 g of salicylic acid with 1.11 mL of acetic anhydride?
2.12
Iron Test: Salicylic acid
Dark purple
Phenol
Iron Test: Commercial aspirin
Pale yellow
No Phenol
Explain why acetic acid is unlikely to be a contaminant in your solid aspirin.
Acetic acid will not crystallize due to the water and will therefore not contaminate the solid aspirin. Acetic acid is water soluble. We remove acetic acid while washing the product with water on the filter during the filtration.
Aspirin tablets that have been stored for a long time may have a vinegar-like odor and give a purple colour with FeCl3. What reaction would cause this to happen?
A purple colour with FeCl3 means that salicylic acid is present. A vinegar-like odor means that acetic acid is present. These two facts mean that the product started degrading to salicylic acid and acetic acid, which means the aspirin synthesis is a reversible reaction.
In preparation of aspirin, if the water used for washing crystals is not cold, how would this affect the melting range of final product? Explain!
Using warm or room temperature water for washing the crystals in the preparation of aspirin can negatively impact the melting range of the final product. It can result in lower yields, impurity retention, and the formation of larger or less-defined crystals. Cold water is preferred because it promotes rapid cooling, crystal formation, and effective removal of impurities, ultimately leading to a more precise and narrow melting range
In preparation of aspirin, if crystals of the final product is not dried, how would this affect the melting range of final product? Explain!
Failure to properly dry the crystals of the final product in the synthesis of aspirin can introduce moisture, impurities, and solvent effects, all of which can influence the melting range. To obtain accurate and meaningful melting point data, it is essential to thoroughly dry the crystals to remove moisture and ensure the purity and integrity of the final product
In preparation of aspirin, if crystals of the final product is not dried, how would this affect the calculated percent yield? Explain!
The failure to properly dry the crystals of the final product can lead to an overestimation of the actual yield and an inflated percentage yield. Thorough drying is essential to remove moisture, prevent the inclusion of impurities, and obtain accurate measurements, thereby ensuring an accurate calculation of the percentage yield. By properly drying the crystals before measuring the actual yield, the weight obtained will reflect the true weight of the acetylsalicylic acid product, without the contribution of moisture or residual solvents. Consequently, the calculated percentage yield will be more accurate and reflective of the efficiency of the reaction and the amount of desired product obtained.
In preparation of aspirin, if the mixture of crystalline product and ethanoic FeCl3 produces a colored solution, how would this affect the purity of product? Explain!
If the mixture of the crystalline product and ethanoic FeCl3 produces a colored solution, it suggests the presence of impurities in the product. The color development indicates the potential presence of related compounds, byproducts, or unreacted starting materials. A colored solution affects the purity assessment by indicating a lower purity of the product. Further analysis with appropriate techniques is recommended to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the impurities and their impact on the overall purity of the synthesized acetylsalicylic acid.
In preparation of aspirin, if the mixture of crystalline product and ethanoic FeCl3 produces a colored solution, how would this affect the melting range of final product? Explain!
if the mixture of the crystalline product and ethanoic FeCl3 produces a colored solution, it suggests the presence of impurities in the product. The impurities can influence the melting range by introducing additional melting peaks, broadening the range, or causing a shift in the melting point. Additional purification and characterization steps are necessary to ensure an accurate determination of the melting range and assess the purity of the synthesized acetylsalicylic acid.
What is the purpose of adding sulfuric acid?
It's a good catalyst to speed up the reaction.
what is the purpose of testing with the FeCl3?
To check if any free OH groups are present, to see if the Aspirin has been purified properly or as close to the commercial aspirin.
Which functional group is present in the product?
The functional groups that are in aspirin are carboxylic acid and ester.
Discuss significance of FECl3 test results
Iron (III) Chloride reacts with phenol groups. If there is an -OH group, it will react. Therefore, since salicylic acid has an -OH group, the FeCl3 will turn the solution purple.
Morphine is an analgesic available at the drug store. Using acetic anhydride and morphine, one can easily synthesize a recreational drug. Which one is it? Hints: Search the structure of morphine. And then search the structures of the the options presented below.
Heroin
In today's experiment, which of the following is the crystallization solvent?
Water
One of the chemicals that you will be dealing today reacts vigorously with small amount of water and creates splash. A similar accident happened at UTEP in the past, and someone lost his one eye due to that. After that accident, UTEP changed the policy of eye protection and now safety glasses are no longer allowed in the lab. Which of the following compounds we are talking here?
Acetic anhydride
What are the byproducts of aspirin synthesis?
Acetic acid
Aspirin synthesis can be classified as which of the following types of reactions?
Esterification
If you increase the amount of acetic anhydride the yield will be improved.
False
Today, you used acetic anhydride, which is an acetylating agent. Which of the following agents can also be used as an acetylating agent? (Negative credits will be applied to incorrect answers. Select 2 correct answers to get full credits.)
Acetyl chloride
Acetyl-coenzyme A
Fill the box with the possible product of the reaction:
Product 3
Aspirin forms a beautifully colored blue complex with copper(II) acetate. The name of the dicopper complex is copper aspirinate. You are given 0.2 g of copper(II) acetate and 0.4 g of aspirin to synthesize copper aspirinate. Considering you have 80% yield of the copper aspirinate, how much mmol of copper aspirinate you have? The reaction is shown below. Do not forget to balance the following reaction.
0.44 mmol
Which of the following is the first step of the reaction mechanism for aspirin synthesis?
Answer 3
Let's assume that you were given 16.0g salicylic acid, 25.0mL of acetic anhydride and 10 drops of 85% phosphoric acid. If you obtained 80% reaction yield, then how much aspirin you have synthesized?
16.7g
The following compounds are what type of isomers?
Structural Isomer
What is the purpose of adding 15 mL of room temperature water to the heated reaction flask?
To quench/decompose the excess acetic anhydride
What is the limiting reagent in the synthesis of aspirin?
Acetic anhydride
An -OH substituent on a ring is considered _ . It will result in primarily _ products.
> activating
> ortho and para
Nitration reactions are examples of
> electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions
The nitronium ion forms from the reaction of:
> sulfuric acid
> nitric acid
You will characterize your nitration product using:
> TLC
> mixed melting point
What solvent will you use to dissolve your product prior to spotting it on your TLC plate?
> acetone
What will you return to the stockroom at the end of the lab period?
> stop watch
Based on your knowledge of the effects of substituents on electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, the product of the nitration of methyl benzoate should be primarily
> methyl-m-nitrobenzoate
True or False: Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions
> true
The second step of electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) is different from the electrophilic addition (EA) reaction of alkenes. How?
> in EAS, the second step regenerates aromaticity
Which of the following describes the rate determining step of electrophilic aromatic substitution?
> a carbocation is generated
> the aromatic ring is the nucleophile
> the pi electrons of the aromatic ring attack the electrophile
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, how might ring substituents affect the reaction?
> electron-donating groups can increase the electron density of the ring and enhance the reaction rate
> electron-withdrawing groups can decrease the electron density of the ring and decrease the reaction rate
Ring substituents possessing _ are often _ .
> lone pairs
> activating groups
A(n) _ substituent on a ring will result in primarily meta products. It is considered _.
> carboxylic acid
> deactivating
You will add all of your nitrating solution to the methyl benzoate. If you add your nitrating solution too fast, at a rate greater than _ _ , your product will _ because _ will form.
> two drops
> per minute
> not be as pure
> side products
Which reagents are toxic and can cause severe burns
> sulfuric acid
> nitric acid
The Fischer esterification reaction produces a(n) _ from the reaction of a(n) _ and an alcohol in the presence of an _ catalyst.
> ester
> carboxylic acid
> acid
What is the purpose of the acid catalyst?
> to protonate the leaving group, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack
> the carbonyl carbon is _ - hybridized. The tetrahedral intermediate in the Fischer esterification is _ - hybridized
> sp2
> sp3
All reaction steps in the Fischer esterification are reversible. This means that without an excess of one reaction, at equilibrium carboxylic acid and alcohol _ .
> remain in solution
Because the Fischer esterification is reversible, in your reaction you will add excess _ to drive the reaction to produce more _ .
> alcohol
> product
True or False: During this lab you will check out 2 automatic pipettes per hood.
> true
t-BME stands for:
> t-butyl methyl ether
Which characterization technique produces a spectrum that highlights characteristic infrared absorption frequencies of functional groups?
> IR
Which chemical will be used to dry the ester layer for 5 minutes before it is safe to smell your solutions?
> sodium sulfate
What is the next step after adding 5 drops of sulfuric acid to each test tube?
> heating the solutions in a water bath heated to 65-80*C on a hot plate for 10 minutes
In the elimination step of Fischer esterification, which molecule is eliminated if the tetrahedral intermediate contains a protonated -OH group?
> water
True or False: If you add water to one of your Fischer esterification reactions, the reaction will favor the formation of the ester product.
> false
True or False: The carboxylic acids you will be using in this lab are pleasant smelling.
> false
True or False: You should place your face directly over a test tube to smell the ester
> false
True or False: You should use the densities of the liquids to determine volumes of alcohol needed in mL
> true
Why is the ether the top layer instead of the bottom layer in your separation?
> ether is less dense than water
During the esterification reaction, 2 layers will form in your test tubes. Esters are more likely to be found in the _ layer.
> top organic
In organometallic reagents, the metal carries a partial _ charge and the carbon atom carries a partial _ charge.
> positive
> negative
Organolithium reagents are _ reactive than organomagnesium reagents because the electronegativity difference between carbon and lithium is _ than the electronegativity difference between carbon and magnesium.
> more
> greater
A carbanion (such as CH3-) is the conjugate base of a very weak acid (CH4). This makes it a _ base. The pKa of CH4 is _.
> strong
> 50
Organometallic reagents are made by mixing the metal with a(n) _
> alkyl/aryl halide
The formation of a Grignard reagent occurs through a(n) _ mechanism.
> radical
Solvent plays an important role in Grignard formation. The _ atom on diethylether or THF will coordinate to the metal through the _.
> oxygen
> lone pair
Grignards react with _ to form alcohols.
> carbonyls
Grignards react with O2 to produce _.
> peroxides
Grignards react with carbon dioxide to form _ .
> carboxylic acids
Use a graduated cylinder to measure reagent volumes _ than 1 mL and a syringe to measure reagent volumes _ than 1 mL.
> greater
> less
You need to add _ at the conclusion of the Grignard reaction to get the neutral product.
> acid
You will isolate the product by performing an extraction. When you add your product to the separatory funnel and add methyl tert-butyl ether, your product will be in the _ layer.
> top
How will you get rid of the biphenyl by-product?
> recrystallization
You will characterize your product using:
> melting point
> TLC
To exclude air/moisture from this reaction, we will use
> a drying tube
Because several competing reactions can occur with Grignard reactions all glassware must be free of _.
> water
How do you introduce liquid reagents to your reaction?
> through septa via syringe
For the gelatin of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), the borate ion acted as a chemical crosslinker rather than a physical crosslinker
> false
To prevent competing side reactions during a Grignard reaction what compound(s) must be excluded from the reaction vessel?
> o2
The magnesium atom of a Grignard reagent is electron deficient. Therefore coordination of this to a proton on a solvent stabilizes the Grignard reagent.
> false
A benzene is substituted as seen in the image below. If a nitronium ion reacted with this substituted ring, where would it go?
> meta position
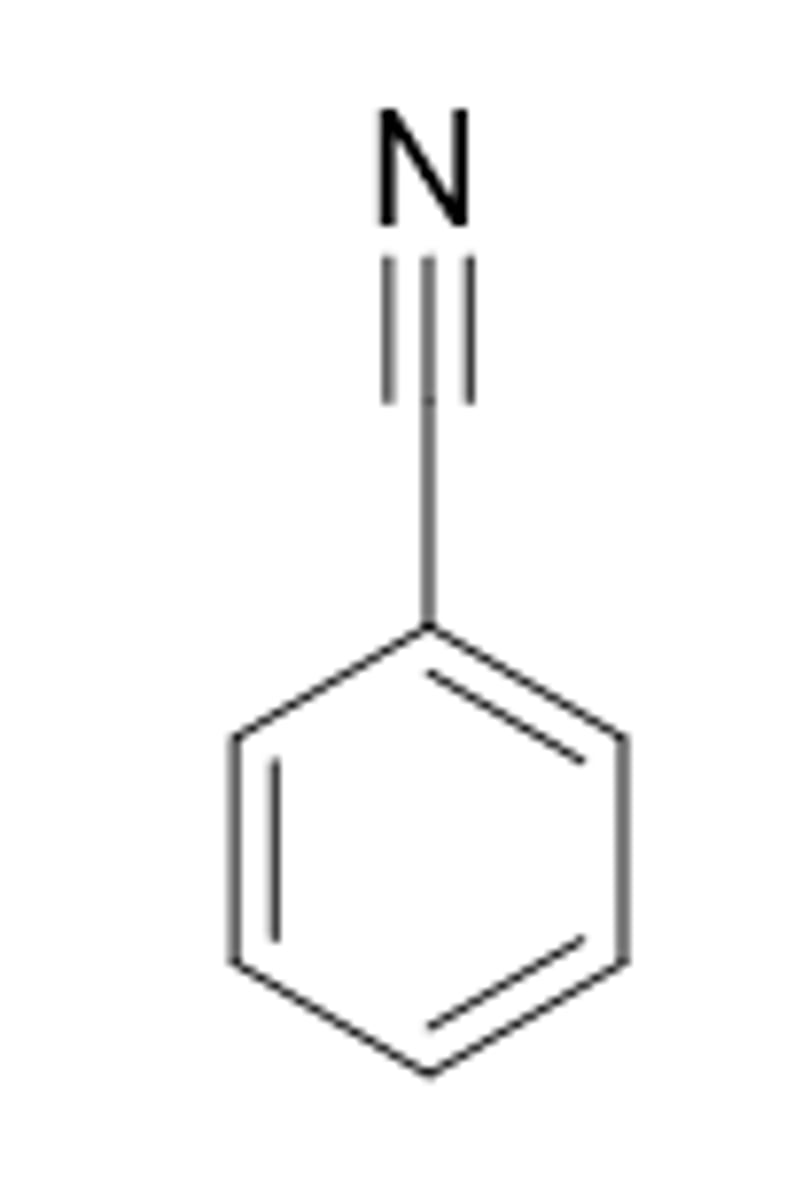
What is the hybridization of the circled carbon in molecule shown below?
> sp2
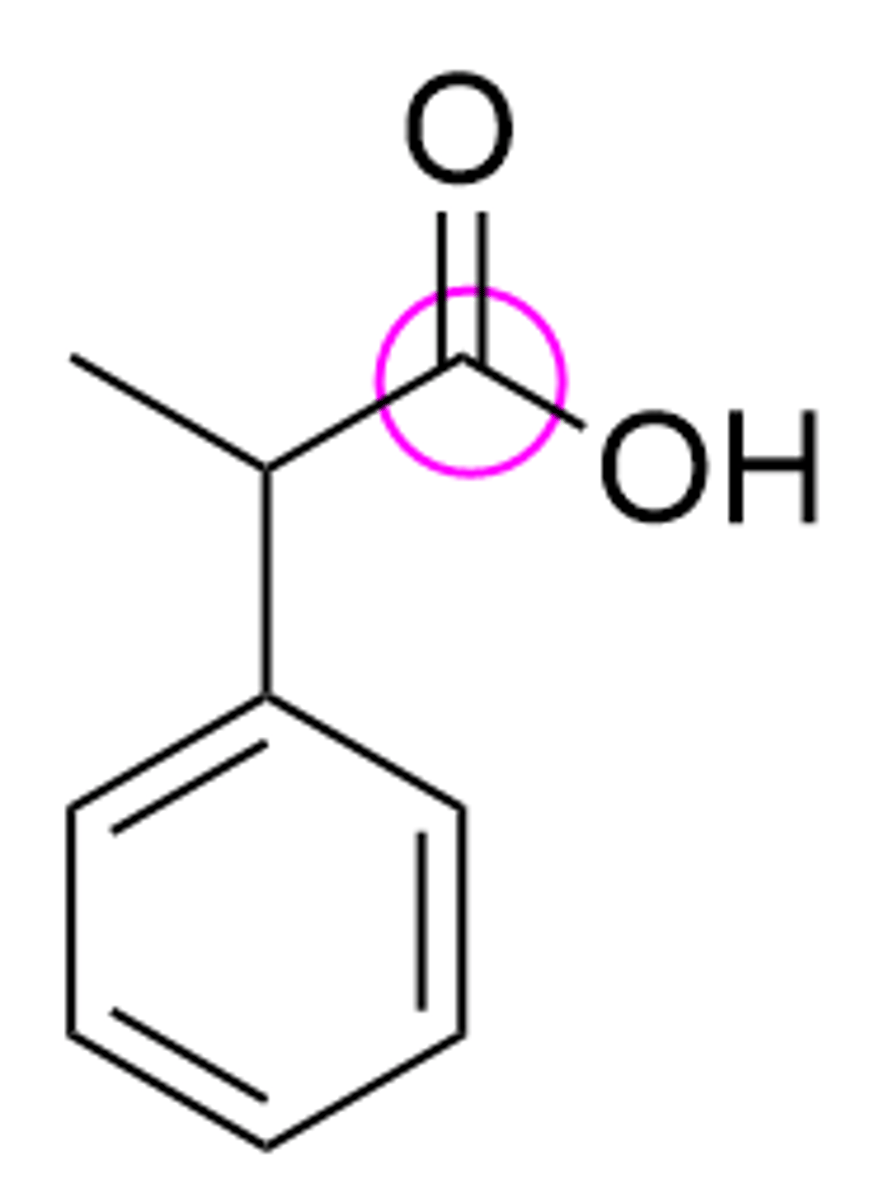
A student is running a Fischer esterification reaction. They are using 0.75 mL of acetic acid and 3.0 equivalents of octyl alcohol. How many mL of octyl alcohol will they use?
6.19 mL
This reaction only yields 1.3 mL octyl acetate. What is the percent yield?
49.8%
Joel takes a TLC plate of the following reaction. Which lane on the silica TLC plate would most likely come from the starting material?
> lane A
The less polar a compound is, the further it will move up a TLC plate.
> true
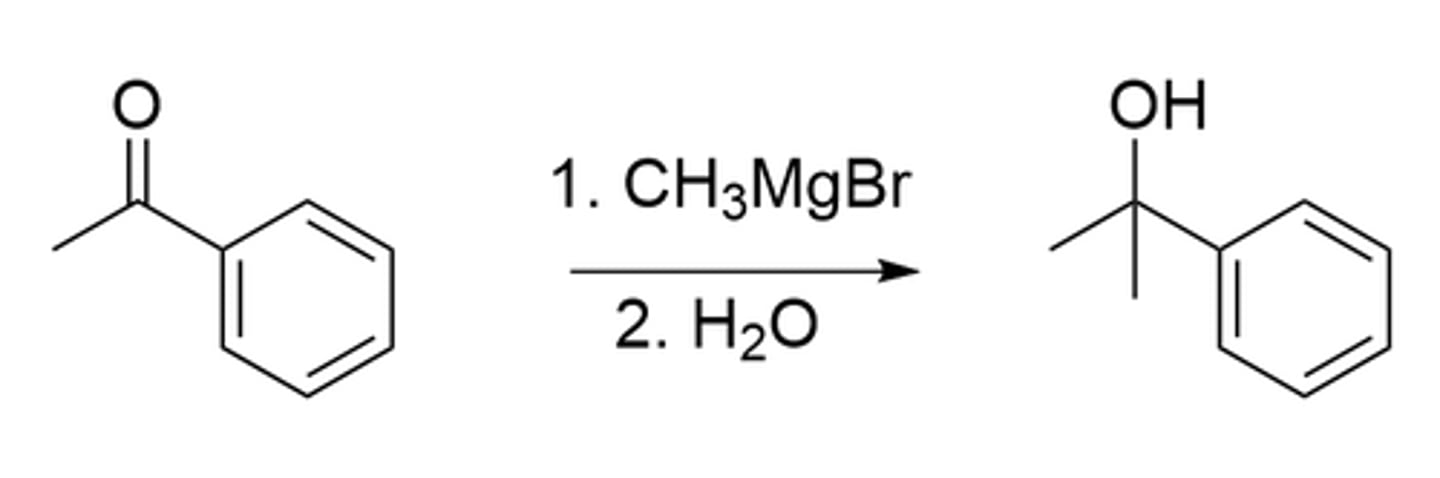
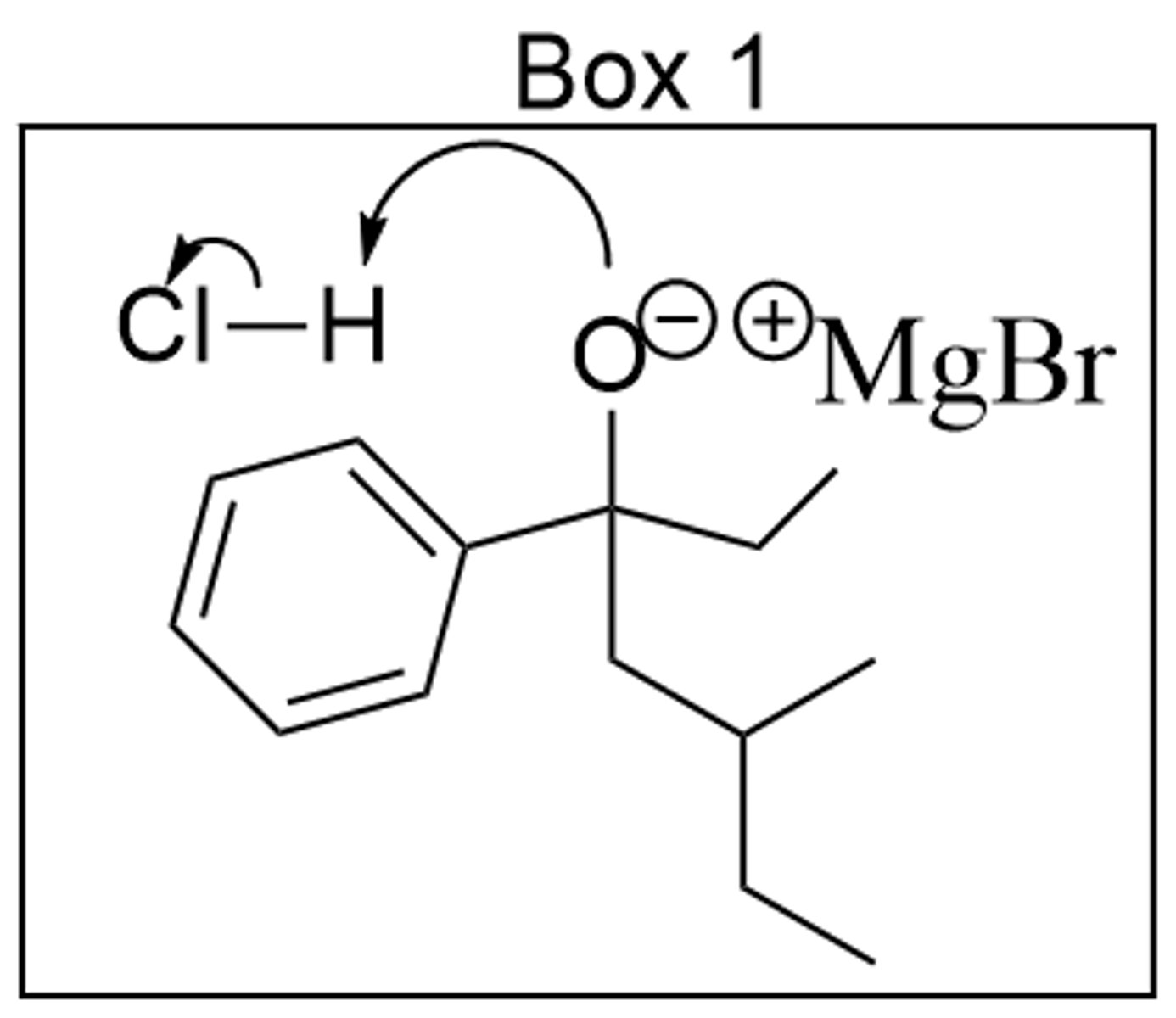
Which best belongs in Box 1?
> see image
Which of the following best describes the side product of this reaction and belongs in Box 2?
> ClMgBr
What, if anything, is incorrect with the mechanism in Box 1?
> an arrow is missing
What, if anything, is incorrect with the mechanism in Box 2?
> nothing is incorrect
What, if anything, is incorrect with the mechanism in Box 3?
> nothing is incorrect
What, if anything, is incorrect with the mechanism in Box 4?
> an "n" is missing
> the parentheses are not around the repeating unit
What, if anything, is incorrect with the mechanism in Box 5?
> an "n" is missing
> the parentheses are not around the repeating unit
> the label is incorrect and should be "terminated by combination" rather than "termination by disproportionation"