Polymers and Proteins
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are polymers?
Very large molecules with a carbone backbone
What are monomers?
Small molecules that combine to form polymers
Describe the polymerisation of addition polymers
Monomers added together
All atoms are used to form the polymer
Alkenes undergo polymerisation
The double bond is broken
New single C-C bonds are formed
Involves use of a catalyst
No small molecules/atoms eliminated
What is the general reaction for addition polymers?
(catalyst)
nR-C=C-R’ —> -(-C(R)-C(R’)-)n-
Describe the polymerisation of condensation polymers
Reaction between monomers with two reactive groups (ie: diols, carboxylic acids, amines)
Elimination of smaller molecules (H2O)
2 reactive functional groups remain at either end of growing chain
Carboxylic acids + alcohols form polyesters
Describe the structure of polyethene
Made of chains that vary in length and molecular mass
Held together by dispersion forces
Disp. forces stronger in regions where chains are arranged in orderly fashion
What is the equation for polyethene?
(catalyst)
nCH2=CH2 —> (-CH2-CH2-)n
What type of polymer is polyethene?
Addition polymer
What are the two types of polyethene?
Low Density Polyethene (LDPE)
High Density Polyethene (HDPE)
What is the structure of LDPE? How is it formed?
Produced at high temperatures (200-300°C) and high pressures (1000-3000atm)
Significant amount of branching (small side chains)
What are the properties of LDPE?
The significant amount of side chains:
Reduce strength of dispersion forces
Creates lots of space in the product
Low MP, low density, soft and flexible
Structure is amorphous (non-crystalline)
Eg: cling wrap, flexible plastic bottles, plastic toys
What is the structure of HDPE? How does it form?
Produced at lower temperatures (60°C) and low pressure (1-4atm)
Unbranched chains allow close approach of polymer chains
Held together by strong dispersion forces
What are the properties of HDPE?
High mechanical strength
Higher density
Higher MP
Eg: chopping boards, water pipes, buckets
What is a polyester?
A polymer with many ester links within the chain
What are the two configurations of polyester monomers?
Single monomer: hydroxyl group at one end, carboxyl group at other
Two different monomers: one has a diol, other is a dicarboxylic acid
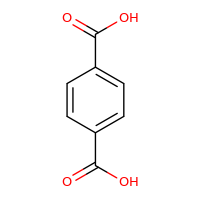
Name this monomer unit
Benzene-1,4-dioic acid
What is the general formula for formation of polymers?
A + B —> (A+B)n + 2nH2O
What is PET?
Polyethylene terephthalate
What are the properties of PET?
Permanent net dipole exists around each ester link
IMF: dipole-dipole and dispersion forces
Form crystalline structures when cool slowly, giving increased strength
What is a polyamide?
A condensation polymer where monomer units connect via amide linkages
What are the two configurations of polyamide monomers?
Two different monomers - one is a diamine, one is a dicarboxylic acid
Single monomer - amine group at one end, carboxylic acid at other end
What is needed for a protein to be considered a protein molecule?
Has 50+ amino acids
What is the primary structure of a protein?
Specific amino acid sequence
Always listed from -NH2 end of molecule
Determines how it will fold/curl in on itself
Conformation governs how protein interacts with other molecules, determining its function
Alteration in sequence affects conformation and ability to function correctly
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
Regular repeating structures
Regular arrangement of various sections of the protein
Structures include: Alpha-helix (coiled section), beta-pleated sheets (corrugated structure)
Stabilised by C=O on one part of the chain and N-H group on another
Describe the structure of alpha-helix arrangement
Occur between lone pair of e- on O of C=O and H on N-H located four peptide links apart
Describe the structure of beta-pleated sheet arrangement
Occur where alpha amino acid residues have smaller side chains
Sections of protein chain can fit closely alongside each other
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
Overall three-dimensional structure of a protein
Can form several structures:
Long, narrow: fibrous proteins such as keratin
Spherical, globular: enzymes
Caused by interactions between residue side chains
What are α-amino acids?
Contain both (-NH2) and (-COOH) groups
Form the backbone of proteins
What are the names of molecules that are formed from amino acid links?
Peptides
Can be dipeptides, tripeptides, polypeptides and proteins
What classifies a non-polar alpha amino acid?
Only C and H on side groups
Ie: Ala, Gly, Ile, Leu, Phe, Val
What classifies a polar alpha amino acid?
Can either:
Form ions (ionic bonds in addition to all 3 IMF’s)
Has extra -NH2, -COOH
Not form ions
Has extra -OH, -C(=O)-NH2, S
What are the properties of alpha-amino acids?
Soluble in water
Solids at room temp (high MP)
White, crystalline solids
What is a zwitterion?
A particle that has a net neutral charge, but has both a +ve and -ve charge on it
Ie: N+H3-CH2-C(=O)-O-