IB Biology - Topic 6.1 + D.2: Digestive System
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
outline the process of digestion
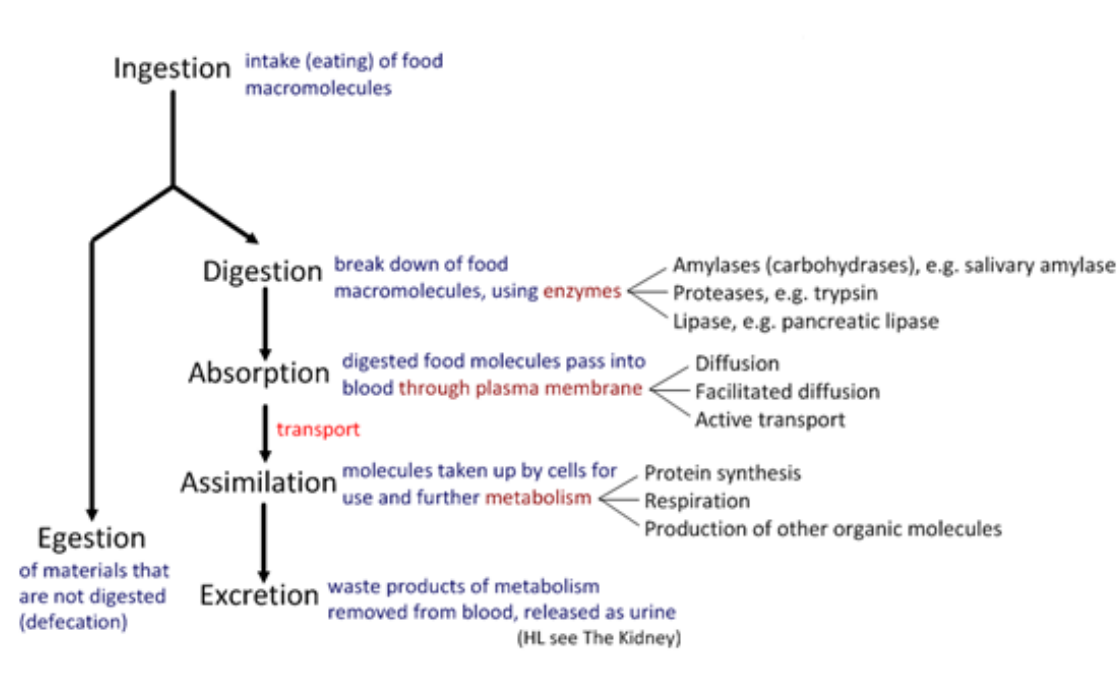
explain why digestion is necessary
large molecules need to be digested before the nutrients can be absorbed
polymers are insoluble and are required to be dissolved in a solution
macromolecules can be reassembled and assimilated to be useful to the human body
explain how food molecules are split
hydrolysis
explain why enzymes have a role in digestion
glands release enzymes into the gut that are used in catabolic reactions (breaking down molecules)
draw and label the digestive system
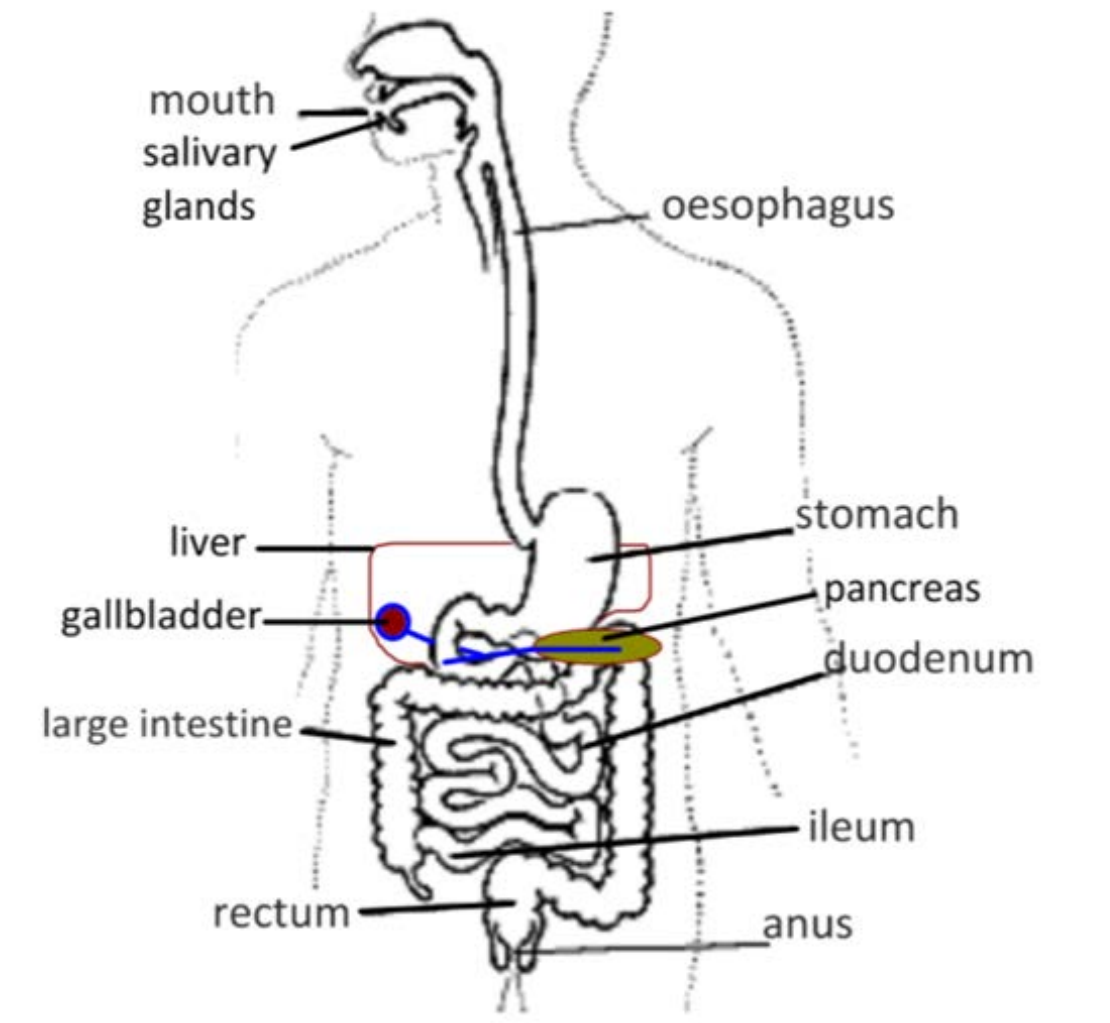
outline the process of digestion (mouth)
mechanical digestion crushed the food; salivary glands (an exocrine gland) secretes saliva which moistens the food to make a bolus for swallowing; salivary amylase beings the chemical digestion of starch
outline the process of digestion (esophagus)
peristalsis, wave of muscle contractions, pushes the bolus into the stomach
outline the process of digestion (stomach)
muscle contractions continue to mix the food; the acid in the stomach (hydrochloric acid) kills bacteria; pepsinogen secreted by the gastric cells is turned into pepsin in the presence of the acid and begin the digestion of proteins
outline the process of digestion (duodenum, small intestine)
bile is secreted into the duodenum from the liver/gall bladder; acid from the stomach is neutralized and fats are emulsified into small droplets for easier reactions; pancreatic amylase and lipase digest carbohydrates and fats
outline the process of digestion (ileum, small intestine)
absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream via villi
outline the process of digestion (large intestine)
water is reclaimed back into the bloodstream; feces stored in the rectum
outline the process of digestion (egestion)
poop
name the 4 digestive exocrine glands
salivary glands
pyloric glands (stomach)
pancreas
liver
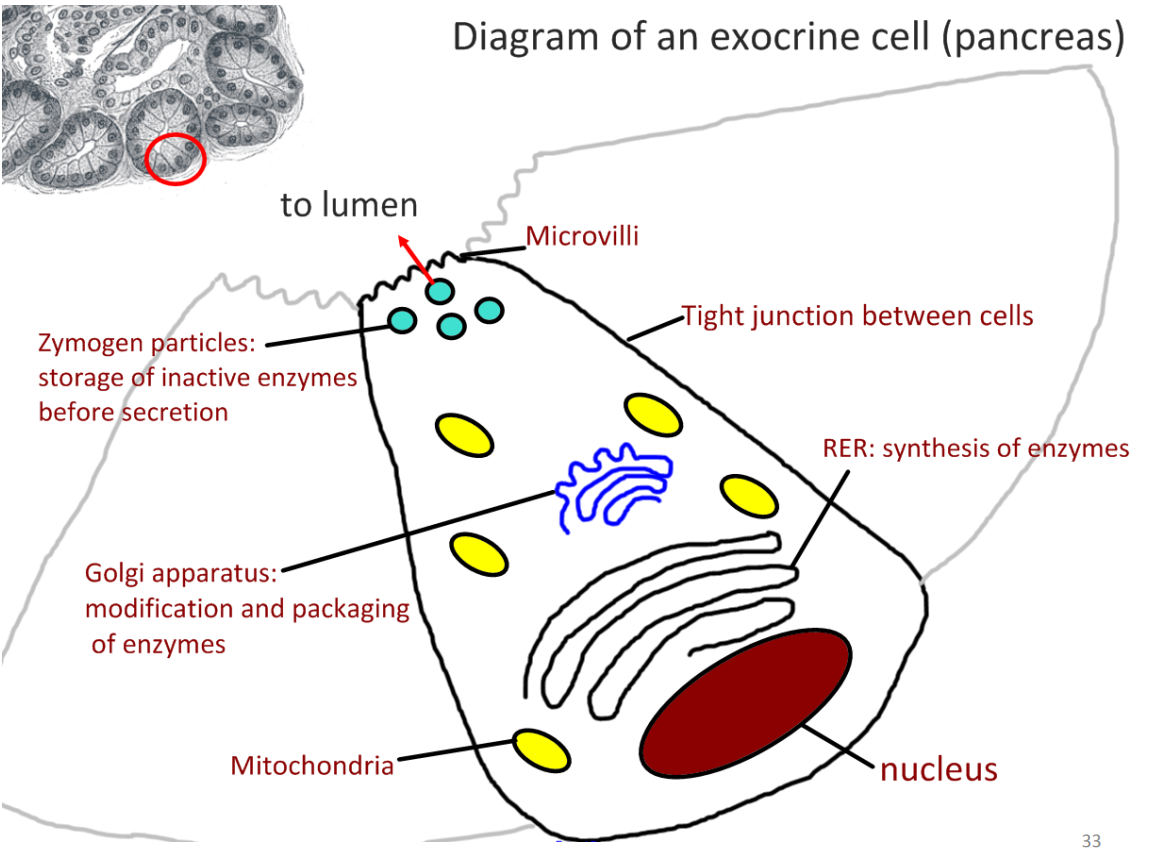
explain why the exocrine glands contain so much rough ER and Golgi apparatus
mass synthesis of enzymes for digestion
draw and label a diagram of an exocrine cell
explain the role of hydrochloric acid in the stomach
lowers the pH to around 2 to kill bacteria and denature proteins
explain the parts of the stomach that aid it in digestion
muscular walls that contract to mix food and enzymes, stretching of muscles also triggers enzyme secretion; gastric pits release gastric acid and mucus; muscular sphincters control entry and exit of chyme
list the pancreatic enzymes that are release into the small intestine
pancreatic amylase: breakdown of carbohydrates into monomers of glucose
pancreatic lipase: breakdown of lipids into monomers of fatty acids and monoglycerides
pancreatic trypsinogen: digests proteins into monomers of free amino acids
explain the reason for villi
villi are projections that increase the surface are for maximum absorption
explain why rich blood supply in the villi is important
to create concentration gradients for molecules to diffuse through
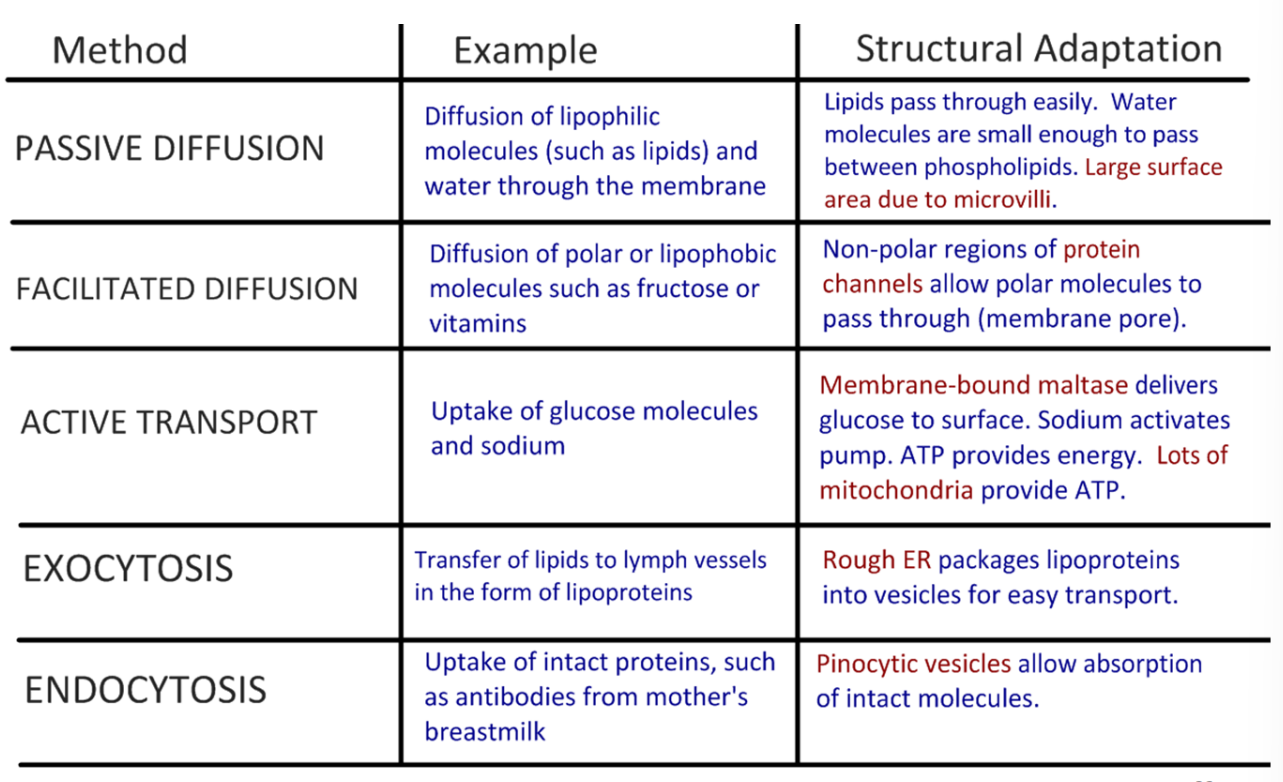
outline how the ileum absorbs molecules
active transport; the epithelial cells of the ileum pump sodium ions into the lumen of the small intestine, maintaining a concentration gradient; passively, reentry of sodium is accompanied by nutrients; these nutrients pass through the epithelial cells and enter the capillaries
outline the control of digestive juice secretion
combination of nervous and hormonal control
food in stomach stimulates stretch receptors (nervous) that triggers gastrin (hormone) into the bloodstream to produce HCl
chyme in the small intestine triggers release of secretin (hormone) that triggers secretion by liver and pancreas
draw and label a villus and microvillus cell
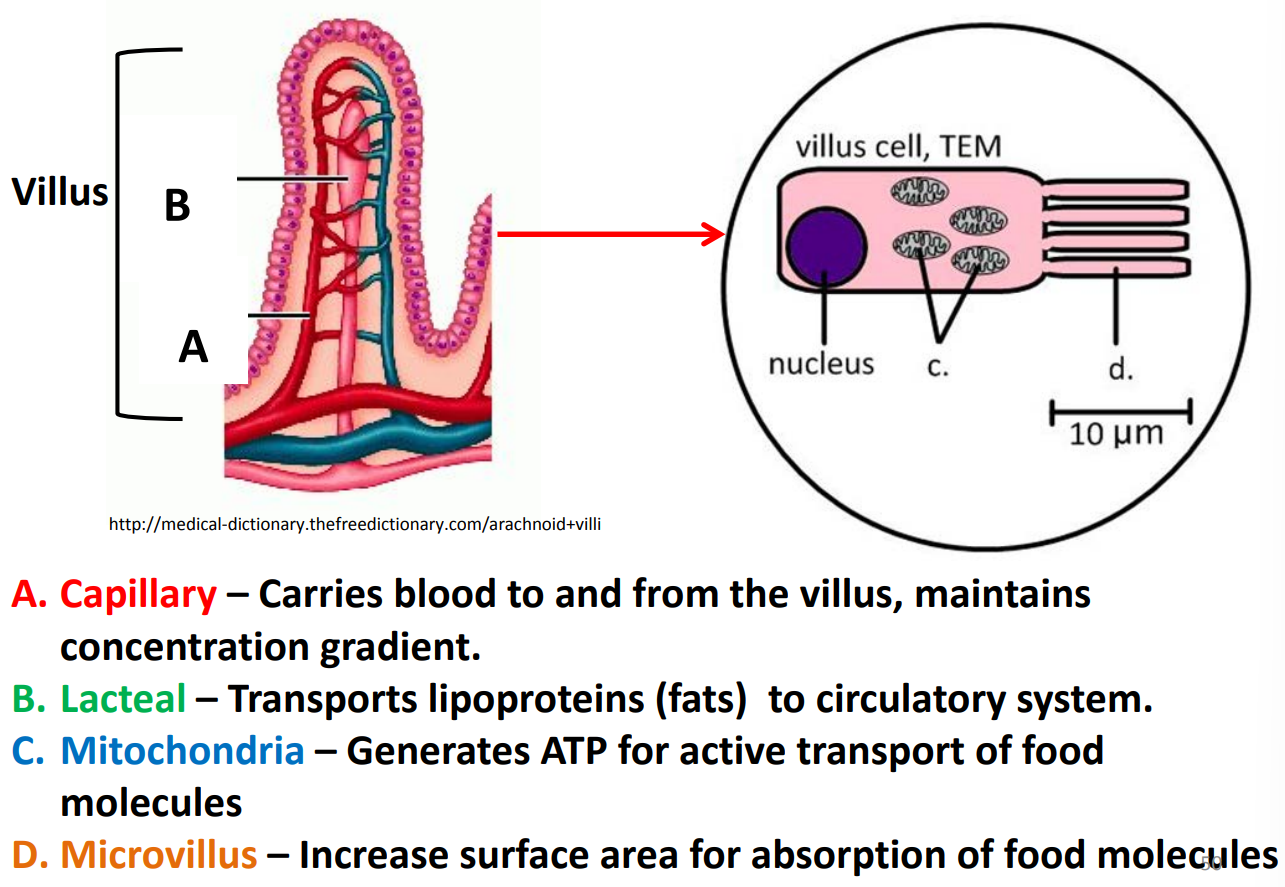
explain the significance of lacteals
allow glycerol and fatty acids to be easily absorbed (lipids)
explain what vitamins are
organic compounds that cannot be synthesized in the body; some water soluble some lipid soluble
explain what minerals are
inorganic elements; all water soluble
draw and label a diagram of a section of ileum
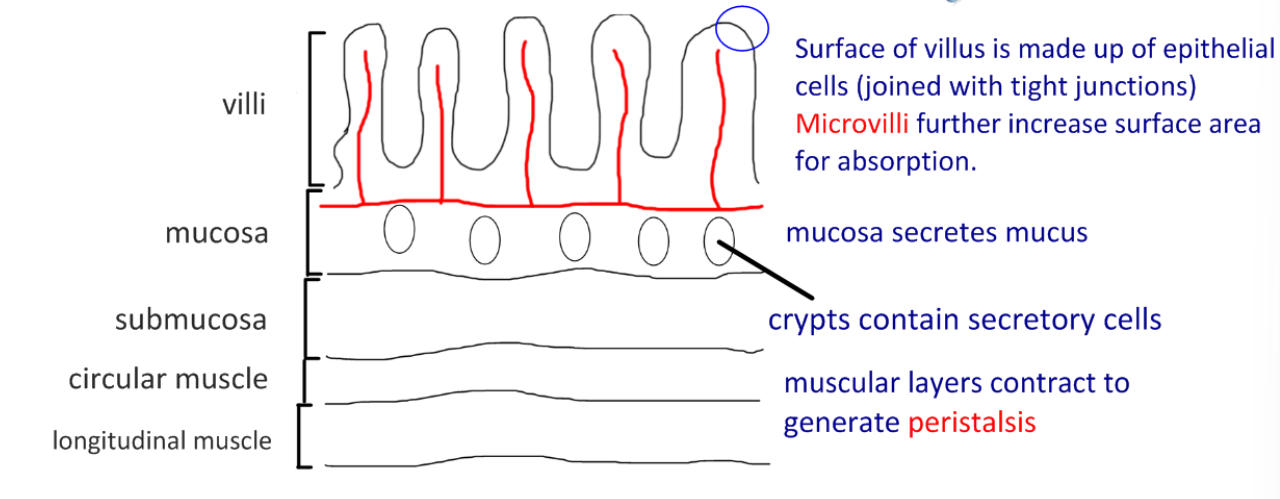
outline the functions of the colon (large intestine)
maximize surface area for absorption of water + vitamins
store feces temporarily
secrete mucus for lubrication to push feces
produce good bacteria
list some benefits of fiber rich diets
reduce huger
aids peristalsis
clears out waste products
prevent constipation
reduce risk of appendicitis, cancer, + hemorrhoids
slows rate of sugar absorption
outline the different types of membrane transport used in the absorption of digested food