Linkage & Genetic Variation Analyses
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
how do alleles from linked gene assort
if 2 genes are completely linked, the alleles from the parent will assort together 100% of the time
what are parental & recombinant genotypes
parental - the chromosomes of the parent
recombinant - the recombined chromosome of the child
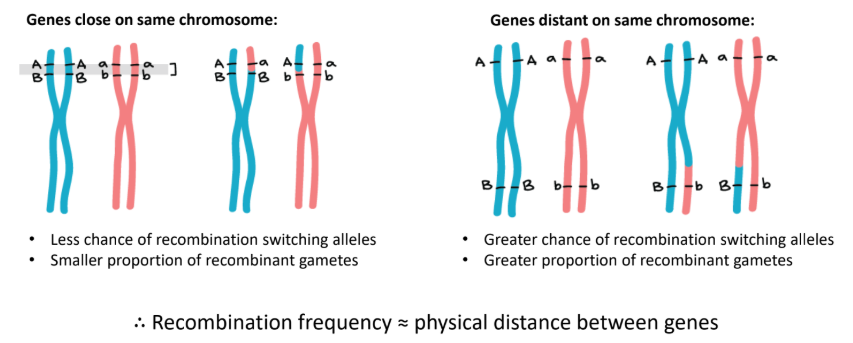
why can we not be sure of the dihybrid & test cross ratios for recombination of alleles that are “linked'“
when genes are “linked” close together on chromosome, it is less likely they will be reassorted independently. This is because it is less likely that chromosome will split during meiosis to separate these genes hence the genes are sorted dependently, and so ratios cannot be determined
what is coupling & repulsion phase for parental alleles
refers to whether the dominant & recessive alleles are on the same or different parental genes

what is recombination frequency
refers to the frequency in which recombinant genotypes appear
determined by distance between genes
how is recombination frequency (RF) calculated
RF = (number of recombinants/total progeny) x 100
max RF = 50%
why is max RF 50%
since each meiotic event only involves one of the sister chromatids
hence even if any participating chromatid underwent recombinant their sister wouldn’t hence 50%
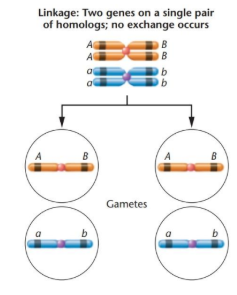
how can recombination frequency help define linkage
genes with RF < 50% are linked
genes with RF = 50% are not linked
what is the genetic mapping principle
the RF is correlated with the distance between genes
map distance = map units (mu) or centiMorgans (cM)
1mu/cM = distance that will produce 1% RF
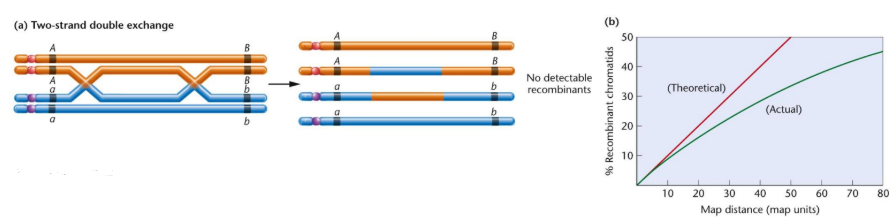
what are double crossovers
refers to 2 crossover events between loci which restores them to parental arrangement
further 2 genes apart = ↑ chance of double crossover
how can kai-squared test be used for measuring “unlinked” genes
hypothesis are based on gene being linked
null hyo = variation due to chance, gene are unlinked
alt. hypo = variation is due to another reason, gene are linked
what are some of the benefits of a trihybrid cross
faster
more accurate (tests for double recombinase)
how do we calculate RF from a trihybrid cross
consider only 2 genes at a time
find all combinations of those 2 genes that match the parental combinations
add those together, anything else is recombinant, thus can calculate RF
repeat for the other 2 combinations of step 1
what are 2 ways to identify double recombinant progeny for a tricross map
the smallest number since double recombination is rare
look for combination that are parental on the outside but recombinant in the middle (i.e. a different allele)
how do we take into account double crossovers
(original recombinants + 2 x double recombinants) / total
how can we calculate if interference changes the proportion of double crossovers
chance of DCO =
(chance of crossover between A & B) x (chance of crossover between B & C)
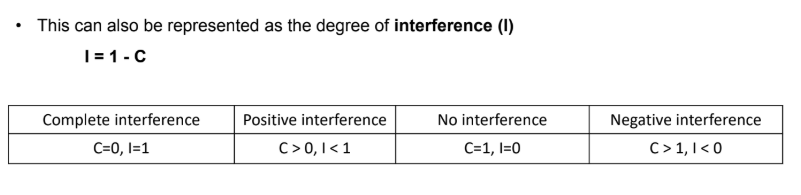
what is the coefficient of coincidence & interference (C)
C = observed/expected
I = 1-C
what are some uses for genetic maps
Used to identify disease causing rare disease causing alleles
Molecular markers mostly used in humans
Linkage must be considered in genetic counselling/ risk calculations
Assist in genome sequence assembly
what are some “small variant” DNA changes
SNV (single nucleotide variant) - single change in the nucleotide
indel - insertions / deletions
what are some “large variant” DNA changes
refers to large changes in DNA makeup
deletion
duplication
inversion
insertion
translocation
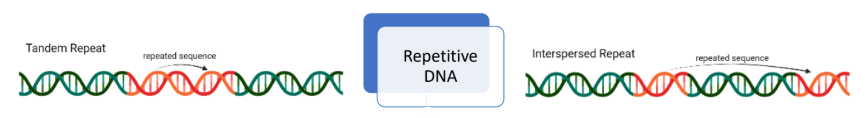
what are different variations of DNA repeats
tandem
micro-satellites
mini-satellites
interspersed
transposons
retroelements
what is the human reference genome
a standardized sequence comprised of non-pathogenic sequences, used to compare human variations
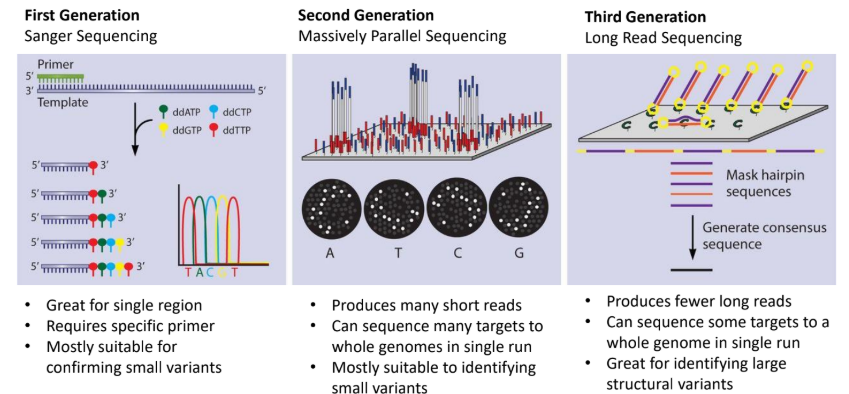
what is first generation (sanger sequencing)
primer binds to template and ddntps are sued to reconstruct the sequence and thus identify the sequence present
suitable for confirming small variants
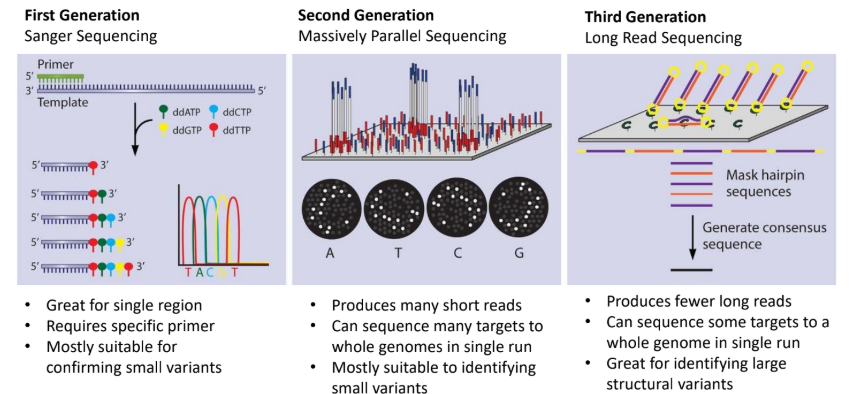
what is second generation sequencing (massively parallel sequencing)
split your sample into millions of small DNA pieces and sequence them all simultaneously in parallel “lanes” or “clusters” on a solid surface or inside tiny wells
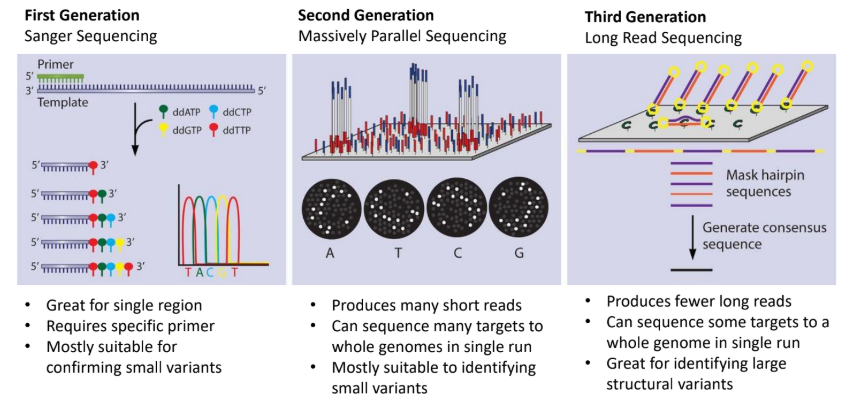
what is third generation (long read sequencing)
sequences long strands of DNA by keeping them intact, thus whole genomes can be sequenced in single runs
good for identifying large structural variants
what are some dis/advantages to sequencing (NGS)
ADV:
can provide complete information (known & novel variants)
non-targeted & target (don’t need to know what your looking for)
DIS:
slower that genotyping
relatively expensive
what are some dis/advantages to genotyping
ADV:
faster than NGS
usually cheap
DIS:
targeted (need to know what your searching for)
provides partial information (only known variants)
what is restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)
refers to how small variants may change the recognition site for a restriction enzyme
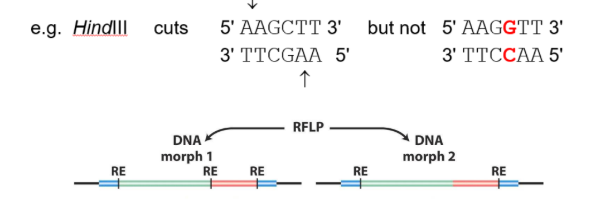
what are 2 methods to identify RFLPs
identifying RFLPs using PCR amplification
amplify region with restriction site
1 with & 1 without will be produced
identifying RFLPs using labeled probes
probe binds to restriction site if present
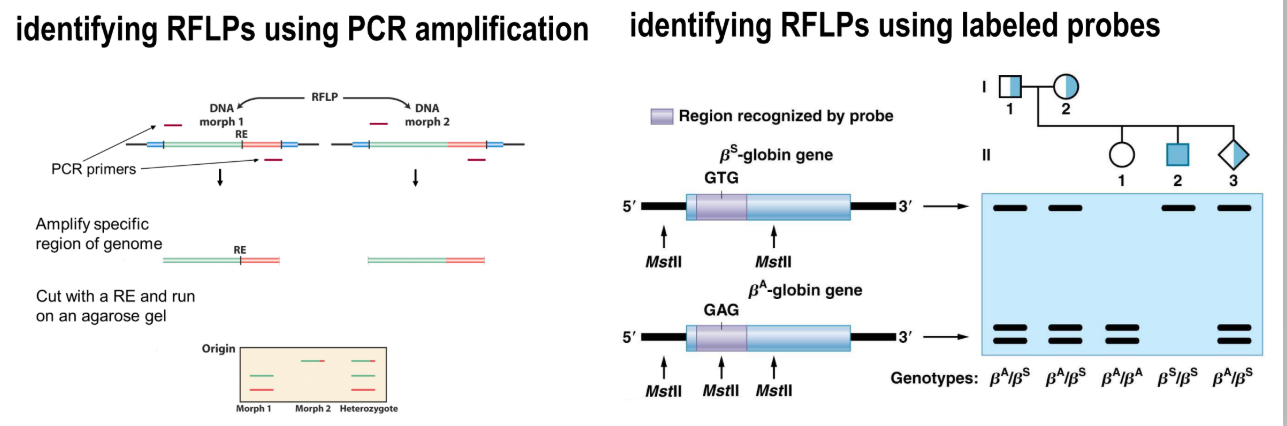
what is a problem with RFLP genotyping
many small variants don’t change restriction cut sites, hence pathogenic changes may not be detected
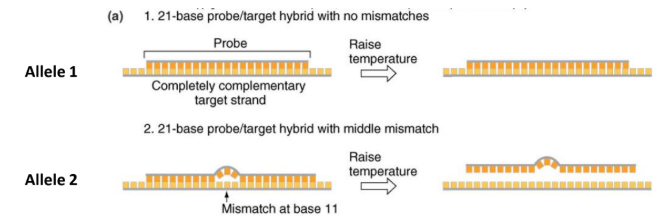
how can probe hybridization identify alleles
a complementary probe binds to a sequence of nucleotides, if the probe is completely complementary it will have the maximum number of H-bonds, if not completely complementary limited number
hence when we heat them the non-complementary one will dissociate first, thus indicating a variant
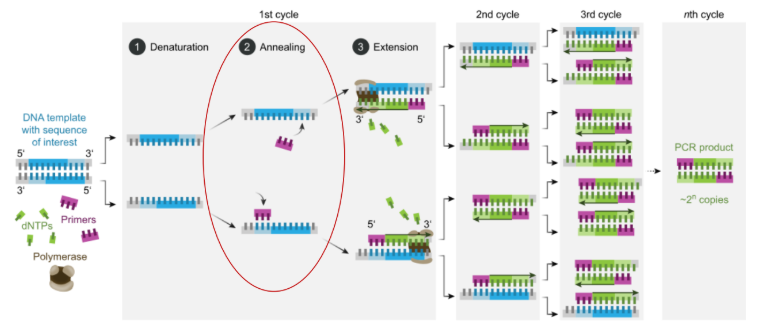
how can PCR be used to detect variants via annealing
change the identity of the primers such that they bind if the variant is present
product changes based on the annealing of the primers
good for SNVs & indels
what are micro/mini satellite repeats
microsatellite - repeats of 2-10bps
minisatellite - repeats of 10-100bps
how can micro- & minisatellite repeats be detected
detected based on the length of the product
gel electrophoresis separates based on length