AQA A Level Chemistry - Haloalkanes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what are the 3 ‘classifications’ of haloalkanes?
primary
secondary
tertiary
what do the classifications of haloalkanes mean?
primary - carbon bonded to halogen is bonded to 1 other carbon
secondary - carbon bonding to halogen is bonded to 2 other carbons
tertiary - carbon bonded to halogen is bonded to 3 other carbons
what is the order of reaction rate of different classifications of haloalkanes?
tertiary - react fastest
secondary - middle
primary - react slowest
why do tertiary haloalkanes react faster than primary haloalkanes?
tertiary haloalkanes react with Sn1 mechanism
primary react with Sn2 mechaism
how does the polarity of the C-X bond change down group 7?
as you go down group 7, polarity decreases
this is because electronegativity decrease down the group
what is the order of reaction rate for different C-X bonds?
C-I → fastest
C-Br → middle
C-Cl → slowest
C-F → doesn’t react
what are the two factors that affect rate of reaction of different C-X bonds/haloalkanes?
bond polarity (much less significant)
bond enthalpy (v. significant)
how does bond polarity affect rate of breaking of C-X bond?
increasing bond polarity means bond is more likely to break
this is because bond attracts nucleophiles more
relatively insignificant
how does bond enthalpy change down group 7?
as you go down group 7, bond enthalpy increases
this is because the X atoms get larger, and have a greater Ar
so the C and X atoms cannot get as close together
so there is more distance between the nucleus of 1 atom and the outer e- of the other
how does boiling point change across the haloalkanes?
increases with increasing chain length
increases going down g7
why does the boiling point increase with increasing chain length?
longer chain means greater Mr
also means more points of contact
VDW forces increase, so require more energy to overcome
why does the boiling point increase down group 7?
permanent dipole-dipole interactions increase as bond gets more polar (insignificant)
Ar of halogen increases, increasing Mr of molecule so increasing VDW forces increasing boiling point
describe the solubility of haloalkanes
although polar, they are insoluble or very slightly soluble in water
soluble in organic solvents so used for dry cleaning fluid/degreasing agents
what is another term for breaking covalent bonds?
fission
what are the two types of fission?
homolytic
heterolytic
what is homolytic fission?
both electrons go to one atom
creates 2 ions
uses curly arrow
what is heterolytic fission?
one electron goes to each atom
always forms 2x free radicals
uses fish hook arrow
what does a curly arrow represent?
movement of a pair of electrons
what is free radical substitution?
reaction of chlorine and alkane in atmosphere to form chloroalkane and HCl gas
requires presence of UV light
give the mechanism for free radical substitution of methane
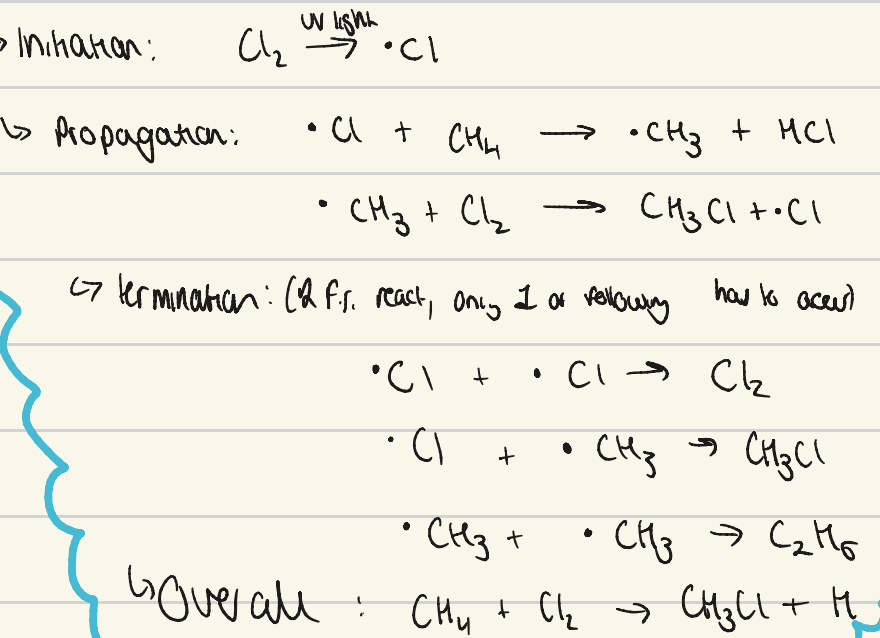
what is the ozone layer and what does it do?
ozone = O3
it absorbs UV light, preventing some of it from reaching earth
reduces sunburn, skin cancer, cataracts
what is ozone depletion caused by?
CFCs
break down into Cl radicals
(F radicals not formed)
what were CFCs used for and why?
used in fridges, propellants in aerosols, flame retardants
non toxic
non flammable
inert
what is a better alternative to CFCs?
HCFs
no chlorine = no chlorine radicals
F free radicals don’t form
what is the initiation step for the mechanism of CFC ozone depletion?
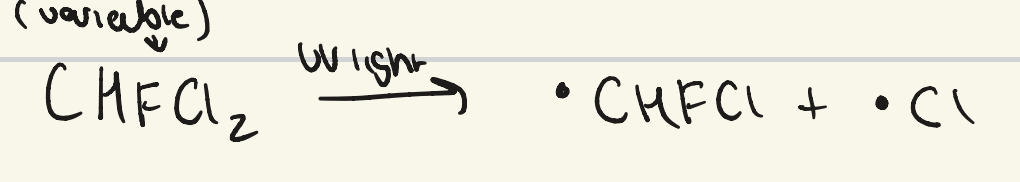
what is the propagation step for CFC ozone depletion?
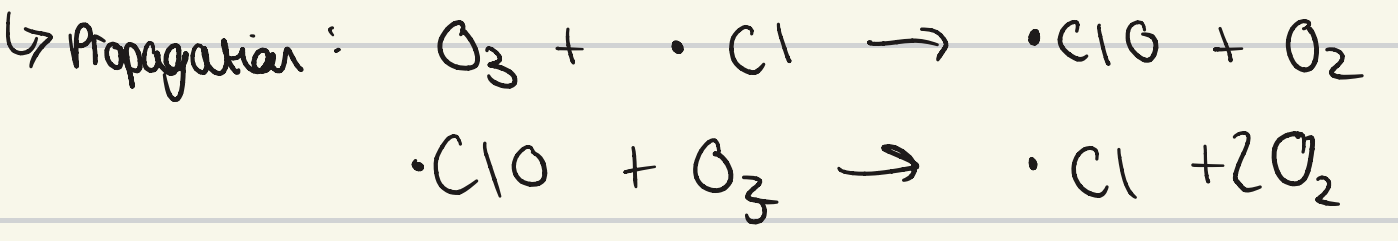
what is the termination step for CFC ozone depletion?
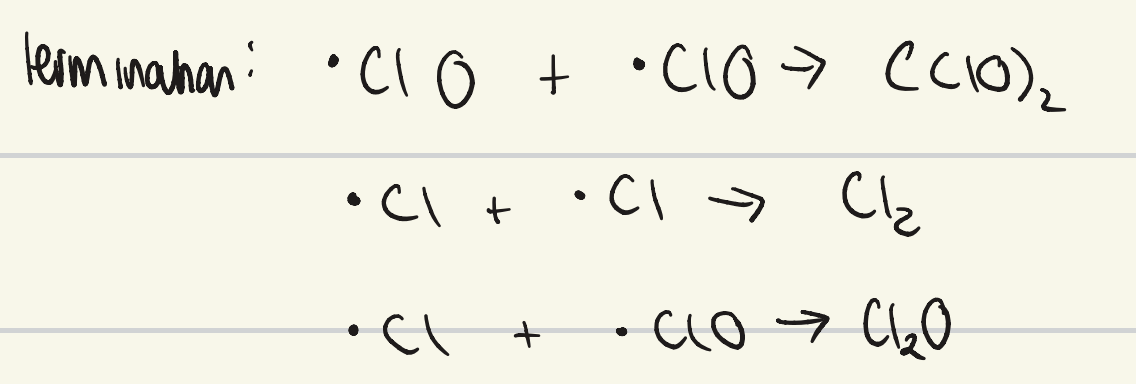
what is the overall equation for CFC ozone depletion?
2O3 → 3O2
what is the other radical that can cause ozone depletion?
nitrogen monoxide
give the mechanism for ozone depletion by the nitrogen monoxide radical
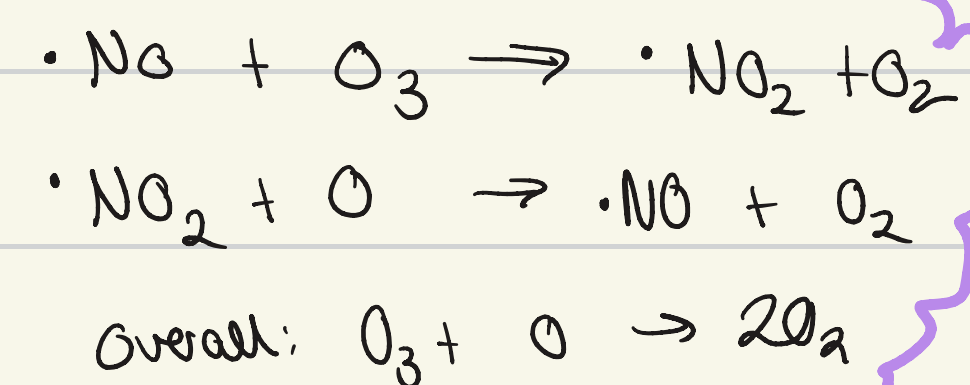
why were CFCs banned?
research by different groups in scientific community provided legislation to ban CFCs
200 countries have pledged to reduce use in Montreal Protocol
alternatives have been synthesized
what is a nucleophile?
electron pair donor
what are the 3 nucleophiles that react with haloalkanes?
hydroxide
cyanide
ammonia
what are the conditions for the reaction of a hydroxide nucleophile with a haloalkane?
uses AQUEOUS NaOH or KOH
reflux to increase temp to increase rate
haloalkane dissolved in a little ethanol (ethanolic)
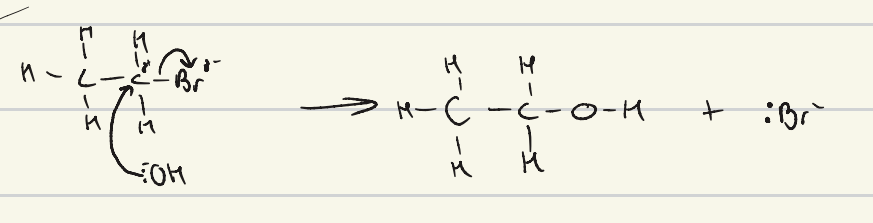
what is the general equation for the reaction of a hydroxide with a haloalkane?
haloalkane + sodium hydroxide → alcohol + sodium halide
give the mechanism for the reaction of bromoethane with hydroxide
what are the conditions required for nucleophilic substitution of cyanide?
aqueous solution of KCN
ethanolic haloalkane
reflux gently
what is the general equation for the reaction of a haloalkane with cyanide?
haloalkane + potassium cyanide → nitrile + potassium halide
R-CH2X + KCN → R-CH2CN + KX
what is the mechanism for nucleophilic substitution of cyanide?

what are the conditions required for nucleophilic substitution of ammonia?
concentrated ammonia solution
ethanolic haloalkane
sealed container under pressure
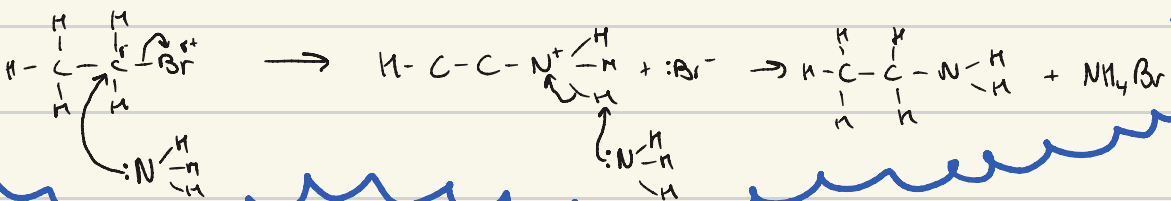
give the general equation for the reaction of ammonia with a haloalkane
haloalkane + ammonia → primary amine + ammonium halide
R-CH2X + 2NH3 → R-CH2NH2 + NH4X
give the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution of ammonia to bromoethane
describe the conditions required for elimination of a halogen
ethanolic NaOH/KOH (NOT AQUEOUS)
this causes the OH- ion to act as a base and accept a proton to become water
hot, reflux
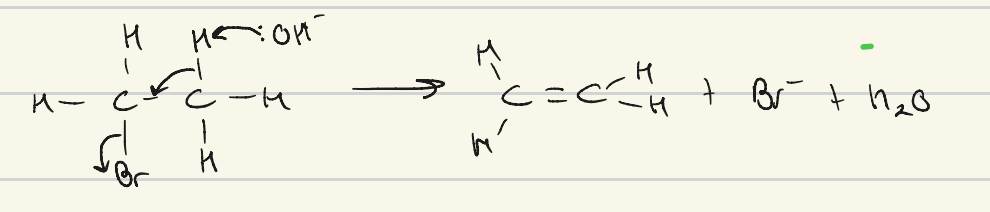
give the general equation for elimination of a haloalkane
haloalkane + potassium hydroxide → alkene + potassium halide + water
R-CH2CH2X + KOH → R-CH=CH2 + H2O + KX
give the mechanism for elimination of bromoethane
C-Br bond breaks as enthalpy < C-H
how does isomerism of the alkenes produced occur through elimination?
on 4+ carbon chain haloalkanes, isomers can be produced
depends on which H the hydroxide targets - either side of the Br
describe how you would carry out a practical to compare the rates of hydrolysis of haloalkanes
add 1 cm³ ethanol to 3 drops haloalkane
stand test tubes in 60C water bath
add test tube of silver nitrate to water bath
add 1cm³ of silver nitrate to each tube and time each until precipitate forms
chloride - white ppt
bromide - cream ppt
iodide - yellow ppt