AP 2.10 - special senses - vision, hearing and balance
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
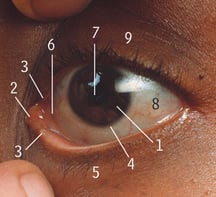
5
Lower eyelid/lower palpebra
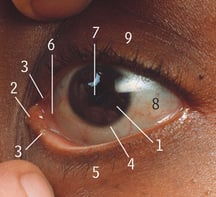
9
Upper eyelid/upper palpebra
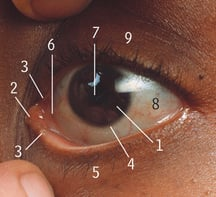
8
Sclera
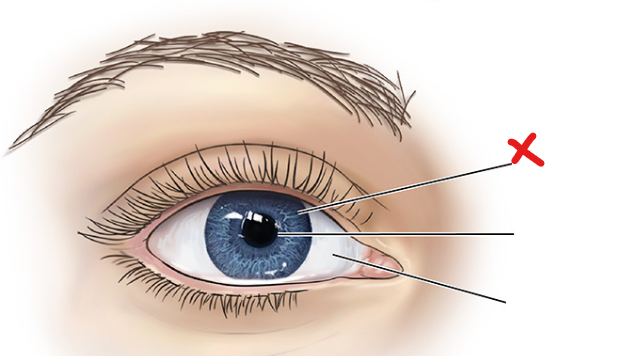
X
Iris
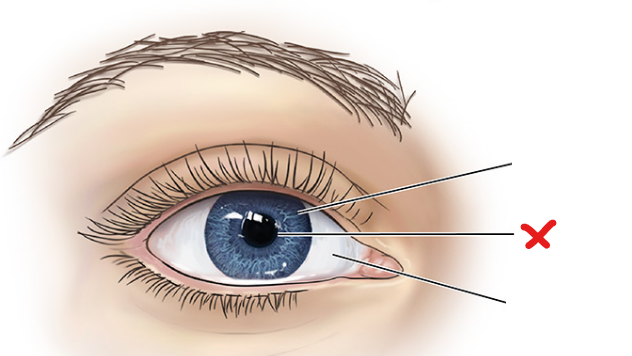
X
Pupil
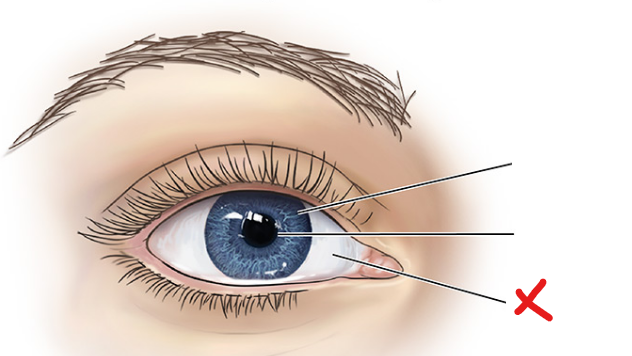
X
Sclera
X
Cornea
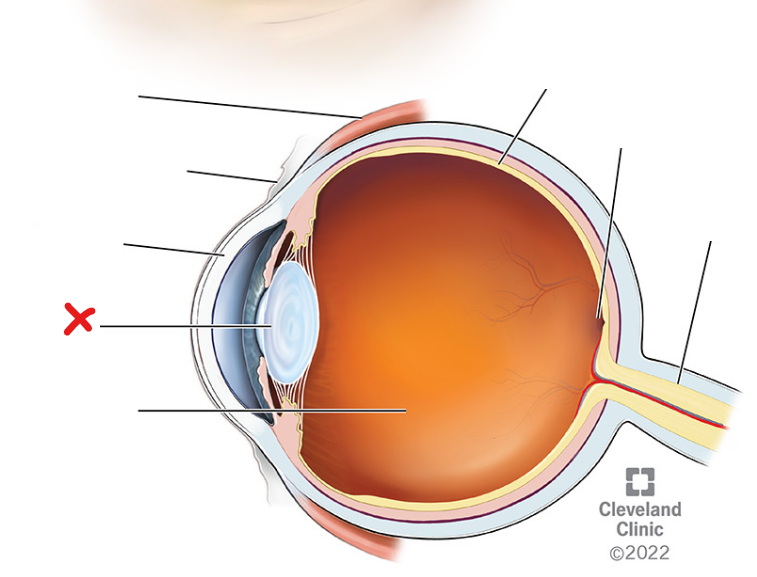
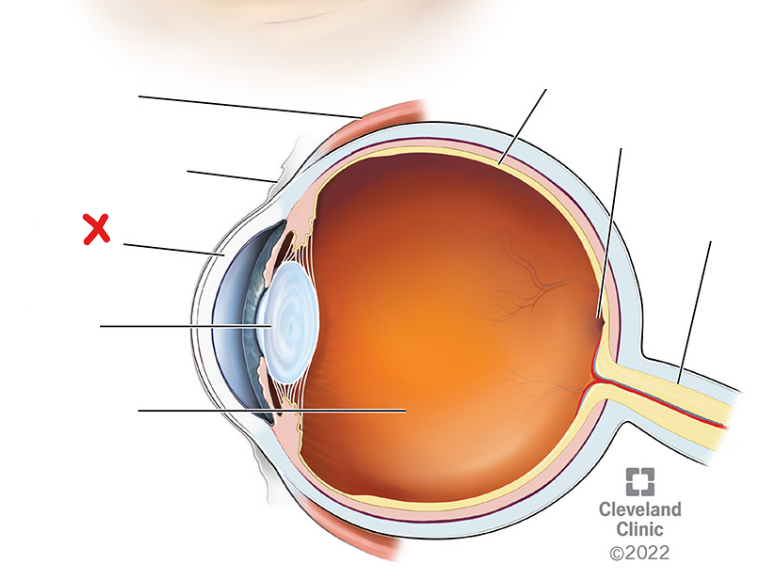
X
Lens
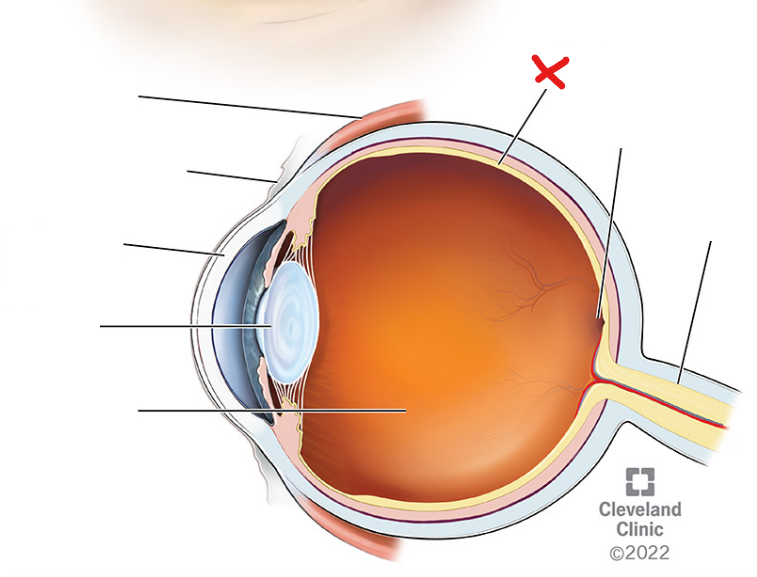
X
Retina
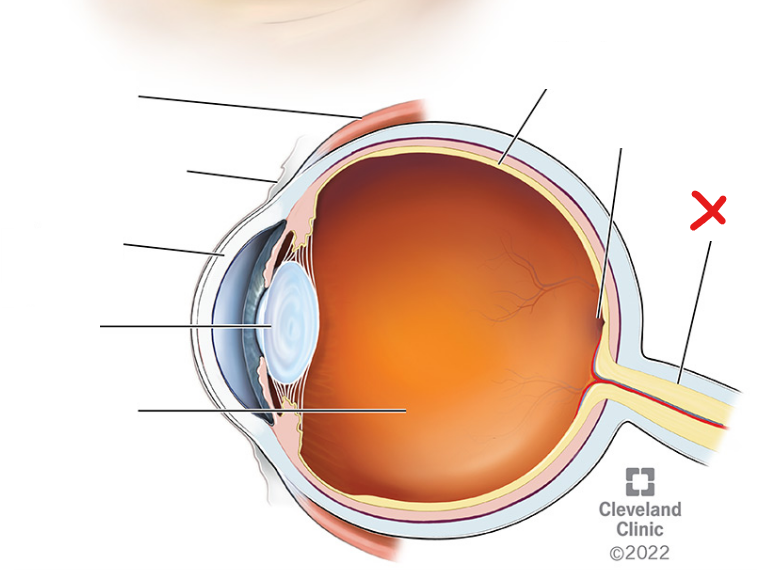
X
Optic nerve
X
Pupil
X
Cornea
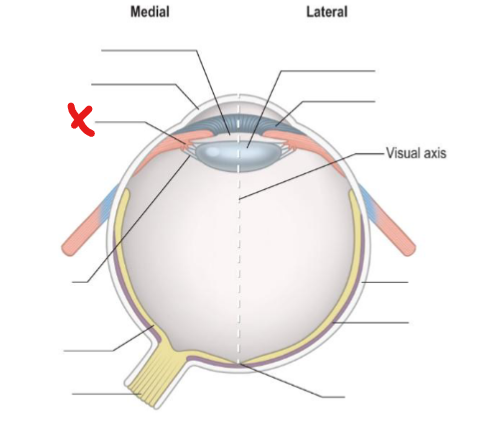
X
Ciliary body
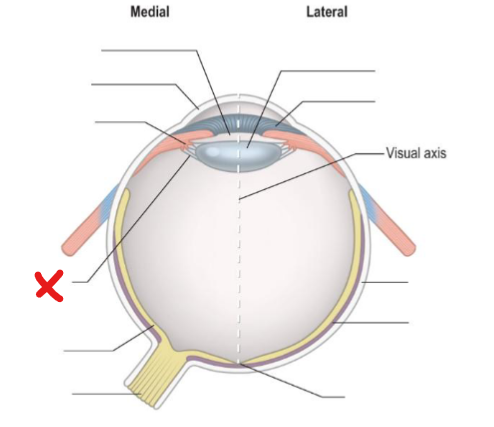
X
Suspensory ligament
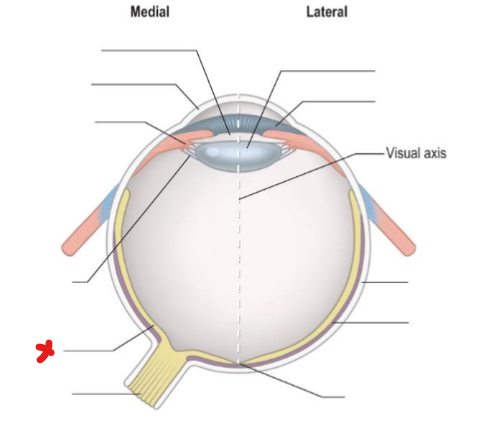
X
Retina
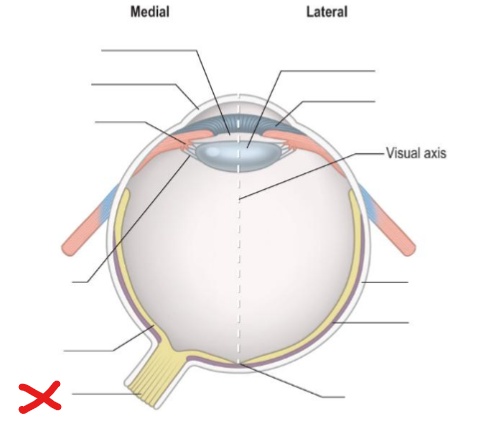
X
Optic nerve
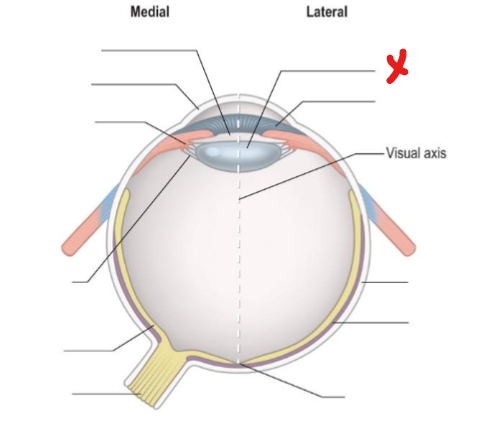
X
Lens
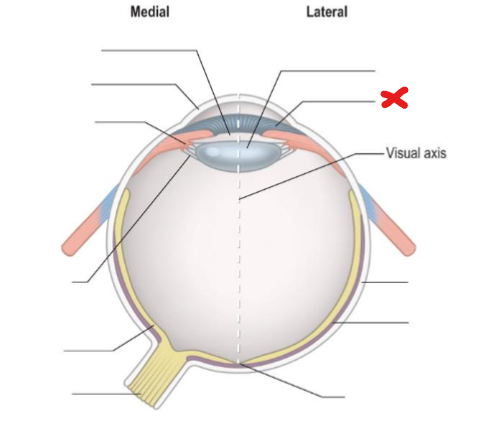
X
Iris
X
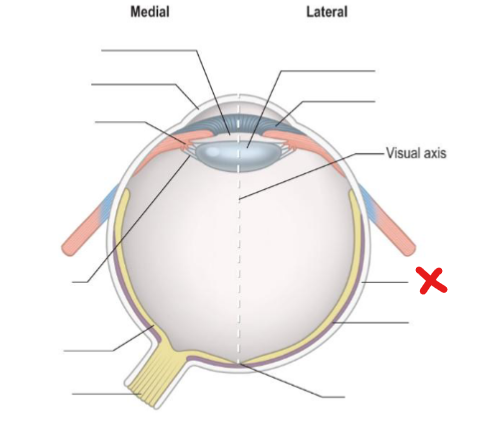
Sclera
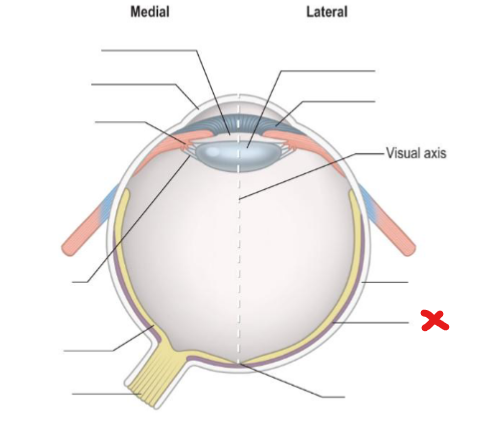
X
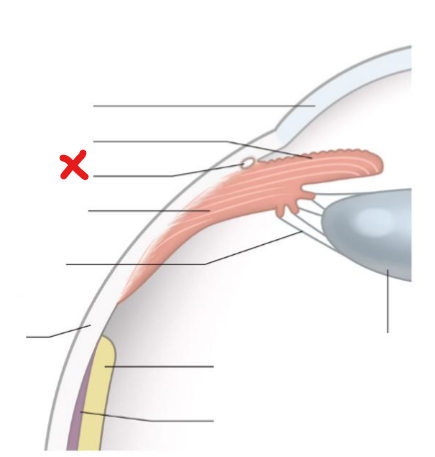
Choroid
X
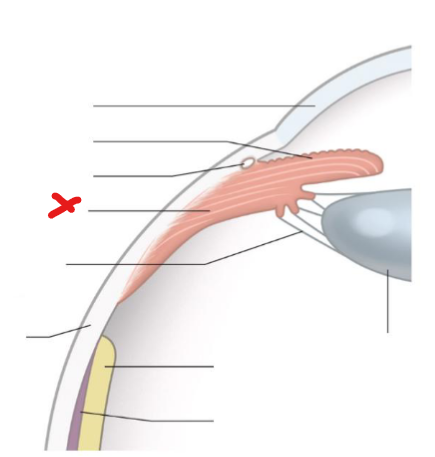
Fovea
X
Canal of schlemm
X
Ciliary body
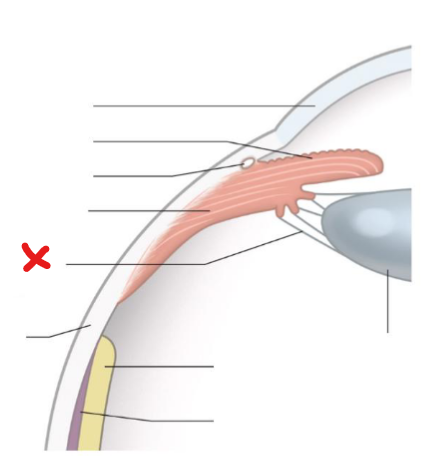
X
Suspensory ligaments
What are the choroid, ciliary body and iris referred together as
Uvea
If the cornea is cloudy what transplant may be indicated
Corneal transplant
What does astigmatism result from
Cornea with irregular radius of curvature
What are the two types of smooth muscle of the iris
Sphincter/constrictor pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae muscle
What type of innervation does the sphincter pupillae muscle receive
Parasympathetic
What type of innervation does the dilator pupillae muscle receive
Sympathetic
What are the two major layers that the retina has
Neural retina and external pigment epithelium
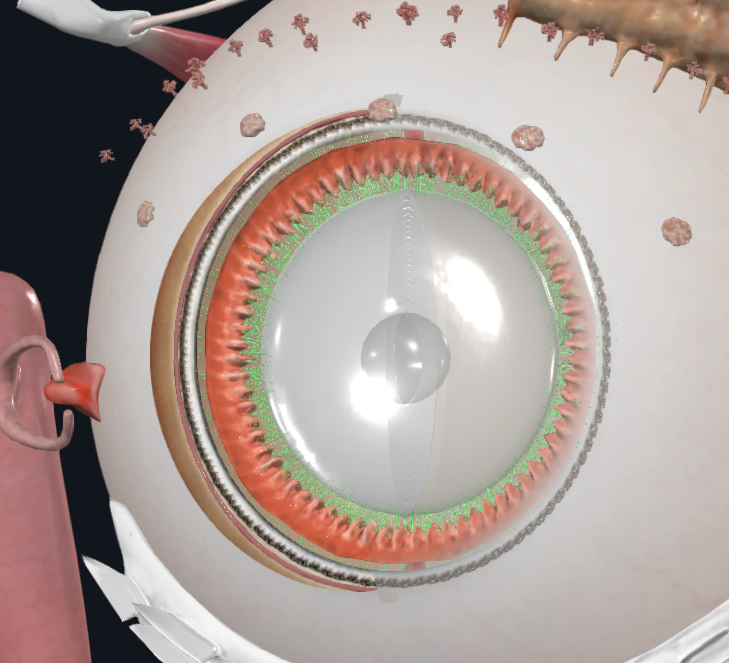
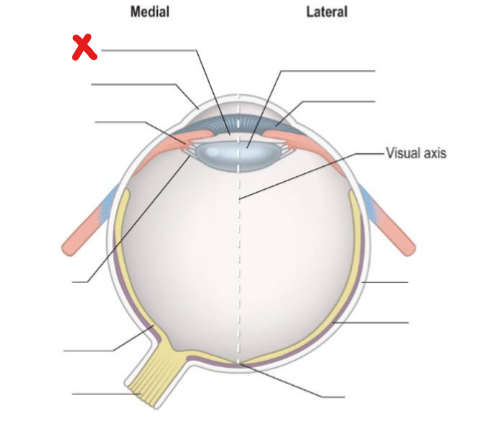
What is highlighted in green
Ciliary body
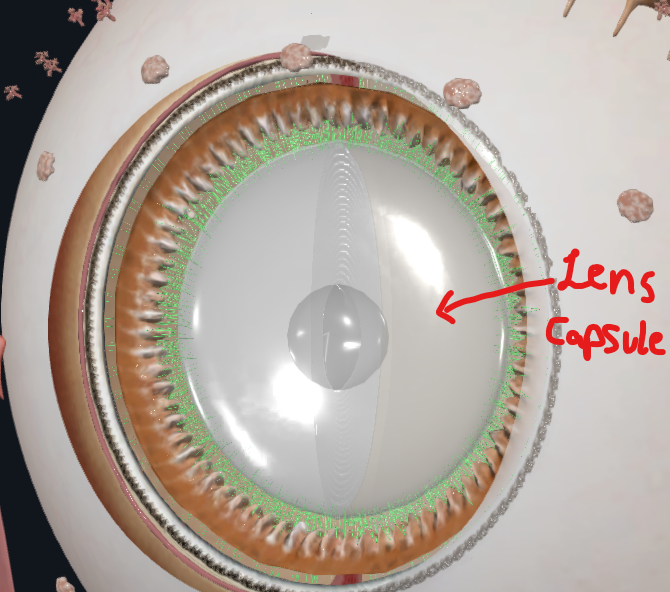
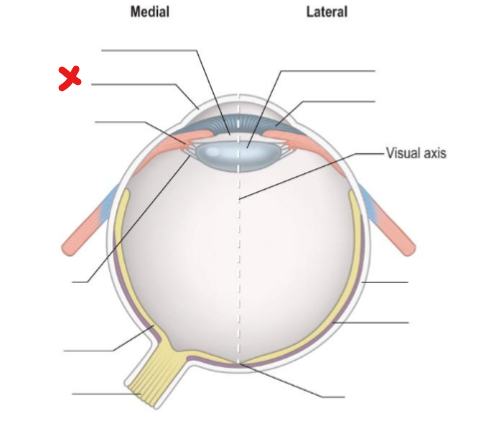
What is highlighted in green
Suspensory ligaments/zonular fibres
When the circular smooth muscle of the ciliary body contractions what happens to the lens?
Lens relaxes and becomes more spherical
What is a common condition affecting the lens
Cataracts
With age, what happens to the lens?
Loss of elasticity
Where is the anterior segment of the eye
In front of the lens
What type of fluid does the anterior segment of the eye contain
Aqueous humour
Where is the anterior chamber of aqueous humour between
Cornea and iris
Where is the posterior chamber of aqueous humour between
Iris and lens
What does the ciliary body secrete
Aqueous humour
What is the pathway of the aqueous humour
Ciliary body in posterior chamber → anterior chamber → canal of schlemm → venous system
What happens if the aqueous humour flow is disrupted
Glaucoma
What fluid does the posterior segment of the eye contain
Vitreous humour
What type of cells are in the retina
Rod and cone cells
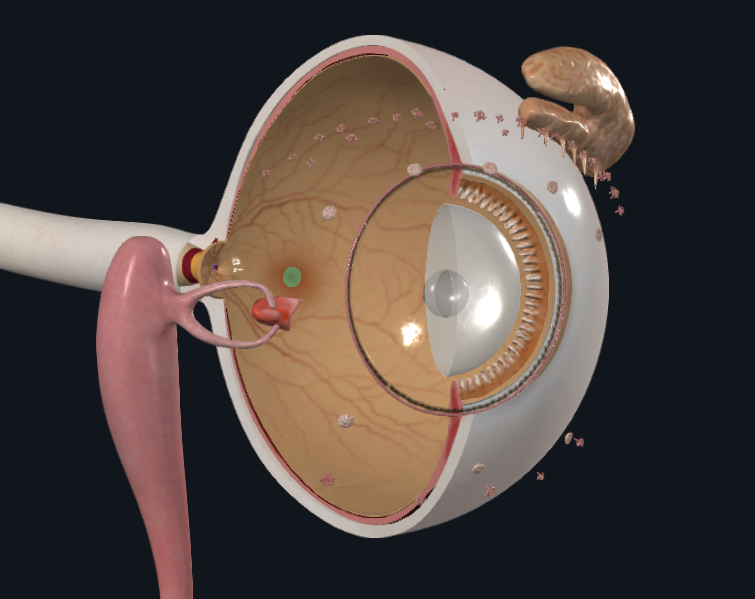
What is highlighted in green
Fovea centralis
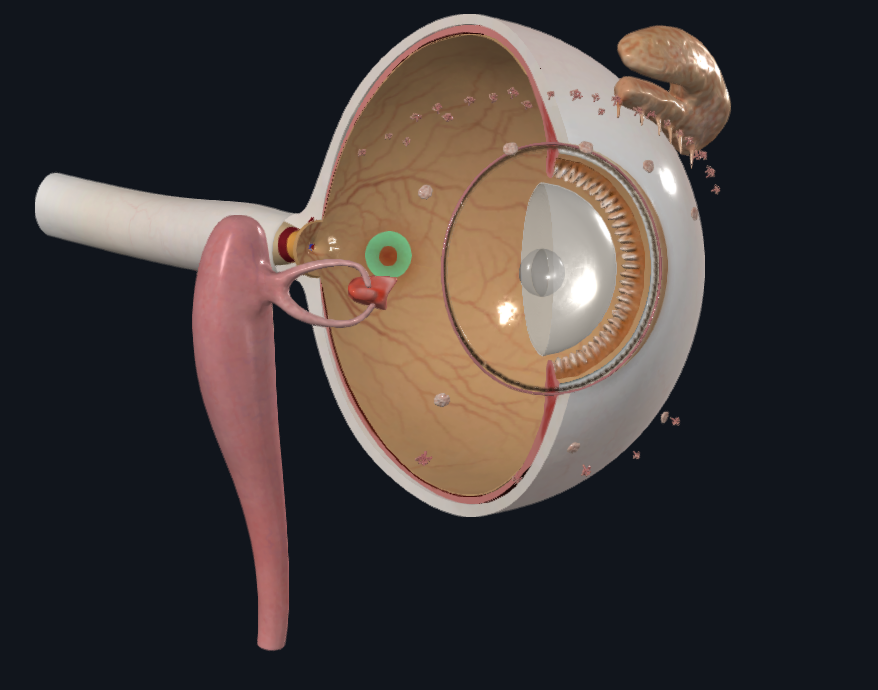
What is highlighted in green
Macula lutea
What layer of the eye is this
Choroid
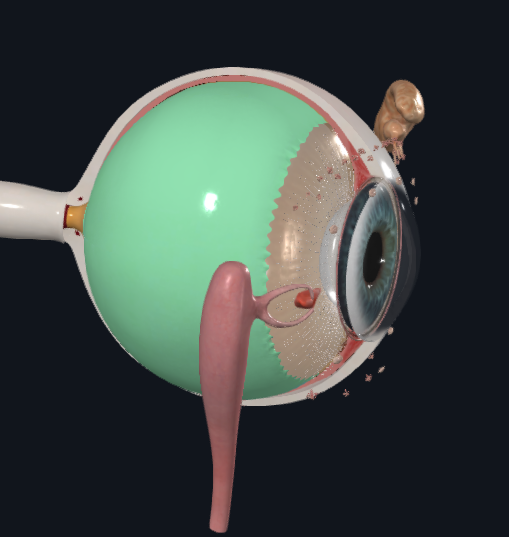
What layer of the eye is this
Retina
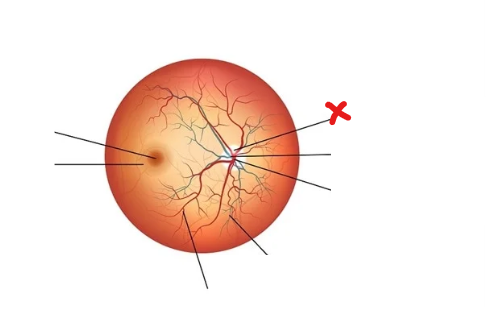
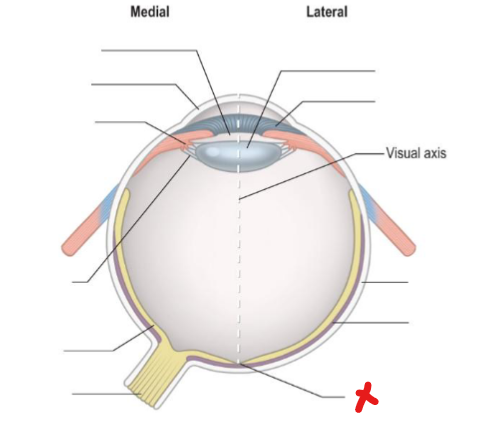
What is X
Optic disc
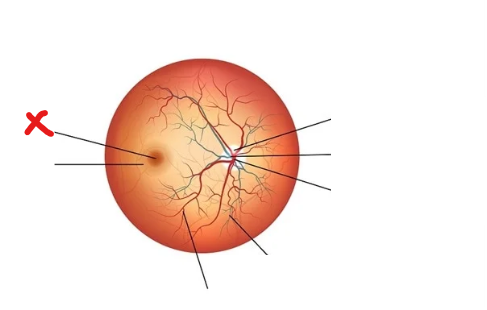
What is X
Fovea centralis
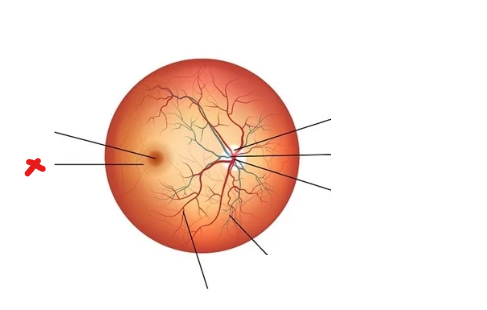
What is X
Macula lutea
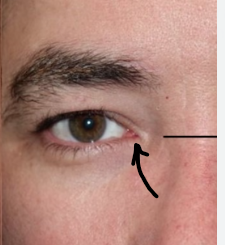
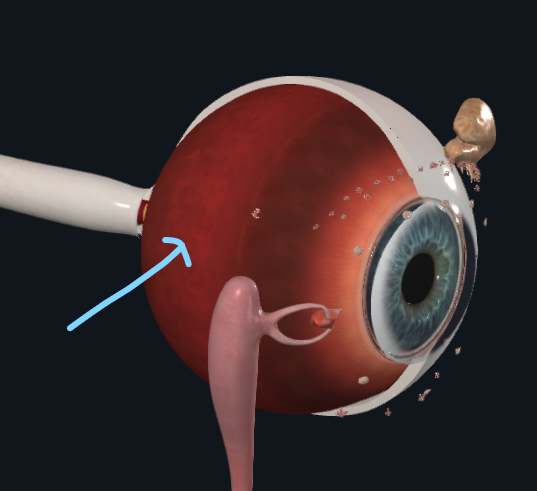
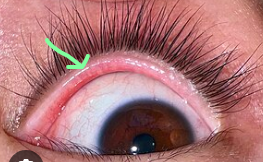
What does the arrow refer to
Medial canthus
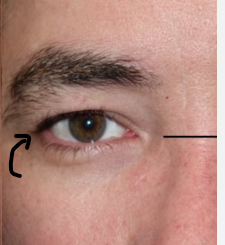
What does the arrow refer to
Lateral canthus
What type of epithelium covers the palpabrae
Stratified squamous epithelium
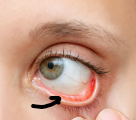
What is the thin moist mucous membrane (arrow)
Conjunctiva
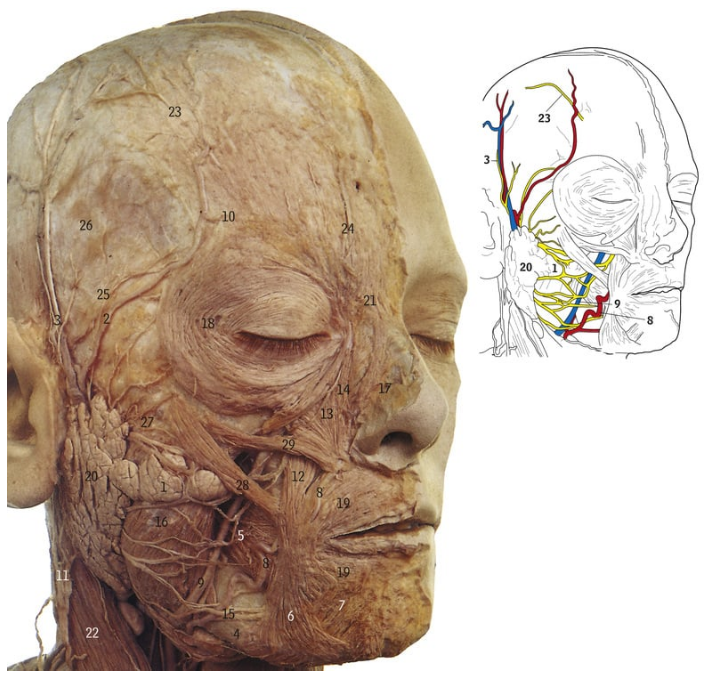
18
Orbicularis oculi
What is the orbicularis oculi supplied by
Facial nerve
What action does the orbicularis oculi do
Closes the eye
What does X refer to
Tarsal plates
What muscle is X
Levator palpebrae superioris
What are the two muscles which elevate the upper eyelid
Levator palpebrae superioris, superior tarsal muscle
What nerve supplies levator palpebrae superioris
Oculomotor
What type of nerves supplies the superior tarsal muscle
Sympathetic nerves
What happens if there is no sympathetic innervation to the superior tarsal muscle
Ptosis
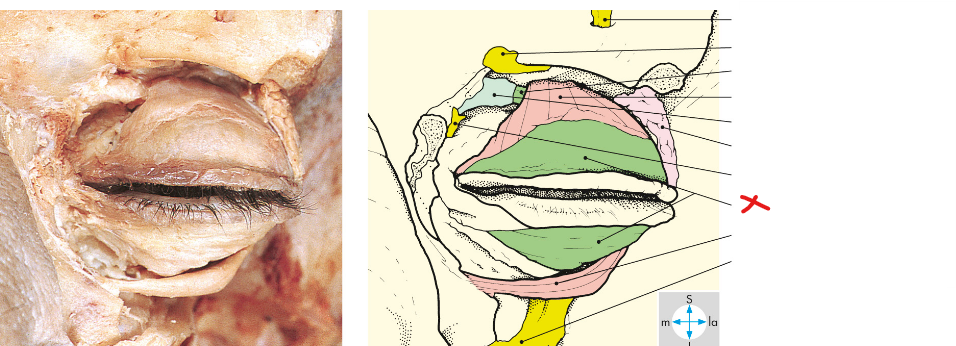
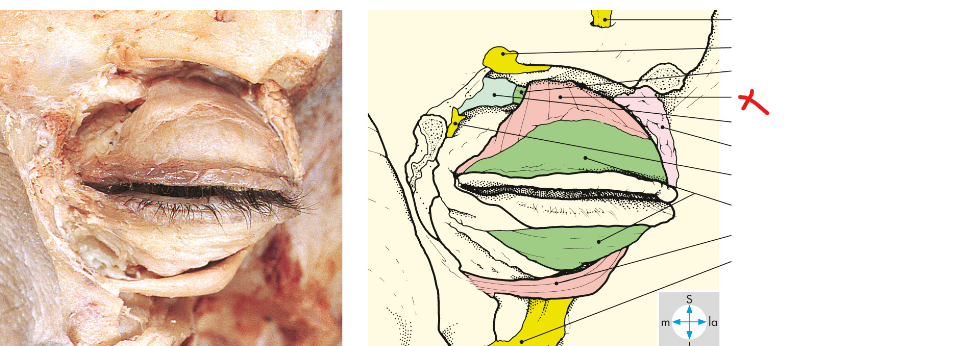
What glands does the green arrow refer to
Tarsal/meibomian glands
What causes lid retraction
Sympathetic overflow
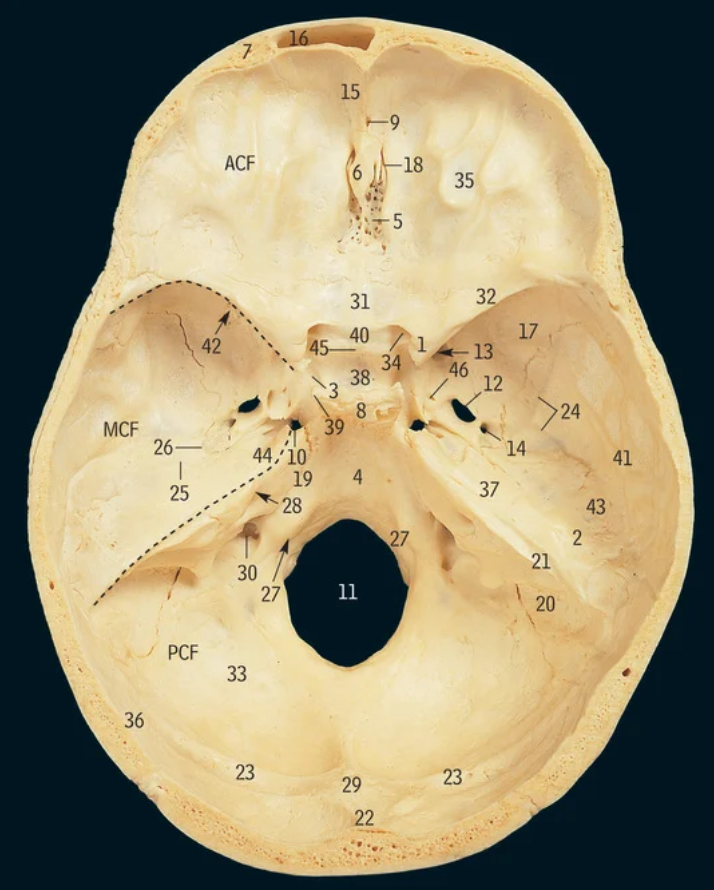
34
optic canal
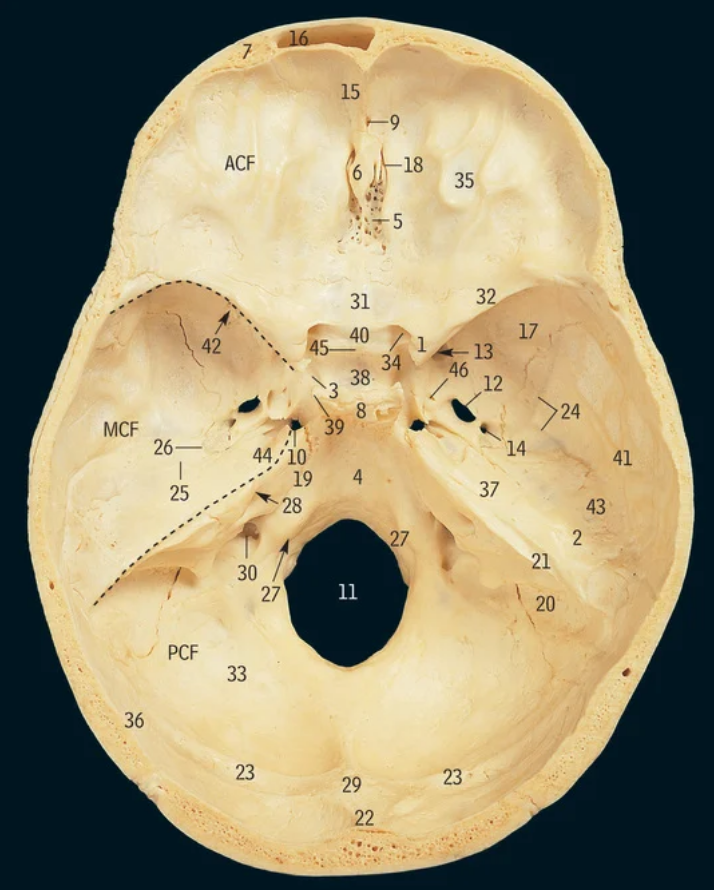
42
Superior orbital fissure
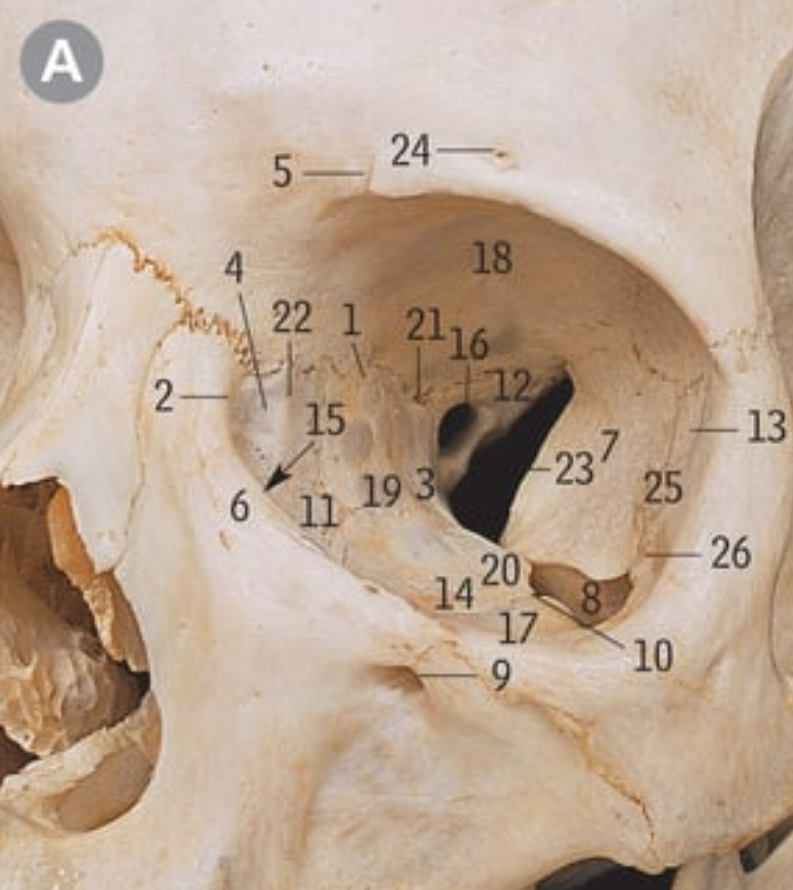
16
Optic canal
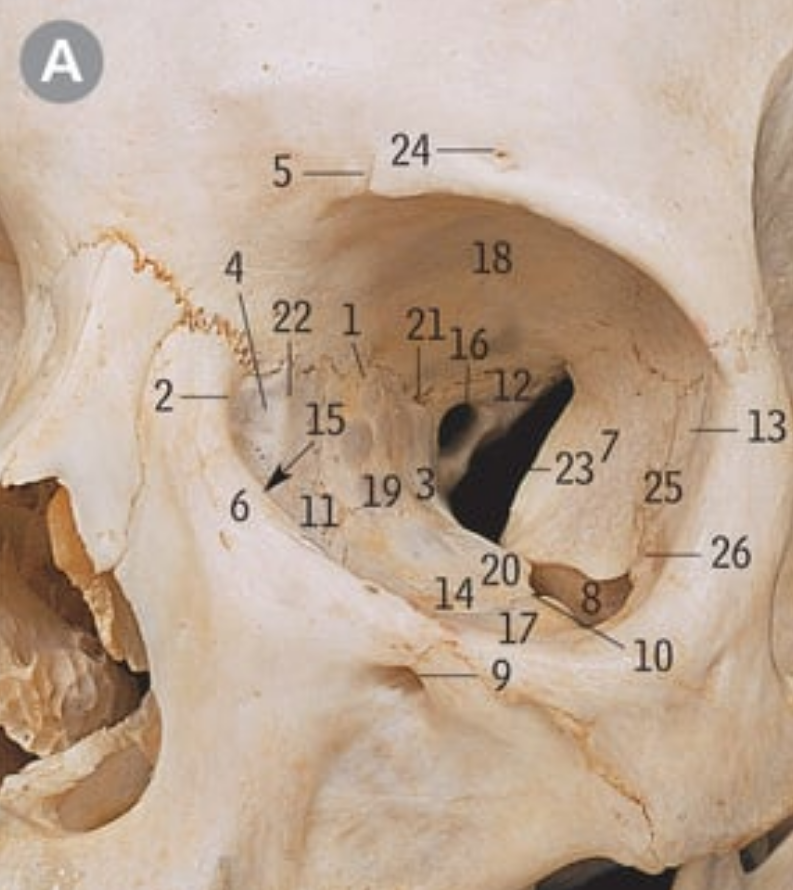
8
Inferior orbital fissure
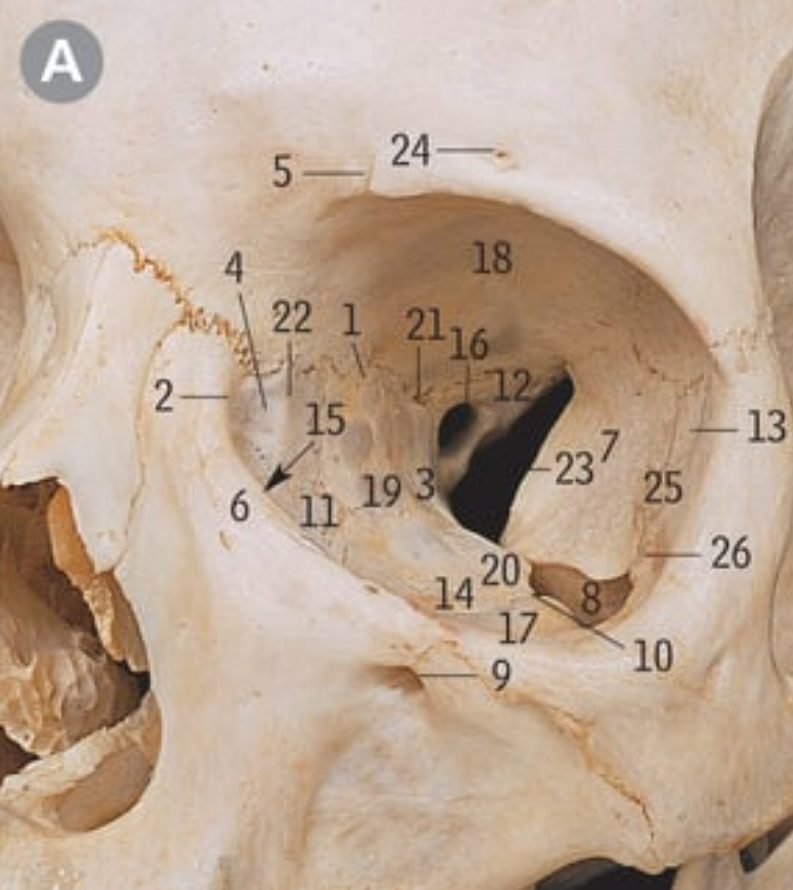
23
Superior orbital fissure
What nerves go through the superior orbital fissure
Oculomotor, trochlear, Opthalmic nerve, frontal nerve, lacrimal nerve, nasociliary nerve, abducens nerve
26
Oculomotor nerve
47
Trochlear nerve
1
Abducens nerve
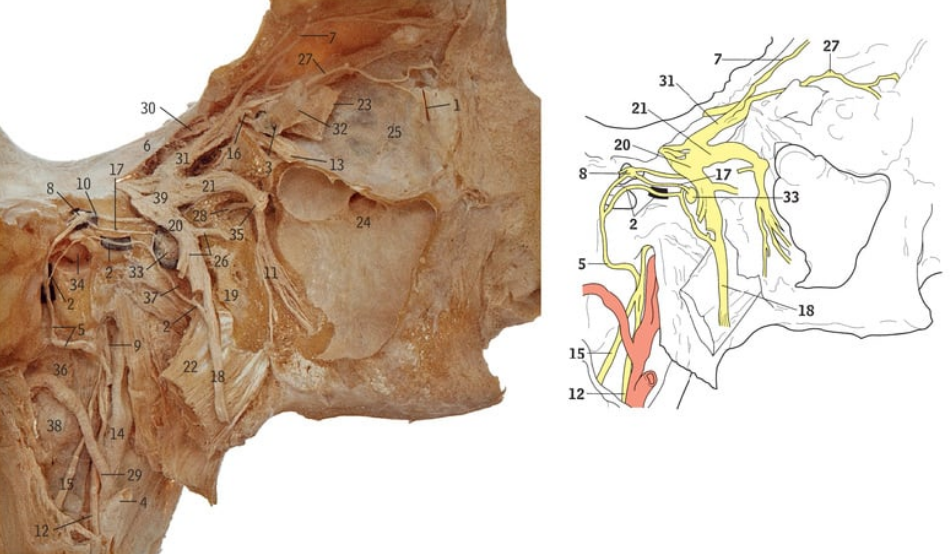
31
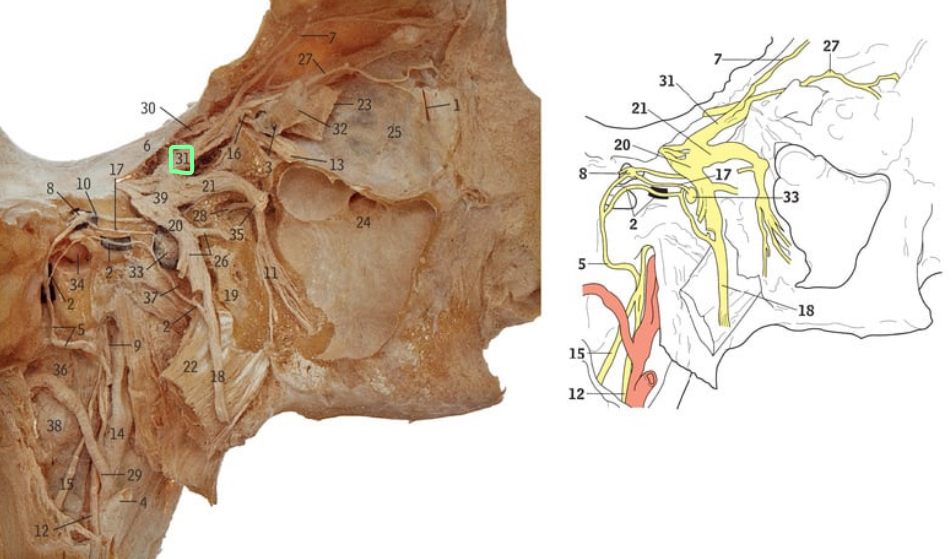
Ophthalmic nerve
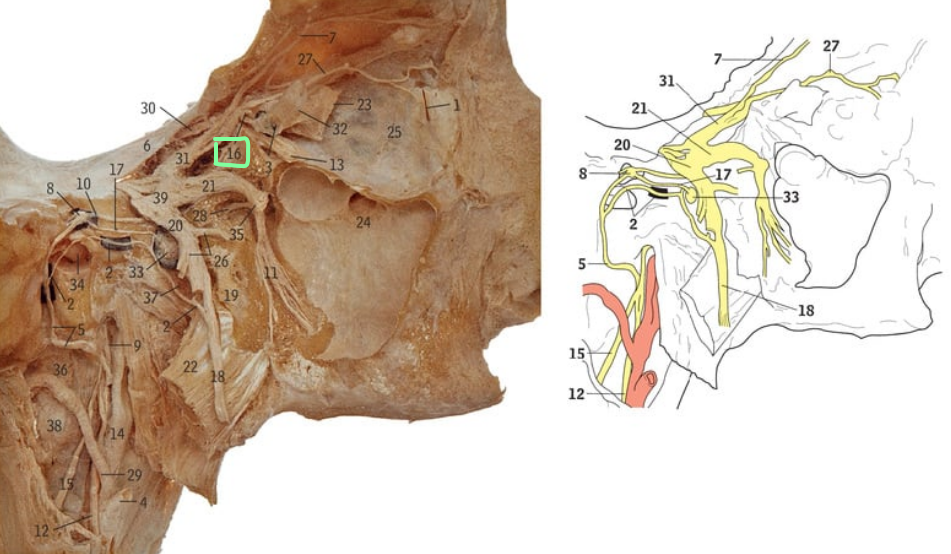
7
Frontal nerve
16
Lacrimal nerve
What type of information does the frontal nerve carry from the superior aspect of the face
Sensory information
What type of information does the lacrimal nerve carry from the lacrimal gland
General sensory information
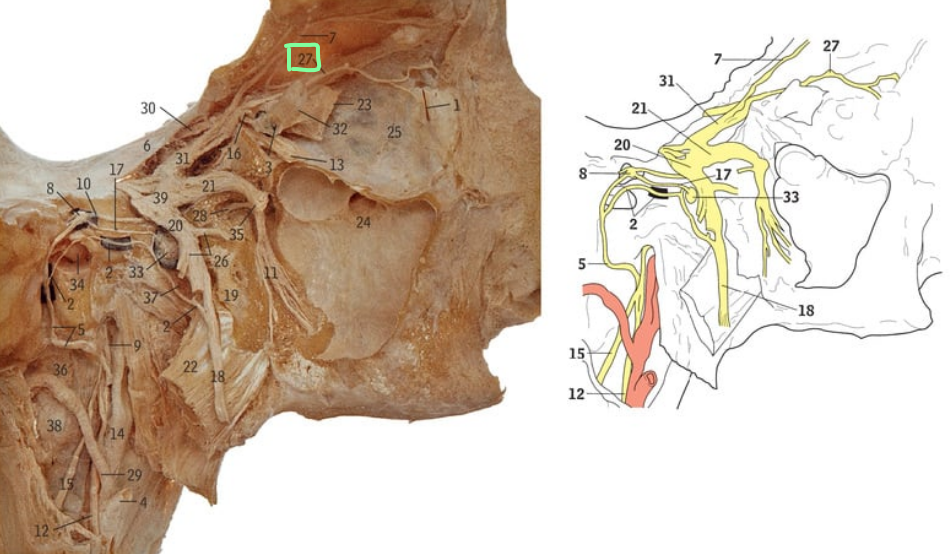
27
Nasociliary nerve
11
Lacrimal nerve
17
Nasociliary nerve
21
Maxillary nerve
What nerve travels through the inferior orbital fissure
Maxillary nerve
12
Maxillary nerve
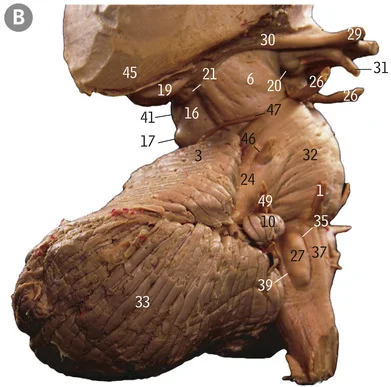
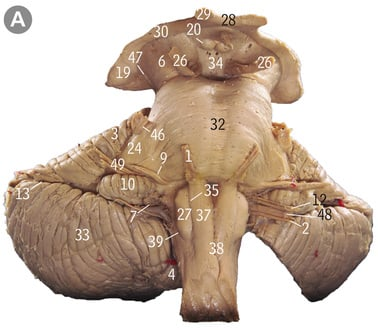
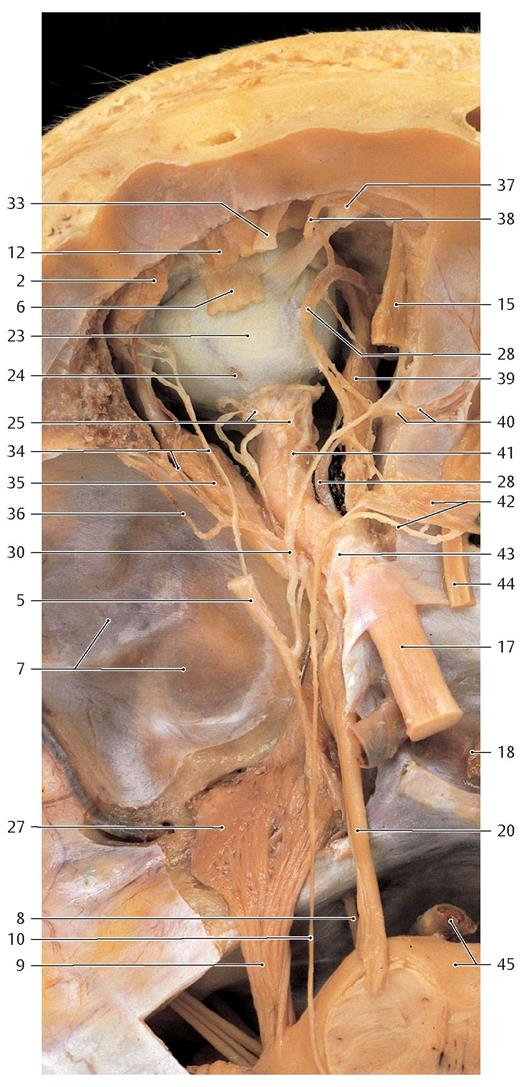
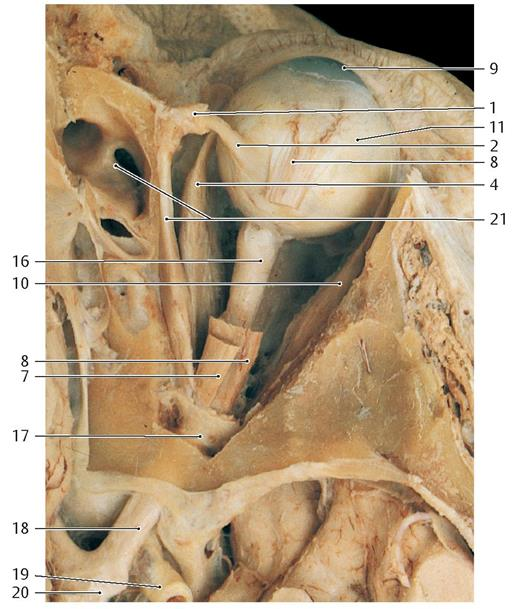
Where do the four recti muscles originate from
Common tendinous ring
43
Common tendinous ring
21
Superior oblique
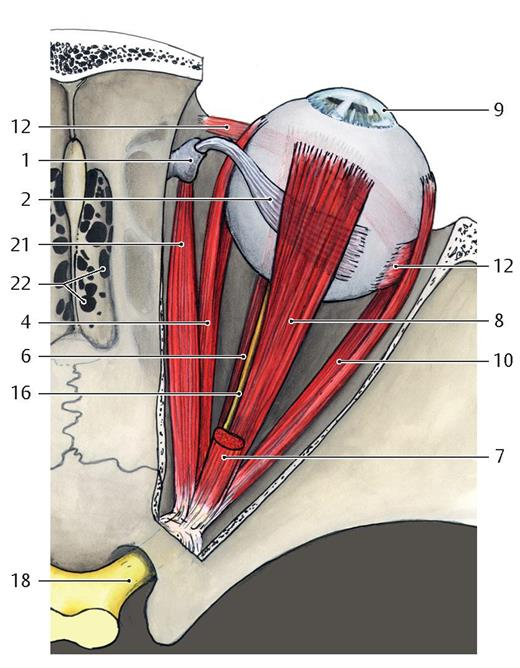
1
Trochlea
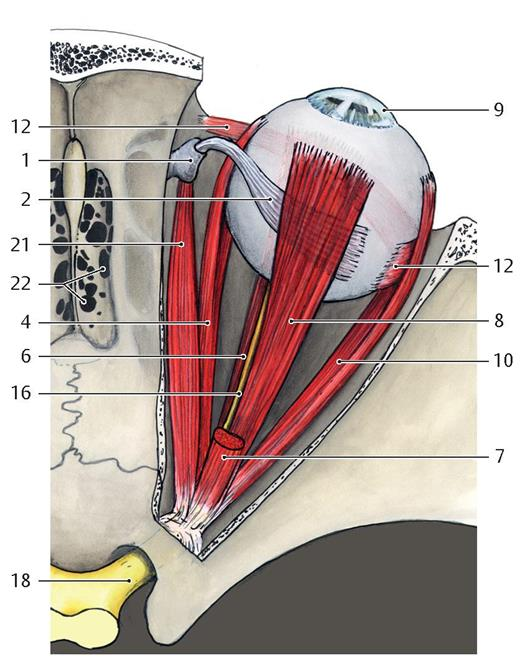
21
Superior oblique
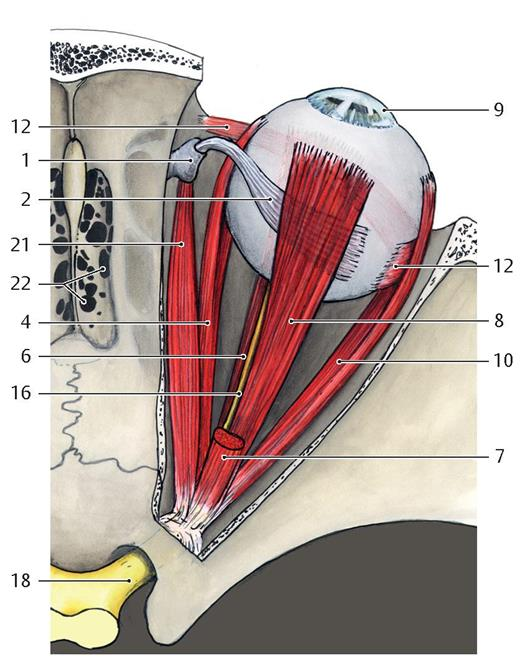
12
Inferior oblique
Where does the superior oblique originate from and insert at
Sphenoid bone, superior posterolateral quadrant of eyeball
Where does the inferior oblique muscle originate from and insert at
Maxilla, inferior posterolateral quadrant of the eyeball
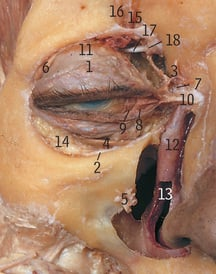
6
Lacrimal gland
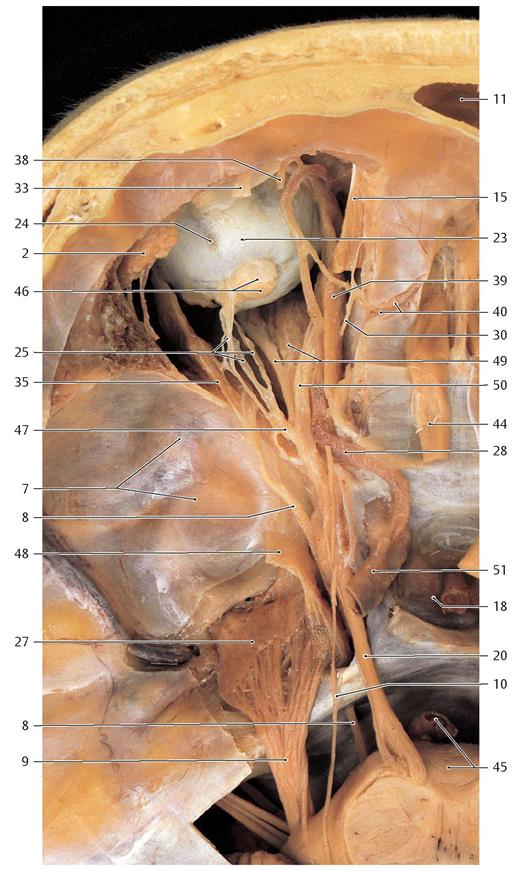
2
Lacrimal gland
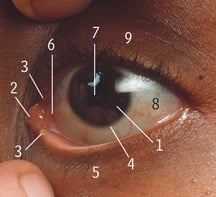
2
Lacrimal caruncle
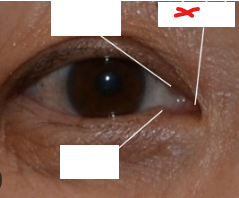
X
Lacrimal caruncle
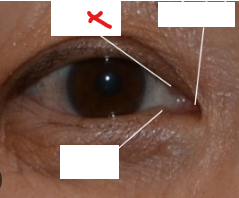
X
Upper punctum