Lesson 39: Glomerular Filtration Rate, Renal Clearance, and Intrarenal Homeostasis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Compare and contrast the chemical composition of plasma to the glomerular filtrate (fluid in Bowman’s space)
Plasma → contains proteins and blood cells
Glomerular filtrate → no proteins or blood cells
GFR is tightly regulated to __________________________
GFR is tightly regulated to maintain stable filtration and homeostasis despite changes in blood pressure or fluid balance
GFR is regulated by _________________________
GFR is regulated by neural & hormonal input to afferent & efferent arteriole vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) that constrict or dilate to change filtration pressure.
When total-body Na⁺ decreases, how is GFR affected?
↓ Na+ → ↓ ECF & BP → Afferent constriction → ↓ GFR → Retain Na⁺ & water → Stabilize BP
When total body Na+ increases, how is GFR affected?
↑ Na+ → ↑ ECF & BP → Afferent dilation → ↑ GFR → ↑ Na⁺ & water excretion → Lower BP.
Define renal clearance
Renal clearance is the volume of plasma completely cleared of a substance by the kidneys per unit time (usually mL/min)
What is renal clearance’s importance in quantifying renal function?
It shows how effectively the kidneys remove a substance from the blood. By measuring the clearance of specific substances—like inulin (for accurate GFR) or creatinine (for estimated GFR)—clinicians can assess kidney filtration and overall renal function
How can GFR be measured?
Inulin – freely filtered, not reabsorbed, not secreted (ClIN – true GFR)
Creatinine – freely filtered, not reabsorbed, secreted in small amounts (ClCr – estimated GFR)
What is the flow of filtration?
Renal artery → afferent arteriole → Glomerular capillary → Bowman’s space → proximal tubule → loop of Henle → distal tubule → collecting duct → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder → urethra
_____________ is the movement of fluid and solutes from glomerular capillaries across barrier into Bowman’s space and occurs due to _________________________. It is also the first step in making urine.
Glomerular filtration is the movement of fluid and solutes from glomerular capillaries across barrier into Bowman’s space and occurs due to Starling Forces. It is also the first step in making urine.
Glomerular filtration is a ____________ process, where ______________ pressures force fluids and solute through membrane.
Glomerular filtration is a passive process, where hydrostatic pressures force fluids and solute through membrane.
As the glomerular filtrate travels through the tubules of the nephron, its composition changes. Why?
The kidney reabsorbs useful substances (like glucose, water, ions) back into the blood.
It can also secrete waste substances from peritubular and vasa recta capillaries into the tubules.
Why is it important to keep proteins in the plasma during filtration?
Plasma proteins (like albumin) help maintain oncotic pressure, which keeps fluid inside blood vessels.
If proteins are filtered out into urine, the blood loses its ability to hold fluid → this can lead to edema (swelling) and low blood volume.
The kidney's filtration barrier (endothelium, basement membrane, and podocytes) is designed to prevent large proteins from passing through into Bowman’s space.
__________ = protein in urine
__________ = blood in urine
Either of these means _____________________
Proteinuria = protein in urine
Hematuria = blood in urine
Either of these means the filtration barrier is damaged
Why is proteinuria important?
it is an early warning sign of kidney damage
if untreated, could lead to chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, or renal failure
The kidneys filter the body’s entire blood plasma about __________ times per day.
The kidneys filter the body’s entire blood plasma about 60 times per day.
What does filtered load measure?
The amount of substance present in Bowman’s Space per unit time.
The excretion rate (amount of substance present in urine per unit time) can be measured by the formula: _______________
Excretion Rate = Ux x V
U → urine concentration of substance (mg/ml)
V → urine flow rate (ml/min)
By comparing Filtered Load vs. Excretion Rate, we can determine ______________________.
By comparing Filtered Load vs. Excretion Rate, we can determine if a substance is being reabsorbed back into the blood or secreted into the urine.
The walls of both afferent arterioles (AA) and efferent arterioles (EA) contain _______________
The walls of both afferent arterioles (AA) and efferent arterioles (EA) contain vascular smooth muscle cells
The pressure pushing blood into the glomerulus is largely determined by ____________
The pressure pushing blood into the glomerulus is largely determined by MABP
_________ is a major determinant (Pushing force) of GFR
PGC is a major determinant (pushing force) of GFR
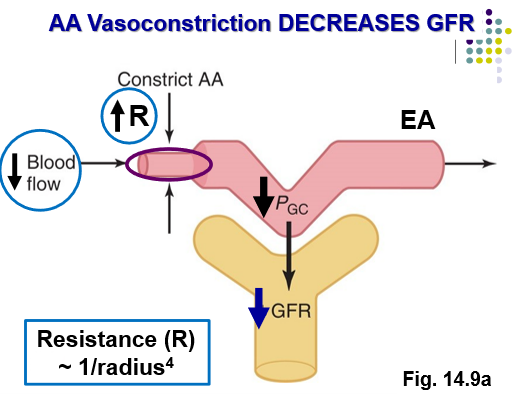
Vasoconstriction of the AA causes….
AA constriction → ↓ PGC → ↓ GFR → ↑ MABP
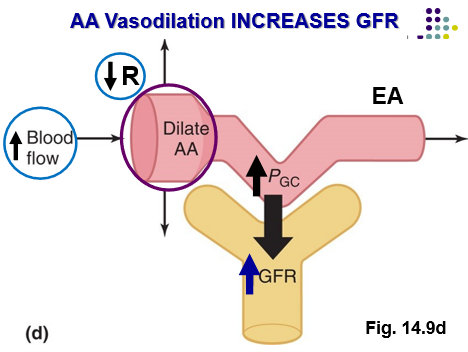
Vasodialation of the AA causes…
AA dilation → ↑ PGC → ↑ GFR → ↓ MABP
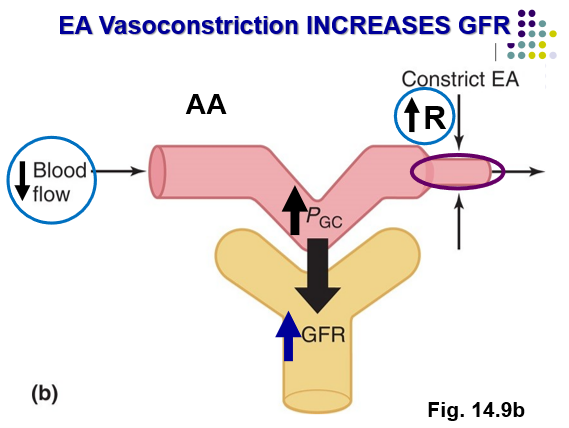
Vasoconstriction of EA causes…
EA constriction → ↑ PGC → ↑ GFR
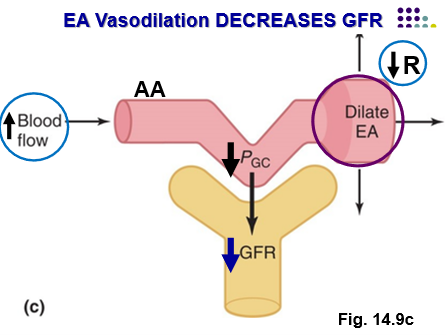
Vasodialtion of EA causes…
EA dilation → ↓ PGC → ↓ GFR
Increased GFR means __________________
Decreased GFR means _________________
Increased GFR means more fluid is filtered/pushed into Bowman’s Space
Decreased GFR means less fluid is filtered/pushed into Bowman’s Space
_____________ pressure (MABP) pushes fluid out (filtration) of the glomerulus and ______________ pressures (Bowman’s space pressure + plasma oncotic pressure) resist filtration.
Upstream pressure (MABP) pushes fluid out (filtration) of the glomerulus and downstream pressures (Bowman’s space pressure + plasma oncotic pressure) resist filtration
What is the formula for net filtration pressure (NFP)?
NFP = PGC – PBS – (πGC – πBS)
PGC –Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure (main force pushing fluid into Bowman’s space)
PBS – Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s space (opposes filtration)
πGC – Oncotic pressure of plasma proteins in glomerulus (pulls water back into blood, opposes filtration)
πBS – Normally ≈ 0 (since no protein should be in Bowman’s space)
What is the formula for GFR?
GFR = Kf (PUF)
o Kf – Filtration coefficient (surface area × permeability of glomerular membrane)
o PUF – Net filtration pressure (same as NFP)
An increase in renal artery pressure would result in ______________
increased PGC and increased GFR
An increase in afferent arteriole resistance would result in ______________
decreased PGC and decreased GFR
A decrease in πGC would result in ______________________
increased GFR
An increase in PBS would result in _______________
decreased GFR
b/c increased backward pressure opposes filtration
obstruction by stone or enlarged prostate
An increase in πBS would result in _______________
increased GFR
b/c proteins in Bowman’s space pull more fluid out of capillaries
Why is inulin clearance the gold standard for measuring GFR?
Inulin is only filtered and not handled in any other way
Freely filtered at the glomerulus (it easily enters Bowman’s space)
Not reabsorbed by the tubules
Not secreted into the tubules
Not metabolized or produced by the body
For the renal clearance of creatine, the rate of production _______________ rate of excretion
For the renal clearance of creatine, the rate of production equals rate of excretion
GFR (ClearanceCr) is ____________ related to PlasmaCr
GFR (ClearanceCr) is inversely related to PlasmaCr

Why is creatinine used to estimate GFR clinically?
o No infusion required (unlike inulin)
o Body makes it naturally (Stable P[Cr])
o Easy to measure (P[Cr] & U[Cr])