VCE Physical Education Unit 3 SAC 2
1.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Victorian Certificate of Education Physical Education AOS 2
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
ATP Breakdown
* ATP is the energy source for all muscular movements. The ATP is split when a phosphate group is removed from the molecule. When it is split it releases energy.
2
New cards
Creatine Phosphate (Chemical)
* Chemical fuel contatining a high-energy phosphate for rapid release of energy.
* Limited CP Storage
* Limited CP Storage
3
New cards
Carbohydrates
* Sugar and starches e.g. bread, pasta, fruit, vegetables.
* The bodys preferred source of fuel under exercise conditions.
* The bodys preferred source of fuel under exercise conditions.
4
New cards
Fats
* Are a concentrated fuel source in dairy products, oils, nuts etc. Preferred fuel source at rest and during prolonged submaximal exercise.
5
New cards
Protein
* Protein if found in meat, fish, eggs etc. Used for muscle growth and repair.
* Minimal Contribution to energy production during exercise.
* Minimal Contribution to energy production during exercise.
6
New cards
At rest exercise Fuel
1. Fats
2. Carbohydrates (Aerobic)
3. Carbohydrates (Anaerobic)
7
New cards
Submaximal Activity Fuel
1. Carbohydrates (Aerobic)
2. Fats
3. Carbohydrates (Anaerobic)
1. Protein
8
New cards
Maximal Activity Fuel
1. Carbohydrates
9
New cards
The cross over concept
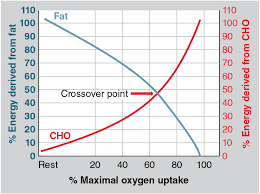
10
New cards
ATP Cycle
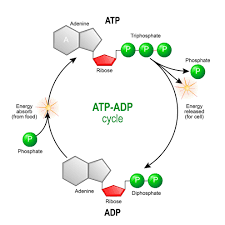
11
New cards
ATP-PC System
* Fuel=Creatine Phosphate
* Intensity=Maximal
* Intensity=Maximal
12
New cards
Anaerobic Glycolysis System
* Fuel=Glycogen
* Intensity=High Intensity 95%-85%
* Rate=Fast
* Yield=2-3 ATP PM
* Duration=10-75 seconds
* Intensity=High Intensity 95%-85%
* Rate=Fast
* Yield=2-3 ATP PM
* Duration=10-75 seconds
13
New cards
Aerobic Glycolysis System
* Fuel=Glycogen/Triglycerides
* Intensity=Submaximal 85%-70% or >70%
* Rate=Slow
* Yield=38 ATP PM or 441 ATP PM (triglycerides)
* Duration=75 seconds +
* Intensity=Submaximal 85%-70% or >70%
* Rate=Slow
* Yield=38 ATP PM or 441 ATP PM (triglycerides)
* Duration=75 seconds +
14
New cards
Factors Affecting Contribution
* The duration of the exercise
* The intensity of the exercise
* Whether sufficient oxygen is present
* Continuous exercise or intermittent exercise
* Available fuel sources
* The intensity of the exercise
* Whether sufficient oxygen is present
* Continuous exercise or intermittent exercise
* Available fuel sources
15
New cards
Writing a response
* All energy systems contribute to energy production
* ATP-PC starts continues to 6-10 seconds
* Anaerobic Glycolysis becomes more dominant
* Aerobic Glycolysis System increases but never becomes dominant.
* Predominant Energy system would be ATP-PC for a 200m event.
* ATP-PC starts continues to 6-10 seconds
* Anaerobic Glycolysis becomes more dominant
* Aerobic Glycolysis System increases but never becomes dominant.
* Predominant Energy system would be ATP-PC for a 200m event.
16
New cards
Intermittent Activity
* Exercise beats that alternate between periods of activity and intensity.
17
New cards
Contributions from the energy systems depends on
* Duration
* Intensity
* Fuel Availability
* Weather Conditions
* Intensity
* Fuel Availability
* Weather Conditions
18
New cards
Lactate Inflection Point (LIP)
* LIP is the highest exercise intensity where lactate removal and lactate production are balanced.
19
New cards
Beyond LIP
* Beyond LIP, lactate production exceeds
* Accumulation of Hydrogen Ions causes fatigue
* Accumulation of Hydrogen Ions causes fatigue
20
New cards
Intensity of LIP
* Generally at 85% Max Heart Rate
* 55-70% VO2 Max
* 55-70% VO2 Max
21
New cards
Oxygen Uptake or Vo2
* The volume of oxygen able to be taken up by and transported to and used by the body for energy.
22
New cards
Vo2 Max Vs. Vo2
* Vo2 Max=The maximum volume of oxygen able to be used by the body.
* Vo2=Is the rate of oxygen
* Vo2=Is the rate of oxygen
23
New cards
Factors Affecting Oxygen Uptake
* Body Size
* Age
* Gender
* Training
* Genetics
* Age
* Gender
* Training
* Genetics
24
New cards
Oxygen Deficit
* Is the period of time at the start of the exercise where the oxygen demand exceeds.
25
New cards
Steady State
* Is the state in which oxygen equals oxygen demand
26
New cards
Oxygen Debt (EPOC)
* At the completion of exercise, oxygen consumption remains elevated, despite a reduction in the demand for energy.
27
New cards
Fast Phase of EPOC
* ATP Resynthesise
* CP Resynthesise
* Restore oxygen to Myoglobin
* CP Resynthesise
* Restore oxygen to Myoglobin
28
New cards
Slow Phase of EPOC
* Return core temperature
* Convert Lactic Acid to h2o
* Lactic Acid converted to Glycogen/protein
* Restore heart rate
* Restore other body systems
* Convert Lactic Acid to h2o
* Lactic Acid converted to Glycogen/protein
* Restore heart rate
* Restore other body systems
29
New cards
Acute Respiratory Responses
* Increase Respiratory Rate = number of breaths per minute
* Increase Ventilation = Volume of air breathed in per minute (RR x TV = V)
* Increased Tidal Volume = volume of air breathed in per breath
* Increased Pulmonary Diffusion = The transfer of oxygen to the alveoli to the capillaries
* Increase Ventilation = Volume of air breathed in per minute (RR x TV = V)
* Increased Tidal Volume = volume of air breathed in per breath
* Increased Pulmonary Diffusion = The transfer of oxygen to the alveoli to the capillaries
30
New cards
Acute Cardiovascular Responses
* Increased Heart Rate = Number of beats of the heart per minute
* Increased Stroke Volume = Volume of blood pumped per beat of the heart
* Increased Cardiac Volume = Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute (HR x SV = Q)
* Increased Systolic Blood Pressure = The pressure exerted by the blood against the arterial walls when the heart contracts.
* Redistribution of blood flow = Altering the percentage of cardiac output that is distributed to various body sites.
* Increased Venous Return = The blood returning to the heart via the venous system
* Increased AVO2 Difference = The difference in the concentration of oxygen in the arterial blood and venous blood.
* Decreased Blood Volume = total quantity of blood in the body (plasma + cellular)
* Increased Stroke Volume = Volume of blood pumped per beat of the heart
* Increased Cardiac Volume = Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute (HR x SV = Q)
* Increased Systolic Blood Pressure = The pressure exerted by the blood against the arterial walls when the heart contracts.
* Redistribution of blood flow = Altering the percentage of cardiac output that is distributed to various body sites.
* Increased Venous Return = The blood returning to the heart via the venous system
* Increased AVO2 Difference = The difference in the concentration of oxygen in the arterial blood and venous blood.
* Decreased Blood Volume = total quantity of blood in the body (plasma + cellular)
31
New cards
Acute Muscular Responses
* Increased motor unit recruitment = The number and frequency of motor units recruited for the muscular contractions.
* Increased muscle temperature = The degree of intensity of heat present in the muscles.
* Increased oxygen uptake and consumption = Volume of oxygen that can be taken up and used by the body.
* Increased Metabolic By Products = Substance leftover from the metabolic processes.
* Decreased Energy Substrate Scores = Fuel sources required for ATP resynthesis.
* Increased muscle temperature = The degree of intensity of heat present in the muscles.
* Increased oxygen uptake and consumption = Volume of oxygen that can be taken up and used by the body.
* Increased Metabolic By Products = Substance leftover from the metabolic processes.
* Decreased Energy Substrate Scores = Fuel sources required for ATP resynthesis.
32
New cards
Relative VO2 Max
* Is a better measurement to compare athletes to one another.
33
New cards
Absolute VO2 Max
* The amount of oxygen breathed in per minute.
34
New cards
Increased Ventilation Formula
* Increased Respiratory Rate x Tidal Volume
35
New cards
Increased Cardiac Output Formula
* Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
36
New cards
Before exercise (increased heart rate)
* Anticipatory Response
* Warming the body up
* Warming the body up