AP Environmental Science Terrestrial and Aquatic Biomes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Aquatic biome
An aquatic region characterized by a particular combination of biotic and abioitic factors.

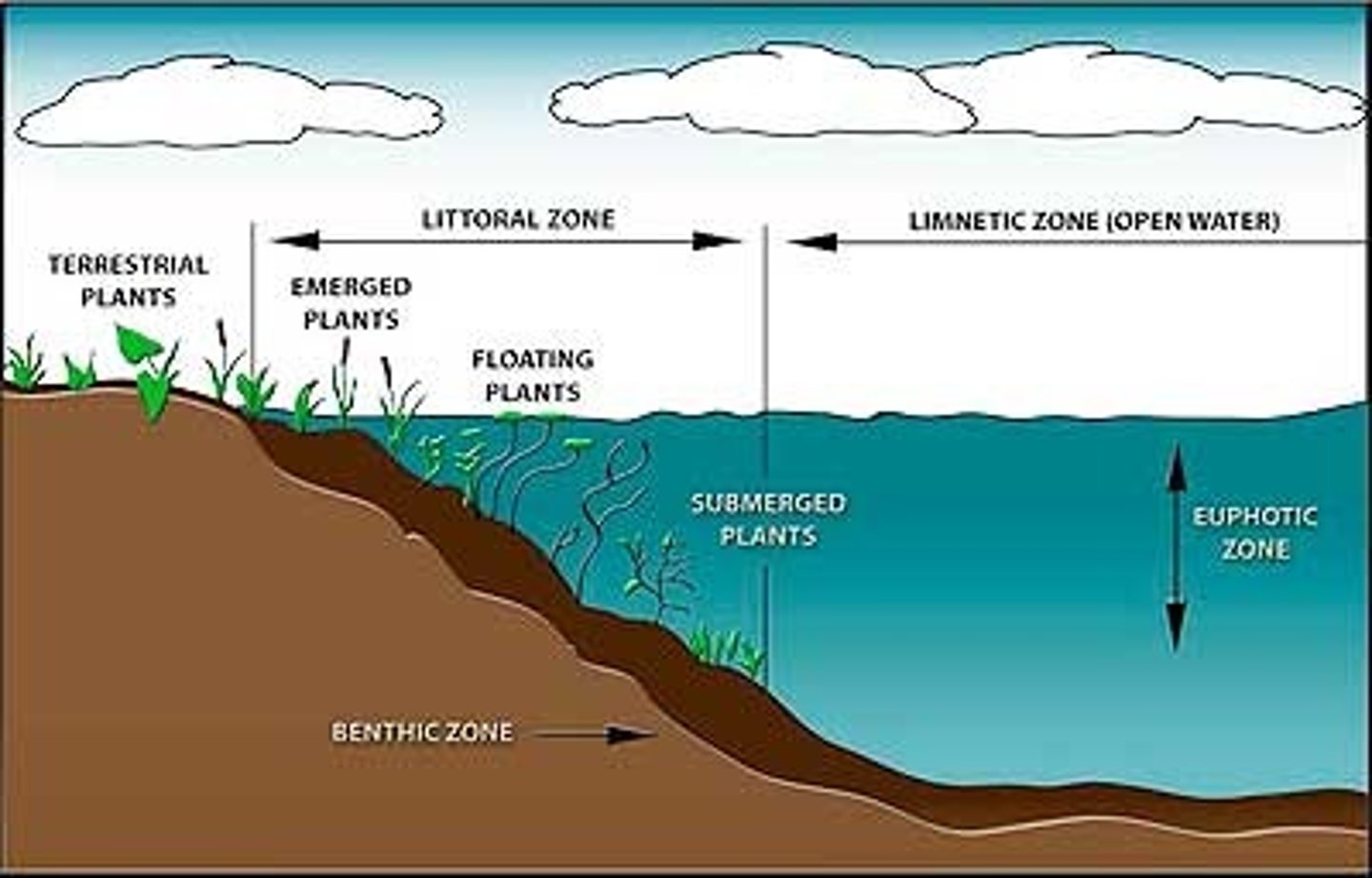
Littoral zone
The shallow zone of soil and water in lakes and ponds where most algae and emergent plants grow.
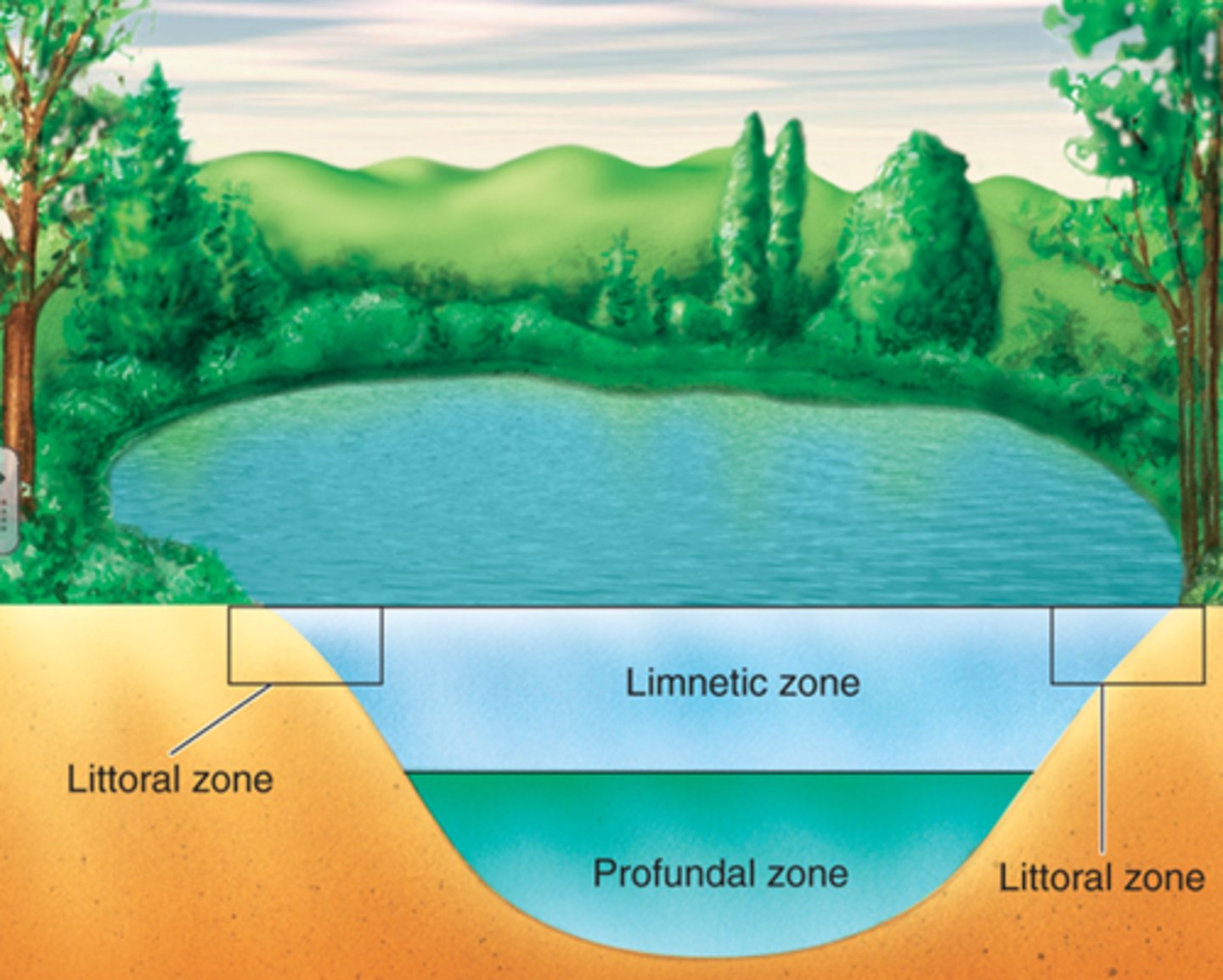
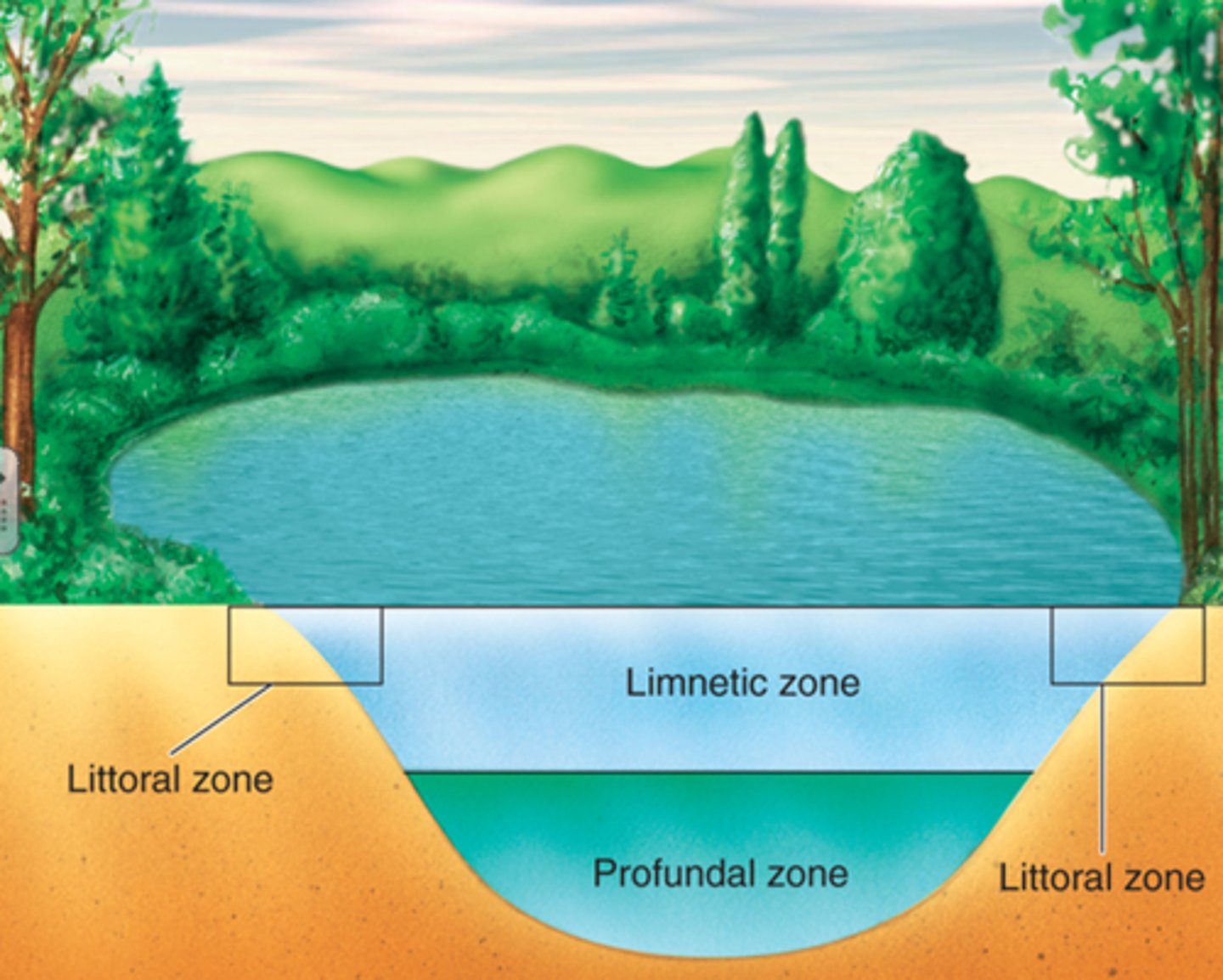
Limnetic zone
A zone of open water in lakes and ponds.
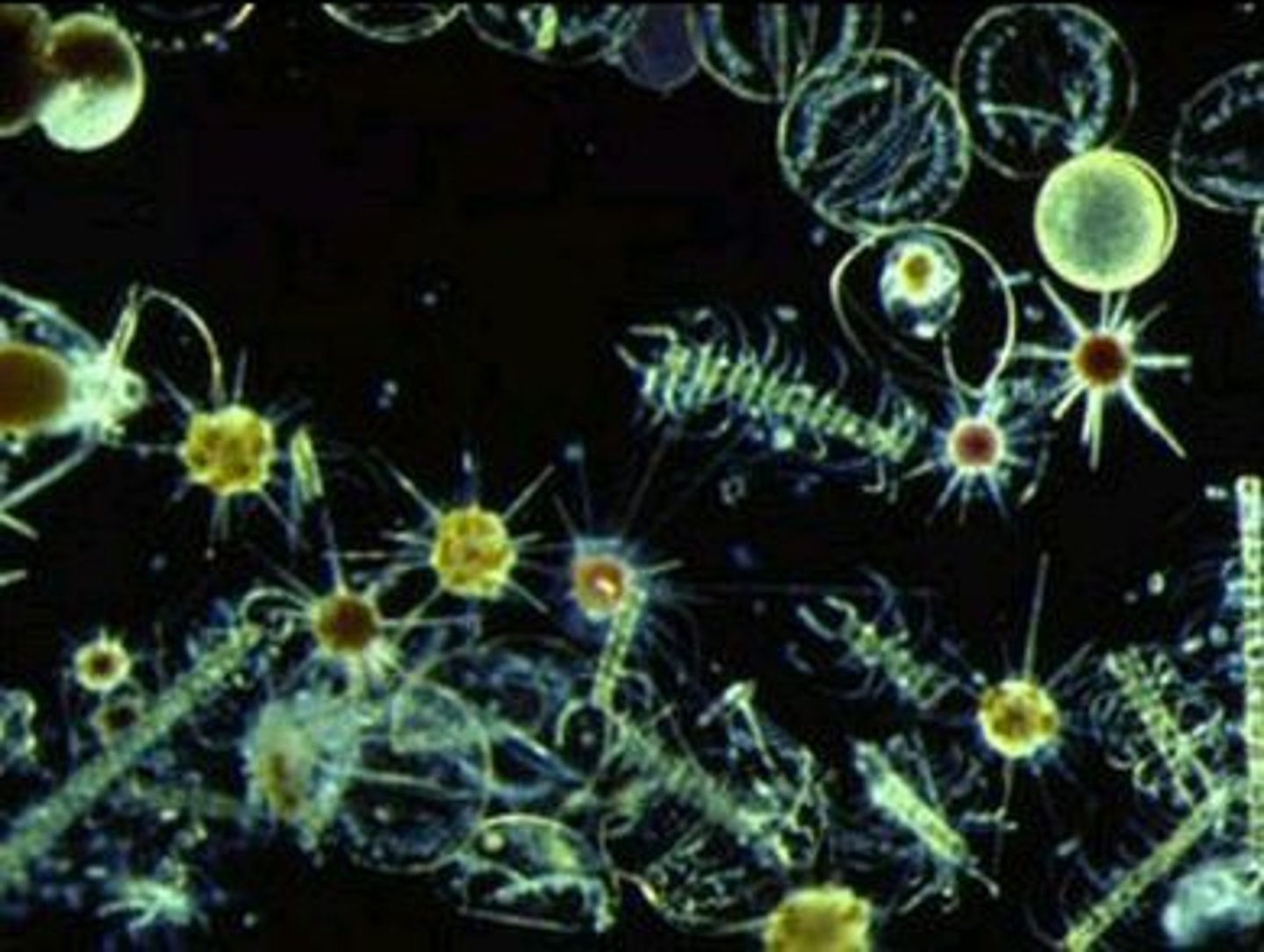
Phytoplankton
Floating algae.
Profundal zone
A region of water where sunlight does not reach, below the limnetic zone in very deep lakes.
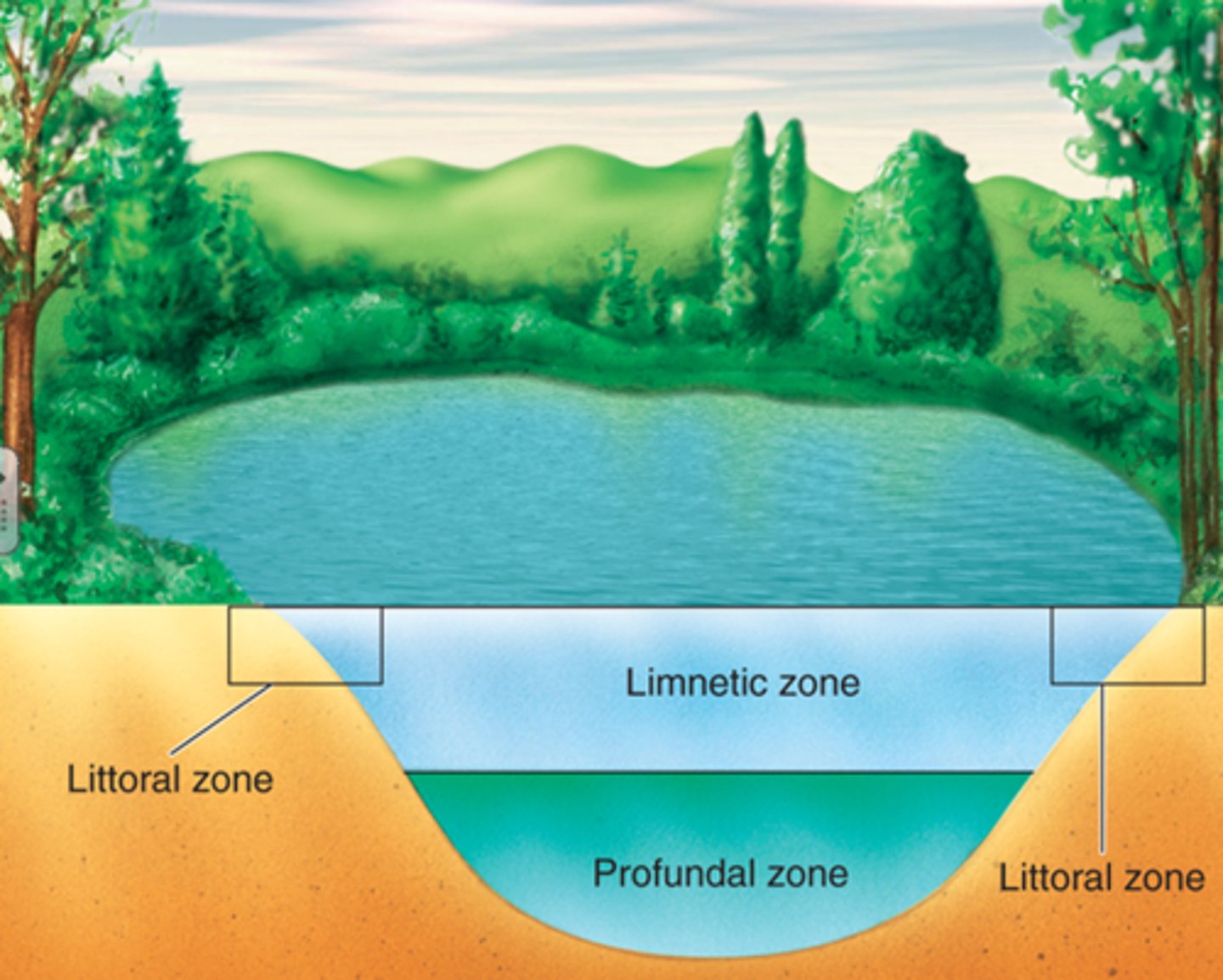
Benthic zone
The muddy bottom of a lake, pond, or ocean.
Oligotrophic
Describes a lake with a low level of primary productivity.
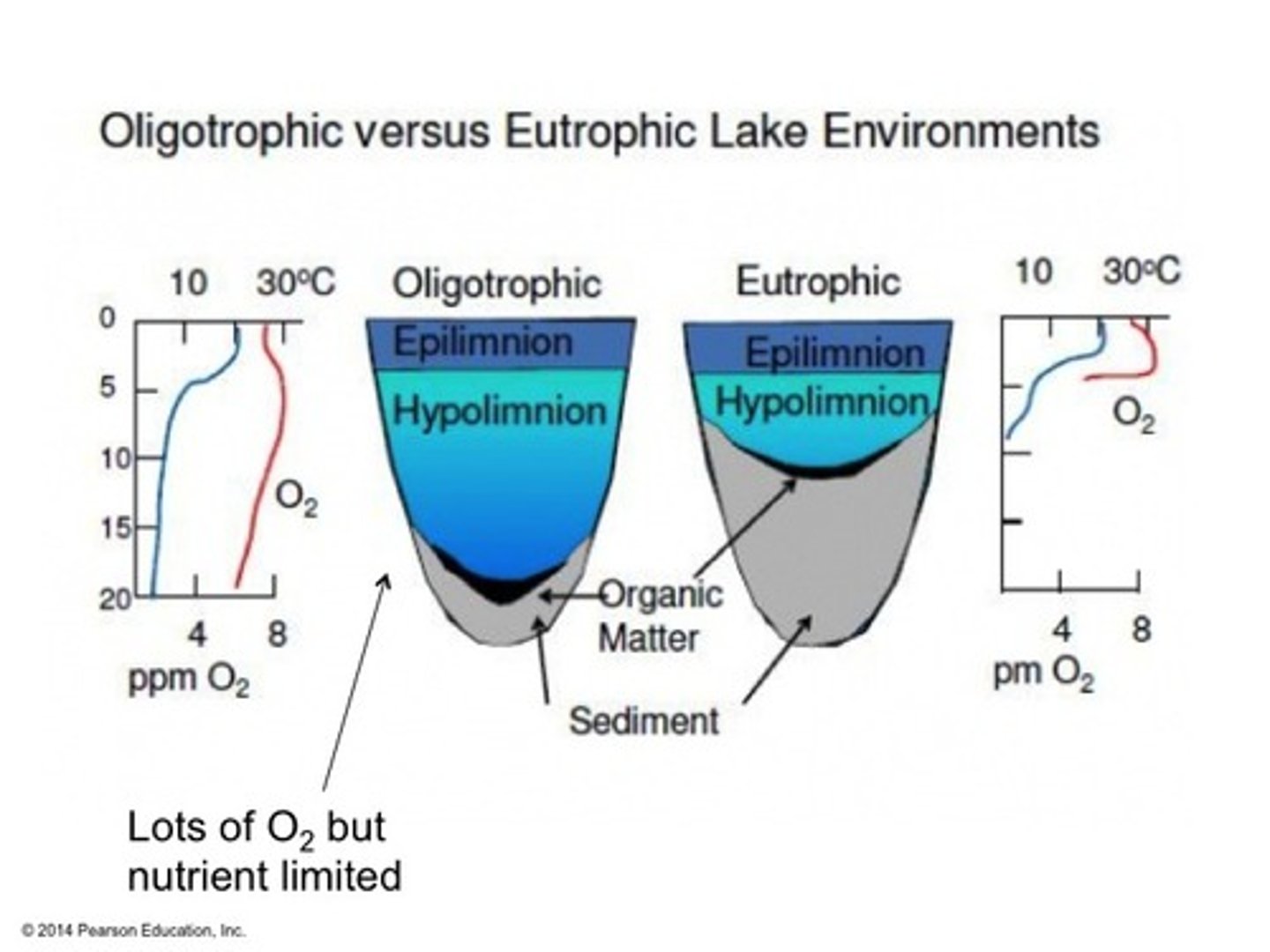
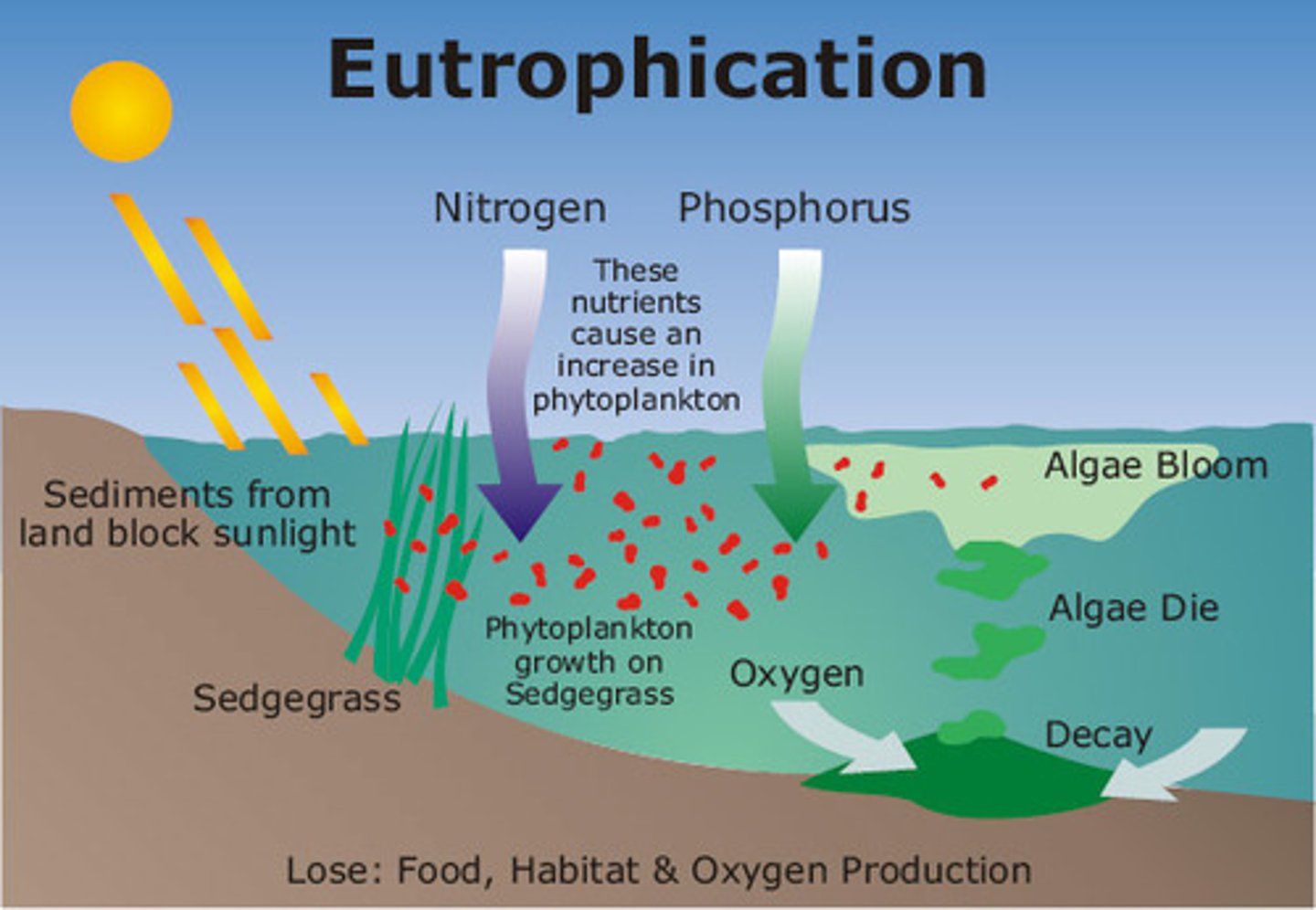
Eutrophic
Describes a lake with a high level of primary productivity.
Freshwater wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation.
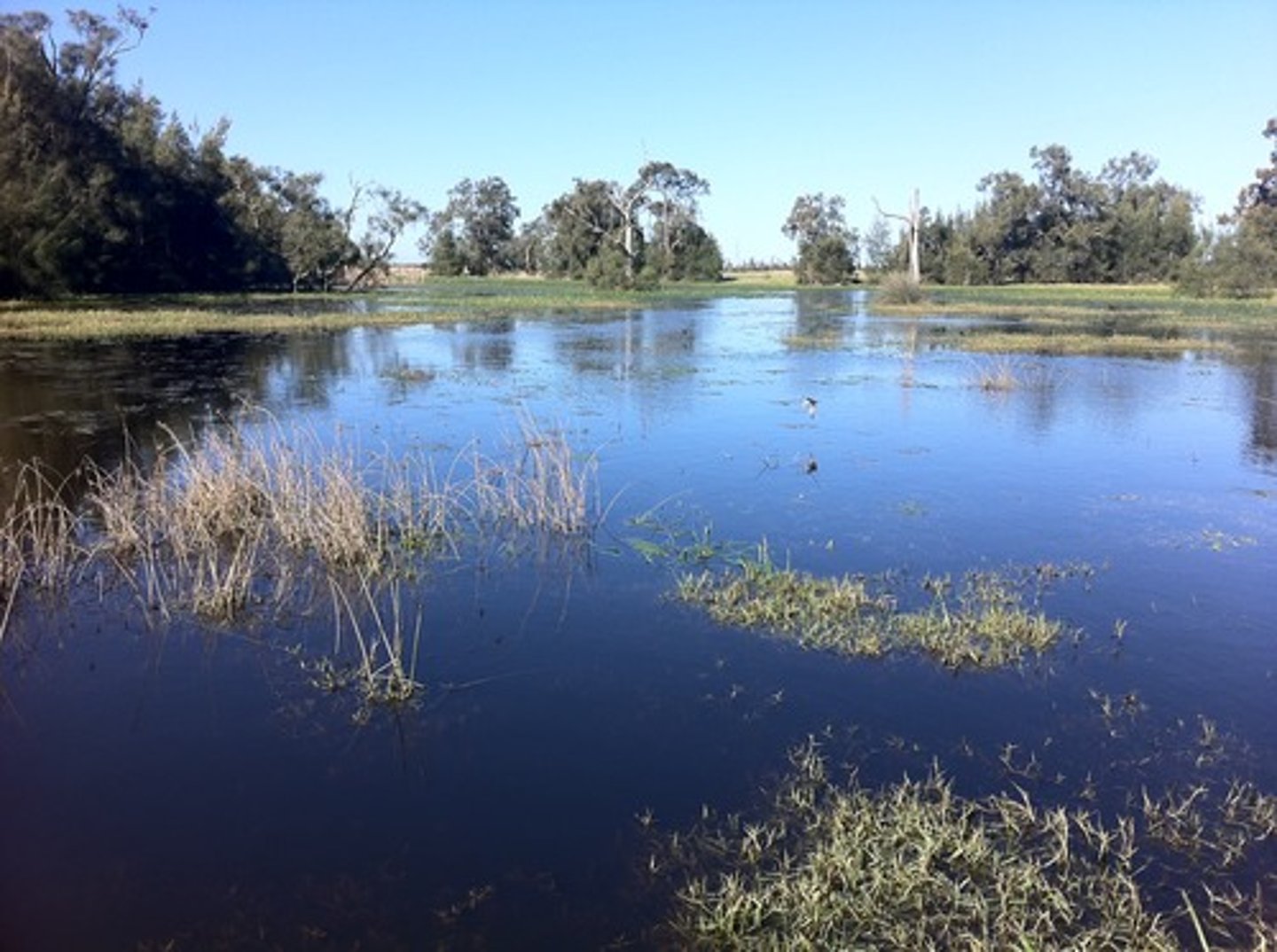

Mangrove swamp
A swamp that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt tolerant trees with roots submerged in water.
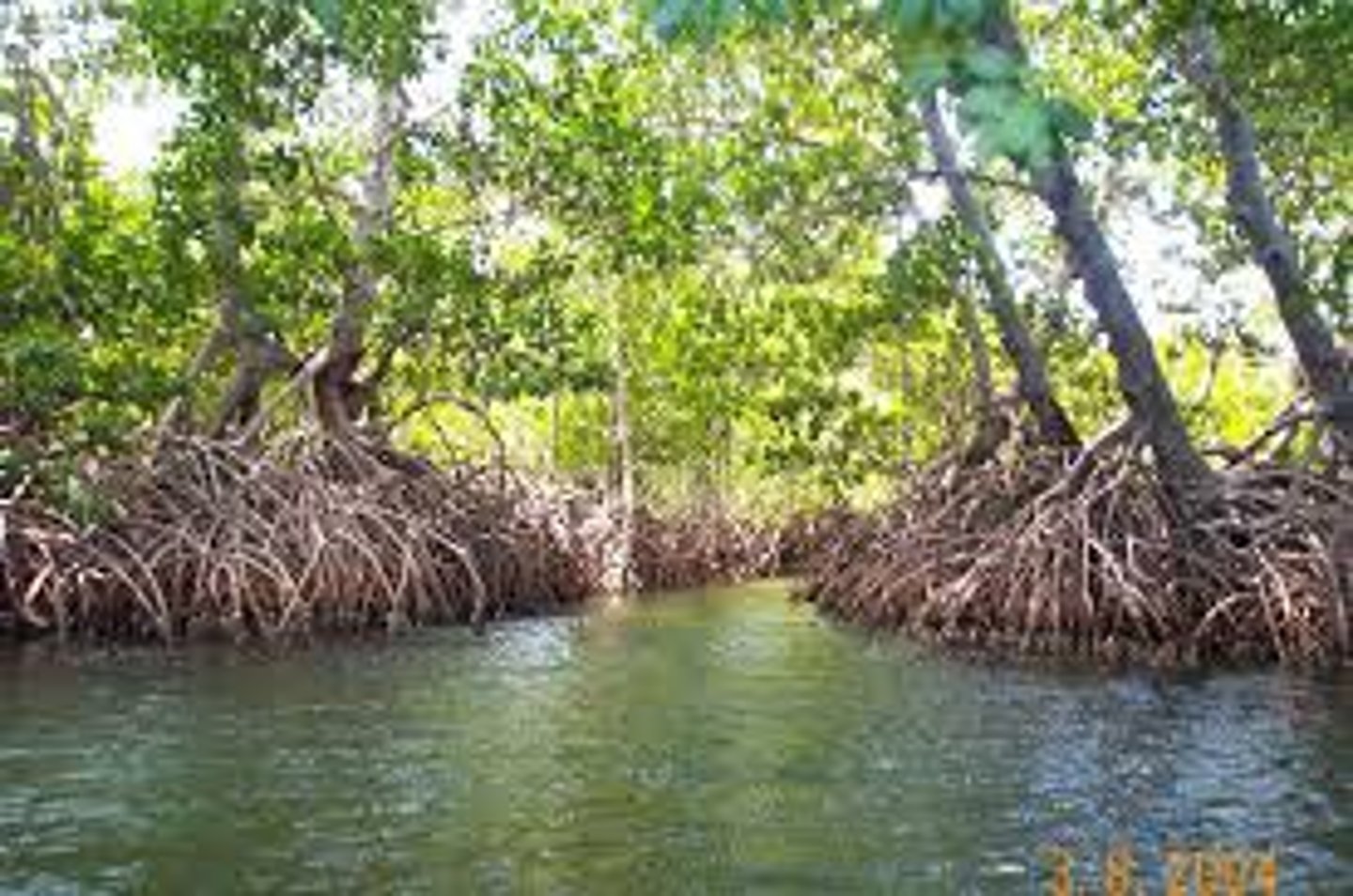

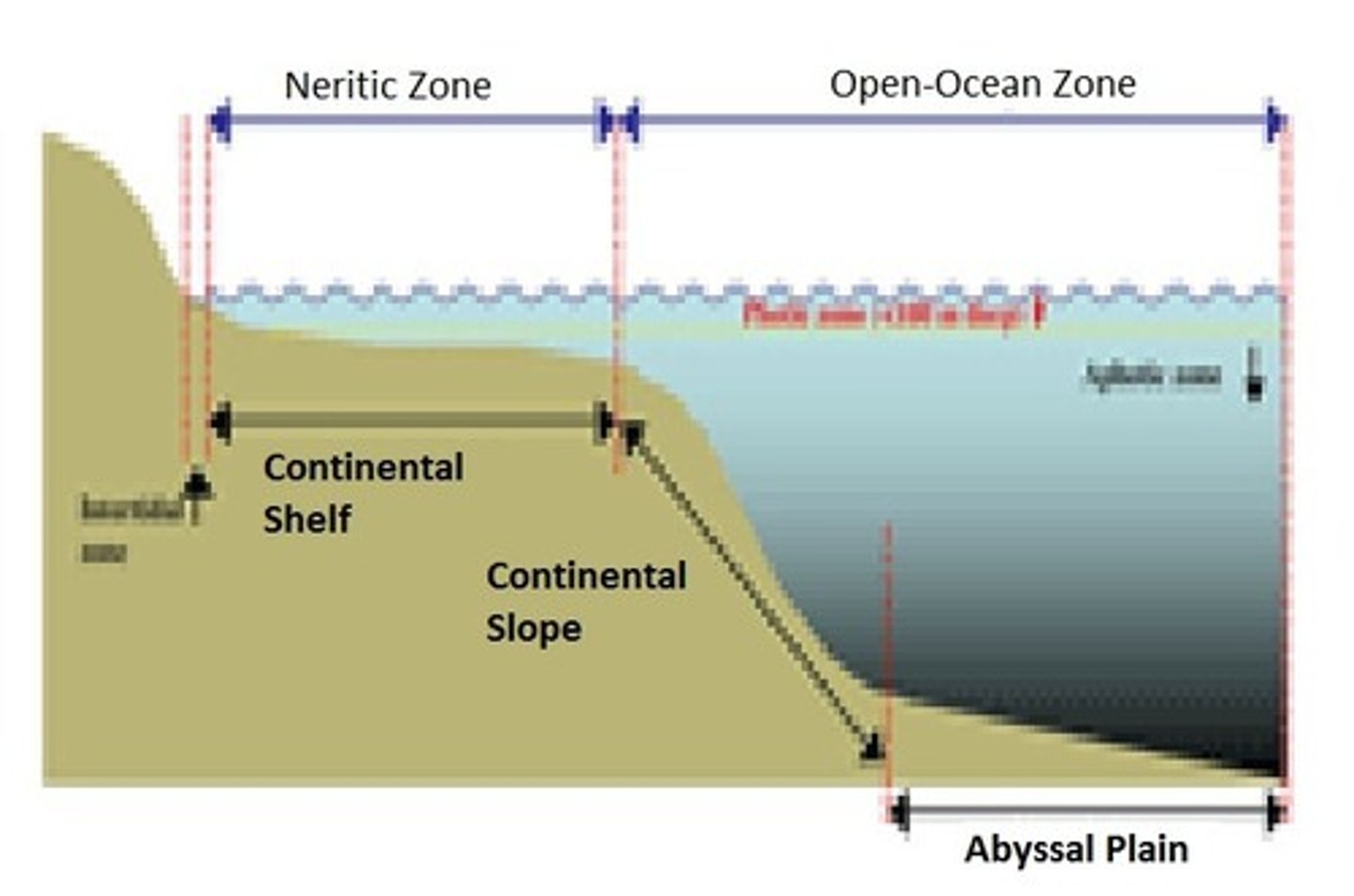
Intertidal zone
The narrow band of coastline between the levels of high tide and low tide.
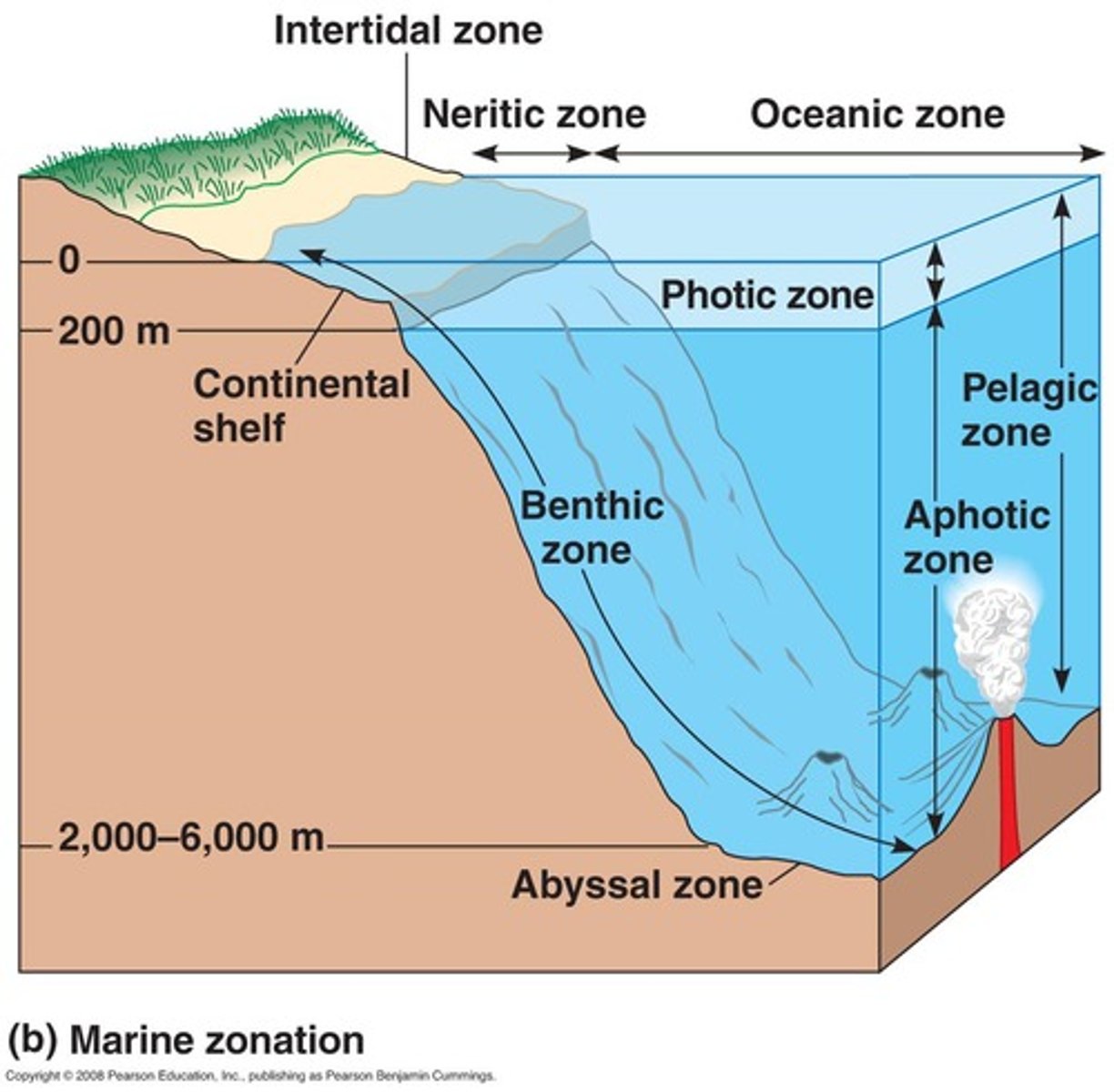
Oceanic Zone
Deep ocean water, located away from the shoreline where sunlight can no longer reach the ocean bottom.
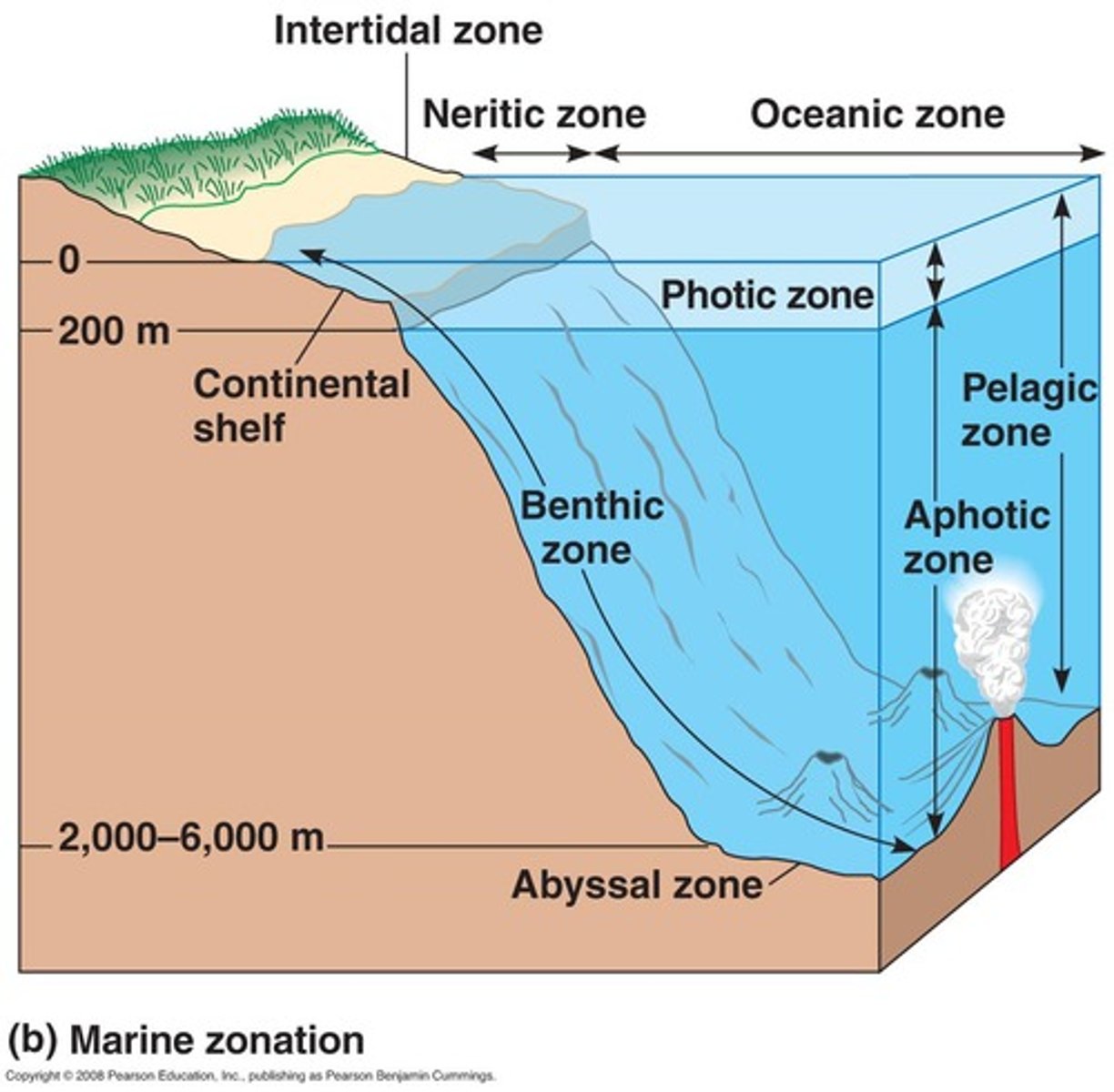
Photic zone
The upper layer of ocean water in the ocean that receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis.
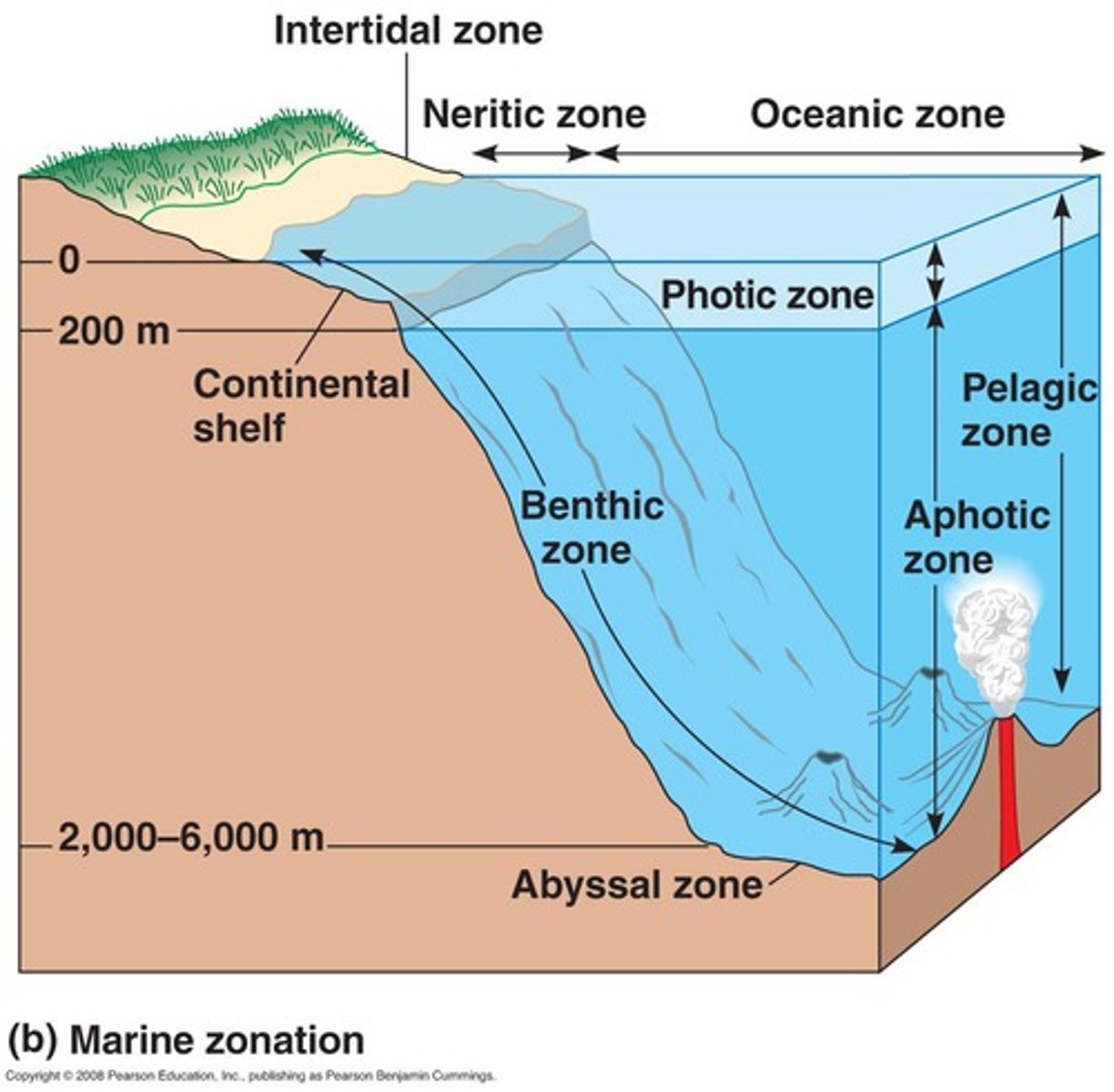
Aphotic zone
The deeper layer of ocean water that lacks sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis.
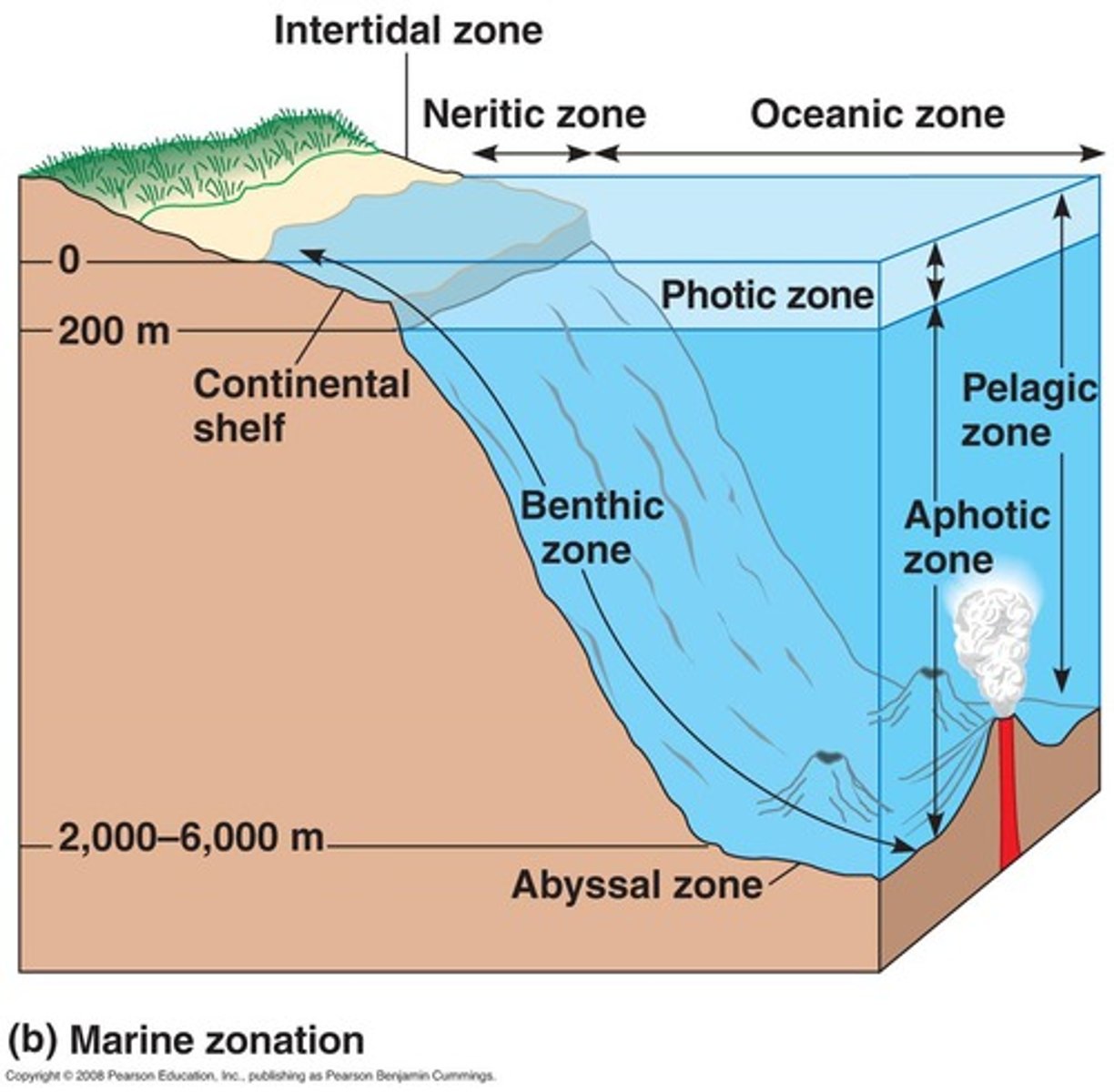
Neritic zone
Shallow waters that receive plenty of sunlight, inhabited by coral reefs and colorful fish

Estuary
Where freshwater from streams and rivers meet with salty water from the ocean. Algae, seaweed, grasses, crabs, oysters, waterfowl and manatees live here.

Abyssal zone
Deep ocean, ranges between 2000-6000 meters below the surface. Very cold, high pressure, chemosynthetic bacteria live near hydrothermal vents
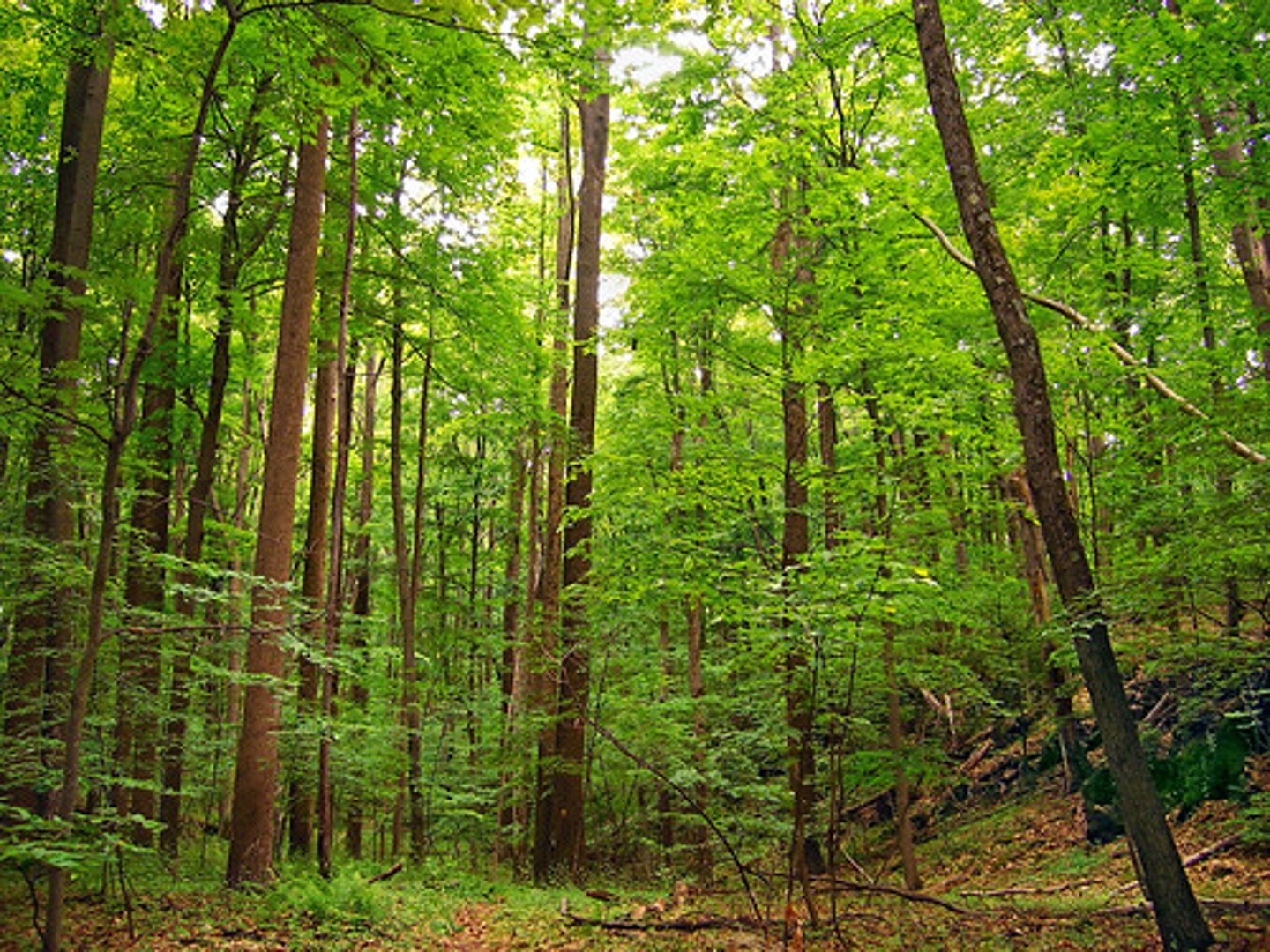
Temperate Deciduous Forest
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (Seasonal Variation)
-Precipitation is relatively evenly spread throughout the year
-Deciduous Trees (Oak, Maple, Beech)
-Europe, China, Eastern North America
-Northern Hemisphere
-Good Soils

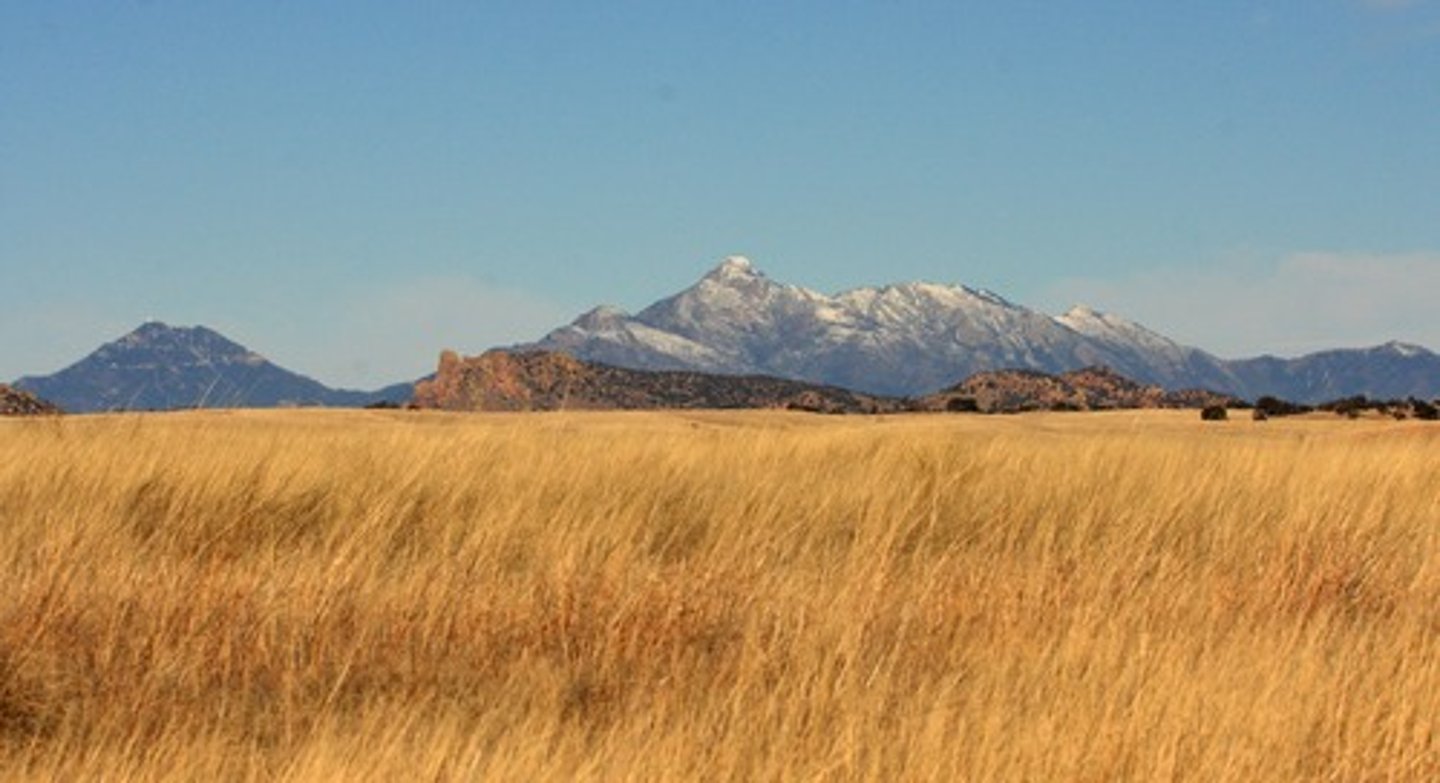
Temperate Grassland
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (seasonal variation is more extreme than temperate deciduous forests)
-Limited amount of precipitation
-Also called prairie or steppe
-Northern Hemisphere
-North America, Middle East, Europe, Asia
-Very fertile soils (used for agriculture)

Temperate Rainforest
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (Seasonal Variation)
-Large amount of precipitation (Less rain in winters)
-Large trees
-Provide lumber and paper
-Northern Hemisphere
-West coast of North America and Canada
-Fertile soils that are susceptible to land slides and erosion if forests are cleared
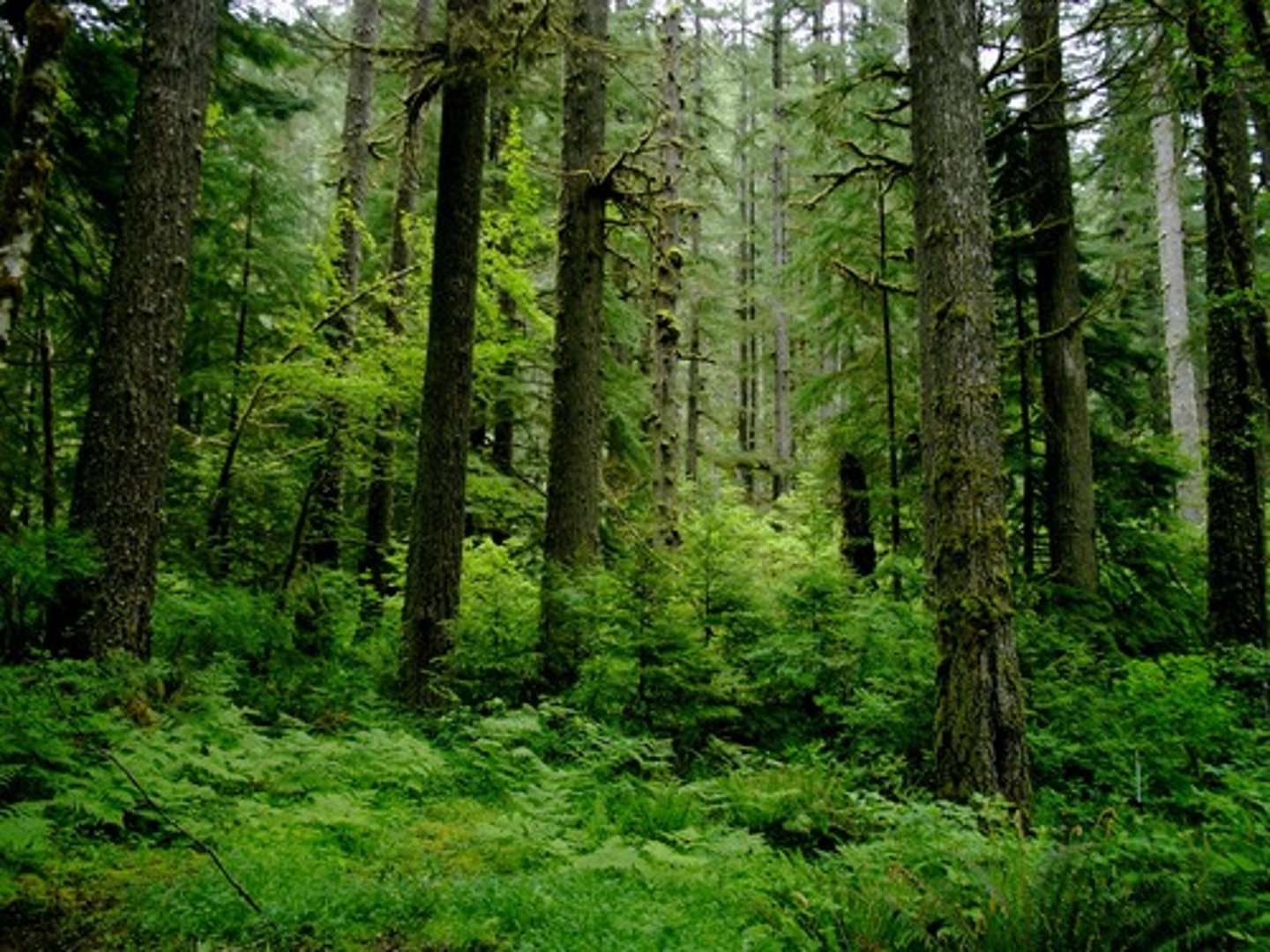

Tropical Rainforest
-Warm all year round
-Very high amount of precipitation (300-500 mm per month)
-Southern Hemisphere
-Central America, Africa, South America, Southeast Asia
-Great Biodiversity
-Poor, thin soils

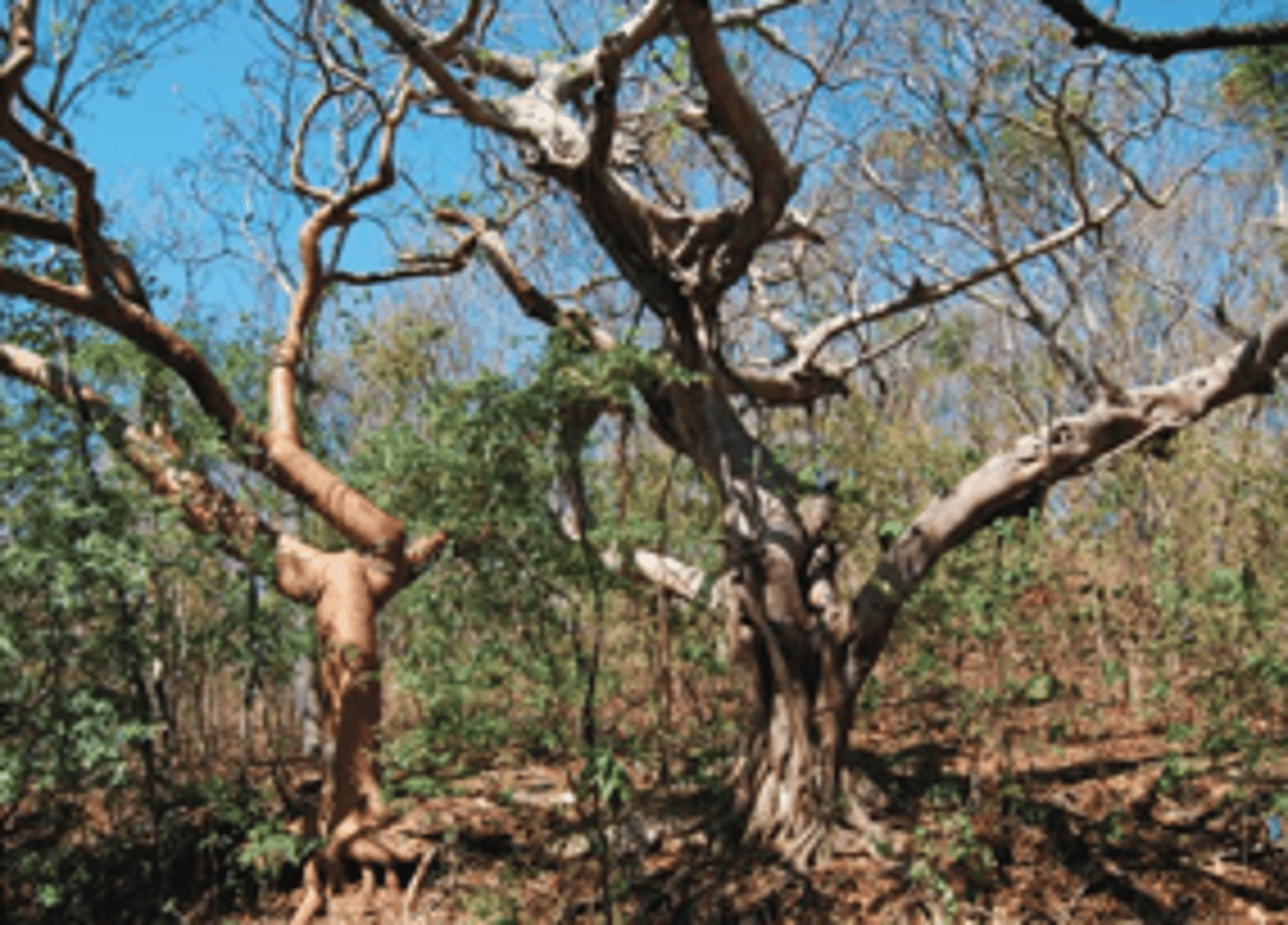
Tropical Dry Forest
-Warm all year round
-Extreme wet and dry seasons
-Wet summer (October to April) and dry winter (May, June, July, August, September)
-Southern Hemisphere
-India, Africa, South America, northern Australia
-Erosion-prone soils

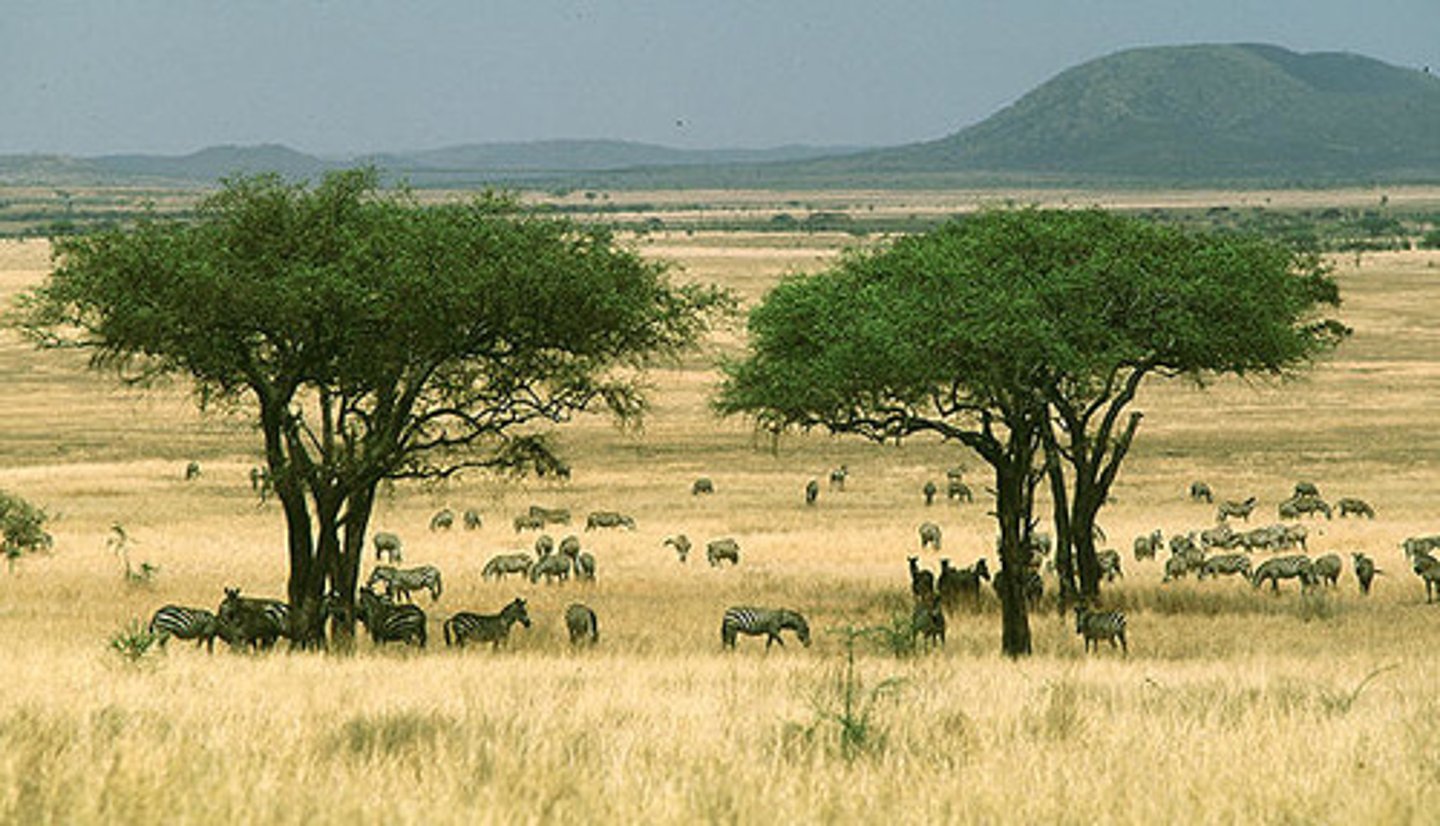
Savanna (Tropical Grasslands)
-Mostly warm year round with slight seasonal variation (warmer in summer)
-Extreme wet and dry seasons
-Wet Summer (not as wet as tropical dry forest)
-Southern Hemisphere
-Isolated Trees
-Africa, South America, India, Australia
-Zebras, Giraffes, Gazelles

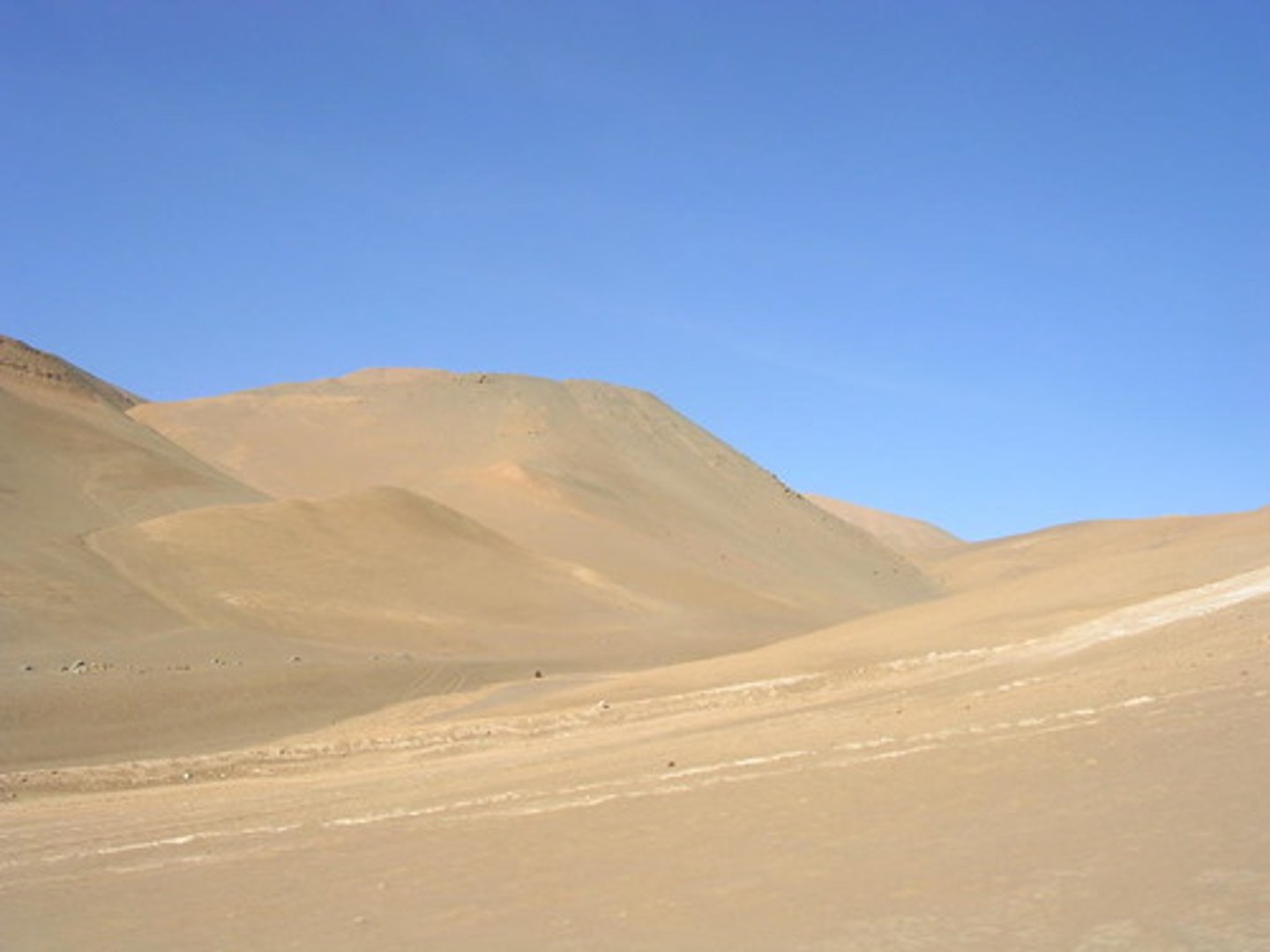
Desert
Driest Biome
-Barely an rainfall
-Saline soils
-Little Vegetation
-Temperatures drop at night
-Northern Hemisphere
-Africa, Mexico, Middle East, Asia

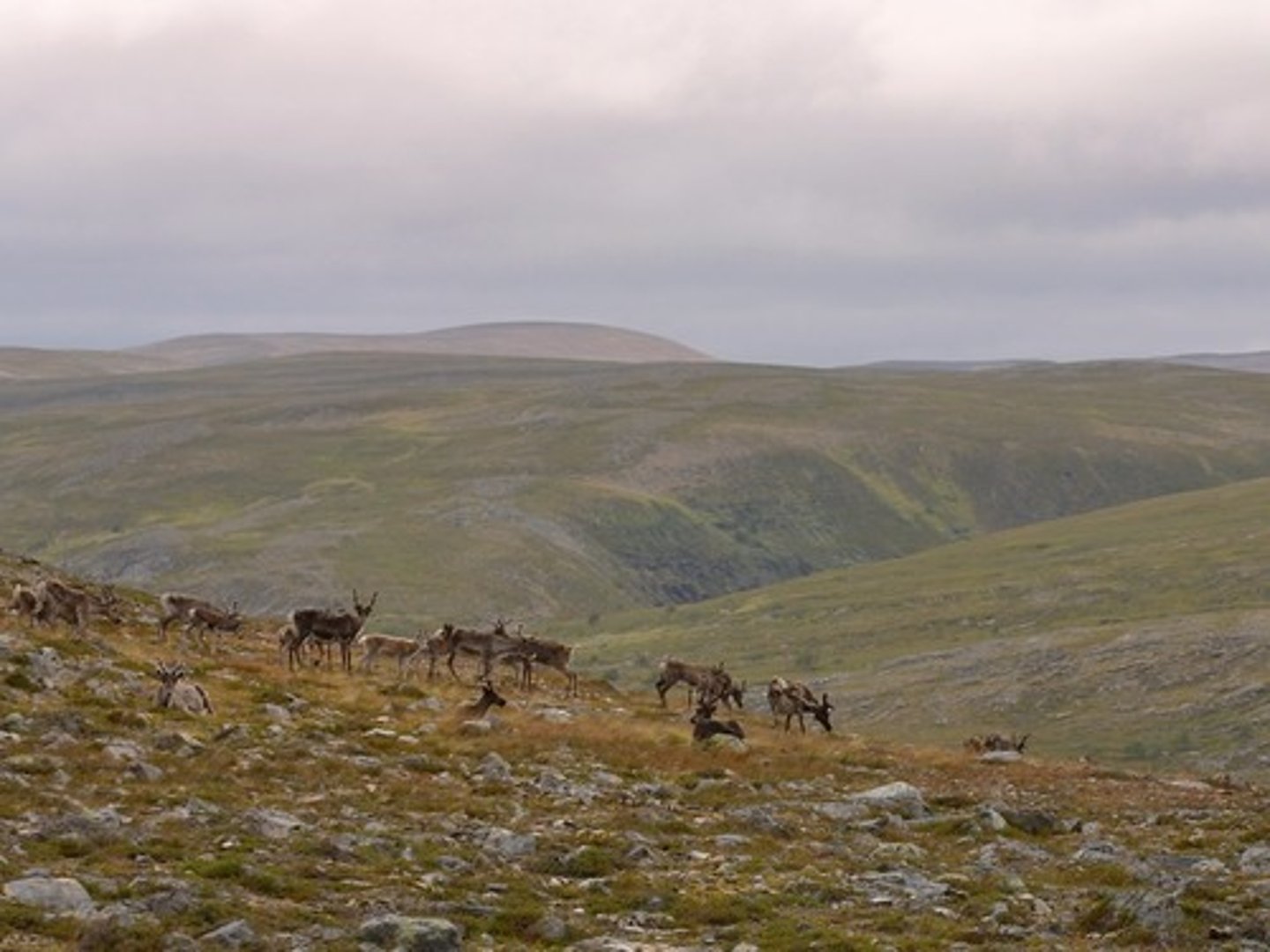
Tundra
-Coldest Biome
-Warmer in summers, but still cold (5 degrees celsius)
-Freezing in winters (-20 degrees celsius)
-Northern Hemisphere
-Dry
-Slightly wet summers
-Soil is permanently frozen (permafrost)
-Also occurs as alpine tundra at the tops of mountains
-Northern Europe, Northern Canada, Northern Asia, Greenland

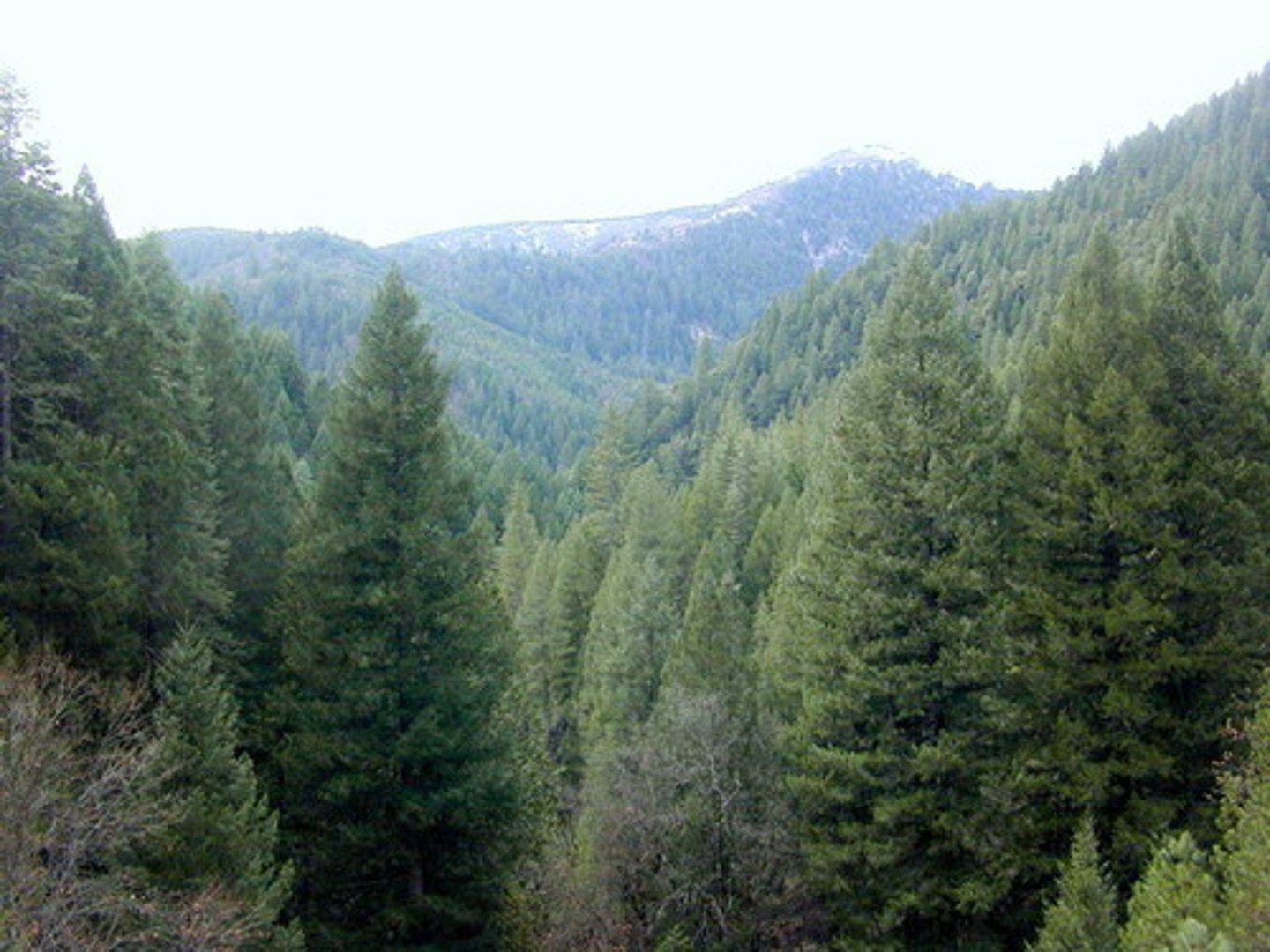
Boreal Forest/Taiga/Coniferous Forest
-Largest Biome
-Northern Hemisphere
-Coniferous Trees (Pinecones)
-Cold. Cooler in summers (never above 20 degrees Celsius)
-Moderate Precipitation
-More wet in summer than winter
-Poor soils
-Moose, Wolves, Lynx, Bears
-Northern Europe, Canada, Northern Asia

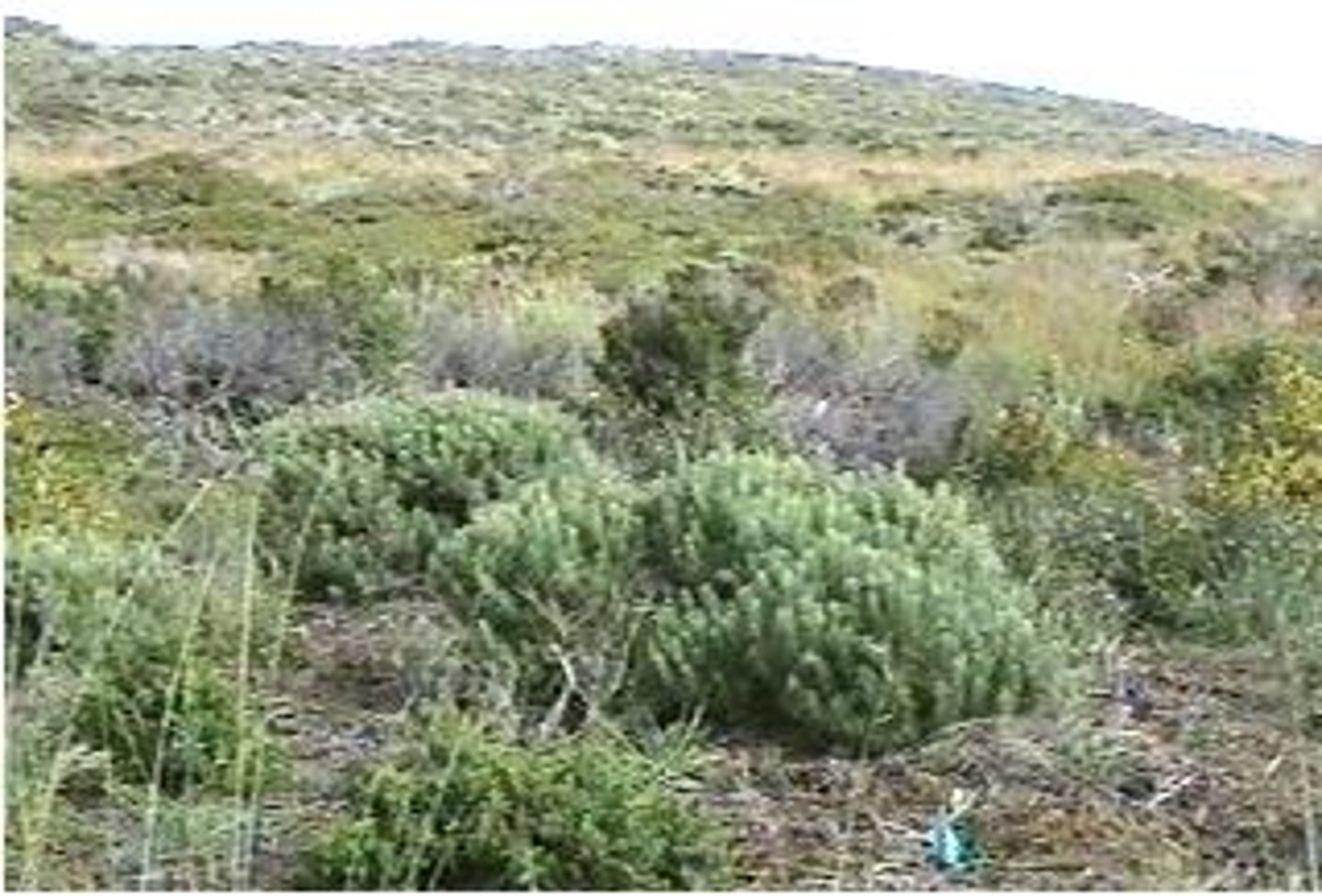
Chaparral
Densely thicketed
-Highly seasonal
-Cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers
-Induced by oceanic influences
-Northern Hemisphere
-California, Mediterranean regions
-Frequent fires

lotic systems
aquatic ecosystems composed of flowing water
lentic systems
aquatic ecosystems composed of ponds and lakes
Marine systems
relating to the sea and to a system of open-ocean and unprotected coastal habitats
Aquifer
A body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater.
Ogallala Aquifer
World's largest aquifer; under parts of Wyoming, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Colorado, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas (the Midwest). Holds enough water to cover the U.S. with 1.5 feet of water. Being depleted for agricultural and urban use.