OCR A 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 Amines, Amino Acids, Amides and Chirality
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
amine
-derived from ammonia molecules
-all contain a N atom
-H are replaced w/ organic group
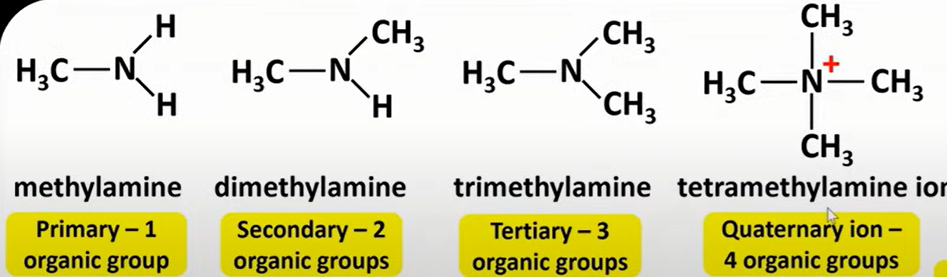
aliphatic amines
-primary; methylamine
-secondary; dimethylamine
-tertiary; trimethylamine
-quaternary ion; tetramethylamine ion
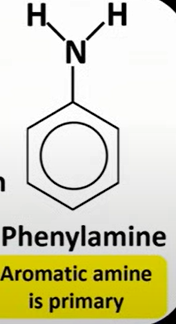
aromatic amine
-primary amine; phenyl amine
amine properties
-act as base
amine as a base
-have lone pair of e that allows them to accept a proton
-when proton bonds to amine via a dative covalent bond; both e in bond come from lone pair in N
what does the strength of amine as a base depend on
-availability of the lone pair of e on N
-higher e density; more readily available the e are; more basic
what does electron density of N depend on
-type of group attached
-the more e on grp the higher e density
-unless phenol as lone pair goes to benzene ring
amine + acid reaction
-neutralise acid to make salt
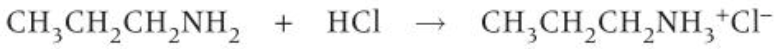
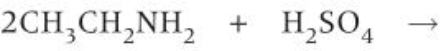
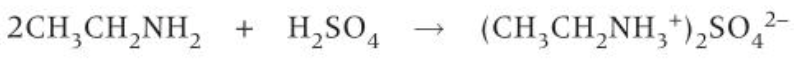
how to prepare primary amines
-reduction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia
-reduction of nitriles
reduction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia
-nucleophilic substitution
-lone pair on N acts as nucleophile and replaces halogen
-ethanol used as solvent; prevents sub of haloalkane to make alcohol
-excess ammonia used; further sub of amine group to secondary/tertiary amine
reduction of nitrile
-C-N func grp can be reduced to NH2
-reacting with H2 gas in presence of Ni catalyst
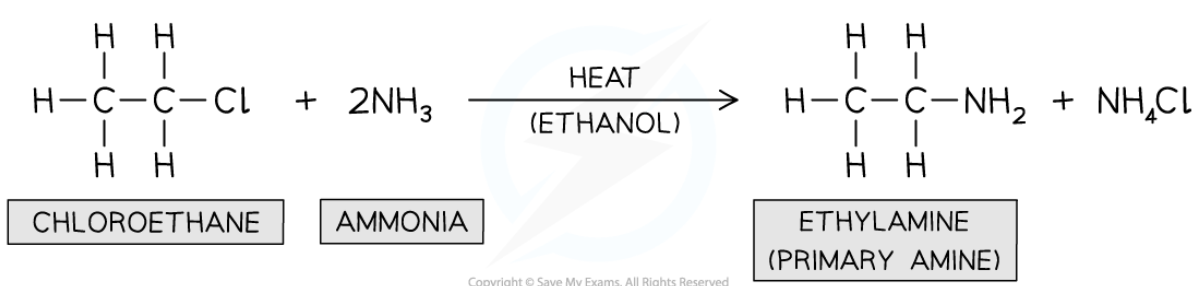
preparation of secondary amine
-react excess haloalkane w/ primary amine
-in ethanol
react haloalkane w/ primary amine
-nucleophilic substitution
-N in amine acts as nucleophile and replaces halogen
-condition:
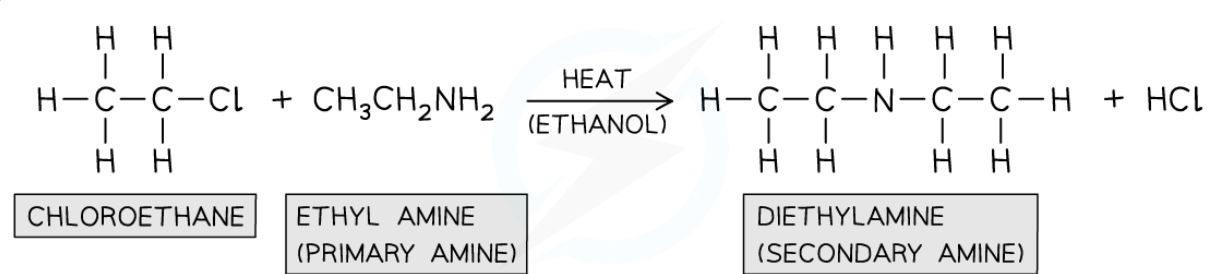
preparing aromatic amine
-nitrobenzene can be reduced to phenylamine
-reduction; reacted with Sn and conc HCl which acts as reducing agent
-heated under reflux in boiling water bath
-phenylammonium salt forms
-addition of excess NaOH sol to produce aromatic amine
amino acids
-organic compounds that contain 2 func grps
-amino grp;-NH2
-carboxyl grp; -COOH
general formula a-amino acid
-RCH(NH2)COOH
amino acid property
-has basic amino grp and acidic carboxyl group
-can act as acid and base
-undergo most reactions of amines and carboxylic acids:
-amines with acids
-carboxylic acids with bases
reaction of amine group
-reacts with acids to make ammonium salt

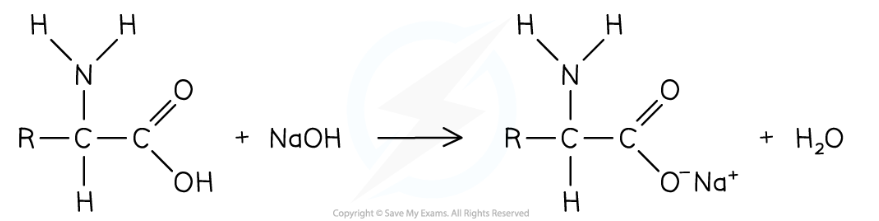
reaction of carboxyl group with aqueous alkali
-amino acid reacts w/ aqueous alkali such as Na/KOH to form salt and water
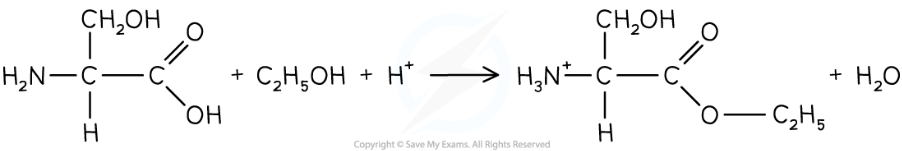
esterification of amino acid with alcohol
-amino acid can be esterified by heating with alcohol
-in presence on conc H2SO4
-carboxyl grp is esterified
-amine grp protonated due to acidic condition
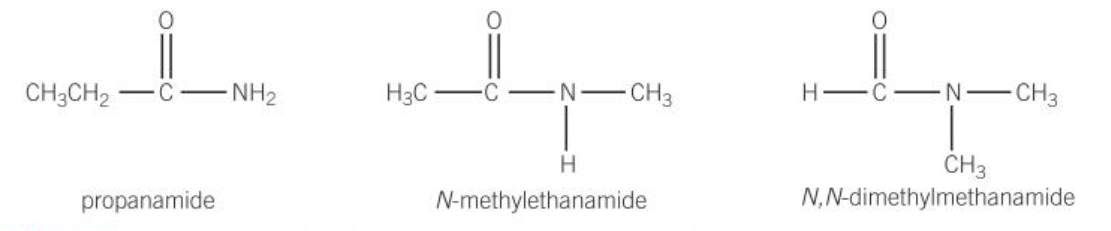
amides
-formed from condensation reaction of acyl chloride w/ ammonia and amides
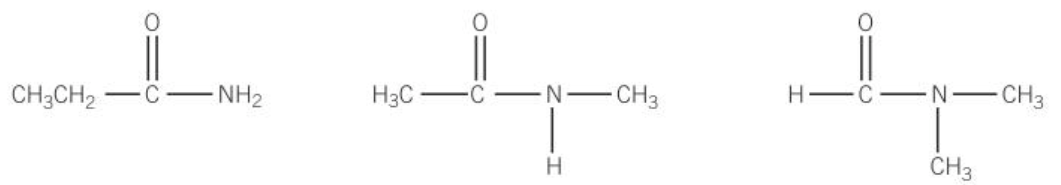
name
o
optical isomer
-form of stereoisomerism
-same structural formula but dif arrangement of atoms in space
-mirror images of each other
-have chiral carbon atom
chiral centre
has 4 dif groups attached to C atom
how to detect optically active compounds
-they rotate plane polarised light
-D enantiomer rotates light clockwise
-L enantiomer rotates light anti-clockwise
how to get plain polarised light
-standard oscillates in all directions
-pass light thru a polaroid filter
-light will only oscillate in 1 direction