Neurones
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
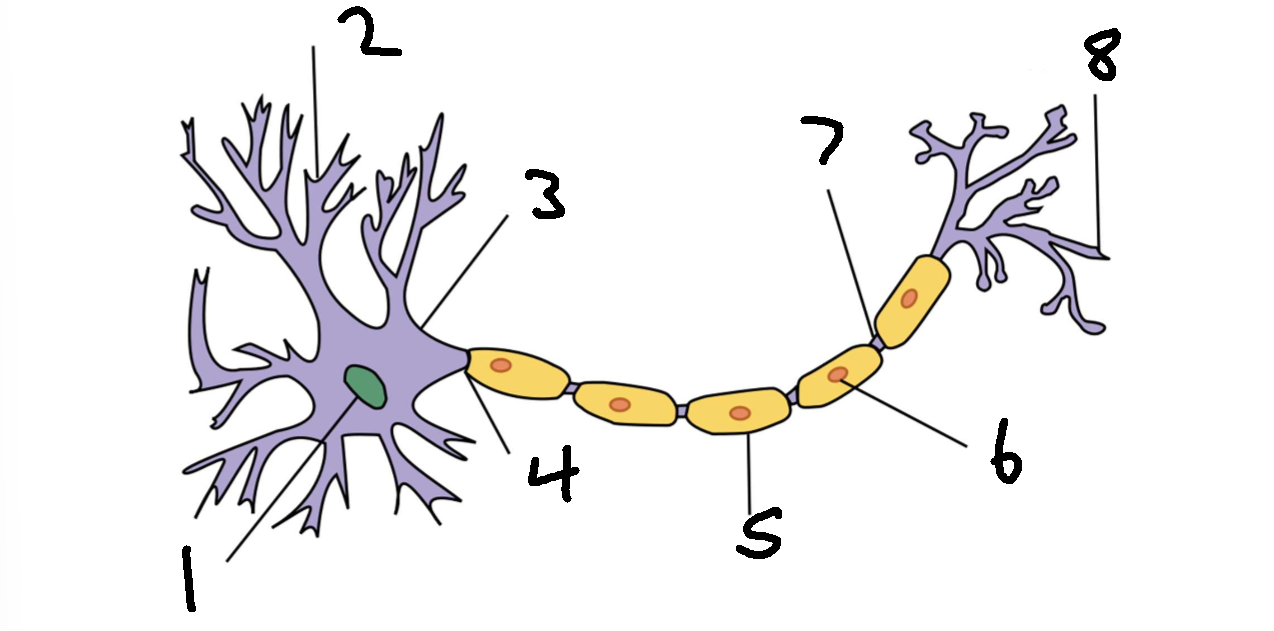
What is 1?
nucleus
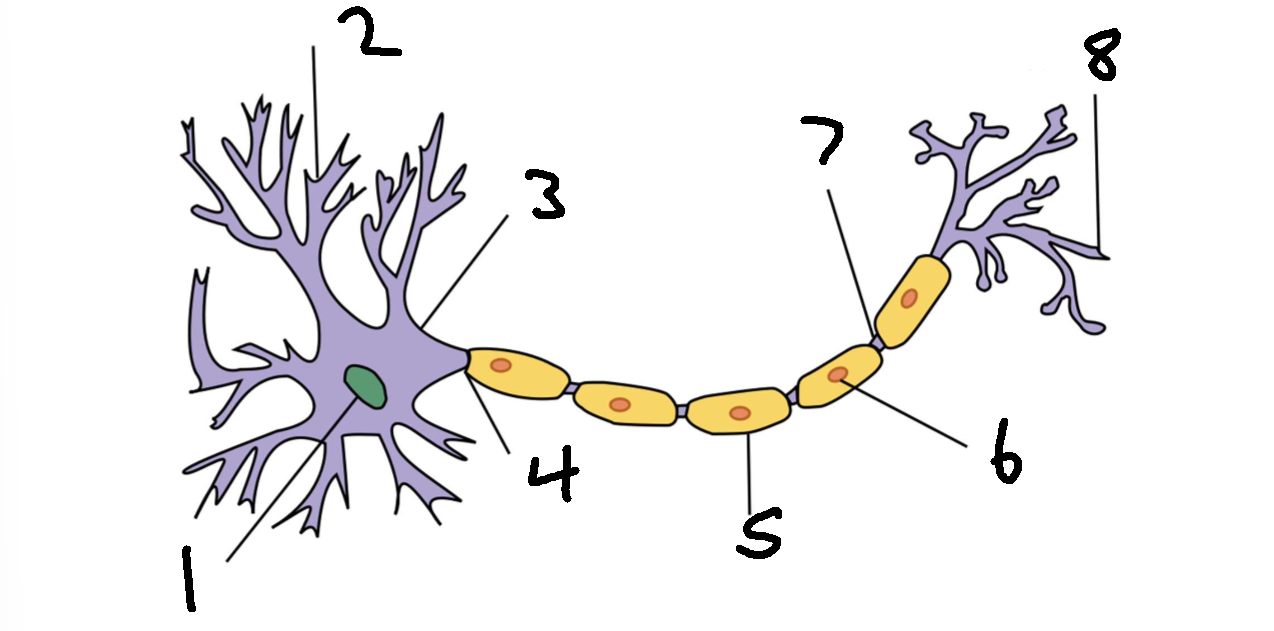
What is 2?
dendrite
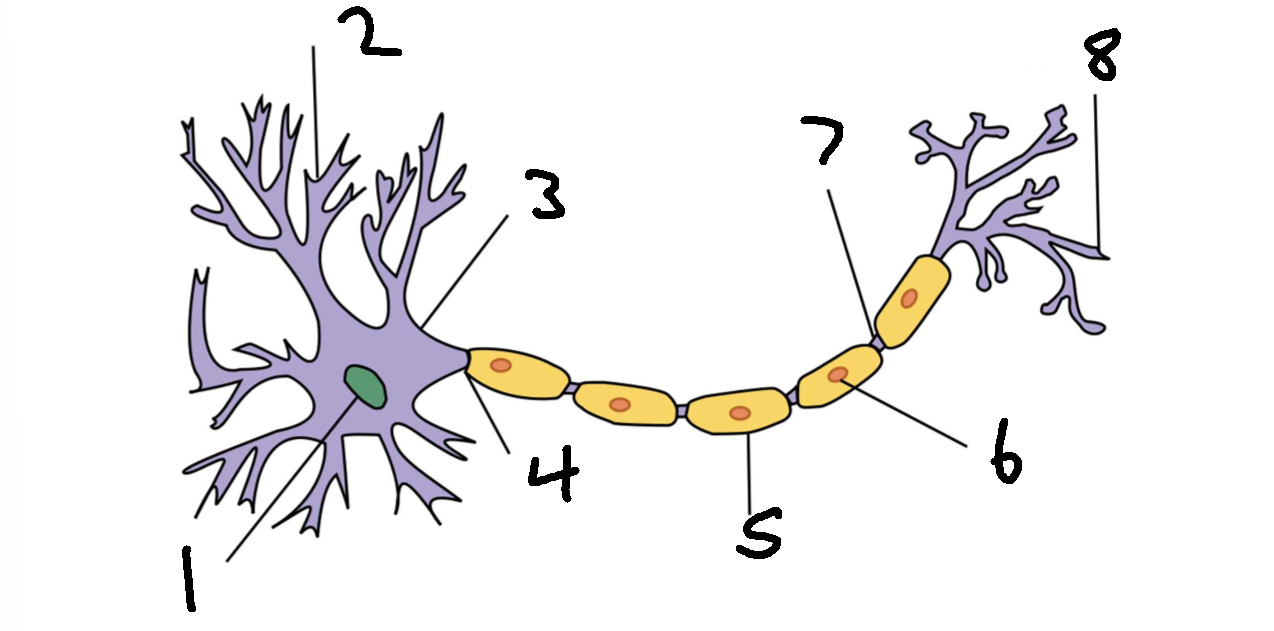
What is 3?
cell body
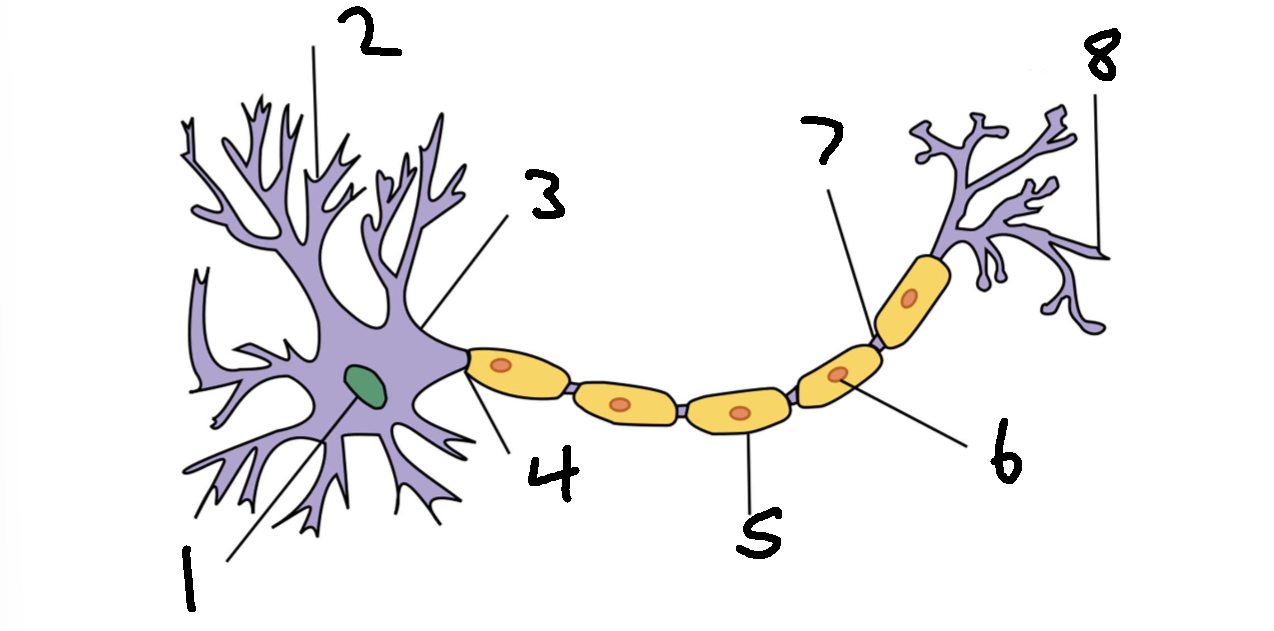
What is 4?
axon
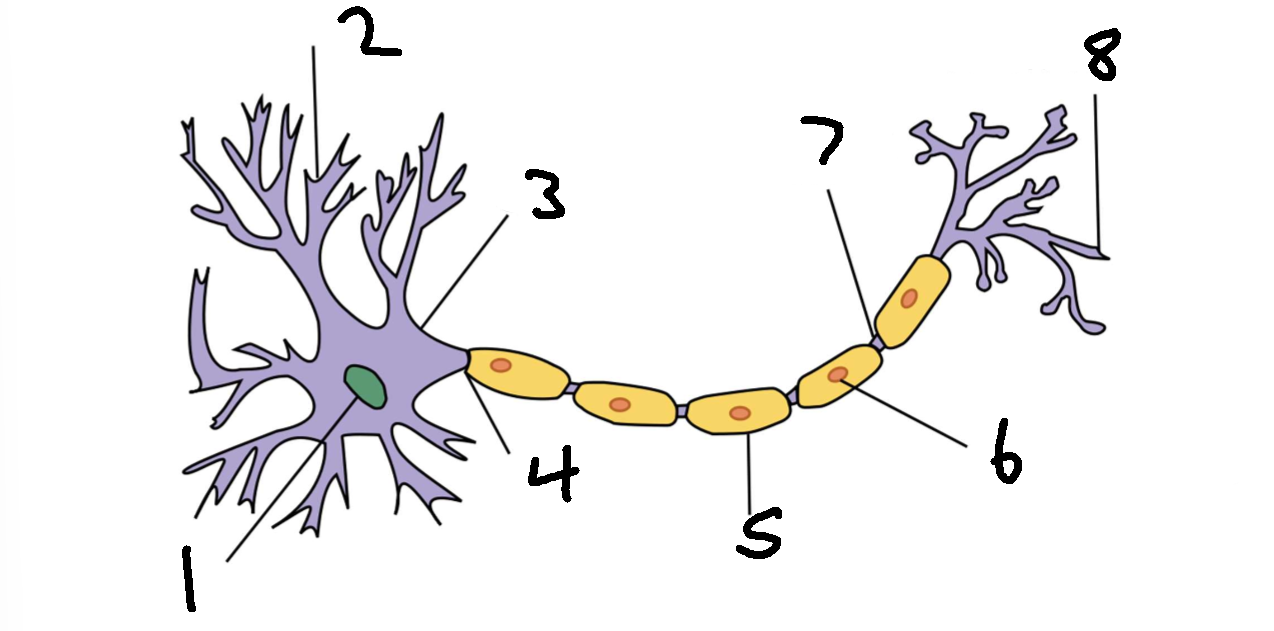
What is 5?
myelin sheath
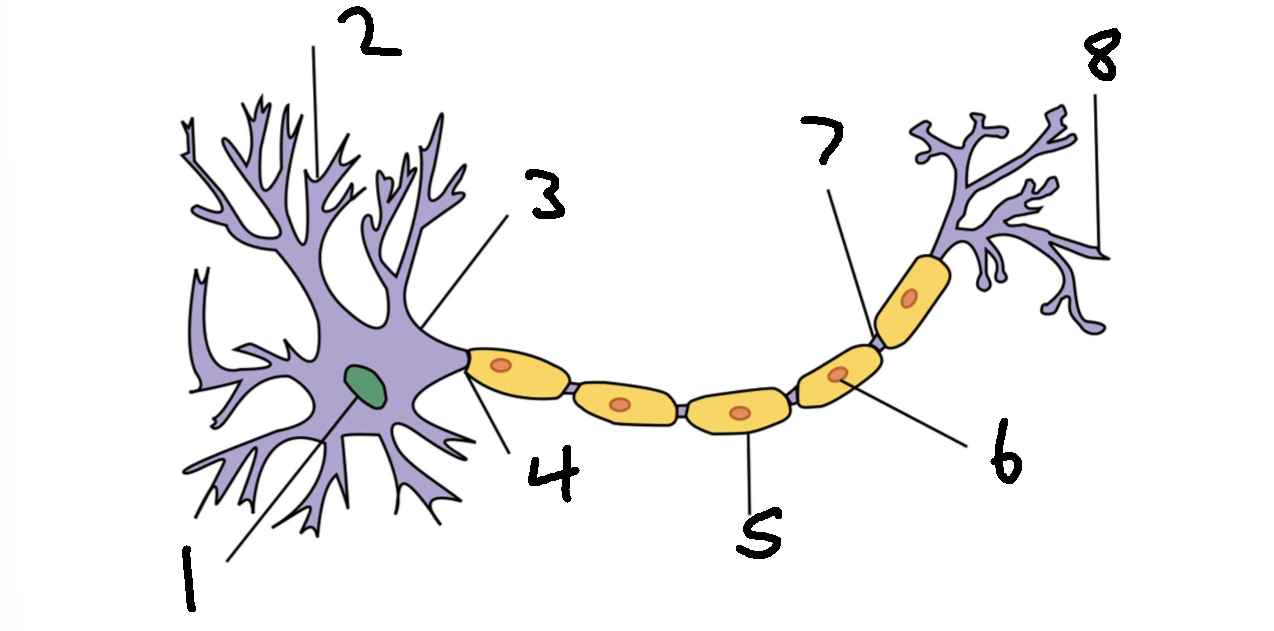
What is 6?
schwann cell
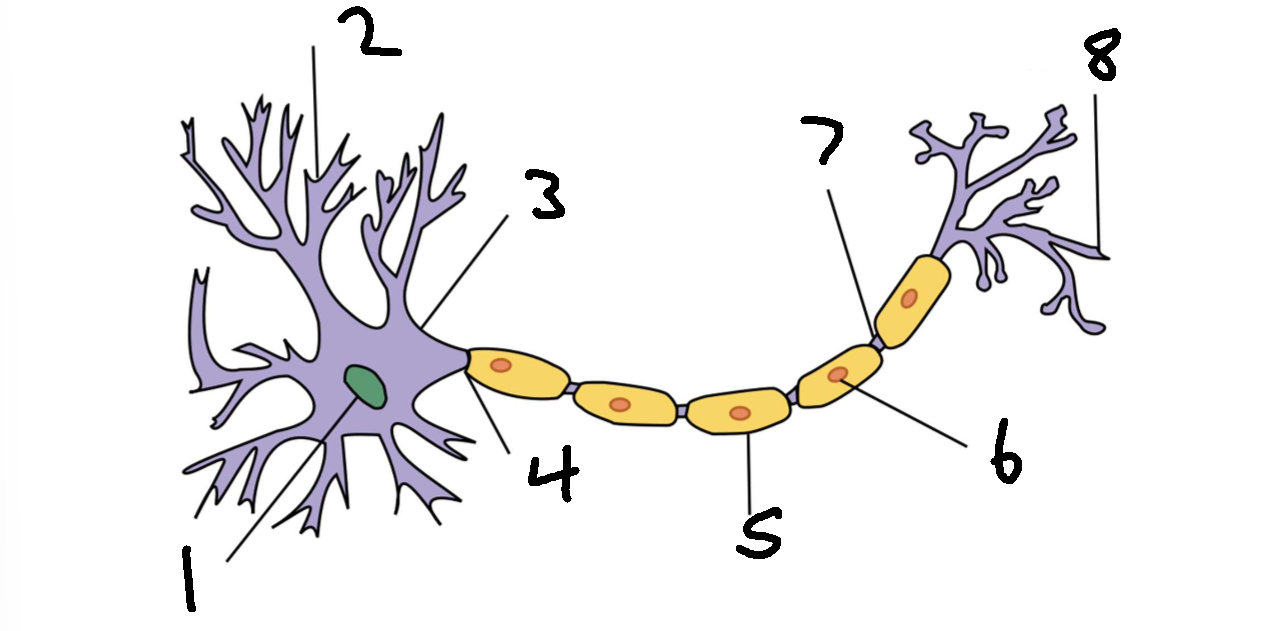
What is 7?
node of ranvier
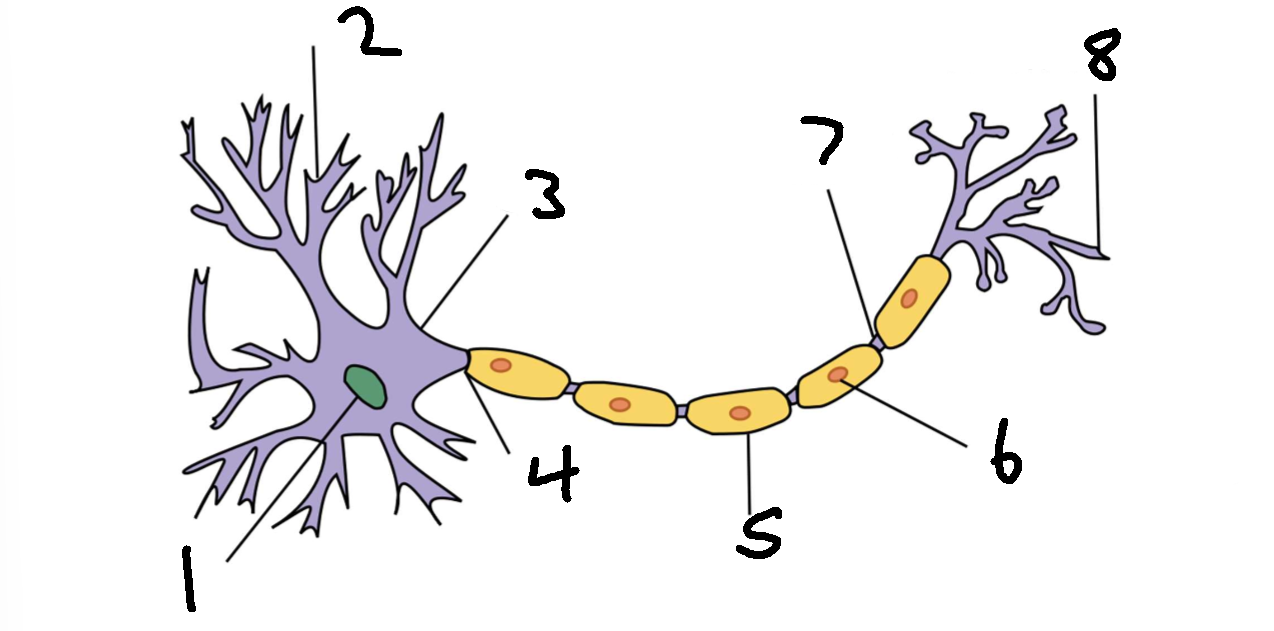
What is 8?
axon terminal
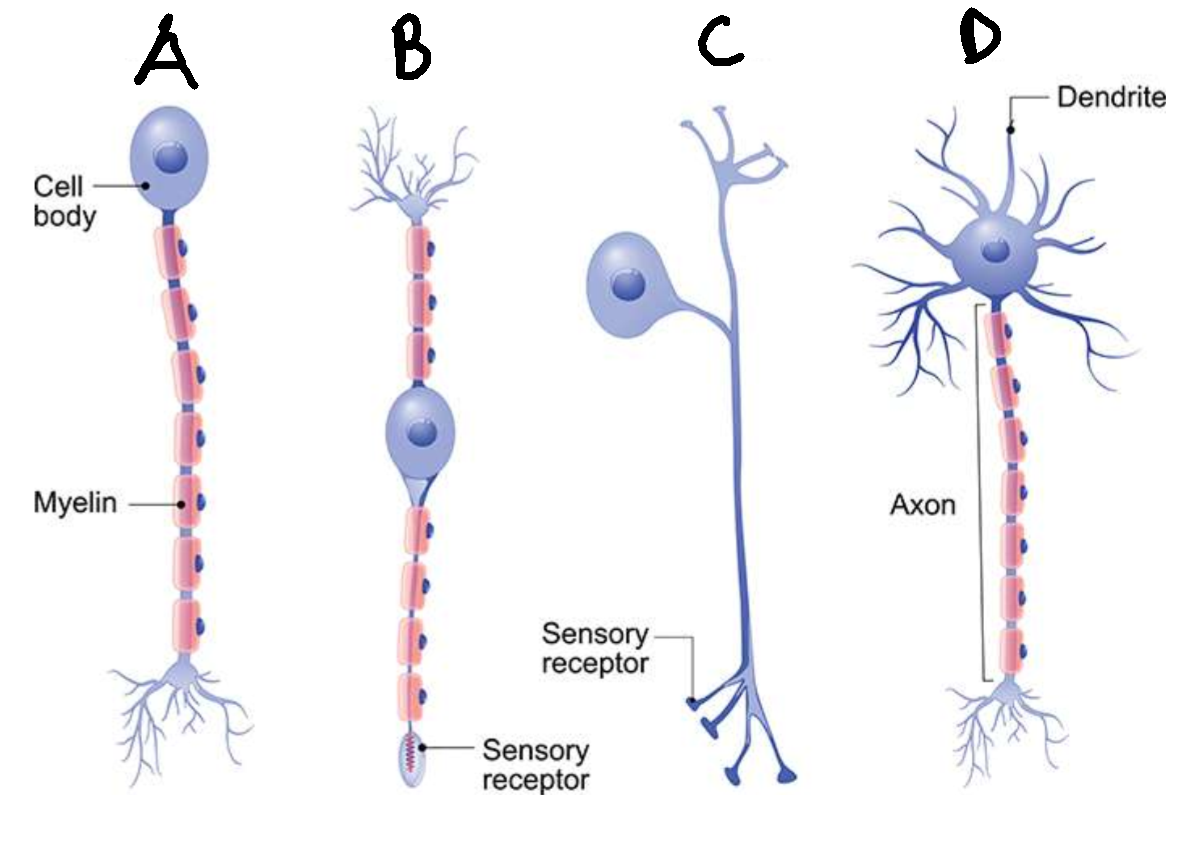
What type of neurone is A?
unipolar
Are neurones A usually sensory or motor?
sensory
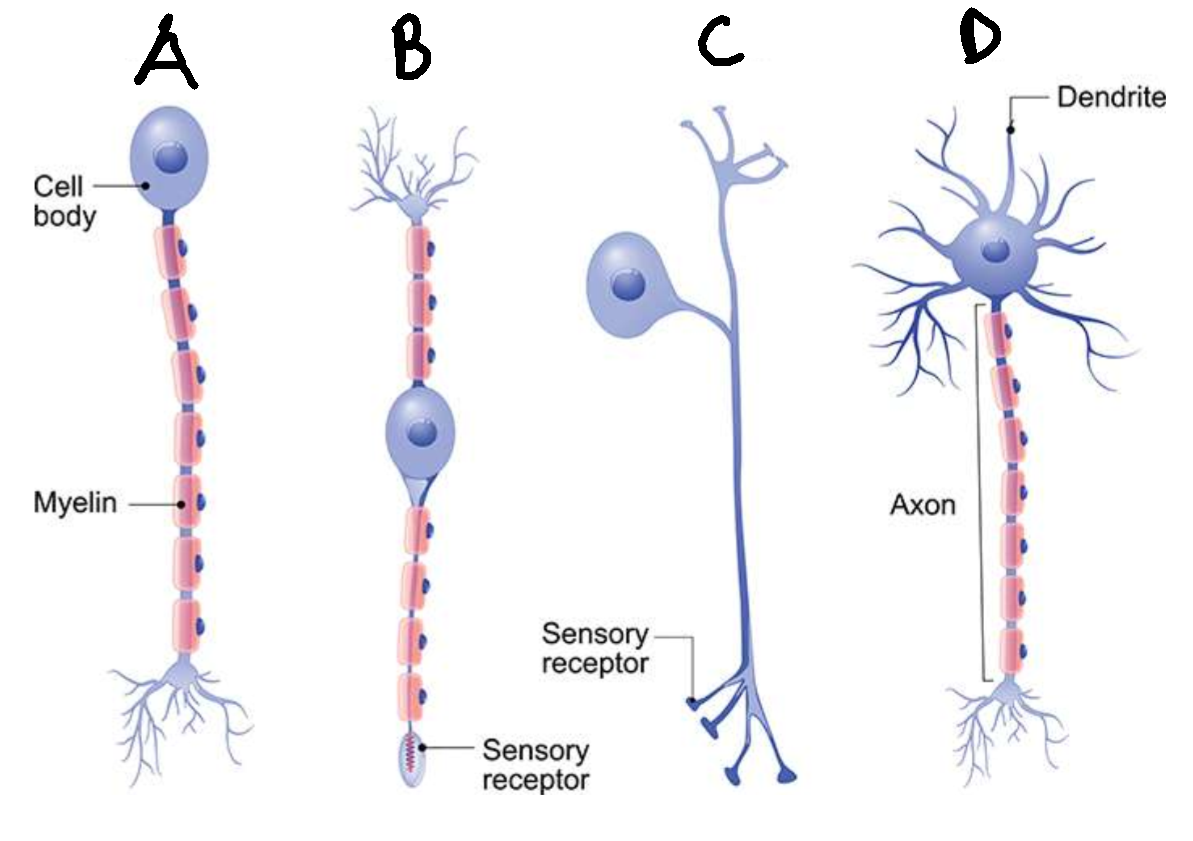
What type of neurone is B?
bipolar
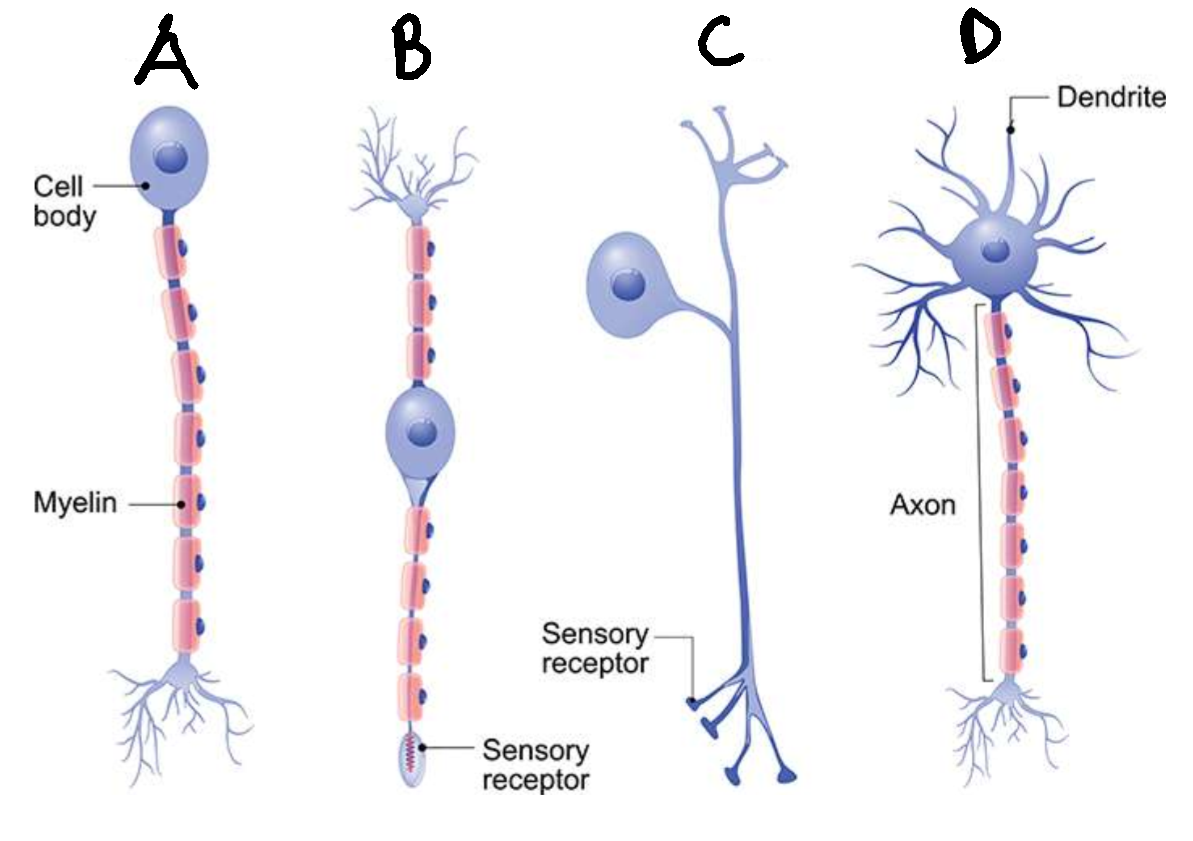
What type of neurone is C?
pseudounipolar
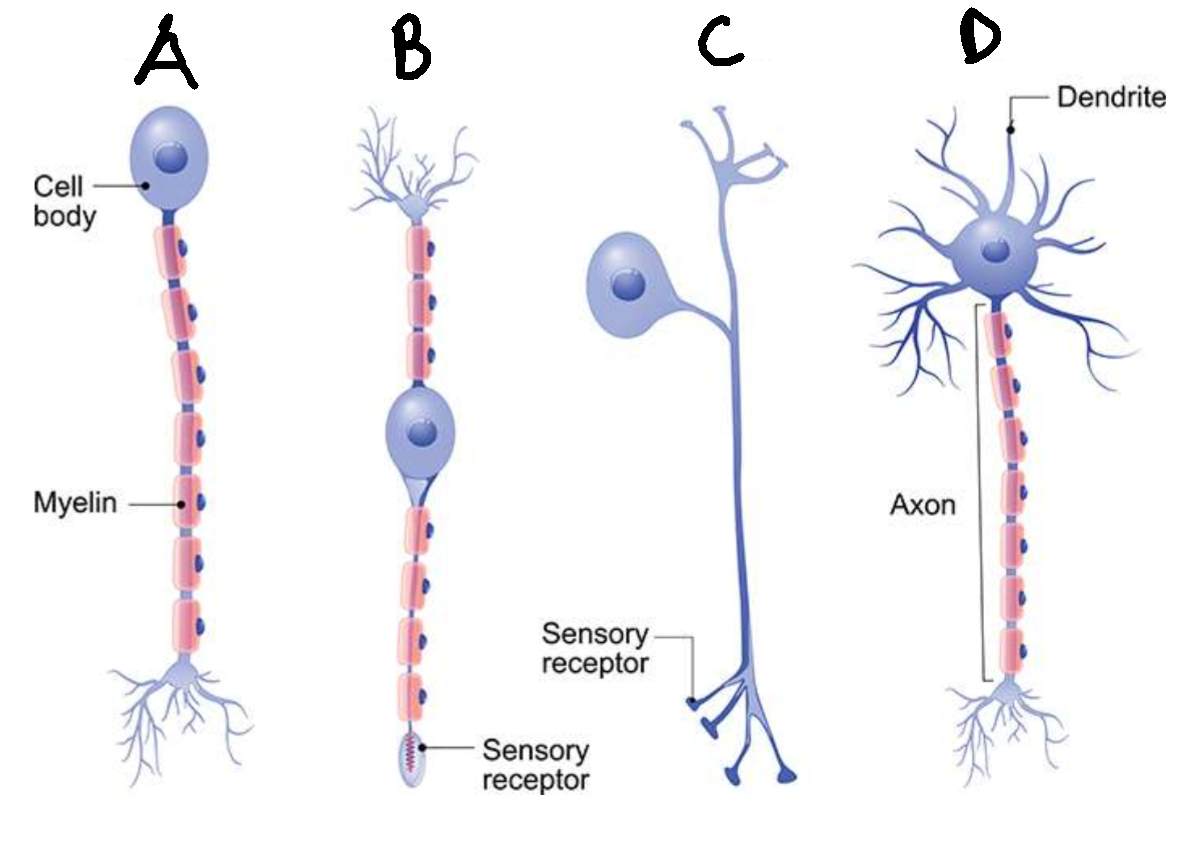
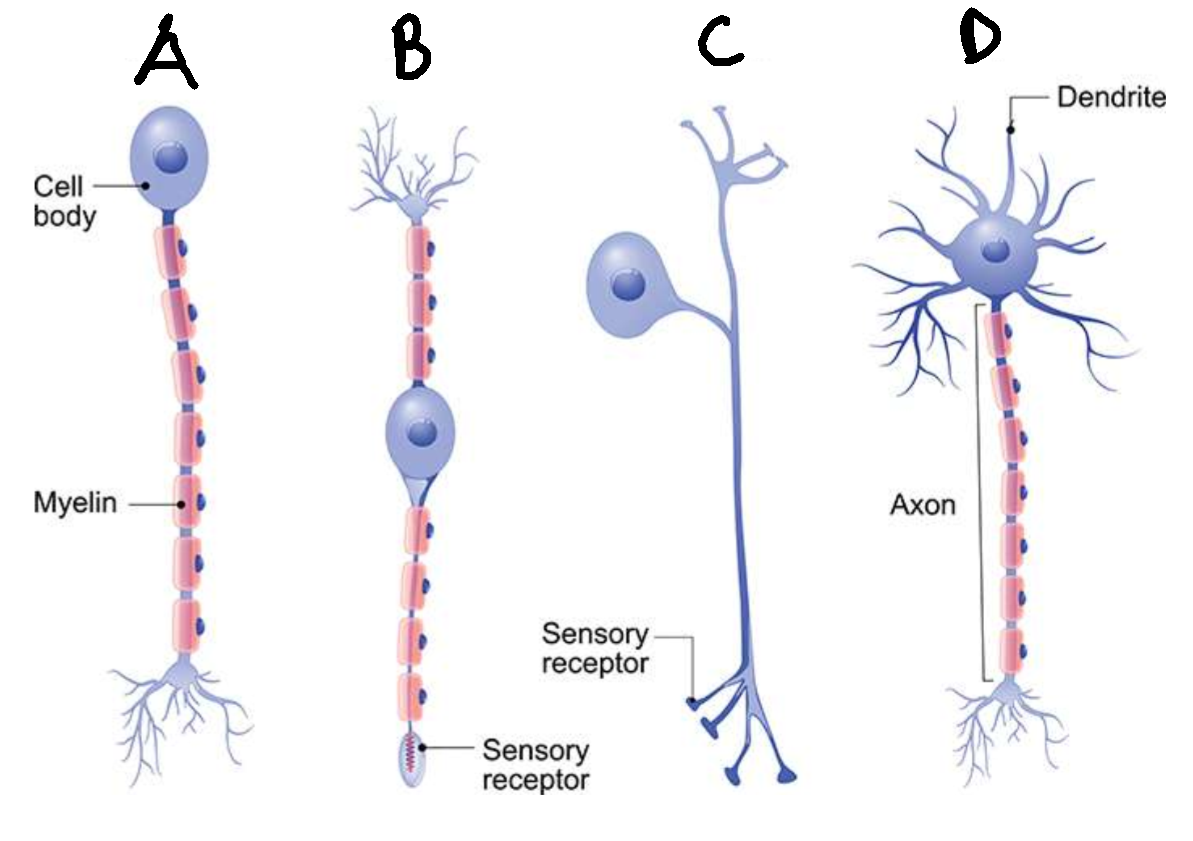
What type of neurone is D?
multipolar
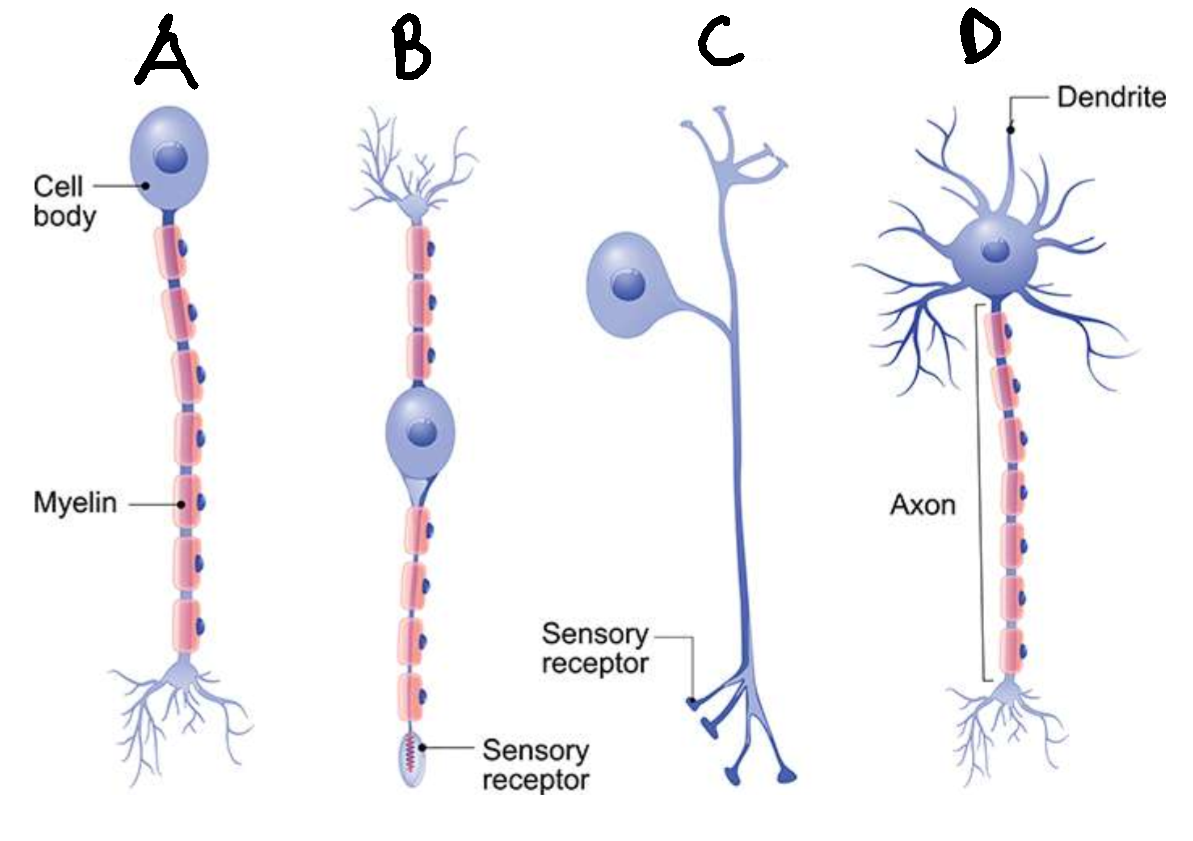
Are neurones D usually sensory or motor?
motor
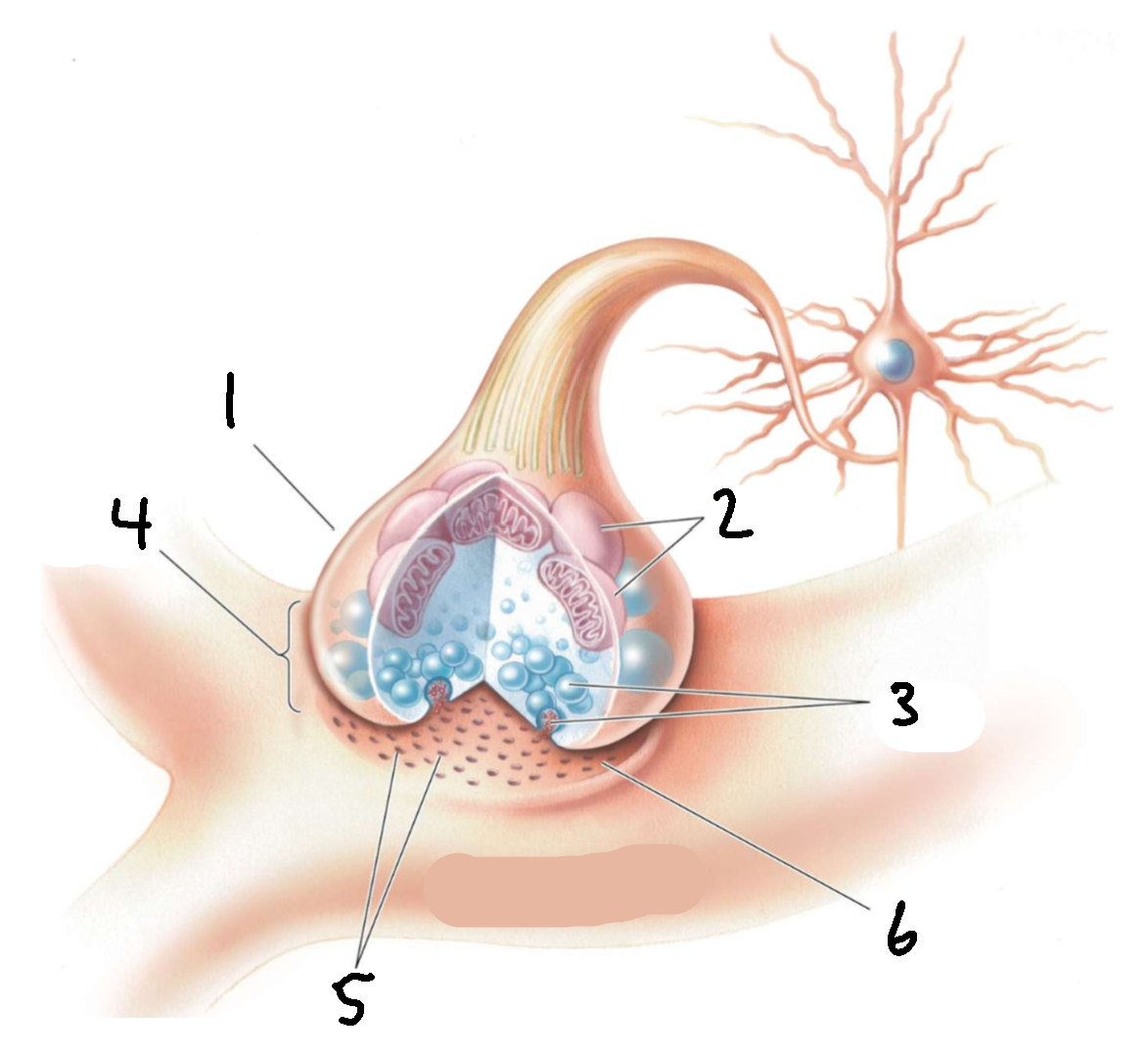
What is 1?
presynaptic axon terminal
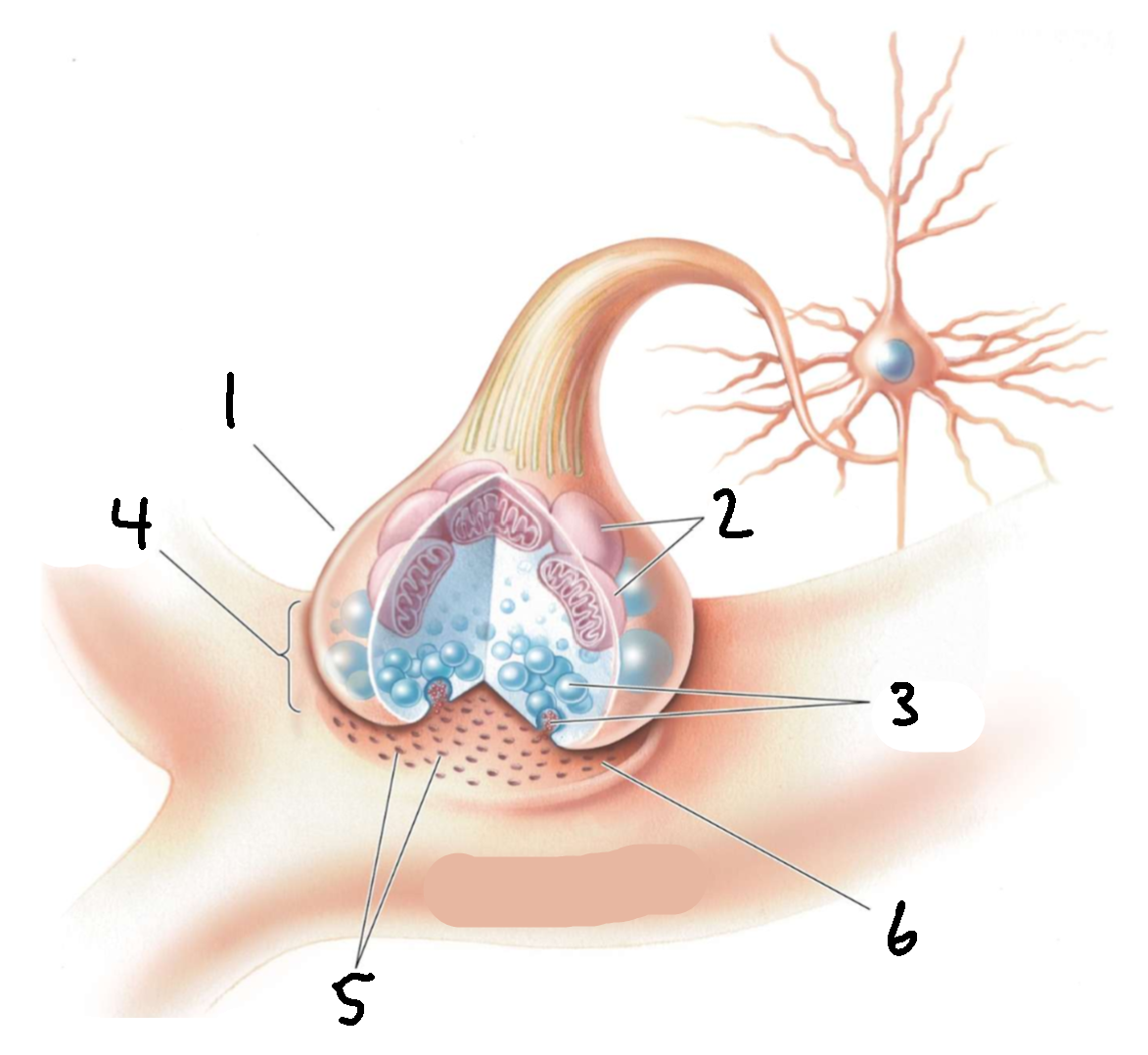
What is 2?
mitochondria
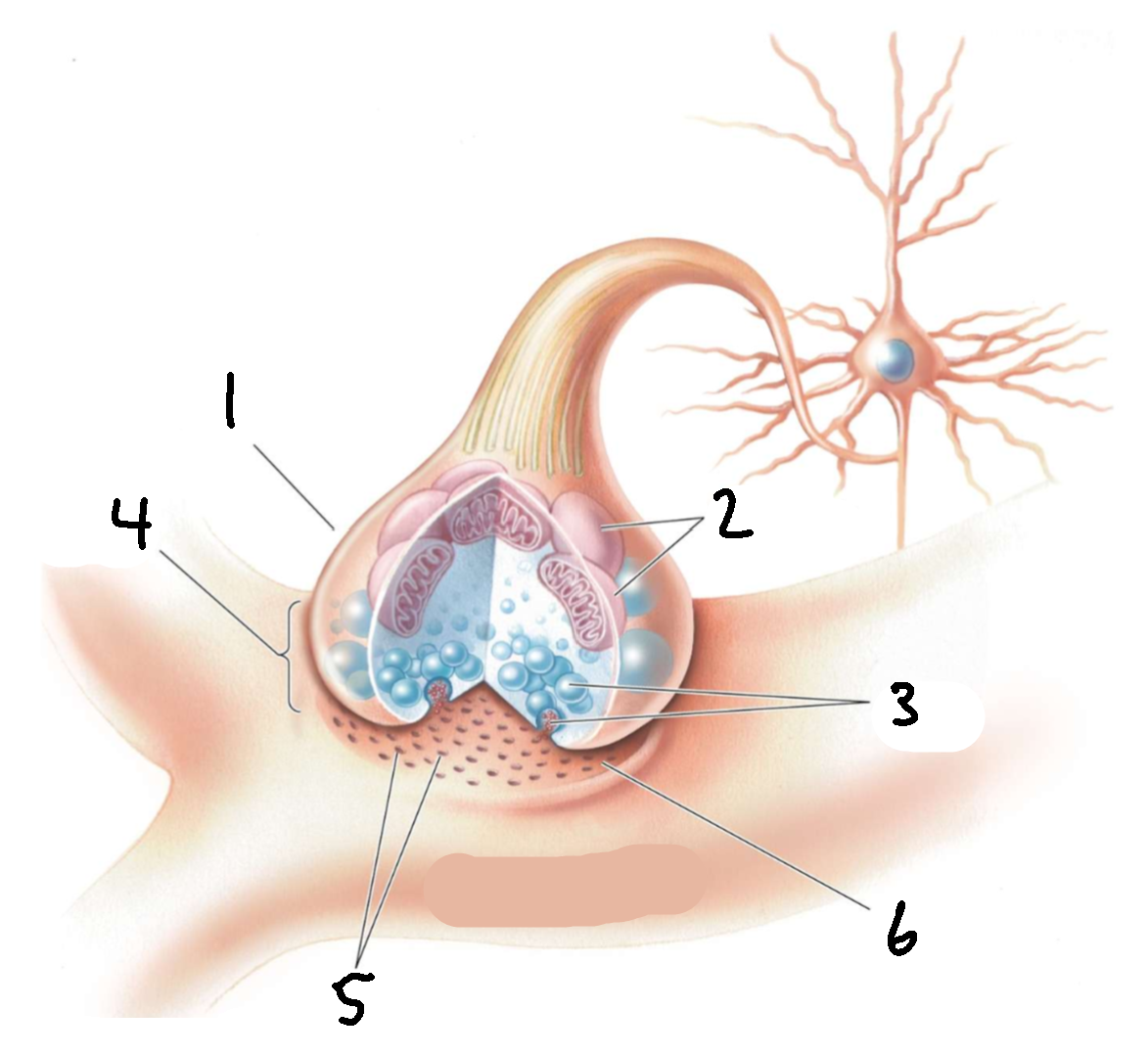
What is 3?
synaptic vesicles
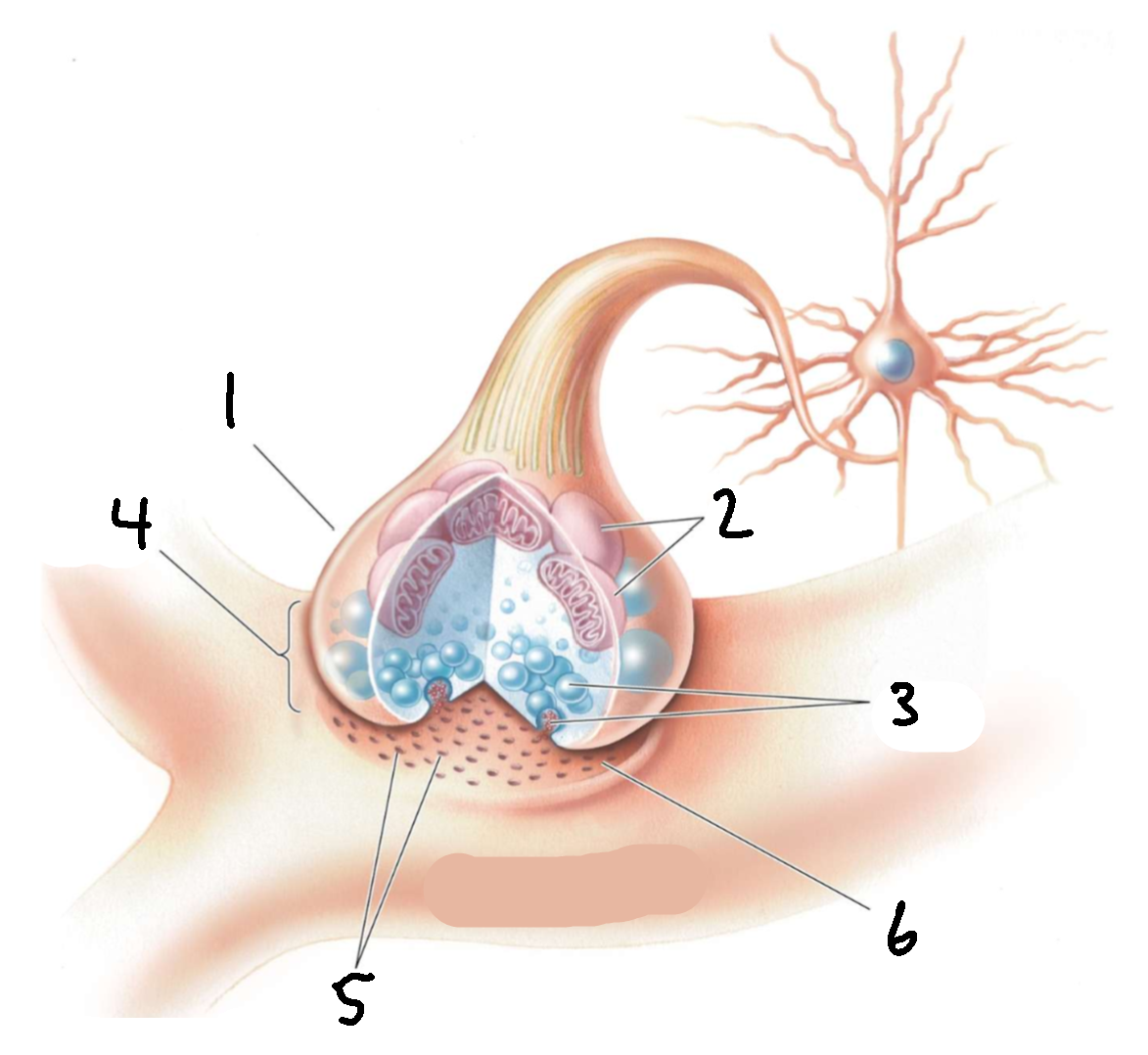
What is 4?
synapse
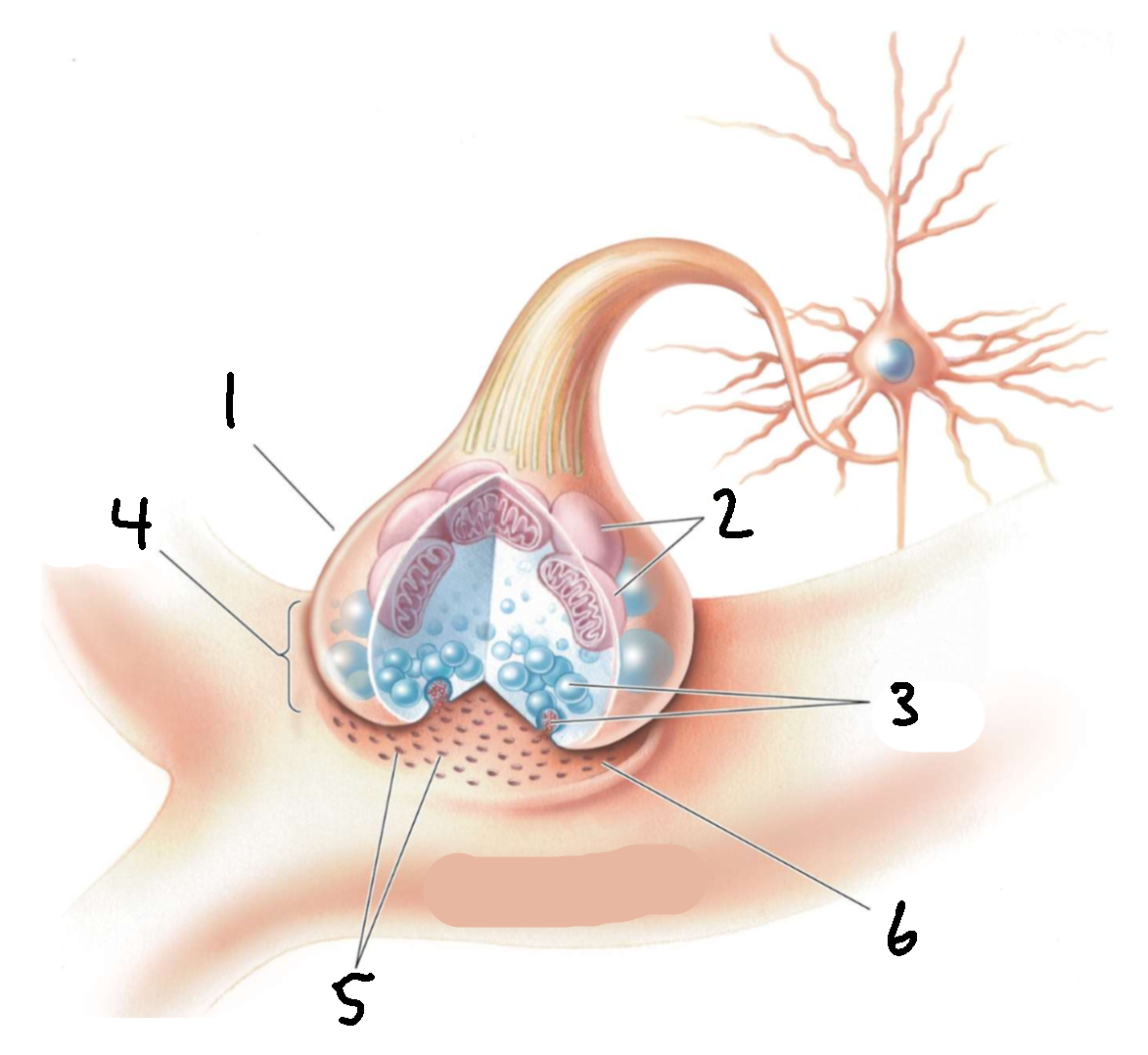
What is 5?
receptors
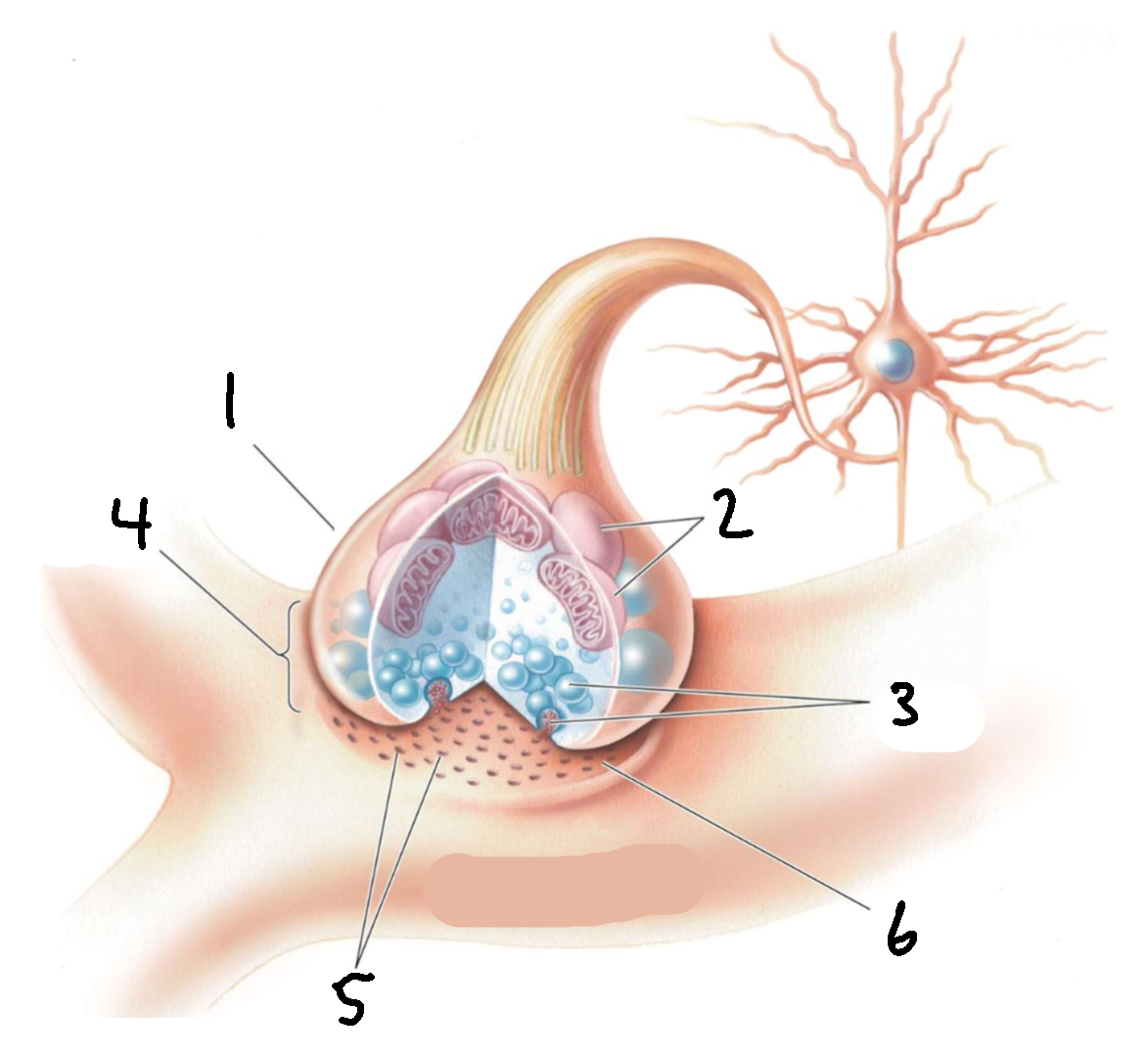
What is 6?
synaptic cleft
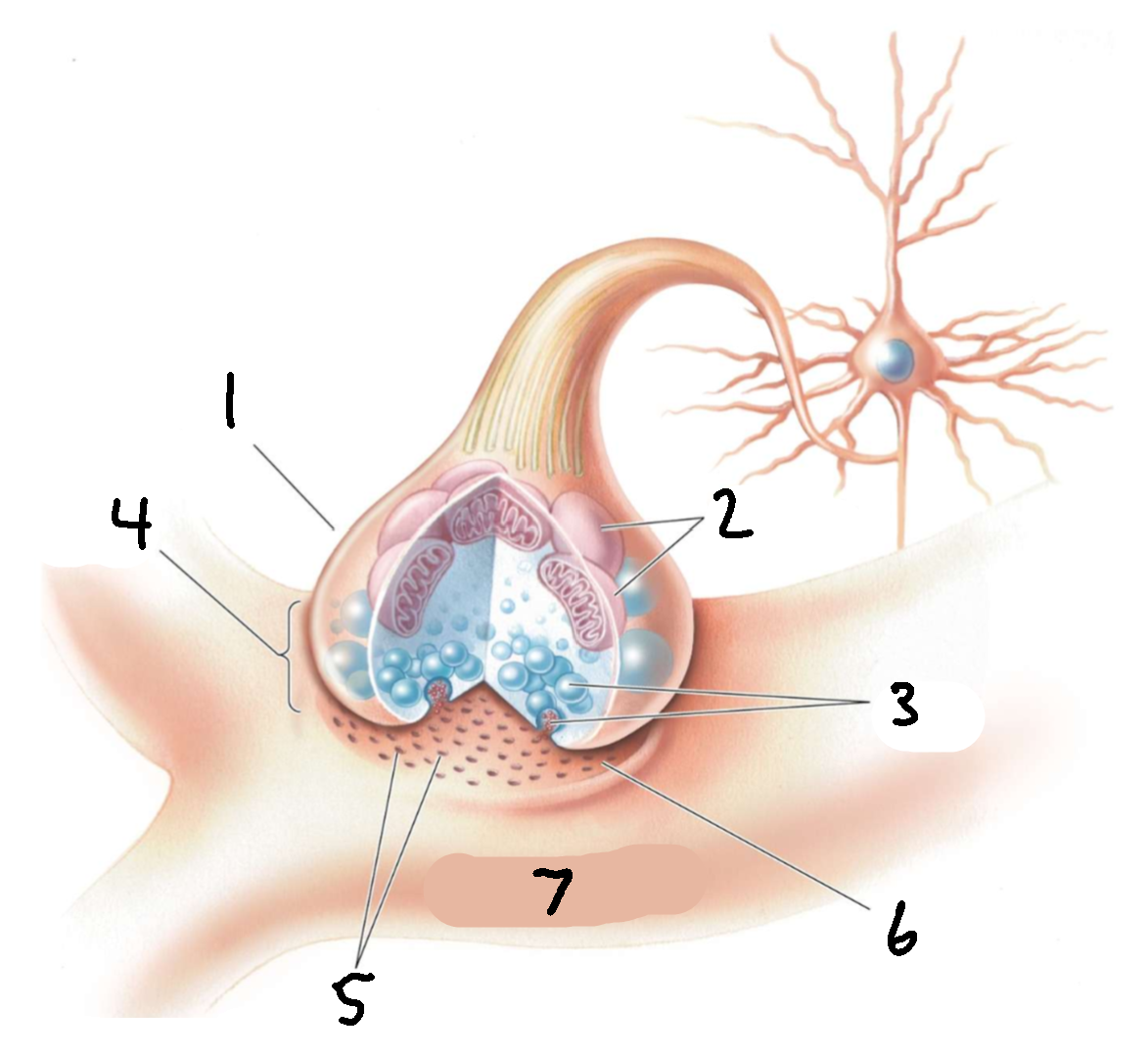
What is 7?
postsynaptic dendrite
Which neurotransmitter passes between motor neurones and striated muscle?
acetylcholine
Which neurotransmitters are principle excitatory and inhibitory in the CNS?
glutamate and GABA
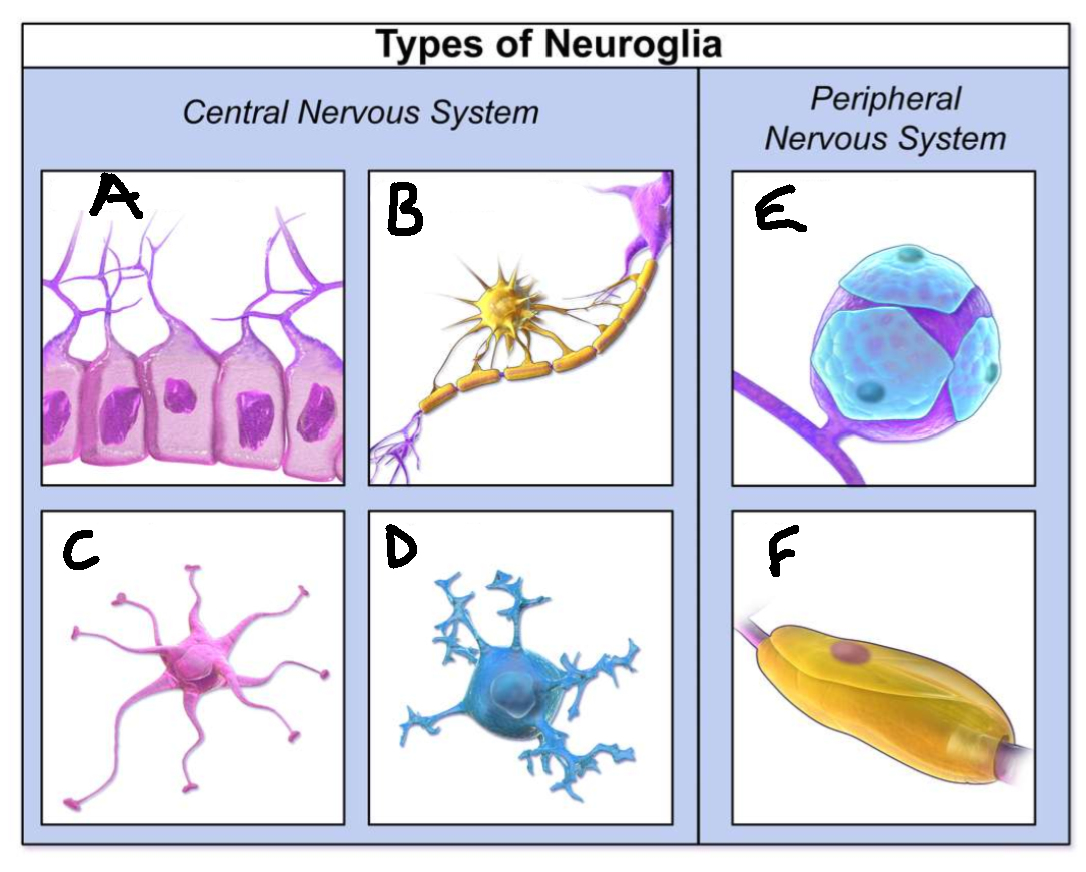
What type of neuroglia is A?
ependymal cells
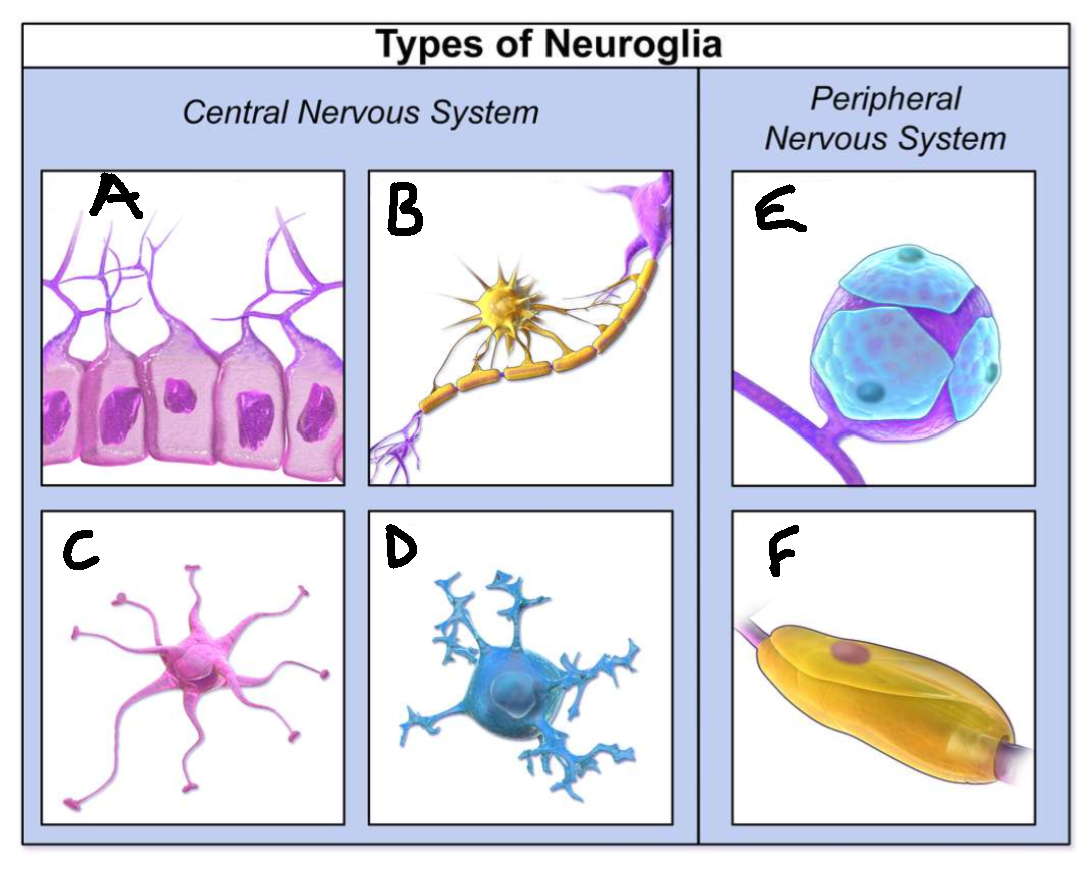
What is the function of A?
line CNS ventricles, helps produce CSF
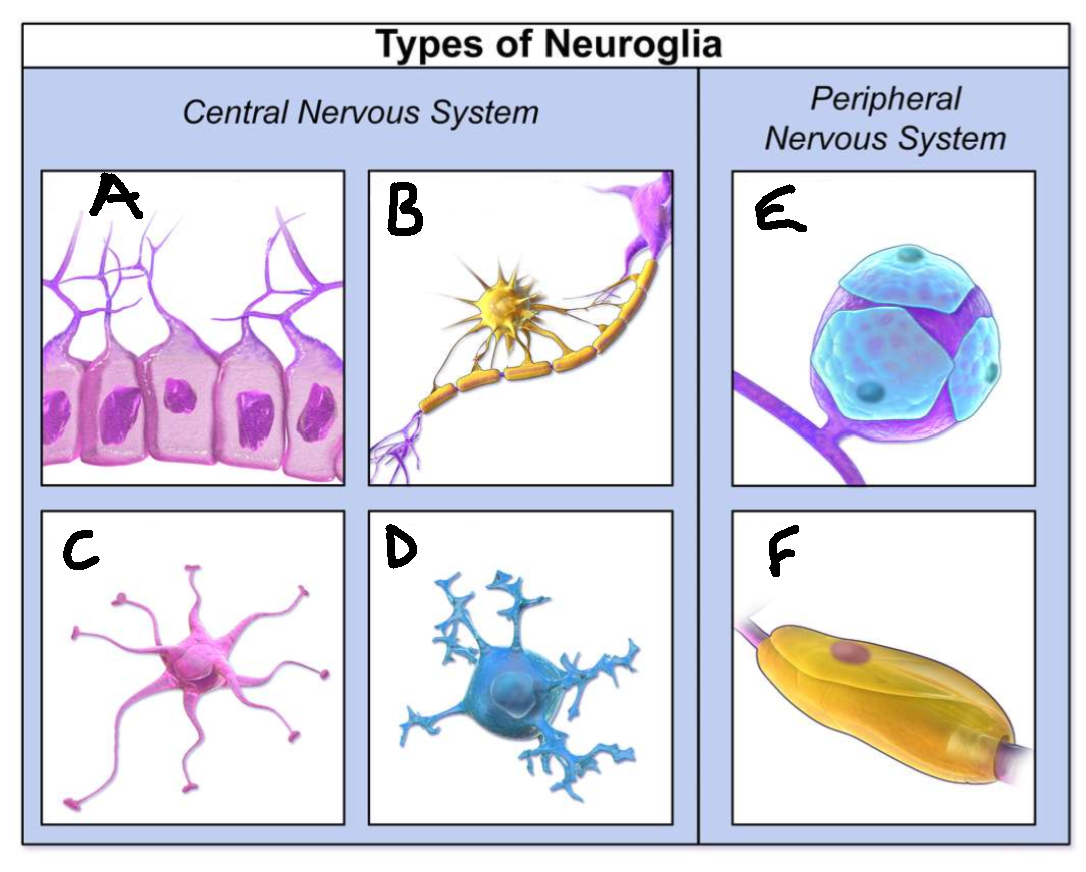
What type of neuroglia is B?
oligodendrocytes
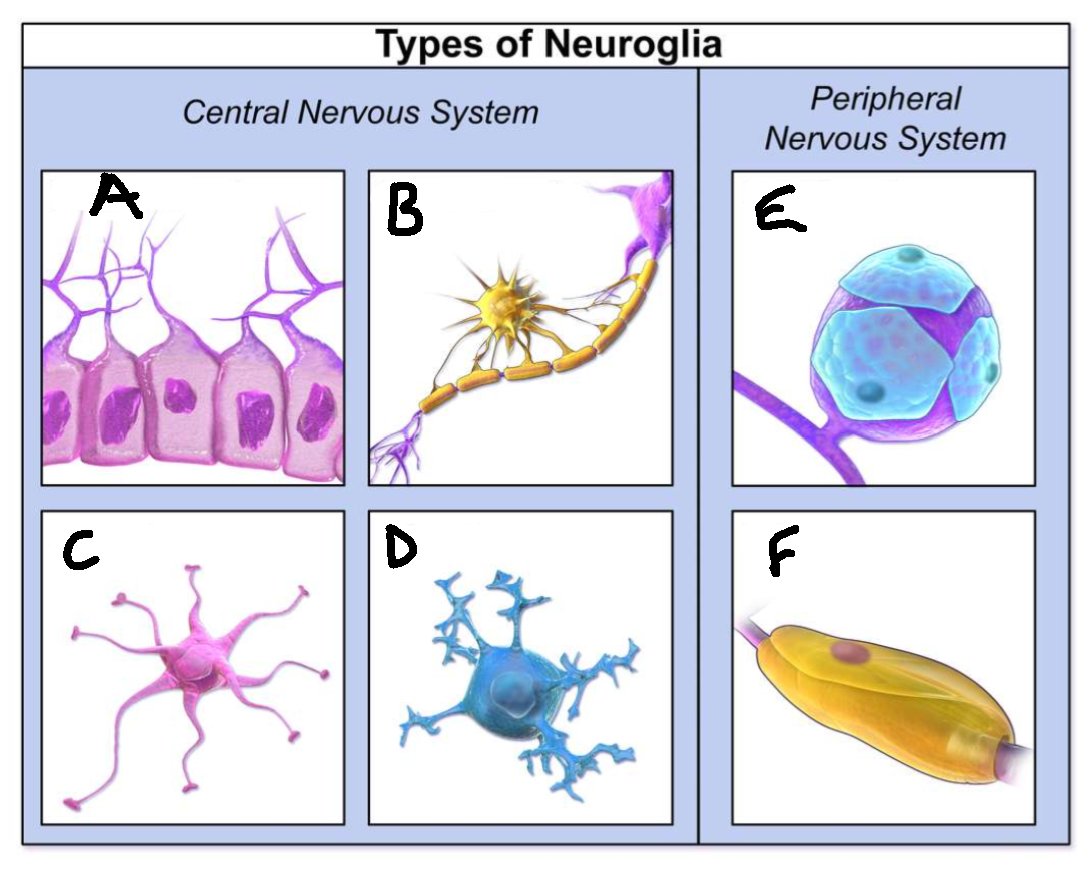
What is the function of B?
myelinates CNS neurones
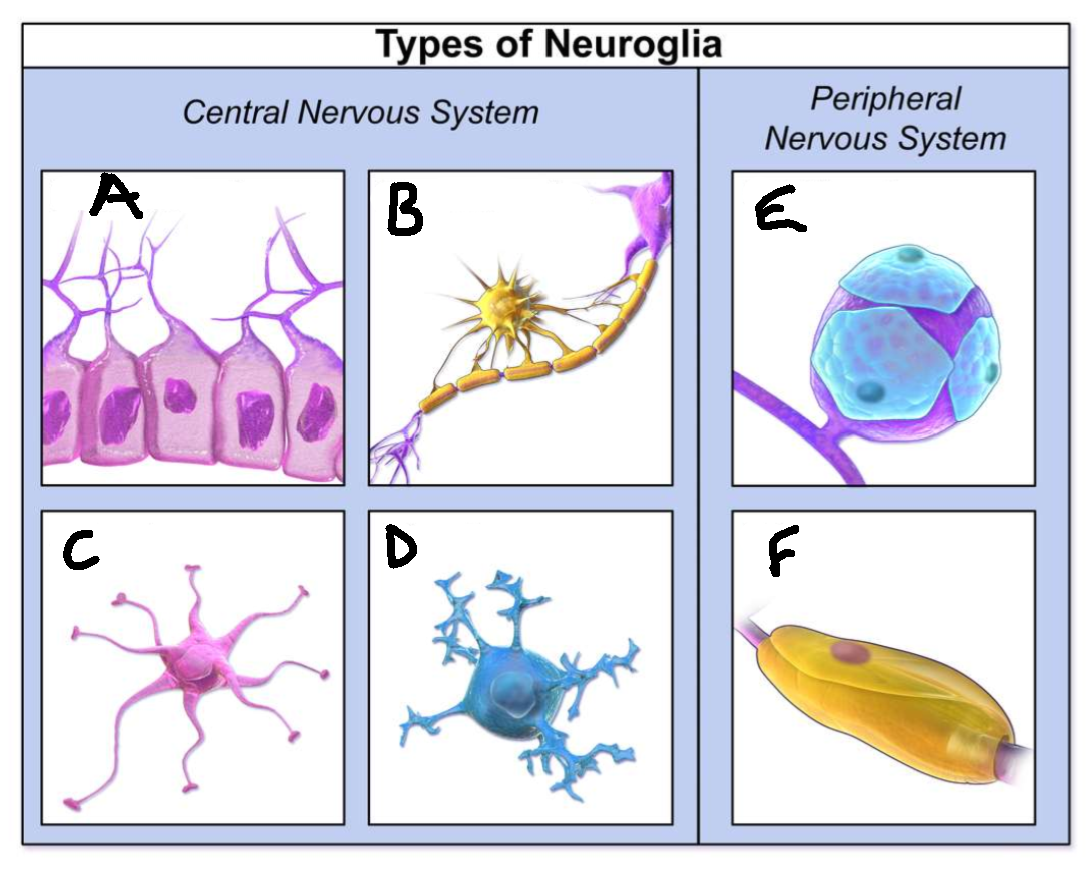
What type of neuroglia is C?
astrocytes
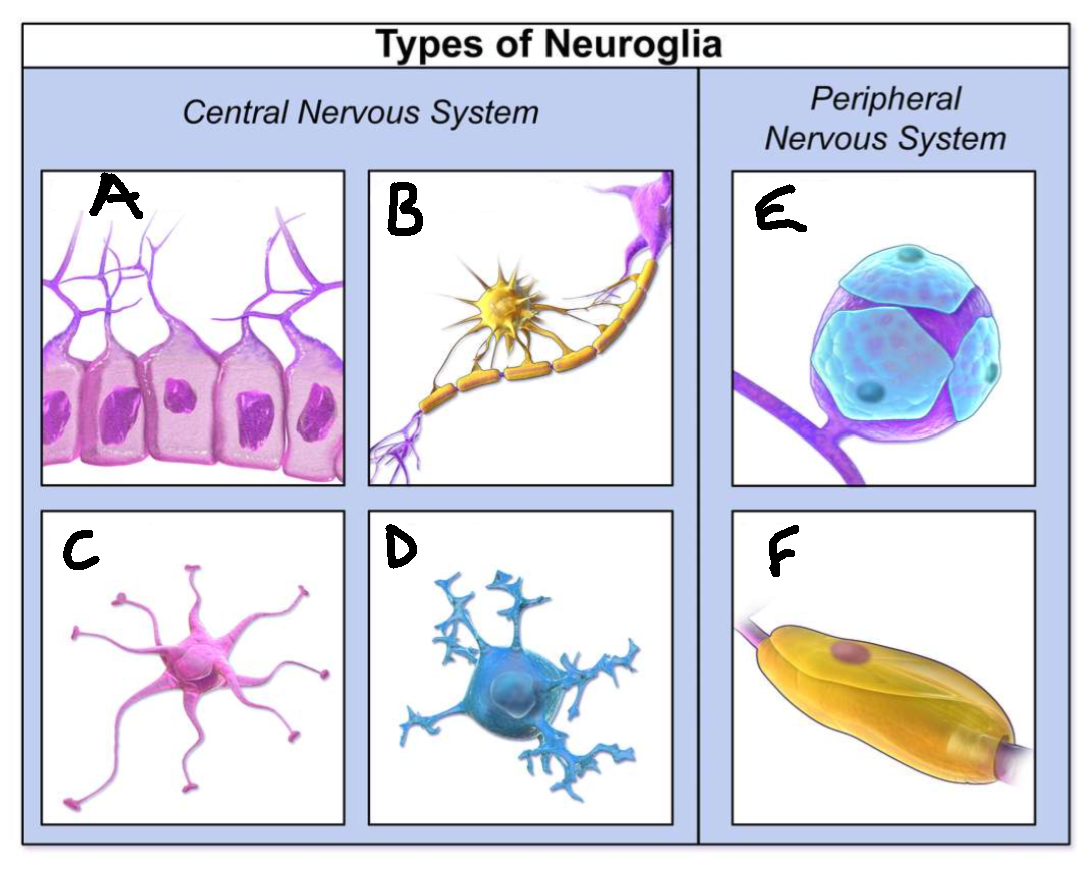
What is the function of C?
controls levels of neurotransmitters and irons around synapses, perivascular endfeet around capillaries
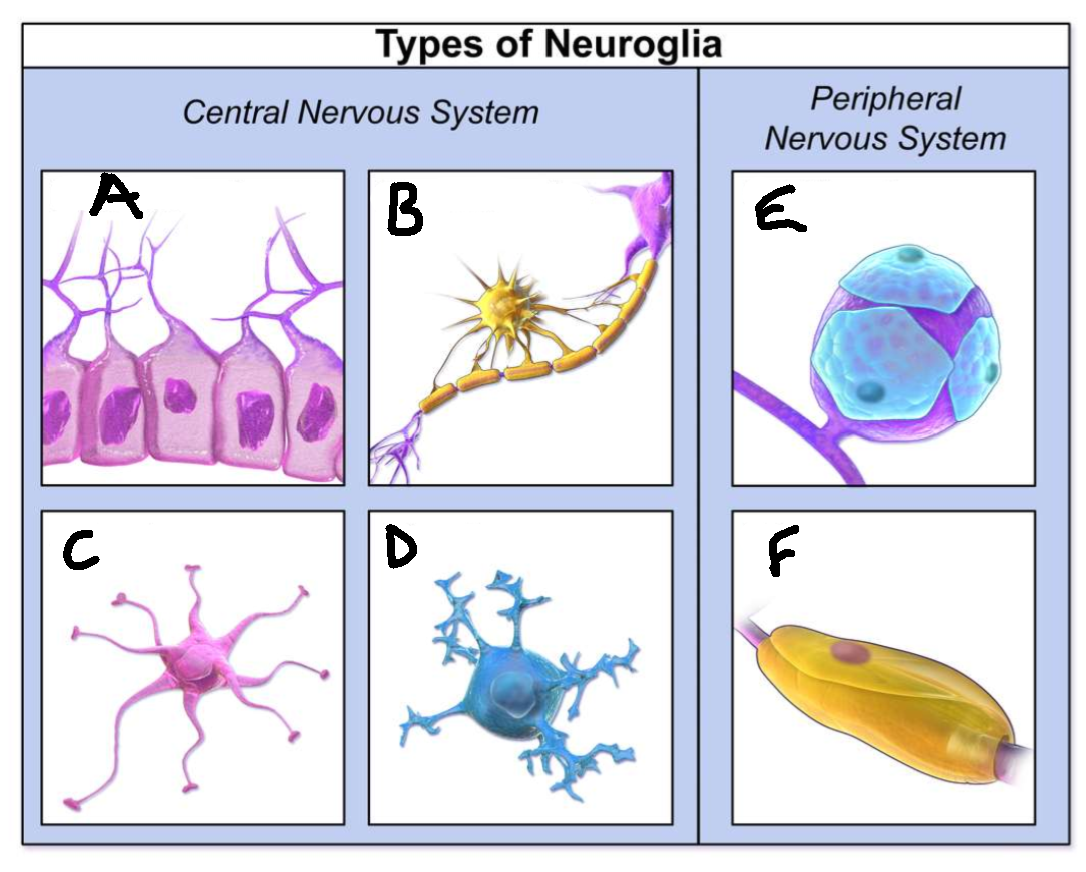
What type of neuroglia is D?
microglia
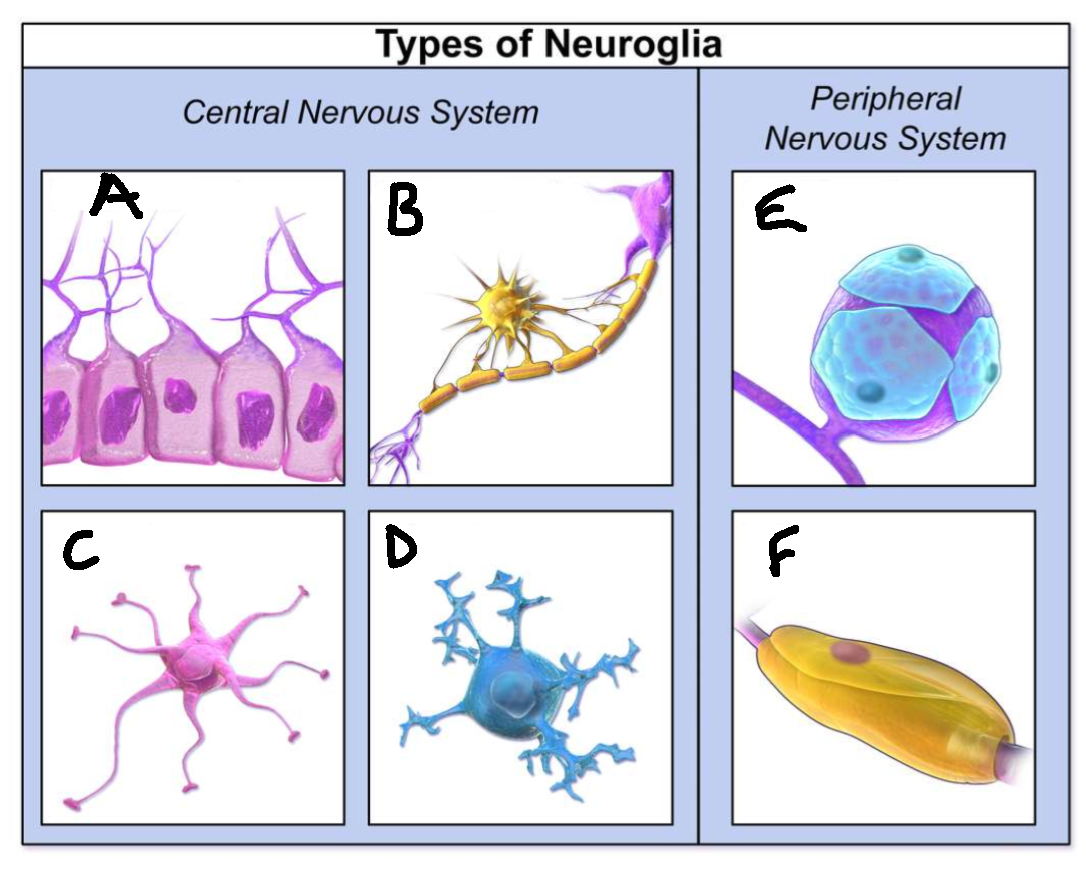
What is the function of D?
phagocyte roll in CNS
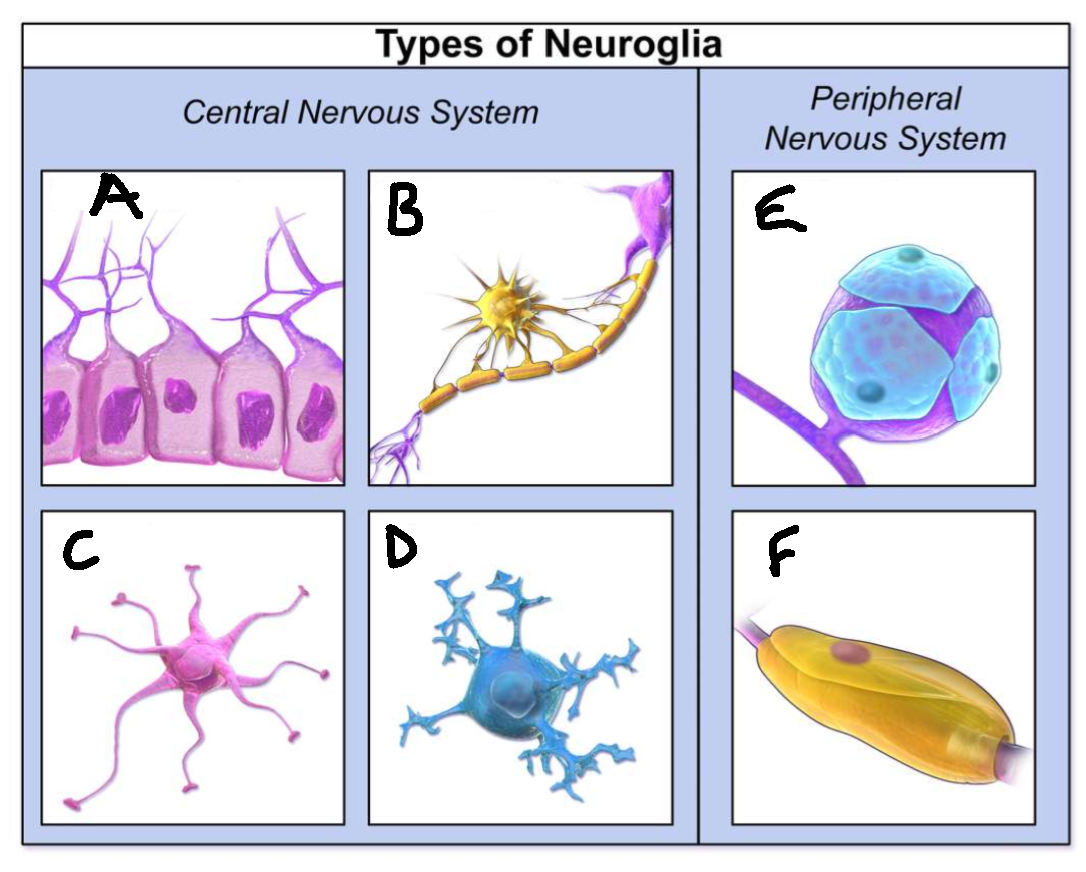
What type of neuroglia is E?
satellite cells
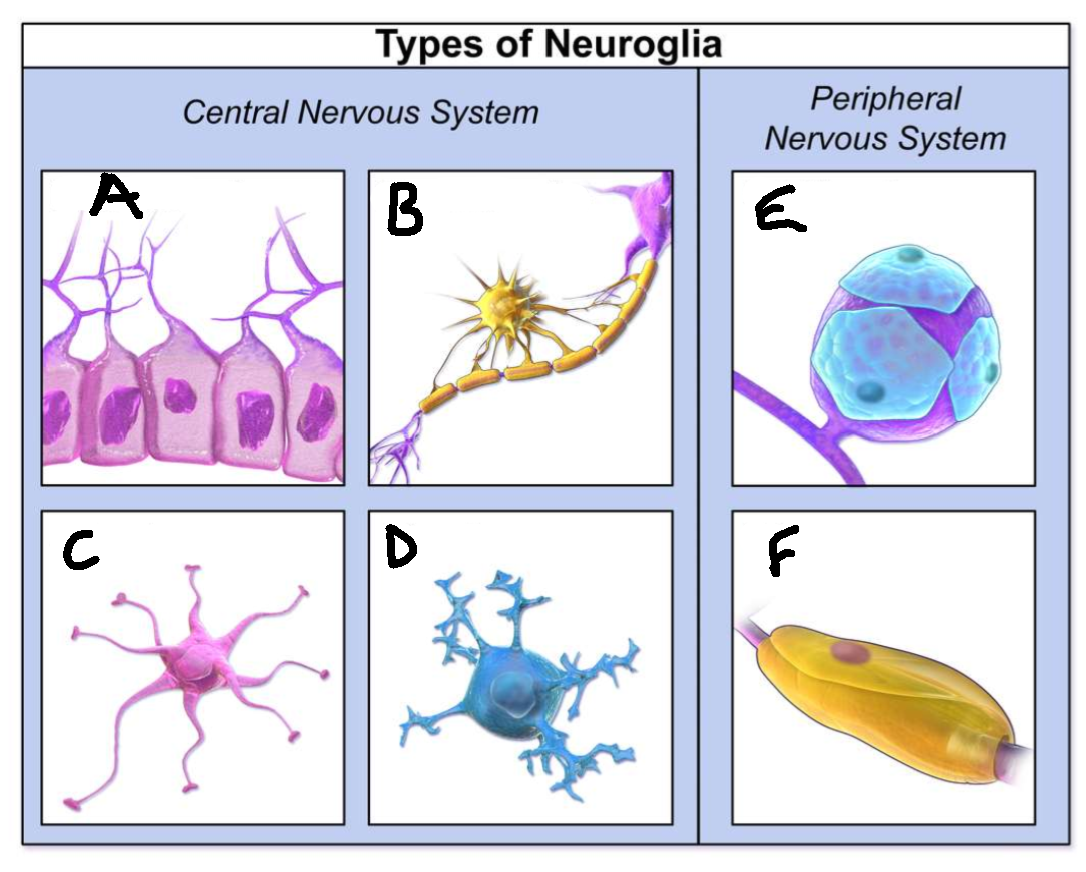
What is the function of E?
regulates chemical environment
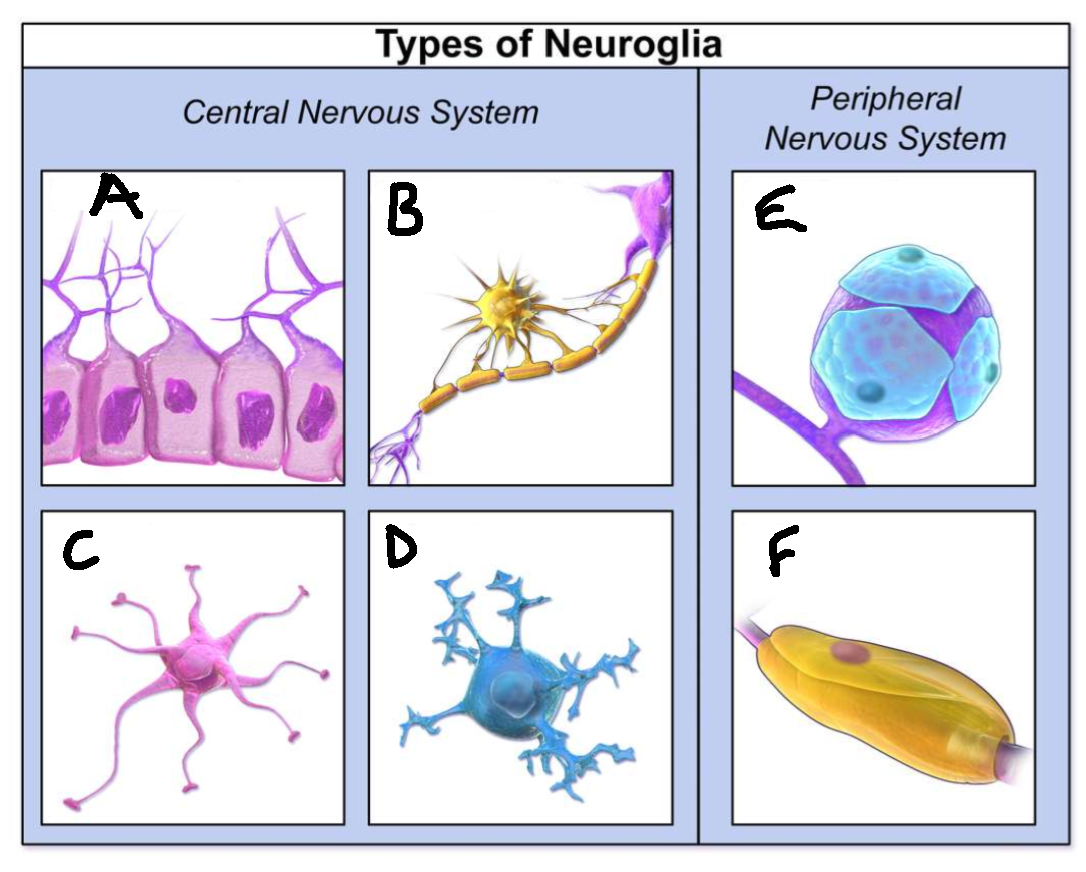
What type of neuroglia is F?
schwann cells
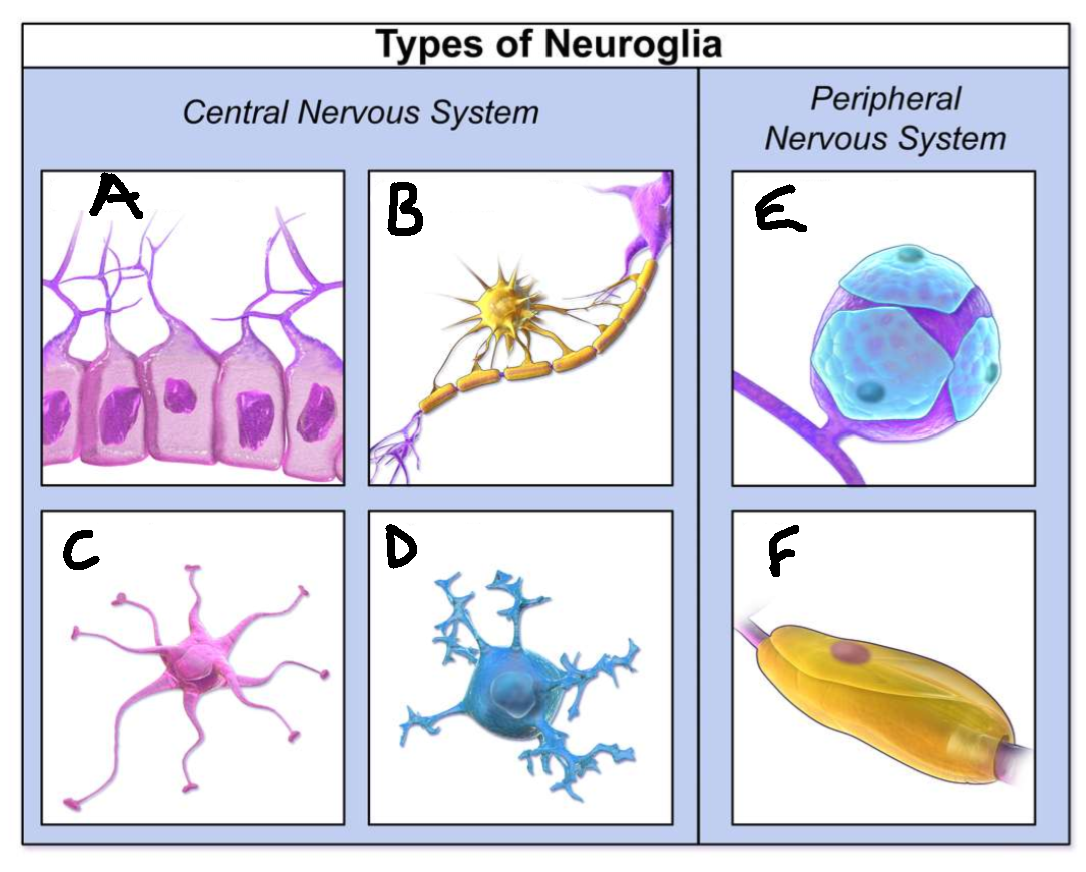
What is the function of F?
myelinate PNS neurones