Anatomy Chapter 1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
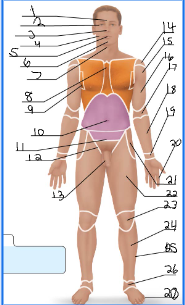
frontal
1
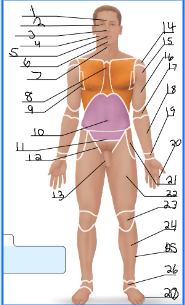
orbital
2
nasal
3
buccal
4
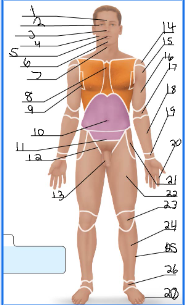
oral
5
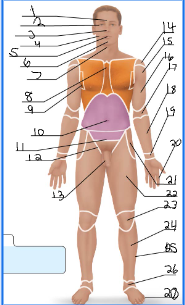
mental
6
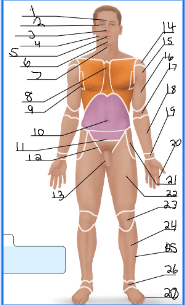
cervical (front)
7
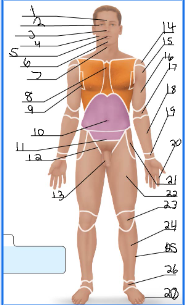
sternal
8
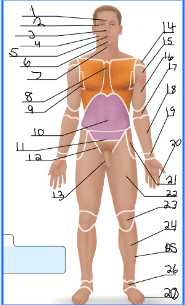
axillary
9
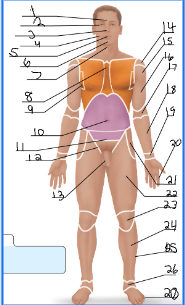
umbillical
10
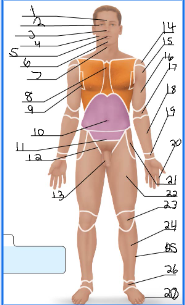
pelvic
11
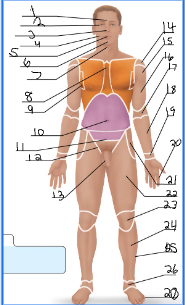
inguinal
12
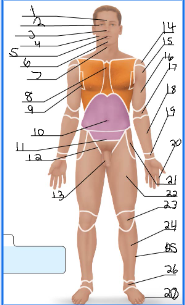
pubic
13
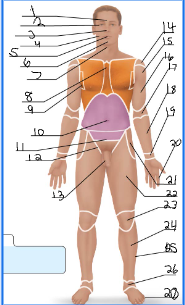
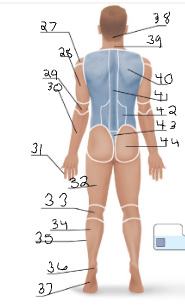
acromial
14 + 27
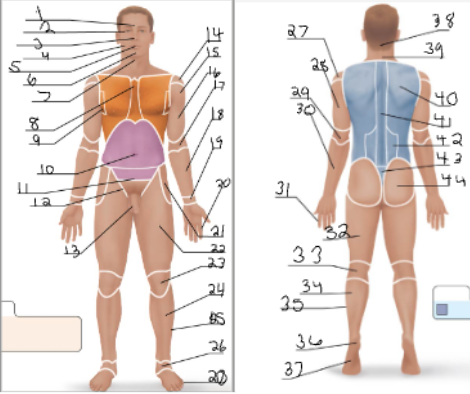
deltoid
15
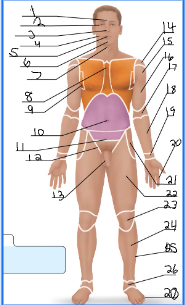
brachial
16 + 28
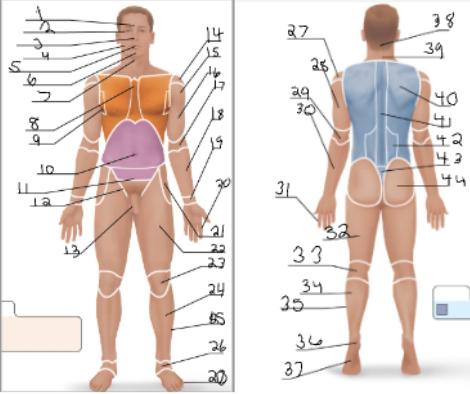
antecubital
17
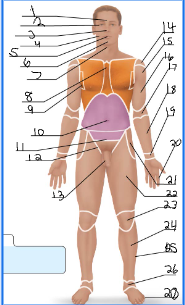
antebrachial
18 + 30
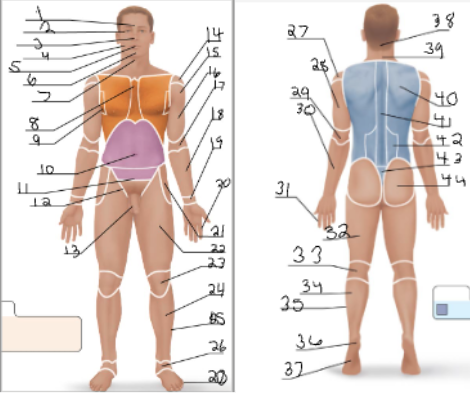
carpal
19
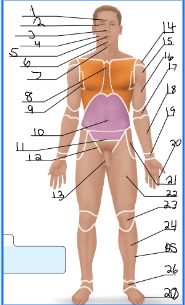
digital
20 + 31
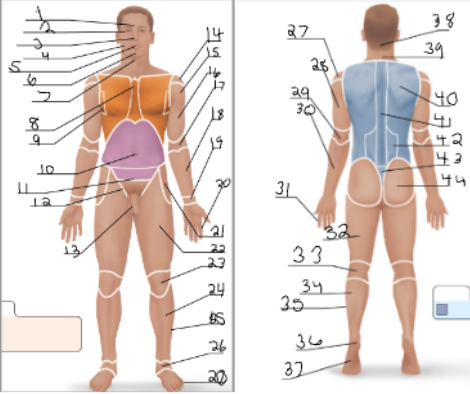
coxal
21
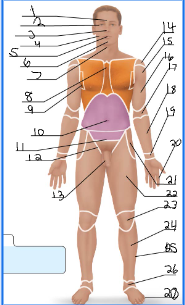
femoral
22 + 32
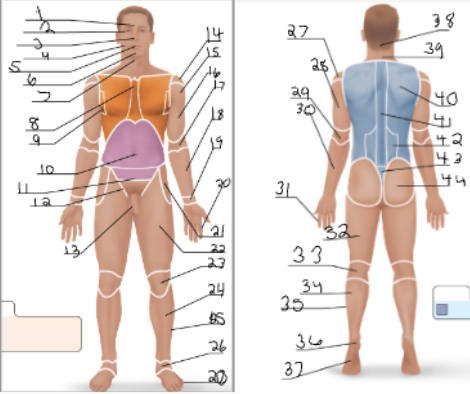
patellar
23
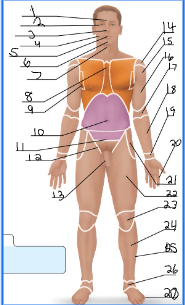
crural
24
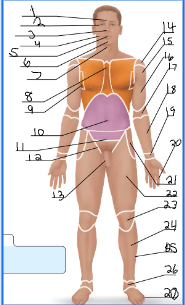
fibular
25 + 35
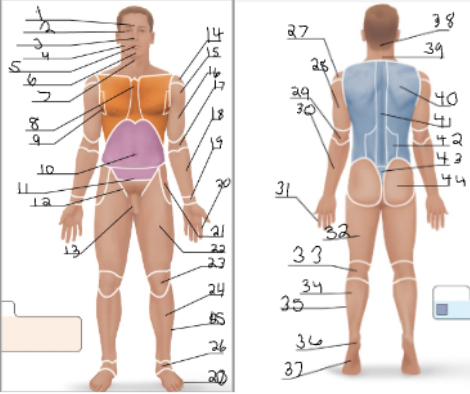
tarsal
26
olencranal
29
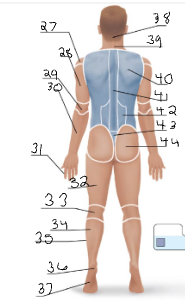
popliteal
33
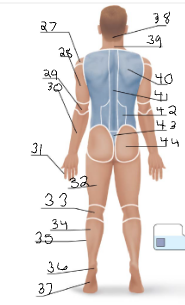
calcaneal
36
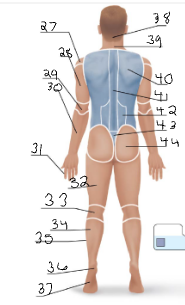
plantar
37
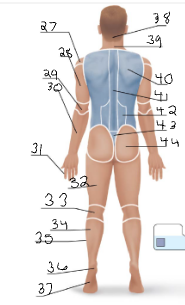
occipital
38
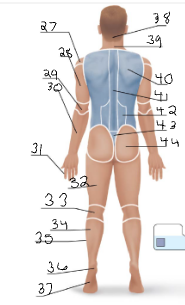
cervical (back)
39
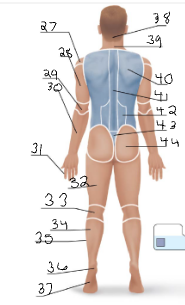
scapular
40
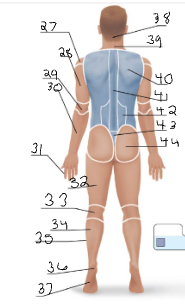
vertebral
41
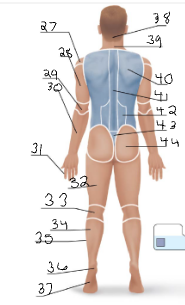
lumbar
42
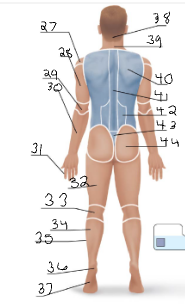
sacral
43
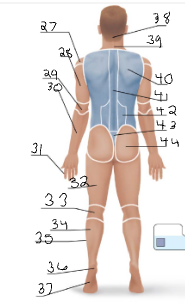
gluteal
44
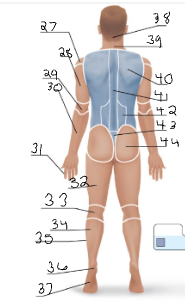
sural
34
Anatomy
Structure and shape of the parts. Observed with gross anatomical studies and microscopic studies.
Physiology
How the parts work and function observed with experiments to observe how the body systems react.
How Anatomy and Physiology are related
Structure determines function
Integumentary
External body covering, location of cutaneous receptors. Includes skin
Skeletal
Protects body organs, a framework the muscles use to cause movement, and blood cells are formed within bones. Includes cartilages, joints, and bones.
Nervous
Control system of the body and responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands. Includes brain sensory receptor, spinal cord, and nerves.
Muscular
Locomotion, and facial expression; maintains posture produces heat. Includes skeletal muscles.
Endocrine
Glands secrete hormones. Includes testis, ovary, pancreas, and glands.
Cardiovascular
Transport blood, carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes. Includes heart and blood vessels.
Lymphatic
Picks up fluid leaked returns it to blood and houses white blood cells. Includes thoracic dust, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels.
Respiratory
Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Includes nasal cavity, pharynx, and left lung.
Digestive
Breaks food down into absorbable units that enter the blood. Includes esophagus and intestines.
Urinary
Eliminates nitrogen-containing wastes from the body; regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood. Includes kindey and bladder.
Reproductive
Production of offspring. Includes ovary, uterus, testes, and penis.
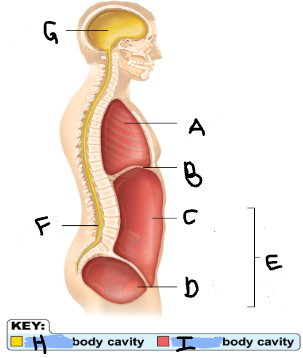
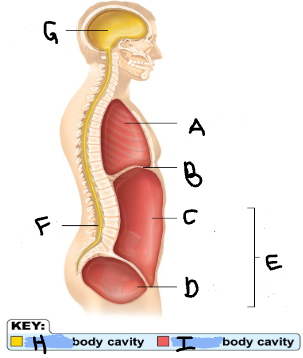
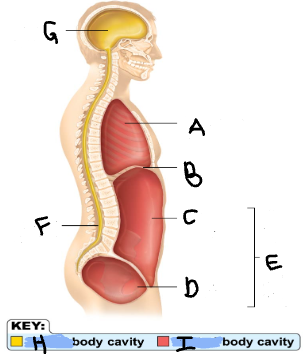
Thoracic Cavity
A
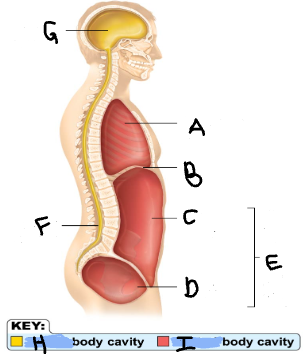
Diaphragm
B
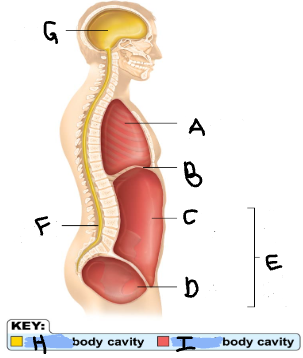
Abdominal Cavity
C
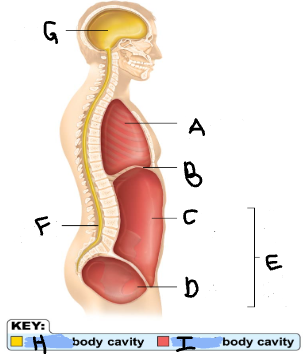
Pelvic Cavity
D
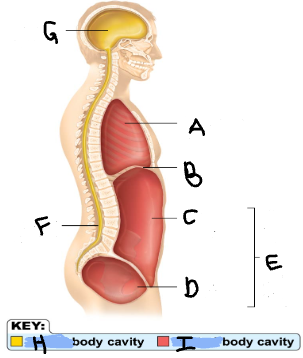
Spinal Cavity
F
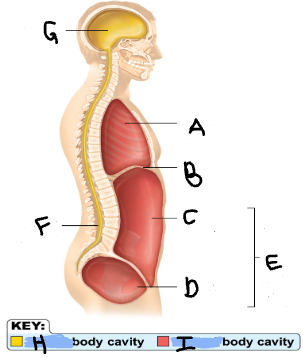
Cranal Cavity
G
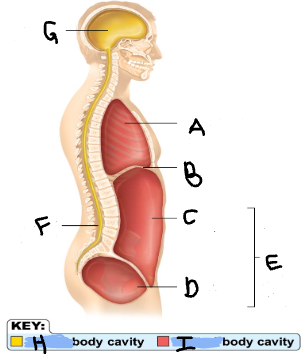
Abdominopelvic Cavity
E
Ventral
I
Dorsal
H
Superior
Toward the head end of or upper part of a structure or the body; above
Inferior
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
Ventral (anterior)
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of
Dorsal (posterior)
Toward or at the backside of the body; behind
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
Proximal
Close to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Superficial
Toward or at the body surface
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
Saggital Section
Body section that splits right and left halves
Transverse Section
Body section that splits superior and inferior
Frontal/Coronal Section
Body section that splits anterior and posterior
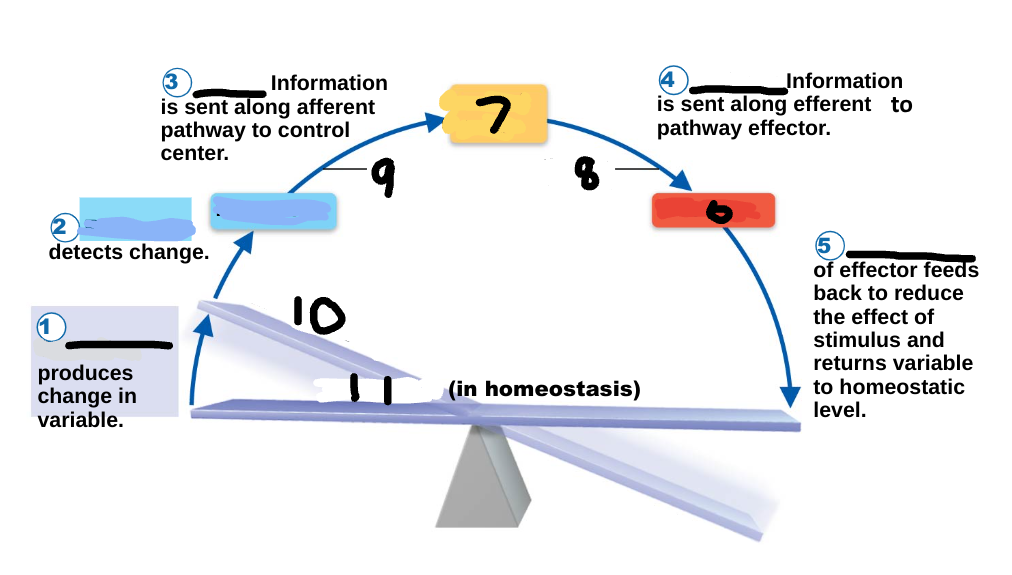
Homeostasis
maintenance of a stable internal environment, a dynamic state of equilibrium, necessary for normal body functioning and to sustain life
Homeostatic imbalance
a disturbance in homeostasis results in disease/illness
stimulus
1
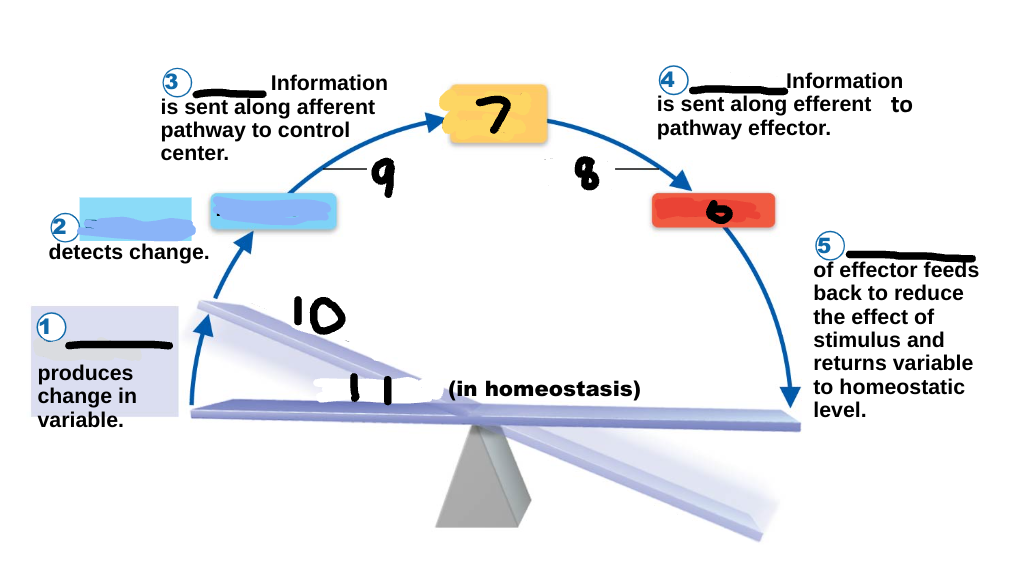
receptor
2
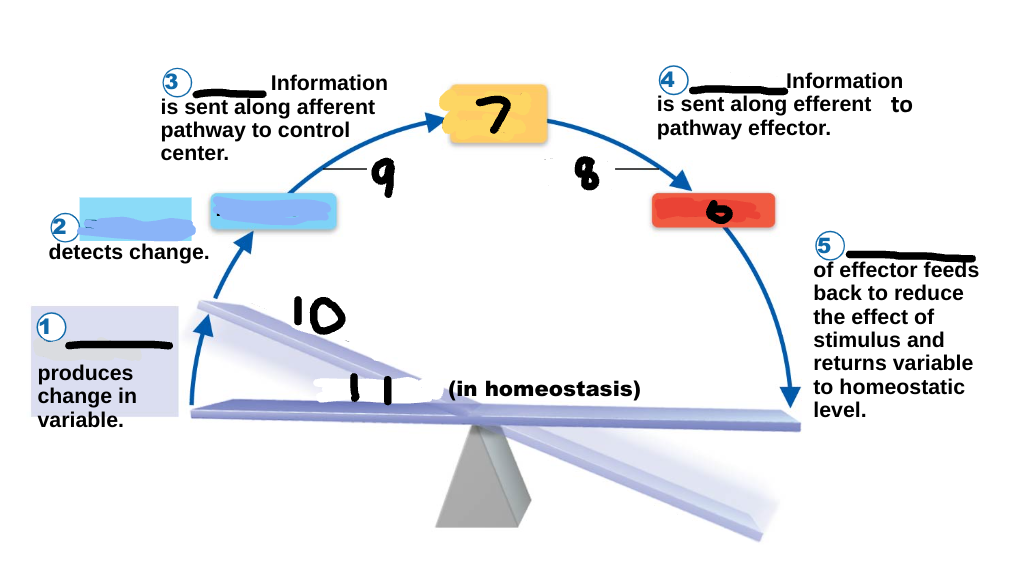
input
3
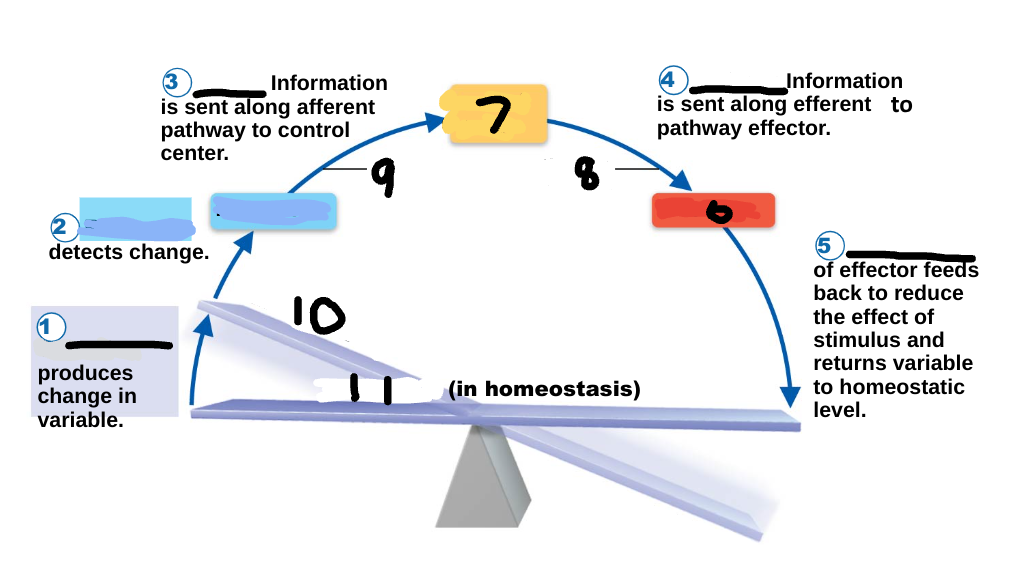
output
4
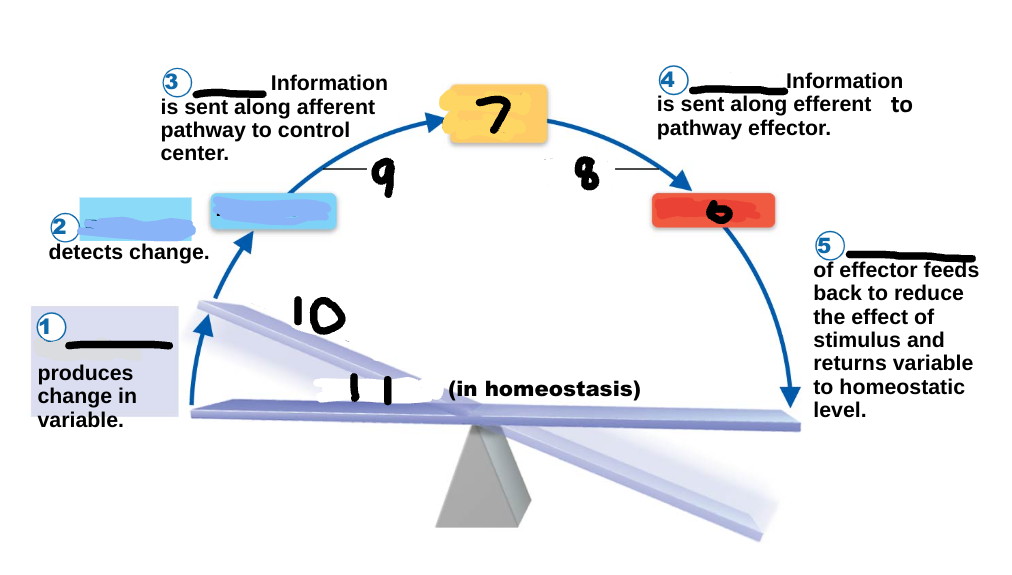
response
5
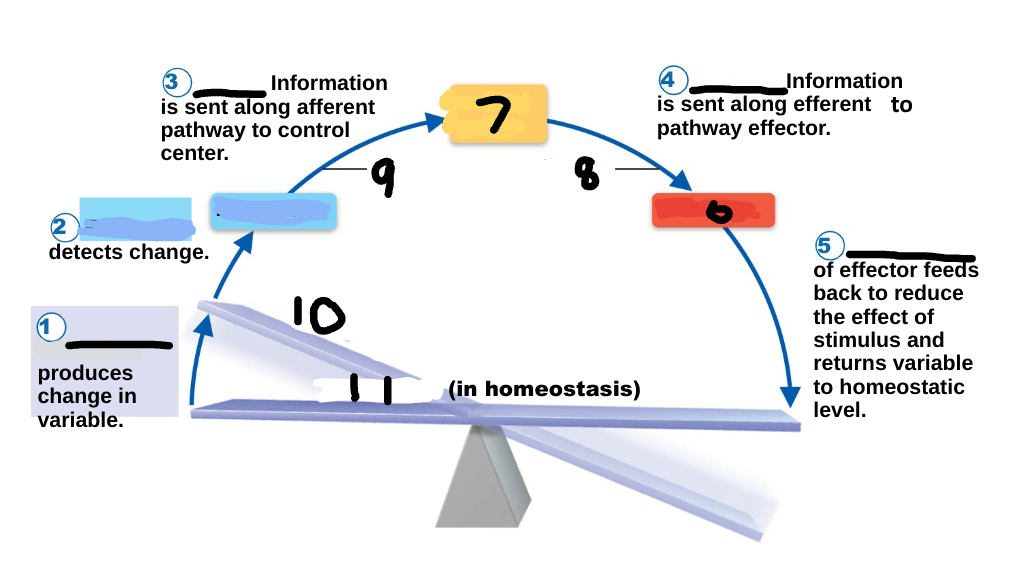
effector
6
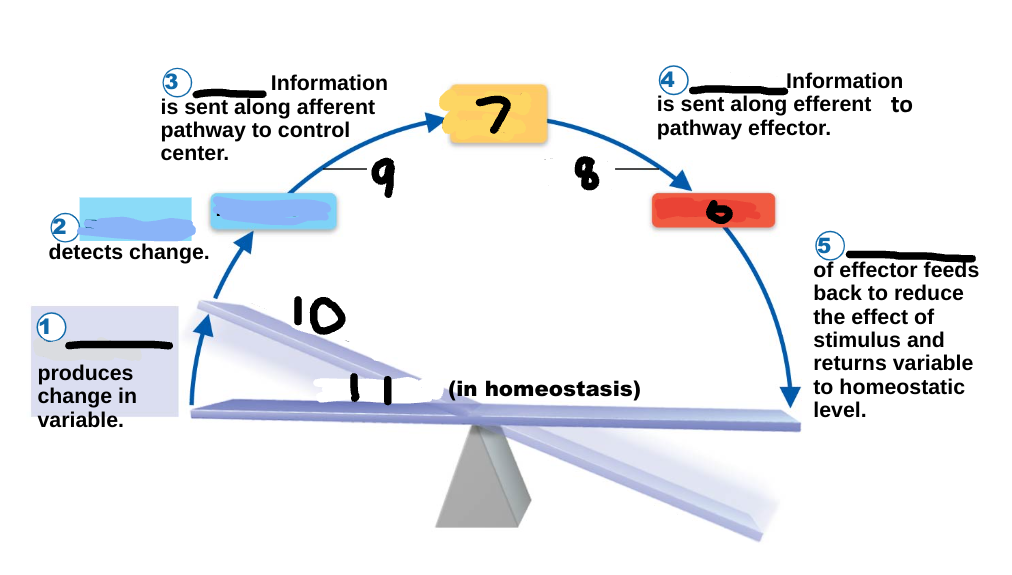
control center
7
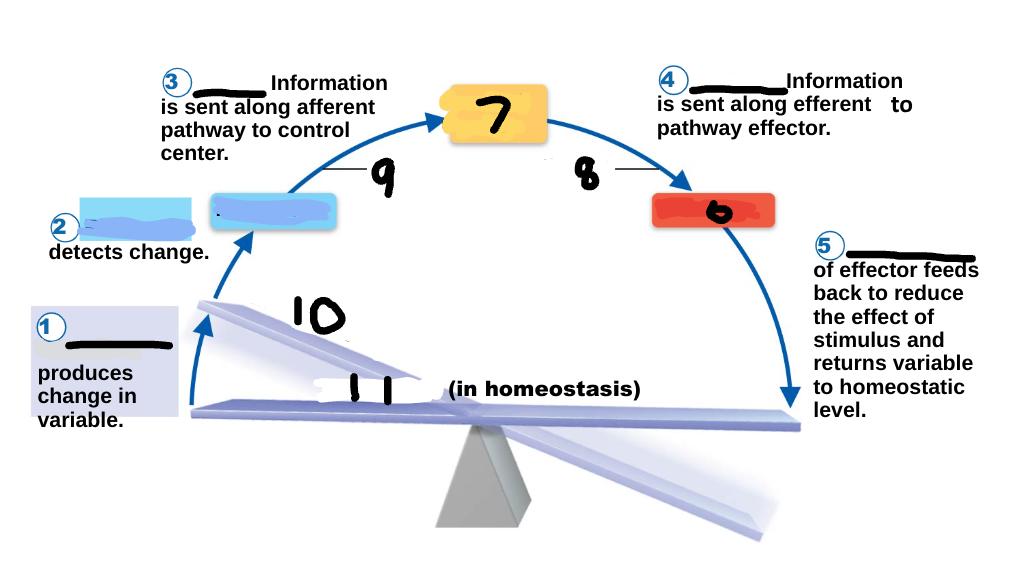
efferent pathway
8
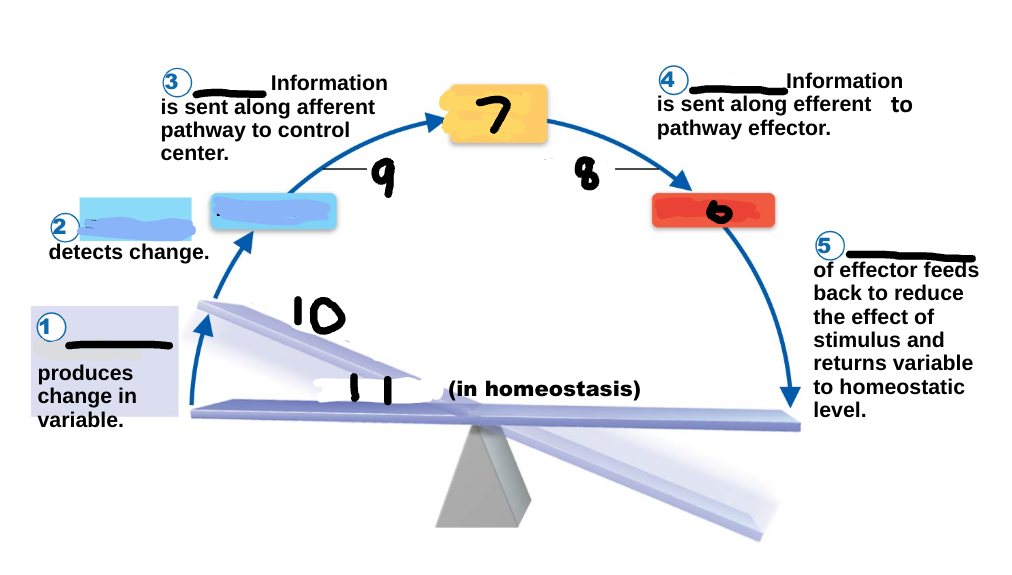
afferent pathway
9
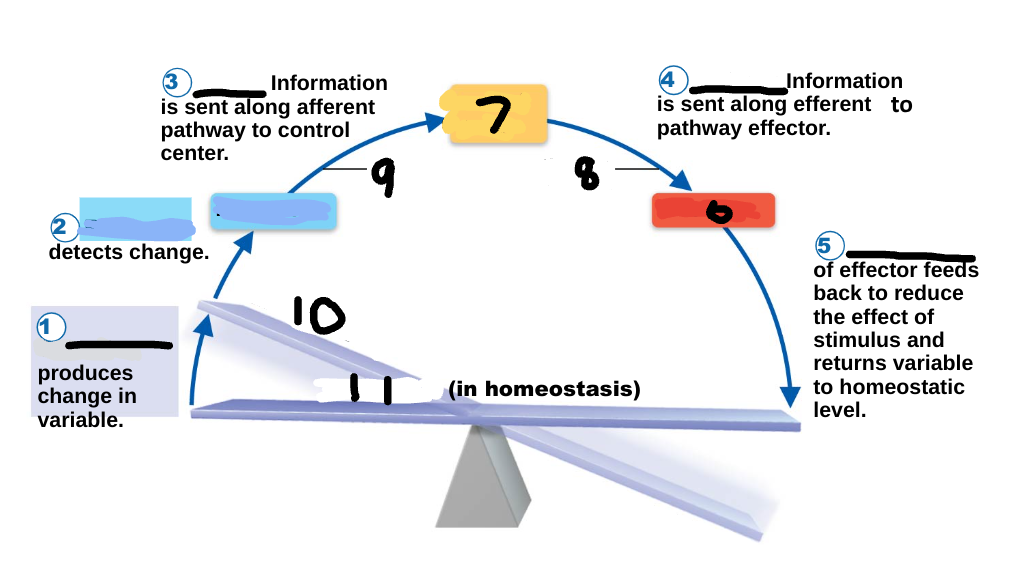
imbalance
10
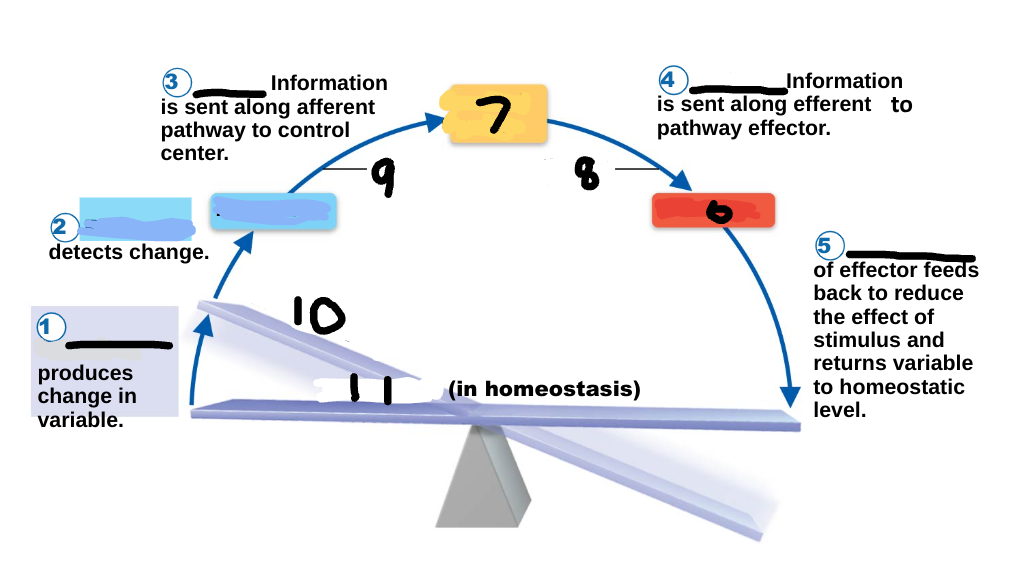
variable
11
Negative Feedback
returns conditions back to “normal” (set point), shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity, ex: body temperature regulation; blood glucose regulation
Positive Feedback
takes body condition away from the normal set point, increases the original stimulus to push the variable farther, ex: blood clot formation; fever; labor; lactation
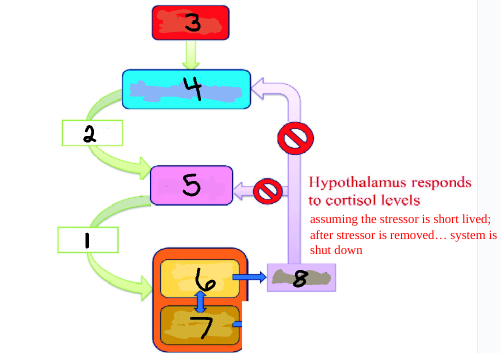
ACTH
1
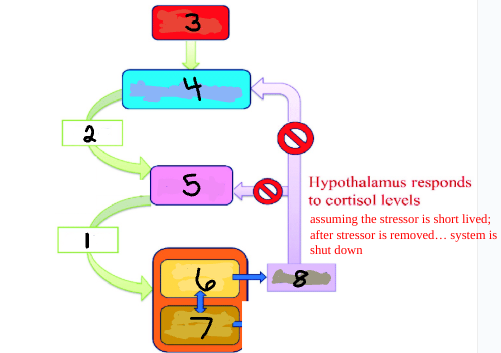
CRH
2
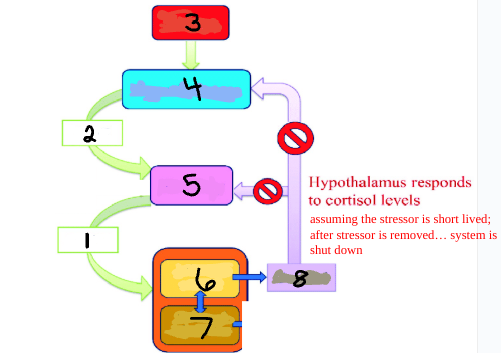
Stress
3
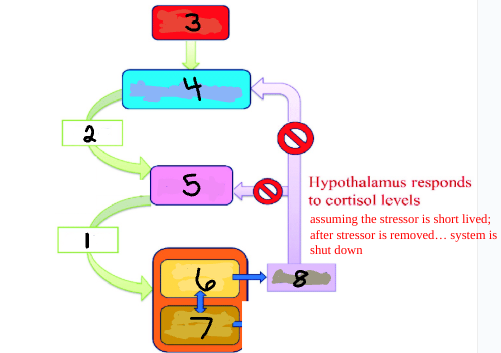
Hypothalamus
4
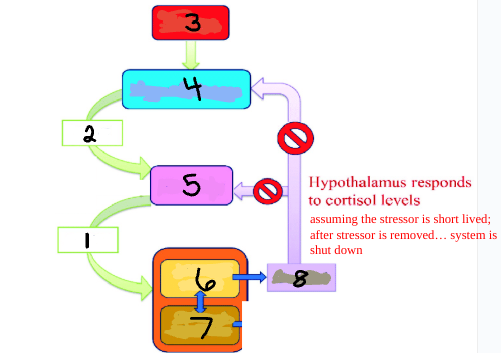
Pituitary
5
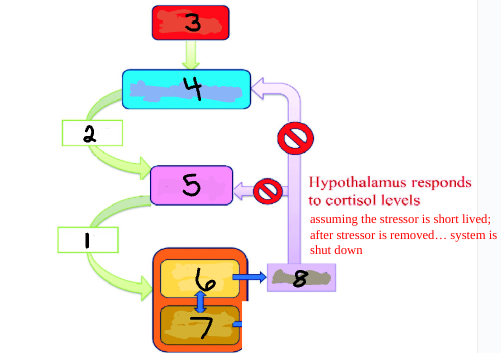
Adrenal Cortex
6
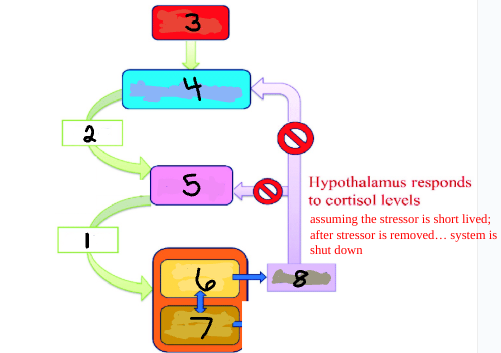
Adrenal Medulla
7
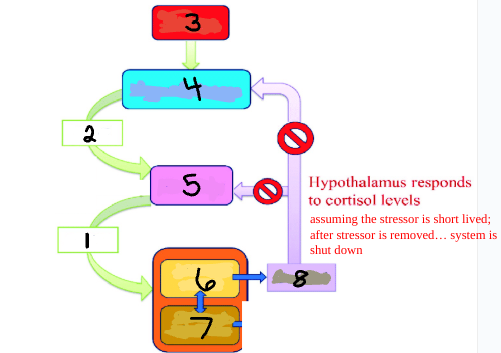
Cortisol
8