atp synthase
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
structure of the protein
f0 is the part the spin and f1 is the alpha and beta bit
P = intermembrane side, stands for positive
N = mt matrix side, stands for negative
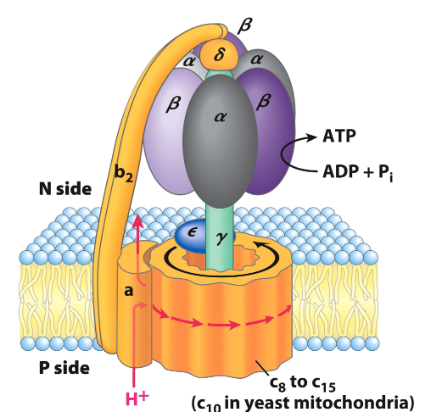
catalytic subunits
each set of alpha and beta sections is one
each set has 3 possible states
atp synthase energentics
atp synthase has low binding affinity for adp but high for atp - helps overcome the second bump on the graph (atp binding energy)
atp synthase stabilizes atp
proton motive force drives the release of ATP and overcomes the largest energy bump on the graph - slowest step helped by the potential energy of the chemical gradient

states of the alpha, beta su
f1 su don’t rotate/spin but conf changes drive chemical rxns
states: empty (open), adp + pi (loose), atp (tight)
binding exchange model
3 nonequivalent adenine binding sites (for the A in ADP / ATP to bind) in the beta su of each set
empty → adp + pi → atp → empty
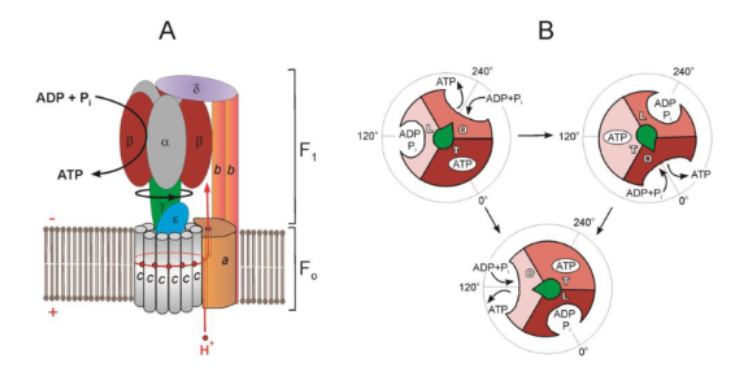
mechanically how does atp synthase work
proton translocation causes f0 rotation, which rotates the gamma shaft and drives the conformational changes
where the shaft is pointing is an empty set
numbers of atp synthase
1/3 of a turn uses 3 protons
1 full turn uses 9 protons and makes 3 atp
2.5 atp are made per nadh and 1.5 atp per fadh2
how much atp is made from glycolysis in total
30-32 atp
but isn’t a perfect system - some e- and h+ are lost to o2 (making h2o2)