Electromagnetism Grade 11
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Joules
Energy is measured in _____
Watts
Power is measured in ____
Coulombes
Charge is measured in ______
Amperes
Current in measured in _____
Volts
Voltage is measured in ______
Ohms
Resistance is measured in _________
Kirchoffs Current Law
At any junction point, the current coming in equals the current coming out.
Kirchoffs voltage law
Around any one path, the sum of the voltages lost is equal to the voltage across the battery. I.E Voltage across all paths is equal.
Ohms Law
The total resistance of any circuit is the ration of the voltage across the artery and the current being drawn by the battery.
Basic principle of Electromagnetism
Whenever there is current in a conductor, a magnetic field is created in the region around the conductor.
Right Hand Rule for a Straight Conductor
Thumb in the direction of the current, fingers wrap in the direction of the magnetic field.
Right Hand Rule for a Solenoid
Curl the fingers of the right hand in the direction of the current, thumb will point to the north.
Magnetic Field Strength of a solenoid or an Electromagnet
Determined by the number of coils, the amount of current, and magnetic permeability of the core material.
Ferromagnetic
High magnetic permeability, increases strength of an electromagnet. “Soft Iron,” such as Fe, Co, and Ni
Paramagnetic
Can rarely be magnetized, and only slightly increase the strength of an electro magnet, Eg, Aluminium and Air
Diamagnetic
Cannot be magnetized under normal conditions and decrease an electromagnets strength. Eg Cu, H2O
The Motor Principle
Whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field the conductor experiences a magnetic force, and thus moves. This force is perpendicular to both the external magnetic field and direct that the current is travelling.
Right Hand Rule for the Motor Principle
Finger Field Thumb Current Palm Force
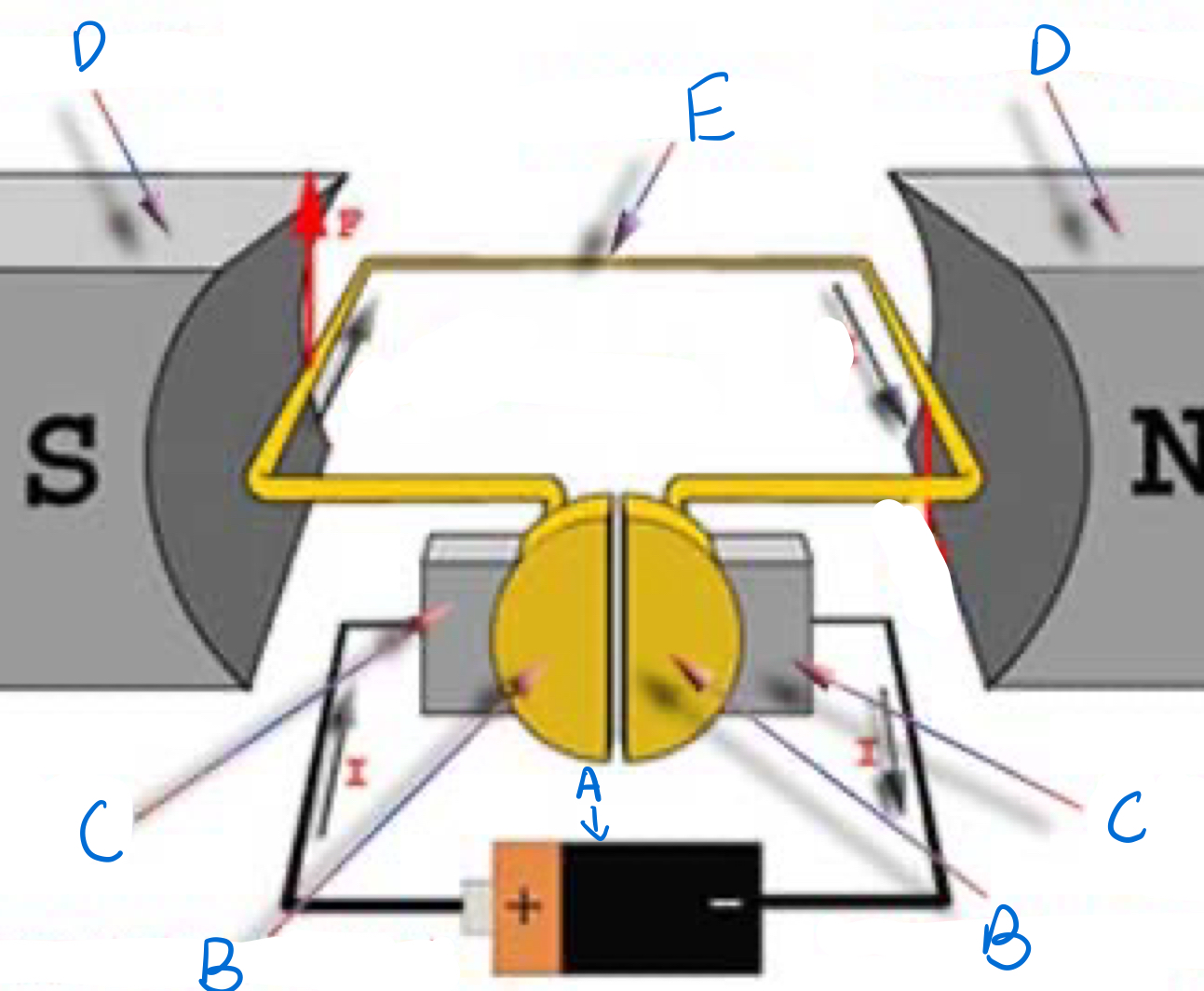
Battery, no
Which part is A and does it spin?
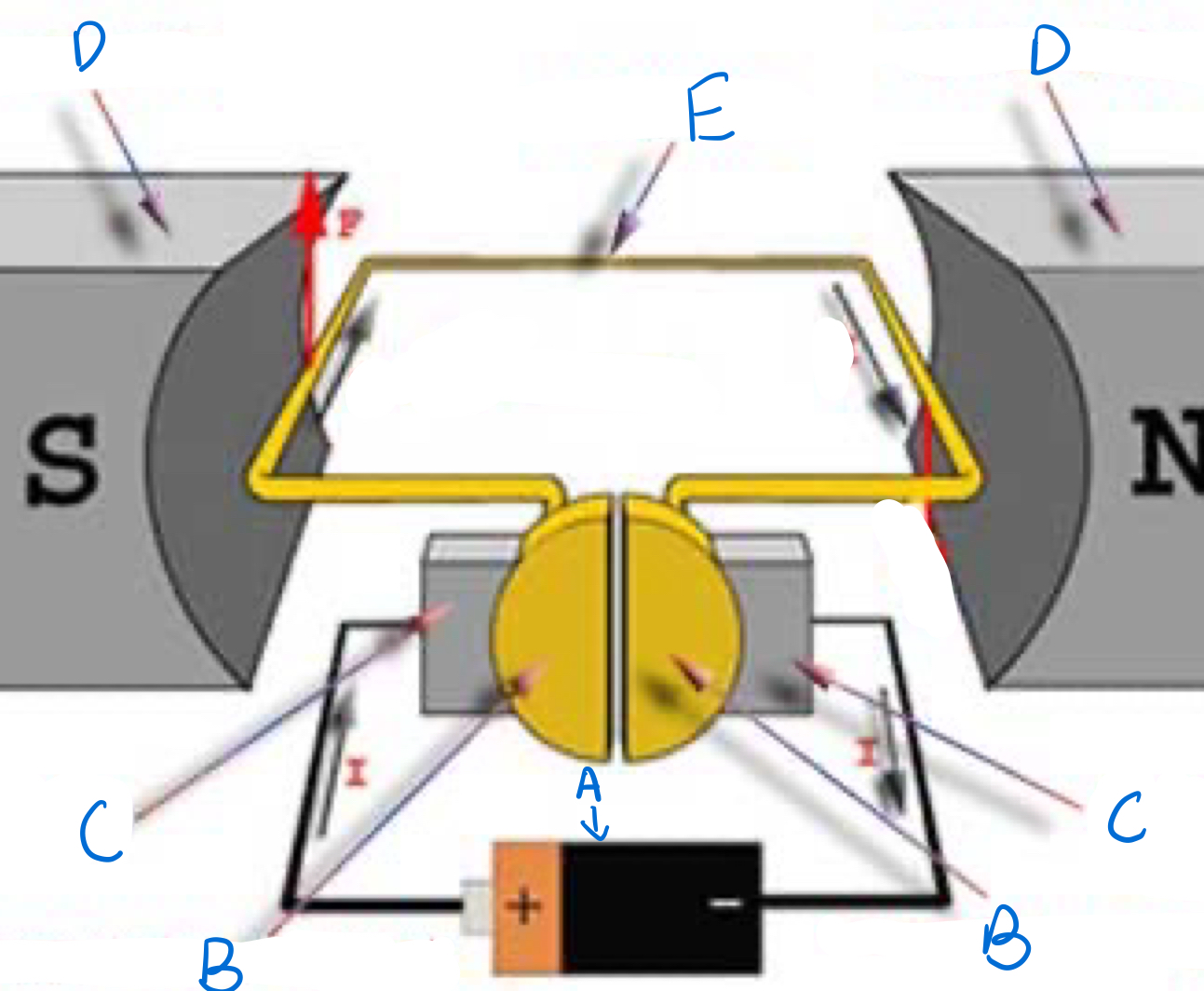
Split Ring commutator, Yes
Which part is B and does it spin?
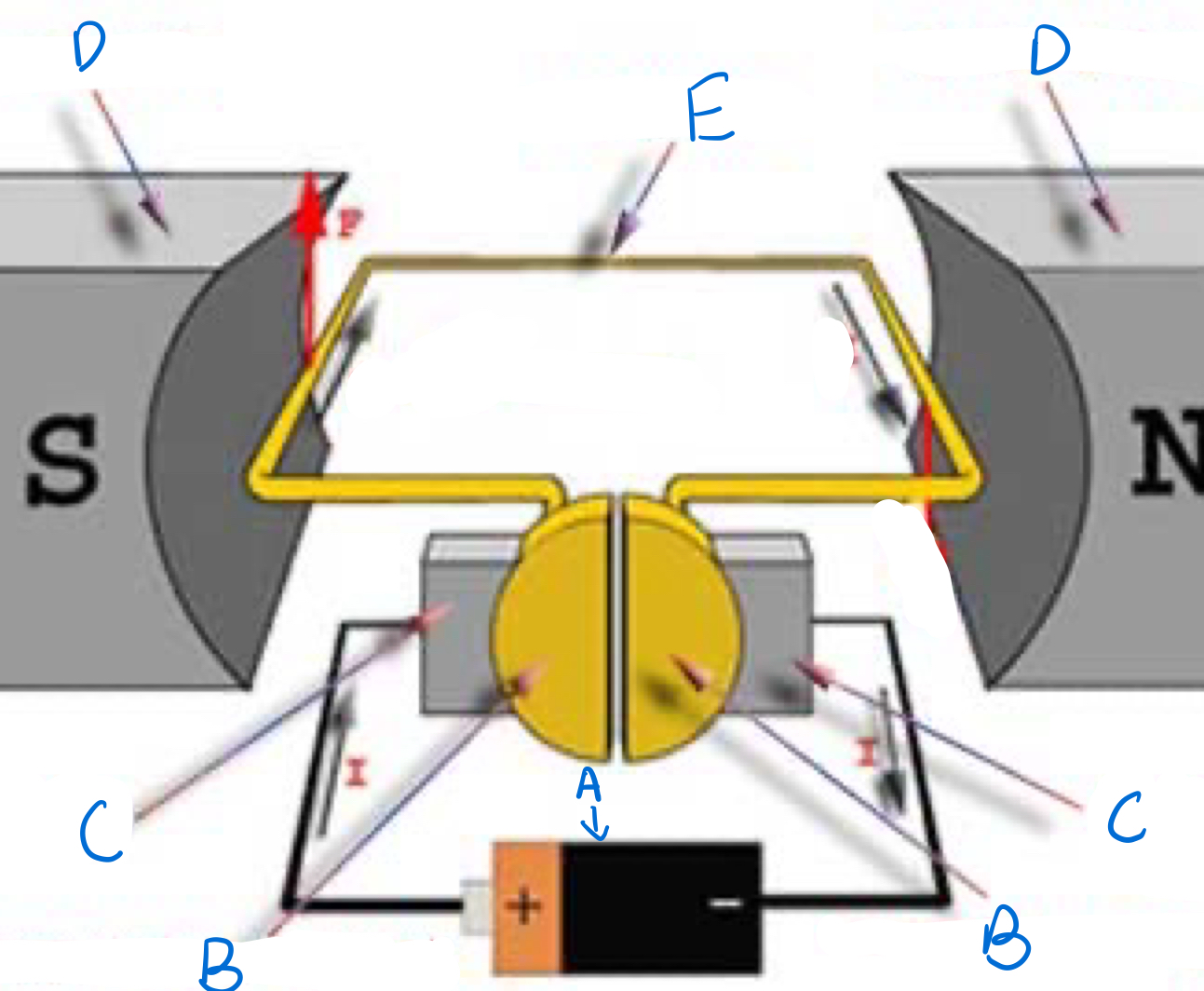
Brushes, no
Which part is C and does it spin?
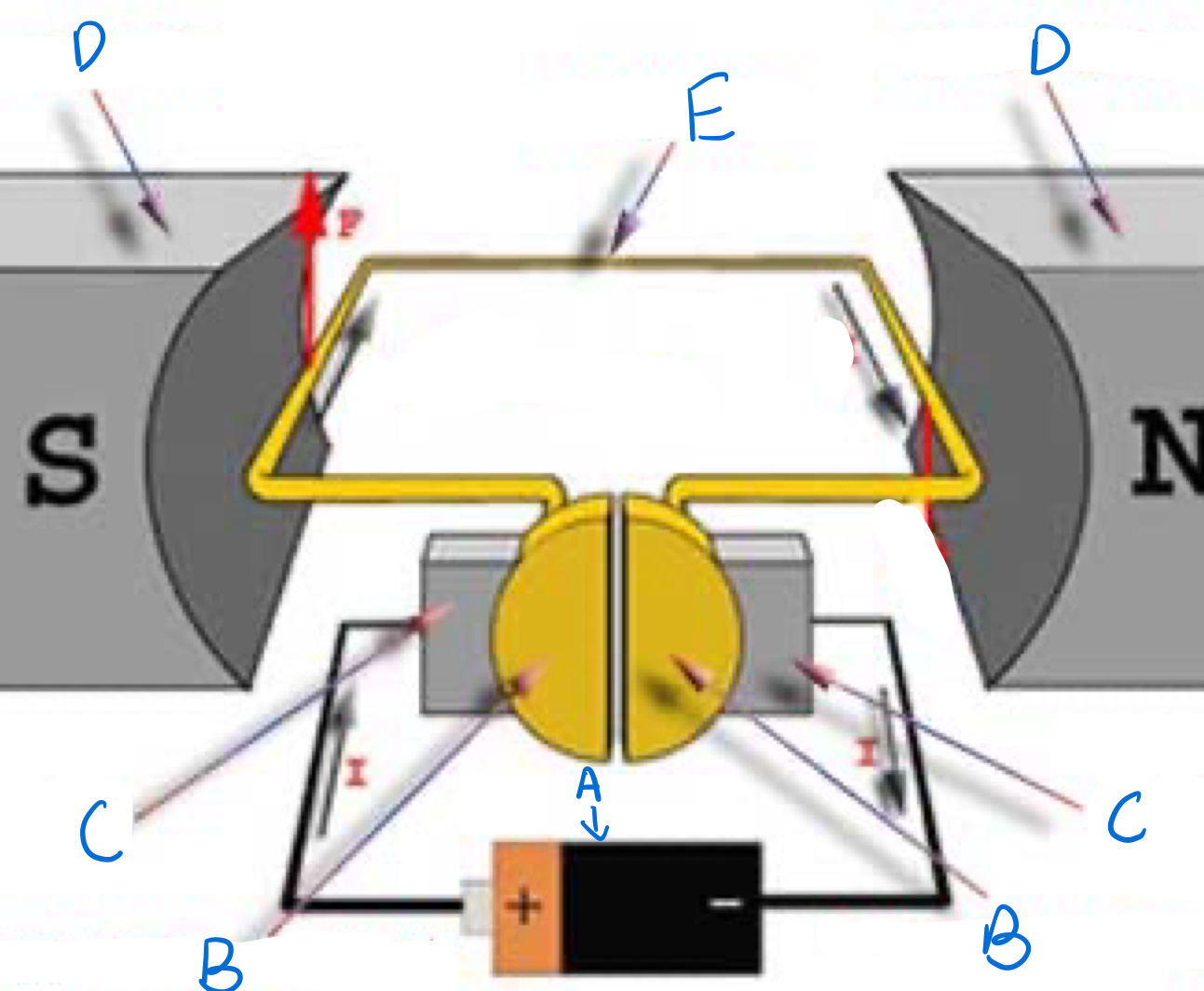
Magnets, no
Which part is D and does it spin?
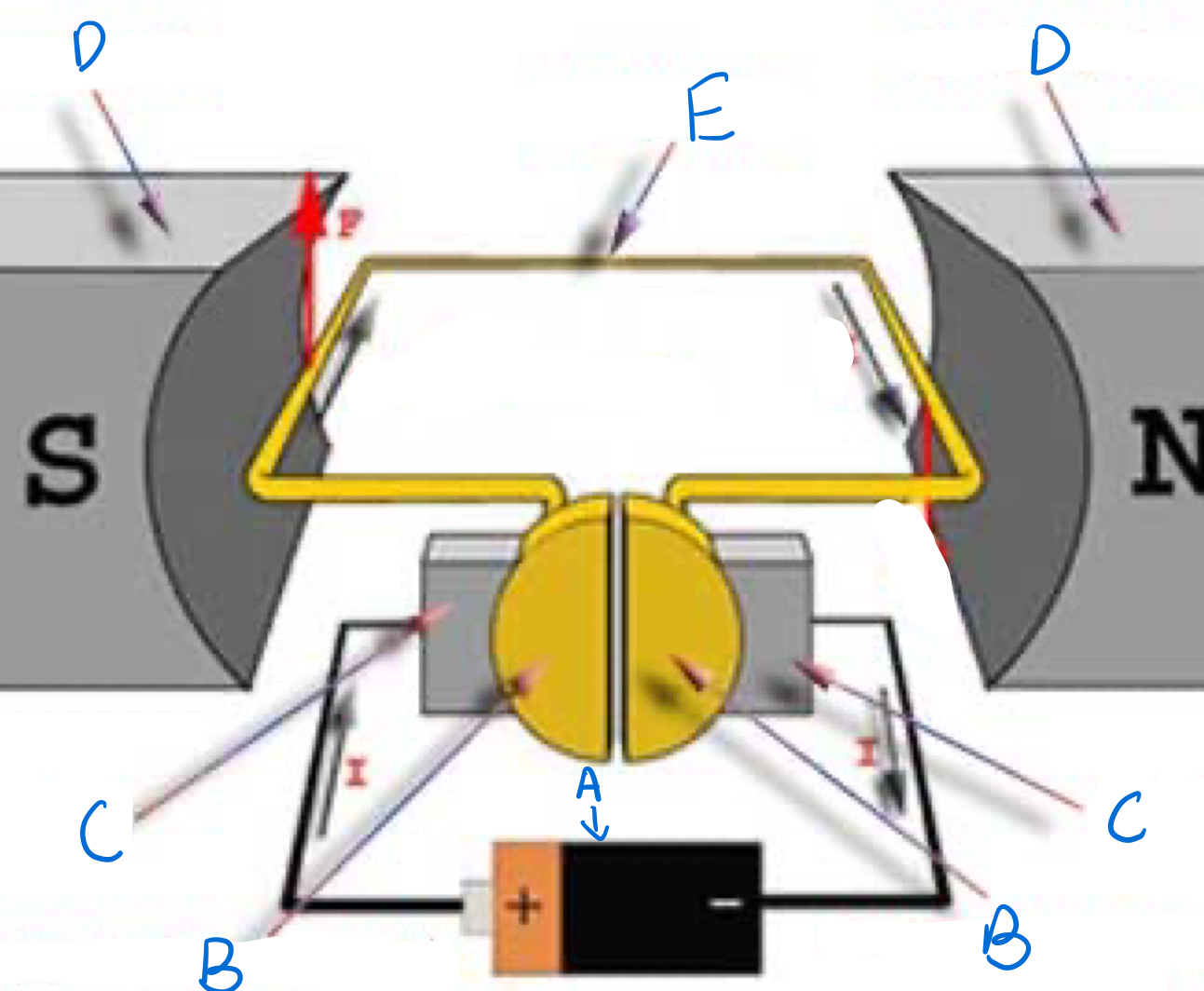
Armature, yes
Which part is E and does it spin?
Generator Effect
Whenever a magnetic field in the region around a conductor is moving or changing in strength, a current is induced to flow through the conductor.
Lenz’s Law
The induced current flow in such a direction that the induced magnetic field opposes the action of the opposing field.
Transformer
The main benefit of AC vs DC currents?
Spin faster (Greater FA) 2. More turns in the coil 3. Stronger external magnets $. Ferromagnetic core
To increase the output of a generator
High voltage
Most efficient way to transport electricity.