Global Politics Vocab
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Negative Peace
absence of war or violence, with tension
feminist peace
A level of peace that removes any form of discrimination based on gender
peace
Freedom from violence and war and the causes thereof.
interstate war
armed conflict between two or more states
direct violence
classic form of violence involving the use of physical force
cultural violence
refers to aspects of culture that can be used to justify or legitimize direct or structural violence such as religion, ideology, or culture
Territorial Conflict
a disagreement over the possession/control of land between two or more territorial entities or over the possession or control of land, usually between a new state and the occupying power
disputes in the south china sea
Example of a territorial conflict. Involves conflicting claims to owning the region by several soveirgn states such as China, Taiwan, Brunei, Malaysia, Phillipines and Vietnam
Annexation of Crimea by Russia
In 2014, Russia invaded the Crimean Peninsula, a part of Ukraine, and then decided to annex it.
interest based conflict
Competition over needs and goods that the other desires or holds onto (weapon sales, discrimination on the factory floor)
Ideological conflict
A struggle between two distinct and opposing sets of beliefs and values (like the ideas of communism vs capitalism in the cold war)
free market economy
an economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets
state led economy
retains private property and free market, but intervenes to grow the economy
identity conflict
involves an incompatibility between two or more aspects of identity (applicable to indigenous populations, previously homogenous states, and heterogenous populations)
Heterogenous
(adj.) composed of different kinds, diverse
homogenous
of the same kind
just war theory
set of principles outlining conditions when the use of violence would be acceptable

Jus ad Bellum Standards (6)
1. just cause
2. right authority
3. right intention
4. last resort
5. probable success
6. proportionality
jus ad bello standards
- Discrimination
- Proportionality
- Indispensability
- Law & Treaty
jus ad bellum
the justification for resorting to war; the justice of war
jus ad bello
Under what circumstances is it right to go to war?
conflict party
any actor that is directly, or indirectly involved in the conflict. Can be state actors, non-state actors, transnational actors.
conflict mapping
visual representation of a narrative's primary conflict
non violent conflict
disagreement by mean of consultation or dialogue (Iran nuclear weapons programme used and P5+1 conversed about conflicting ideas and reached a conclusion)
examples of non violent conflict
peaceful demonstrations, strikes, civil disobedience, political campaigns, diplomacy
violent conflict examples
terrorist attacks, civil war, interstate war, insurgency or guerrilla warfare, genocide
guerrilla warfare
A hit-and-run technique used in fighting a war; fighting by small bands of warriors using tactics such as sudden ambushes
positive peace
looks at the causes of conflict and violence. If the parties involved in a conflict are equal and justice is provided fairly for everyone. the factors and underlying issues that created conflict have been resolved and there is no longer any reason for violence. the tension or contradiction leading to conflict has been resolved.
Galtung's triangle
provides a way to help us understand and unpick the motivations, actions and impacts of the various actors involved in a conflict.
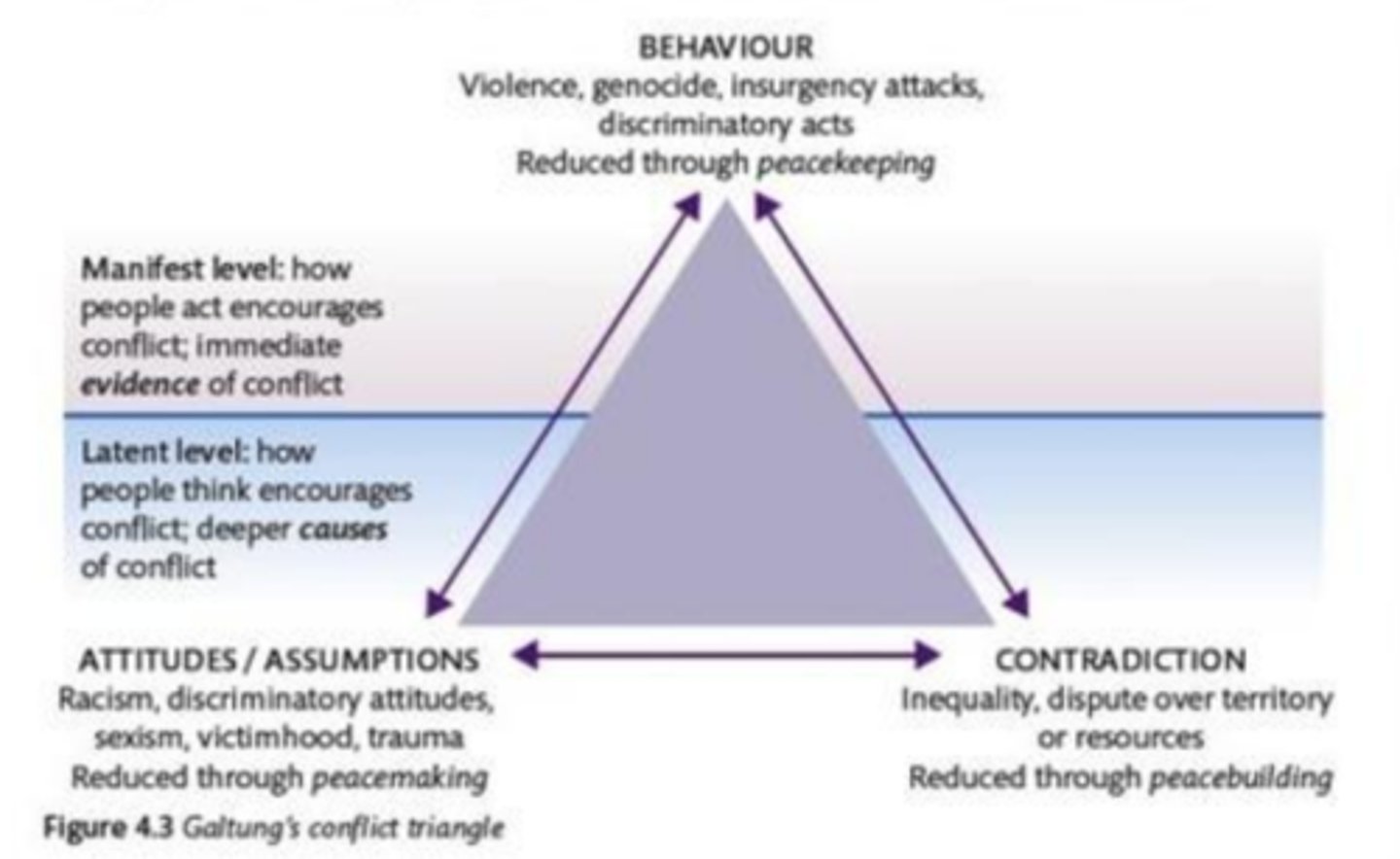
attitudes and assumptions
racism, discriminatory attitudes, sexism, victimhood, trauma. Reduced through Peacemaking
Contradiction
Inequality, dispute over territory or resources. Reduced through Peacebuilding
manifest level
how people act encourages conflict, immediate evidence of conflict
latent level
how people think encourages conflict, deeper causes of conflict
taliban
A group of fundamentalist Muslims who took control of Afghanistan's government in 1996. example of terrorist attacks
structural violence
physical and/or psychological harm caused by impersonal, exploitative, and unjust social, political, and economic systems
structural and cultural violence
Structural violence is reduced when systems of production and distribution are more equitably organized. Cultural violence occurs when symbolic processes are used to justify and legitimize inequitable power relations in political and economic systems.
Death of Tyre Nickols
the murder of Tyre Nichols, and how it represents the failures of the american government on both structural and cultural levels.
extra-state conflict
Those that pitch a state actor versus a non-state actor in some other party's territory (either another state, non-incorporated territory, or territory controlled by a non-state actor).
non-state conflicts
Conflicts between militias, warlords, or ethnic groups without the involvement of national governments.
moore's five areas of conflict
relationship conflict, interest conflict, data conflict, value conflict, structural conflict
Al Fushqa District (example of territorial conflict)
Located on the Ethiopia–Sudan border
Both states claim the region
Abundant natural resources and fertile land
Conflict slightly quelled in 1995 when Sudanese troops pulled out of the region due to pressure from Egypt
Conditions further improved in 2008 when Ethiopia cultivated the land while Sudan had authority over it (this was not stable peace) Ethiopian shifta (rebels) often conducted violent cross-border raids to steal crops and livestock or kidnap people for ransom
Compromise ended in 2020 with the start of the Tigray War
example of interest based conflict
differing views on gun control between american democrats and republicans
non state conflict
happens between two organized armed groups, neither of which the government of a state; involves conflict between groups that are not official representatives of a government
Somalia - civil war (1993)
non state conflict between various armed groups, islamic courts union and transition federal government
afghanistan
non state conflict. taliban and other armed groups fighting against afghan government and foreign forces
peacemaking
The action of trying to establish peace. measures to address conflicts in progress and usually involves diplomatic action to bring hostile parties to a negotiated agreement.
peacebuilding
the use of military peacekeepers, civilian administrators, police trainers, and similar efforts to sustain peace agreements and build stable, democratic governments in societies recovering from civil wars. attempts to target the deeper causes of a conflict and rectify them
peacekeeping
the active maintenance of a truce between nations or communities, especially by an international military force. keeping peace and preventing conflict from resuming
Universalism
the ethical system stating that all people should uphold certain values that society needs to function. This concept is hard to uphold because of relativist forces inherent to state sovereignty
Relativism
the doctrine that knowledge, truth, and morality exist in relation to culture, society, or historical context, and are not absolute.
Positive rights
things that humans should have or be given. Often require an outside agency or entity to provide a service (eg the state.) These are typically entitlements like healthcare, education and food
Negative Rights
refer to things thats humans should be free from. Discourage, limit, or prevent the actions of an outside agency governments, other humans, that causes harm to a person. Includes freedoms like speech, security and mobility
Liberty
refers to having freedom and autonomy. It is often divided into positive and negative
Negative liberty
defined as individuals having the freedom from external coercion
Positive Liberty
defined as individuals having the autonomy to carry out their own rational will.
Equality
Every human being is equally entitled to their human rights without any form of discrimination. Implications: Uniform Entitlement: Advocates for a world wherein everyone, regardless of their identity or status, enjoys the same rights.
Human Rights
the basic rights to which all people are entitled as human beings
The flaws of Human Rights as a concept
Based heavily on western values which results in a heavier focus on individual rights instead of group rights. Human rights also functioning at the detriment of non-western states.
Retributive Justice
The only way for justice to be satisfied is for a wrongdoer to suffer in proportion to the way he's made others suffer
Dispensing Authority
to prepare and deliver substances to the client provided the authority is exercised in compliance with applicable federal and state laws. Retributive justice requires this.
ICC - International Criminal Court
investigates and, where warranted, prosecutes individuals charged with the gravest crimes of concern to the international community: genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity, and the crime of aggression.
Distributive Justice
Calls for social justice and just society - justice in relevance to human rights. Deals with issues of power, opportunity, wealth, and privilege.
need based justice
everyone shouldn't get the same because our needs aren't the same. Justice is getting based on what we need.
Merit-Based Justice
Justice actually means giving unequally, based on what each person deserves
Veil of Ignorance
a device for helping people more fairly envision a fair society by pretending that they are ignorant of their personal circumstances.
Justice as Equality
The belief that everyone should get the same kind and amount of stuff
Justice as fairness
Any inequalities that exist in a social system, should favor the least well off because this levels the playing field of society.
deterrence theory
Rather than making a wrongdoer suffer for what they've done, supporters of deterrence see punishment as being for the good of society as a whole. Sometimes, we punish people to send a message to other people
Universal Declaration of Human Rights
A 1946 United Nations covenant binding signatory nations to the observance of specified rights. this is not a law
Inalienability
"inability of something to be taken from or given away by the possessor"
Critisicism of HUman Rights from a native perspective
- Native people suggest looking at a system where the water, land, and trees have water. Very individualist view of the world
- can't assume that Indigenous people are all on the same page, they are not a conglomerate. Some people send their own to the UN to fight for human rights, while others do not do this at all because they don't see a point in it.
- human responsibilities for one another. The Western way is not wrong, it's just limited and hyper-individualistic
- being Indigenous has more to do with a way of life than it does with heritage
Universal jurisdiction
a legal concept that permits states to claim legal authority beyond their national territory for the purpose of punishing a particularly heinous criminal that violates the laws of all states or protecting human rights
Challenges of enforcing universal jurisdiction
1. Absence of any legislation/inadequate legislation
2. Cases take a ling time to process because of their international nature
3. sovereignty: countries dont have to enforce anything if they don't want to
Alien Tort Statute (ATS)
Statute that gave the federal courts jurisdiction over civil actions for damages brought by non-US citizens for torts committed against them by other noncitizens outside of the US in violation of the norms of customary international law
tort
a wrongful act or an infringement of a right (other than under contract) leading to civil legal liability.
Sosa v. Alvarez-Machain (2004)
held that the ATS grants federal courts jurisdiction over claims based on specifically defined, universally accepted international law norms, upholding the connection between the ATS and Universal Jurisdiction.
This case limited the scope of the ATS and clarified that not all violations of international law could be addressed through U.S. courts under this statute. It established a precedent for judicial restraint in expanding the types of claims recognized under the ATS.
ICJ (International Court of Justice)
World Court created to adjudicate disputes between states
ICC (International Criminal Court)
a permanent tribunal started in 2002 to prosecute war crimes
Qualities of Human Rights
Inalienability, universality, indivisibility, equality, justice, liberty
JULIIE
death of Trayvon Martin
invasion of the human right to safety and autonomy. indicates corruption
Codification
The act or process of rendering laws in written form
Human Rights Covenants
Human rights laws that all countries must follow. the covenants were developed because the UN recognized that the UDHR was limited. After all, it was not law. they must be ratified. sovereignty and the ability to not ratify and codify these laws is a limitation. they are opened for signature and ratification.
Convention on the elimination of discrimination against women (CEDAW)
entered into force after 20 states ratified this covenant, making it international law.
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
Example of a human rights covenant. The right to liberty and security of the person and freedom from arbitrary arrest or detention. The freedom from prison due to debt. The right to equality before the law; the right to be presumed innocent until proven guilty and to have a fair and public hearing by an impartial tribunal.
US has not signed this covenant
A UN Declaration
An example of this is the UDHR.
these are passed as a resolution by the UN General Assembly by a simple majority vote. They are not law and states are not legally obligated to enforce them.
A UN instrument
is also passed as a resolution by the UN General Assembly by a majority vote, but is a law.
Declaration vs instrument
distinguishes an instrument from a declaration is the process of signing and ratification.
Signing refers a state’s representatives agreeing to a treaty in person and signing the document. This is usually a government minister like a minister of foreign affairs or foreign secretary.
Signing
before ratification, is not binding. Agrees to follow the principles proposed by a covenant.
Ratification
Formal approval. Once a treaty is ratified by the national government the state will notify the UN that it has formally accepted the treaty and it then becomes legally binding.
International Law
A series of customs that a state should follow - a law that governs relations among nations. But at the end of the day, sovereignty allows states to do whatever they want. An incentive to follow international law is to keep positive relations between states.
The US and international law
US believes that it infringes on soverignty. US has not signed the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (ICESCR).
sovereignty
state sovereignty is the basis of all International diplomacy and overpowers all instruments, and declarations proposed by the US
ILO Convention No. 138
on the minimum age is the effective abolition of child labour by requiring countries to: 1) establish a minimum age for entry into work or employment; and2) establish national policies for the elimination of child labour.
1st generation rights
negative rights, government should not interfere with individual liberties
2nd generation rights
positive rights, things the government should provide on the basis to protect the neediest of populations
3rd generation rights
Group or solidarity rights. These rights are not universally accepted. E.g. the right to have a healthy environment.