Week 6- Organism-sediment interactions and succession
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Recall the early sequence of early work related to benthic organisms
Recognition that fauna occurred in zones/regions
Described/categorised fauna occurring in zones
Organism-sediment interactions
What organism-sediment reactions were observed at Cape Cod Bay, Massachusetts, US
Transition in fauna from inshore sand to deeper water muds
Silt-clay intensively reworked deposit feeders, fewer suspension feeders
Irregular bottom topography produced by holuthurian molpadia oolitica
What is Molpadia ooltica like
Forms cone shaped faecal mound
Stabiliser
Verticular upward conveyor
Intercone depressions
How does fauna influence the sediment
Organism- sediment- fluid- chemical interactions
Influence all at same time- continuous
How does particle sorting work
Fundamentally changes sediment properties
Finer material is bought to the surface
Set up an organic gradient
What is burrow construction and ventilation
RAefers to the way animals build and manage underground shelters (burrows), focusing both on how they dig and structure the burrows and how they ensure airflow to support breathing, temperature control, and waste gas removal
What do infauna influence
Physical, chemical and biological environment all at the same time
What do physical, chemical and biological parameters influence
Infauna
Who underpinned/summarised organism-sediment reactions
John Gray and Donald Rhoads
Both missed parts of eachothers out
What did Gray say about organism-sediment relations
Attempted to relate individuals, populations and communities to sediments
Took view rhat selecton takes place at larval stage and is then modified by environment
What did gray mean by organism sediment couple
Selection by larvae or adults of suitable sites
and
Population modifies sediment in turn leading to temporal and spatial changes in population
= Community structure therefore can be loosely related to sediment composition but exact constitution may be radically altered by interactions between organisms and sediment
What did Rhoads say about organism sediment coupling
Influenced by in situ observations of fauna
Invented SPI
What did Gray say about ecological significance
A community must be composed of species which interact with each other and the environment and a community has, therefore, an ecological basis
Where could you find evidence to support or refute the concept of benthic succession
Fossil records
Historical record
Environmental gradient
Galway Bay and loch creran pollution studies
What was Bagges evidence from environmental gradients
Compared sequence of communities in polluted estuaries in the Skagerak Baltic region
Compared assemblages before/after onset
What are SAB curves
SAB curves typically refer to Species-Abundance-Biomass curves, used in ecology to visualize and compare the relationships between:
Species abundance (how many individuals there are of each species),
Species biomass (the total mass of those individuals), and
Biodiversity structure in an ecosystem.
What are the effects of organic enrichment
Organic enrichment refers to the increase of organic matter (like decaying plant or animal material, sewage, or food waste) in an ecosystem—usually aquatic or soil environments.
Lots of food
Microbes go crazy
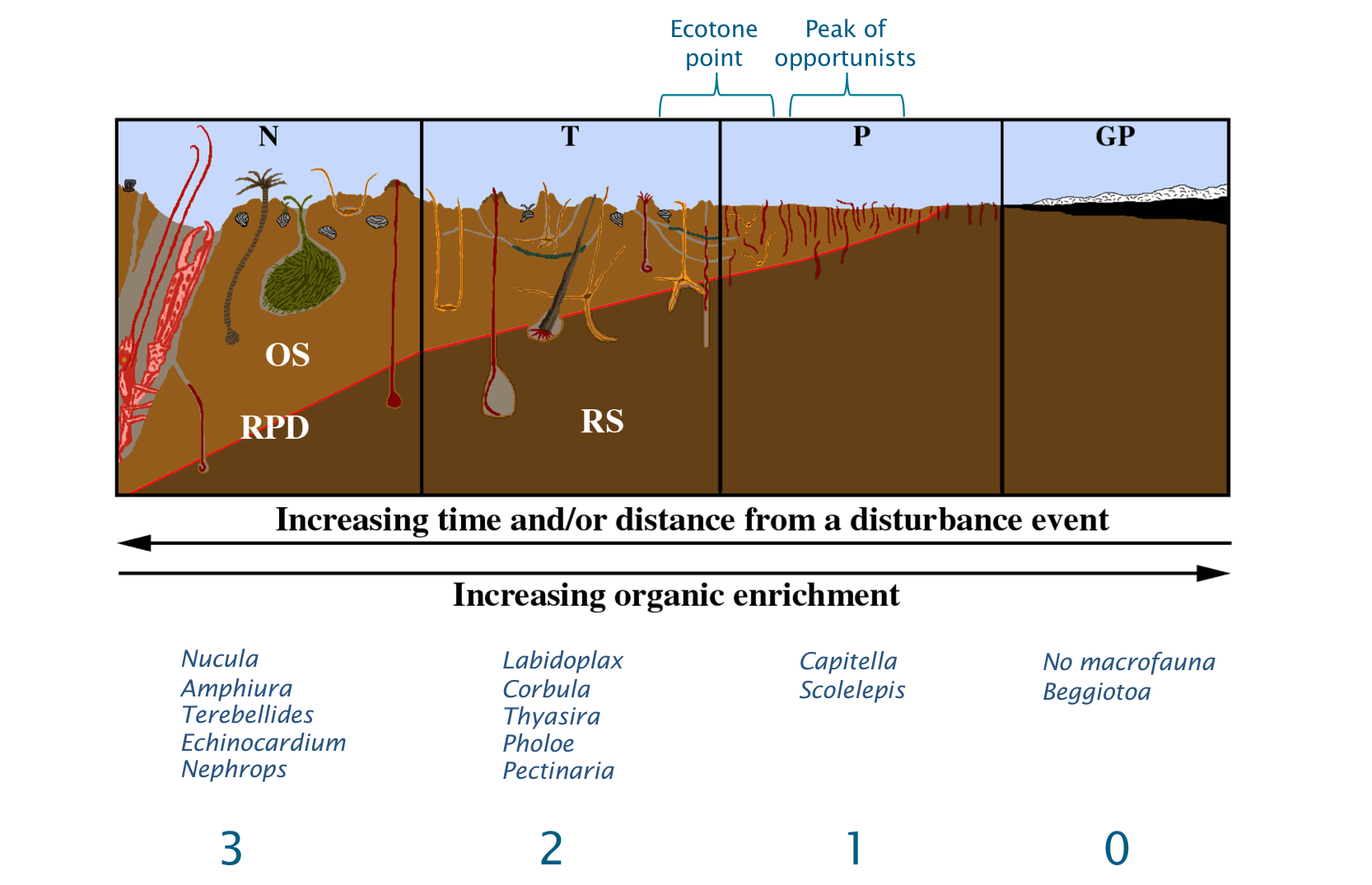
What organisms would you find in different levels of enriched soil
Less - Amphiura, sea pen, nephrops
Medium - Thyasria, Pectinaria, Labidoplax
Very - Capitella, Scolelepsis
What is the Pearson-Rosenberg model of succession
Graphical depiction of moderate succession with interactions
What is succession related to hypoxia like
organic enrichment → hypoxia → disturbance → triggers ecological succession
What is Cranfields biogenic habitat regeneration model
Focuses on understanding how benthic (seafloor) habitats, particularly those formed by living organisms like shellfish, recover after disturbances such as intensive fishing. This model was developed based on studies in Foveaux Strait, New Zealand, where overfishing had significantly degraded oyster reefs
What happened when Snelgrove and Butman critically reviewed OSI literature
OSI relationships tend to be more variable tham traditionally reporteed
Multiple variables correlate woth sediment type
What did Snelgrove and Butman conclude
Paradigms of succession are derived from limited experimentation or correlative field sampling and clearly are inadeqaute as explanations or predictive tools
Does benthic succession exist
Each represents a potential successional endpoint that can persist over time as a recognisable community type within the domain a prevailing environmental conditions