MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATON: POSTURAL BALANCE AND GAIT
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
In our field, balance is often used in association with terms such as ____________ and __________control
stability and postural control
The evaluation of balance is pertinent in the assessment of patients with which deficits?
Neurological Deficits
Orthopedic deficits
Vestibular disorders
True or False:
An object or person is balanced when the forces acting upon them all summate to 0 (equilibrium)
True
Which law was related to the previous flashcard?
Newton's First Law: Law of Inertia
COG of an adult can be located where?
COG of an infant is located where?
2 inches anterior to S2
Xiphoid process
A multidimensional concept, referring to the ability of a person to not fall
Human Balance
The point at which the vector of the total body weight passes
COG (Center of Gravity)
Vertical line running through the COG
Line of gravity
The area of single contact between body and the support surface or, if there is more than one contact with the support surface, the area enclosing all the contacts with the support surface
Base of support
The inherent ability of an object to remain in or return to a specific state of balance
Stability
The inherent ability of an object to remain in or return to a specific state of balance and not fall, or, the inherent ability referring to the motor and sensory systems and to the physical properties of the person
Human stability
True or False:
If the COG of an object is within the BOS we can say that the object is balanced.
True
State if this increases or decreases stability:
Larger BOS
Smaller BOS
Lower COG
Higher COG
COG at center of BOS
COG at edge of BOS
State if this increases or decreases stability:
Larger BOS = increases
Smaller BOS = decreases
Lower COG = increases
Higher COG = decreases
COG at center of BOS = increases
COG at edge of BOS= decreases
If an object becomes unbalanced where would the COG move in relation to the mass?
COG moves to the side with more mass
That feeling when you find a golden scar
dekubopdomnem dekubopdomnem
I, was d knight in shoining armour in ur mooviee

True or False:
During an upright stance, the human body has a relatively low COG and wide BOS.
False
During an upright stance, the human body has a relatively high COG and small BOS.
The act of maintaining, achieving or restoring a state of balance during any posture or activity
Postural control
True or False:
Postural control is one of the prerequisites to the maintenance oa a myriad of postures and activities
True
Postural control is used in the following EXCEPT:
The maintenance of a specified posture such as sitting or standing
Voluntary movement, such as the movement between postures
The reaction to an internal disturbance such as a trip slip or push
None of the above
Postural control is used in the following EXCEPT:
The reaction to an internal disturbance such as a trip slip or push
EXTERNAL disturbance not internal
Postural control strategies may be ___________ (compensatory) or ____________ (anticipatory), or a combination of both
Postural control strategies may be reactive (compensatory) or predictive (anticipatory), or a combination of both
This postural control strategy involves a voluntary movement or increase in muscle activity, in ancticipation of a disturbance
Predictive postural control
This control strategy involves a movement or muscular response following an unpredicted disturbance
Reactive postural control
What were postural control strategies traditionally considered as?
reflex-like responses elicited automatically by a sensory stimulus.
True or False:
Postural responses are now understood to rely on the assessment and control of many variables by the PNS
False:
Postural responses are now understood to rely on the assessment and control of many variables by the CNS
True or False:
Strategies of postural control vary depending on an individual’s goals and environmental context. This implies that balance control is a fundamental motor skill learned by the CNS.
True
Balance emerges from the interaction of the individual, the task, and the environment; Functional tasks require three types of balance control: (Enumerate)
steady-state
reactive
proactive.
Environmental constraints that affect balance control:
support surface
sensory cues
cognitive demands/load
Individual variations that affect balance control:
motor
sensory
cognitive abilities
the ability to control our balance in fairly predictable and nonchanging conditions.
Steady-state balance
is the ability to activate muscles in the legs and trunk for balance control in advance of potentially destabilizing voluntary movements.
Proactive or anticipatory balance
is the ability to recover a stable position following an unexpected perturbation.
Reactive balance control
Reactive balance control relies on __________ mechanisms; on the other hand, proactive balance utilizes __________ mechanisms.
Reactive balance control relies on feedback mechanisms; on the other hand, proactive balance utilizes feedforward mechanisms.
Identify which balance control is needed for this task:
reaching for a heavy object while standing; for maintaining a stable position before reaching for the object
balance control to prevent loss of stability during the reach and lift
balance control if the object is heavier than expected, and lifting it causes us to lose balance
the completion of the task
Identify which balance control is needed for this task:
reaching for a heavy object while standing; for maintaining a stable position before reaching for the object = Steady State balance
balance control to prevent loss of stability during the reach and lift = Anticipatory Balance Control
balance control if the object is heavier than expected, and lifting it causes us to lose balance = Reactive balance control
the completion of the task = Steady state balance
Stability required for tasks like sitting or standing is called:
Static Balance
True or False:
Steady state balance, when controlling postural sway, is quite static.
FALSE:
Steady state balance, when controlling postural sway, is quite dynamic.
True or False:
The berg balance test is useful for young athletic patients.
False:
The berg balance test is useful for geriatric patients.
True or False:
Movement patterns used to recover stability following perturbations are selected by the central nervous system based on several factors such as characteristics of perturbation.
True
In reactive balance control, these strategies are used to maintain balance in a fixed BOS
Anke and Hip Strategy
These strategies are used to maintain balance when the BOS changes
Stepping and Reach to Grasp strategy
Congrats you won a 5 min break
In this balance control, the CNS uses the sensory information gathered and the information from previous experiences to predict forces and control needed for the task ahead with also the ability to change and adapt to new information if the task turned out to be different than expected.
Proactive Balance control
kaya ung mga bata di alam paano mag react to stairs at first
The gold standard for investigating sensory information and organization for balance
Sensory Organization Test
Memorize this Table
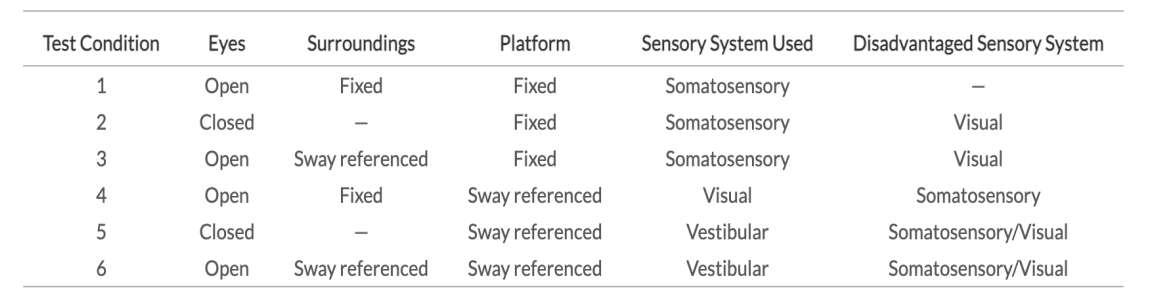
SOT test condition 1:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 1:
Eyes: Open
Surroundings: Fixed
Platform: Fixed
Sensory System used: Somatosensory
Disadvantaged sensory system: N/A
SOT test condition 2:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 2:
Eyes: Closed
Surroundings: N/A
Platform: Fixed
Sensory System used: Somatosensory
Disadvantaged sensory system: Visual
SOT test condition 3:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 3:
Eyes: Open
Surroundings: Sway referenced
Platform: Fixed
Sensory System used: Somatosensory
Disadvantaged sensory system: Visual
SOT test condition 4:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 4:
Eyes: Open
Surroundings: Fixed
Platform: Sway referenced
Sensory System used: Visual
Disadvantaged sensory system: Somatosensory
SOT test condition 5:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 5:
Eyes: Closed
Surroundings: N/A
Platform: Sway referenced
Sensory System used: Vestibular
Disadvantaged sensory system: Somatosensory/Visual
SOT test condition 6:
Eyes:
Surroundings:
Platform:
Sensory System used:
Disadvantaged sensory system:
SOT test condition 6:
Eyes: Open
Surroundings: Sway referenced
Platform: Sway referenced
Sensory System used: Vestibular
Disadvantaged sensory system: Somatosensory/Visual
Normal Values in Relation to Gait
Pelvic Rotation ?
Pelvic Tilt ?
Vertical Displacement ?
Lateral Displacement ?
Cadence ?
Normal Values in Relation to Gait
Pelvic Rotation 8 deg
Pelvic Tilt 5 deg
Vertical Displacement 5 cm
Lateral Displacement 5 cm
Cadence 90-120 steps/min
Percentage Distribution
Stance Phase ?
Swing Phase ?
Double Support ?
Acceleration ?
Midswing ?
Deceleration ?
Percentage Distribution
Stance Phase 60% of gait cycle
Swing Phase 40% of gait cycle
Double Support 20% of gait cycle
Acceleration 10% of swing phase
Midswing 80% of swing phase
Deceleration 10% of swing phase
Inman’s Six Determinants (Braddom):
Pelvic rotation
Pelvic tilt
Knee flexion in stance phase
Ankle flex/ext mechanism
Lateral motion of the pelvis
4 Determinants of Gait (De Lisa & Hoppenfeld)
Pelvic Rotation
Pelvic Obliquity
Lat. Displacement in the coronal plane
Interchange between knee, ankle, foot
Muscle activity during Gait:
Hip flexors- peak activity during?
Hamstrings- peak activity during?
Quadriceps- peak activity during?
Hip abductors- peak activity during?
Ankle DF- peak activity during ?
Ankle PF- peak activity during?
Muscle activity during Gait:
Hip flexors- peak activity during EARLY SWING
Hamstrings- peak activity during TERMINAL SWING
Quadriceps- peak activity during HS to FOOT FLAT
Hip abductors- peak activity during MIDSTANCE
Ankle DF- peak activity during HEEL STRIKE
Ankle PF- peak activity during PUSH- OFF
force which produces the external moments occurring about the hip, knee and ankle during quiet standing and gait.
Ground Reaction Force
Ground reaction force location (HIP):
Loading Response
Midstance
Terminal Stance
Ground reaction force location (HIP):
Loading Response - Anterior
Midstance - Through
Terminal Stance - Posterior
Ground reaction force location (Knee):
Loading Response
Midstance
Terminal Stance
Ground reaction force location (Knee):
Loading Response - Posterior
Midstance - Through
Terminal Stance - Anterior
Ground reaction force location (Ankle):
Loading Response
Midstance
Terminal Stance
Ground reaction force location (Ankle):
Loading Response - Posterior
Midstance - Anterior
Terminal Stance - Anterior
Clinical Test to Assess Contracture of Two-joint muscles in UMN Pathology:
differentiate a rectus femoris from iliopsoas contracture
differentiate a soleus from gastrocnemius contracture
differentiate a contracture of gracilis from short adductors
Clinical Test to Assess Contracture of Two-joint muscles in UMN Pathology:
DUNCAN-ELY TEST
SILVERSKIOLD TEST
PHELPHS
Braddom (Pathologic Gait)
Abnormal Base of Support
Equinus foot or ankle
Equinovalgus foot
Flexion deformity of the Toes
Hitchhiker’s Great toe
Joint Stability
Drop-Off Gait
Knee Instability
Hip Instability
Trunk Instability
Limb Clearance
Stiff knee Gait
Excessive Pelvic Obliquity
Inadequate Hip flexion
Drop Foot
De Lisa/ Magee (Pathologic gait)
Antalgic (Painful) Gait
Steppage Gait/ Drop foot Gait
Festinating Gait
Shuffling Gait
Ataxic Gait
Arthrogenic (Stiff Hip or knee) Gait
Spastic Paretic Stiffed-legged Gait
Dynamic Knee Recurvatum
Diplegic Crouch Gait
Equinus Gait
Gluteus Maximus Gait
Trendelenberg /Gluteus Medius Gait
Psoatic Limp
Hemiplegic Gait
Short Leg Gait
Cause of antalgic gait?
Pain on weight bearing
Characteristics of antalgic gait:
_______ steps with overall __________ of gait; decreased ________ time on the affected leg
Characteristics of antalgic gait:
Short steps with overall slowness of gait; decreased stance time on the affected leg
Cause of steppage gait?
“functionally long” lower leg (example, plantarflexion contracture)
Characteristics of steppage gait:
Excessive hip and knee ___________
Characteristics of steppage gait:
Excessive hip and knee flexion
Cause of festinating gait?
Parkinson’s
Characteristic of festinating gait?
________ , ________ steps
Characteristic of festinating gait?
Short, quick accelerating steps
Cause of Ataxic gait?
Poor balance / Cerebellar lesion
Characteristic of Ataxic Gait?
Wide ______ and variable motion from stride to stride
Characteristic of Ataxic Gait?
Wide BOS and variable motion from stride to stride
Cause of Spastic Paretic Stifflegged gait/ Circumducting gait?
Weak hip flexors, weak hams, spastic plantarflexors
Characteristics of Spastic Paretic Stifflegged gait/ Circumducting gait:
Decreased knee _______; compensatory ______ and excessive _______ motion
Characteristics of Spastic Paretic Stifflegged gait/ Circumducting gait:
Decreased knee flexion; compensatory vaulting and excessive pelvic motion
Cause of Dynamic Knee Recurvatum:
Weakness of quads, plantarflexor weakness or spasticity/ contracture, weak dorsiflexors
Characteristics of Dynamic Knee Recurvatum:
____________ of knee during _________
Characteristics of Dynamic Knee Recurvatum:
Hyperextension of knee during stance
Cause of Diplegic Crouched gait:
Tight hip flexors, plantarflexor weakness, heelcord contracture
Characteristics of Diplegic Crouched gait:
Excessive knee _______ in stance with _______ and _______ of the hips, _______ and forefoot _______during stance, reduced knee _______ in swing
Characteristics of Diplegic Crouched gait:
Excessive knee flexion in stance with adduction and IR of the hips, equines and forefoot abduction during stance, reduced knee flexion in swing
Cause of Equinus gait
Heelcord contracture, dorsiflexor weakness, inappropriate plantarflexor activity
Characteristics of Equinus Gait:
Excessive ___________ in ___________ or ___________
Characteristics of Equinus Gait:
Excessive plantar flexion in stance or swing
Cause of Trendelenburg gait?
Weakness of hip abductors
Characteristics of Trendelenburg gait?
Uncompensated: _____________
Compensated: _____________
Characteristics of Trendelenburg gait?
Uncompensated: excessive pelvic drop
Compensated: excessive lateral lean towards affected extremity
“Never let the future disturb you. You will meet it, if you have to, with the same weapons of reason which today arm you against the present”
Marcus Aurelius