addition alkyne reactions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
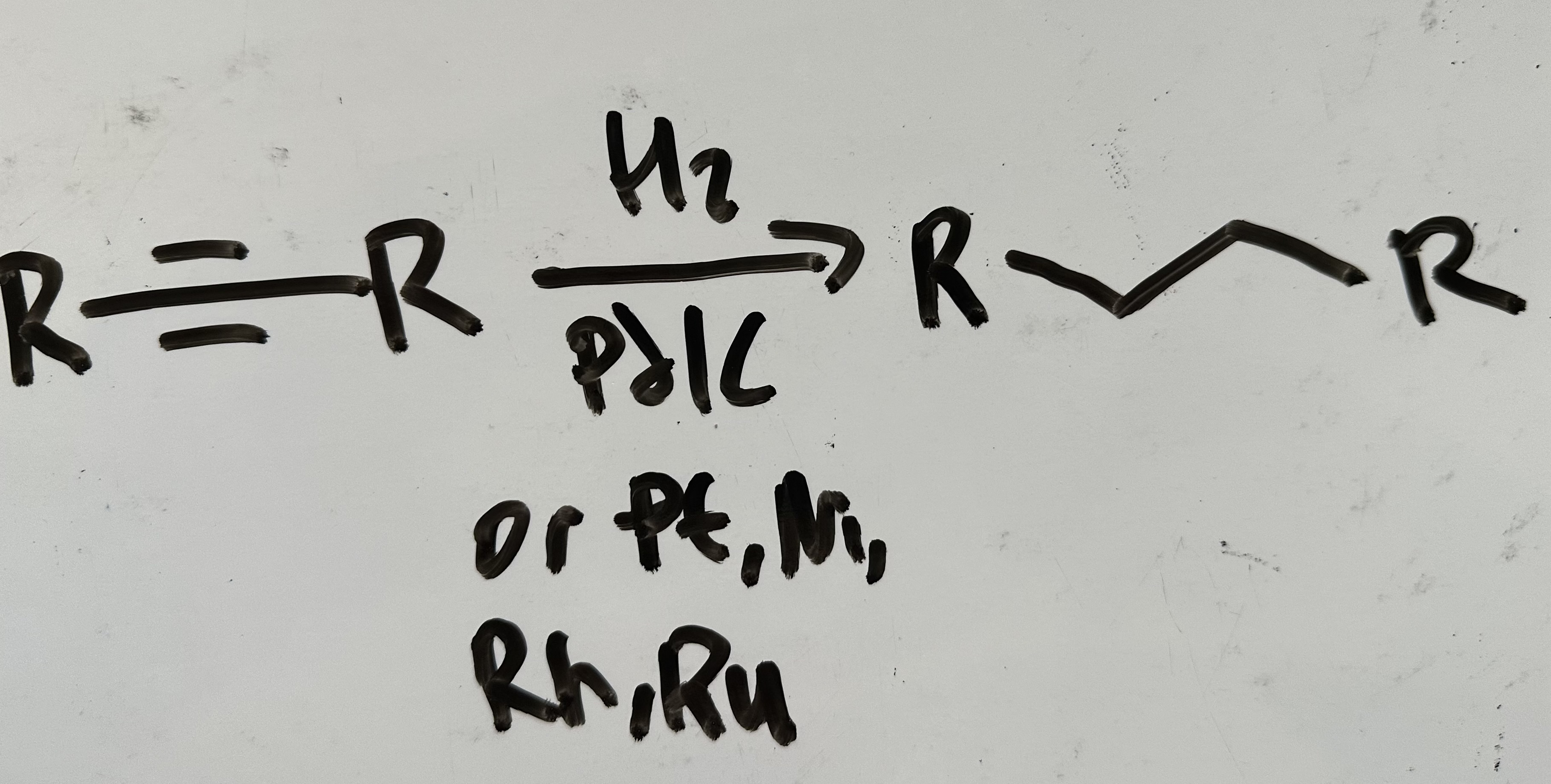
hydrogenation to alkane
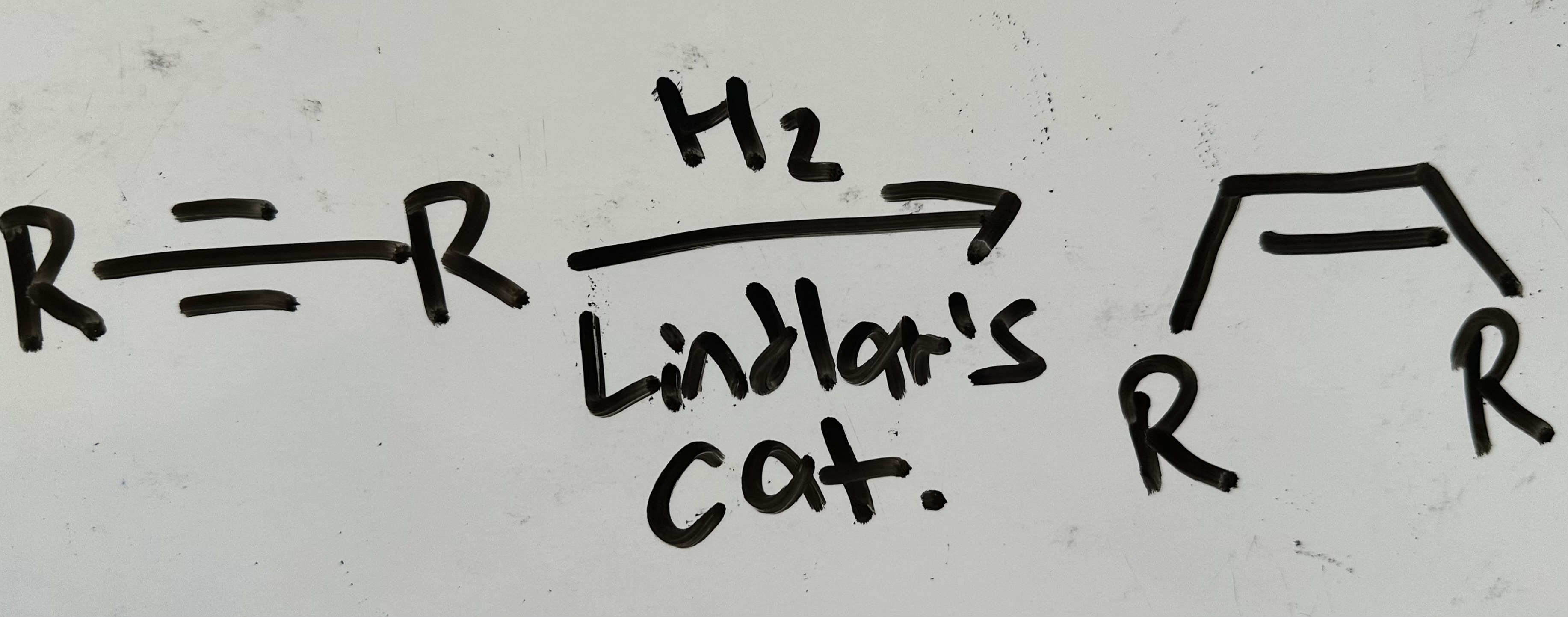
hydrogenation to alkene
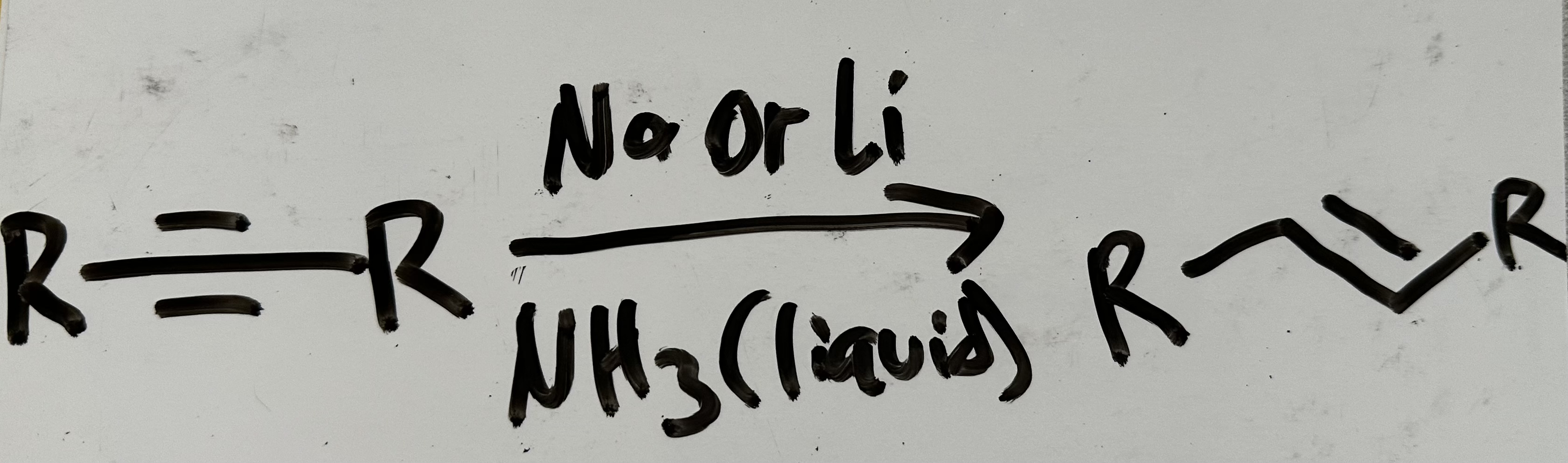
Dissolving metal reduction
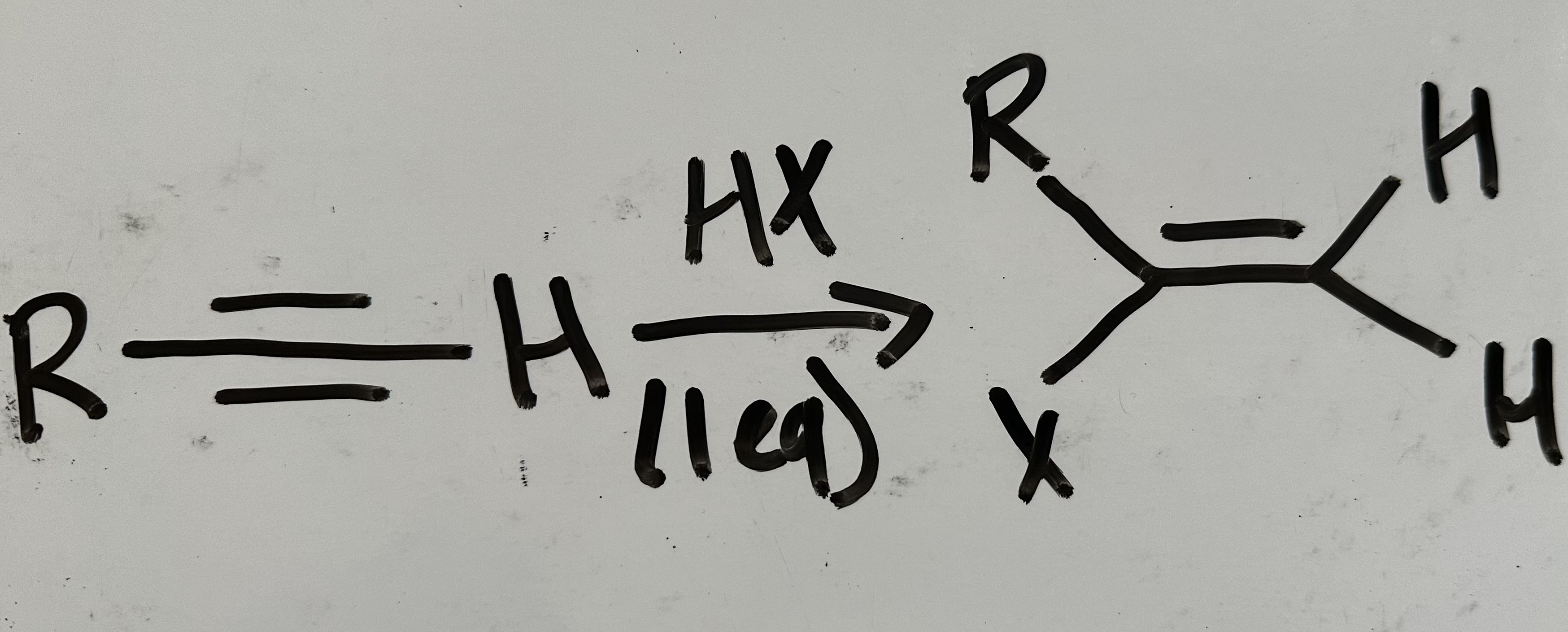
hydrohalogenation (1 eq)

hydrohalogenation (2 eq)

radical hydrohalogenation (1 eq)

radical hydrohalogenation (2 eq)
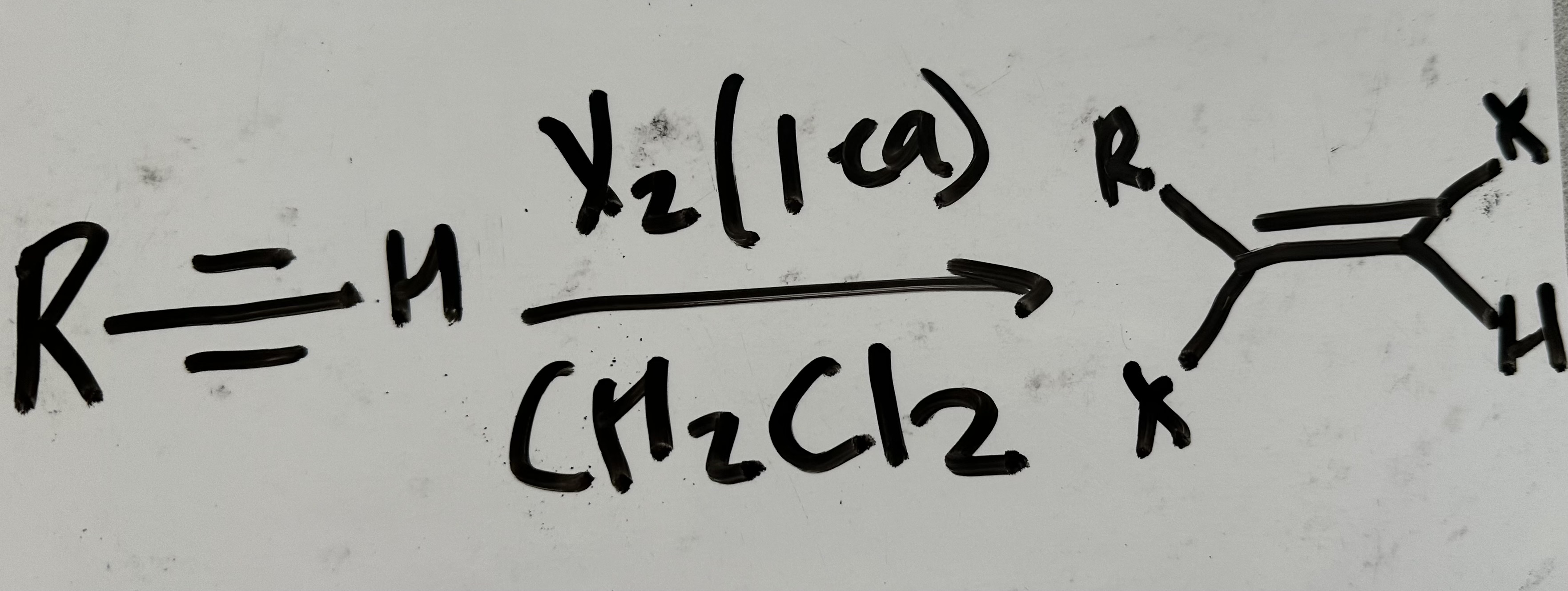
halogenation (1 eq)

halogenation (2 eq)

acid-catalyzed hydration
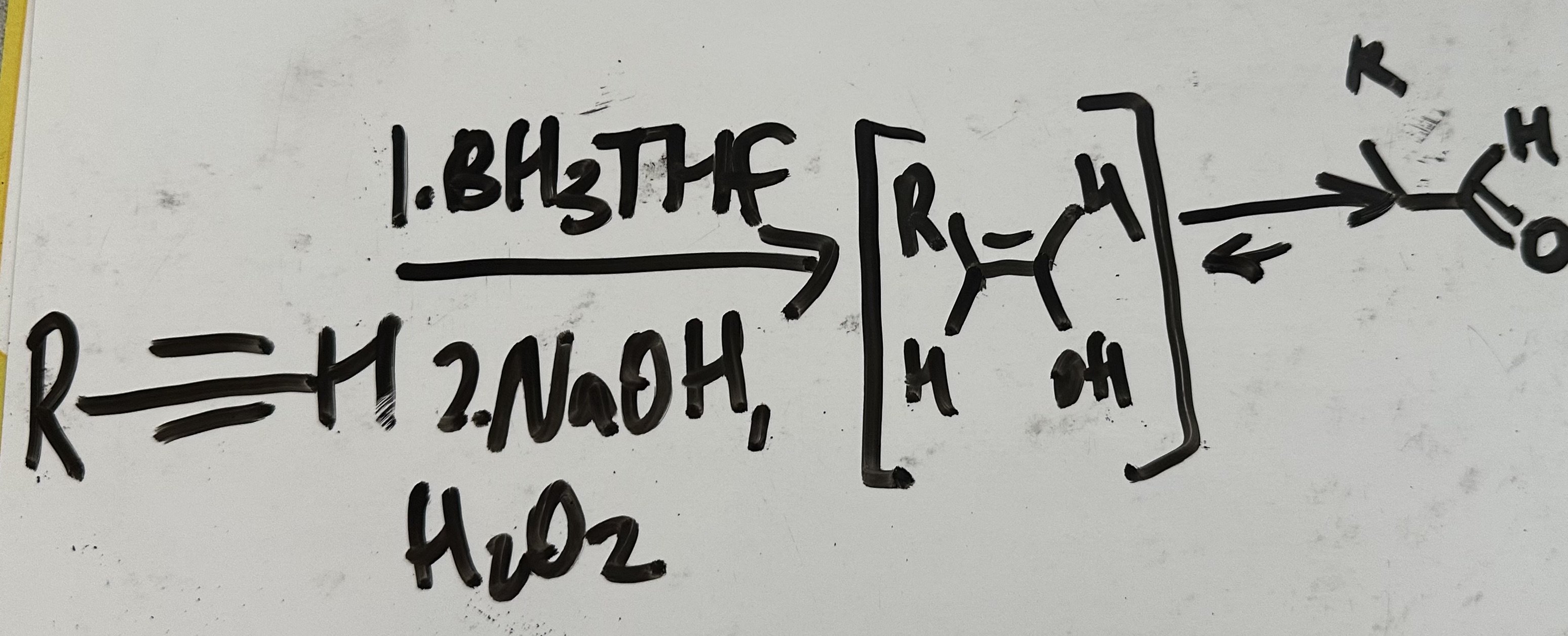
hydroboration-oxidation
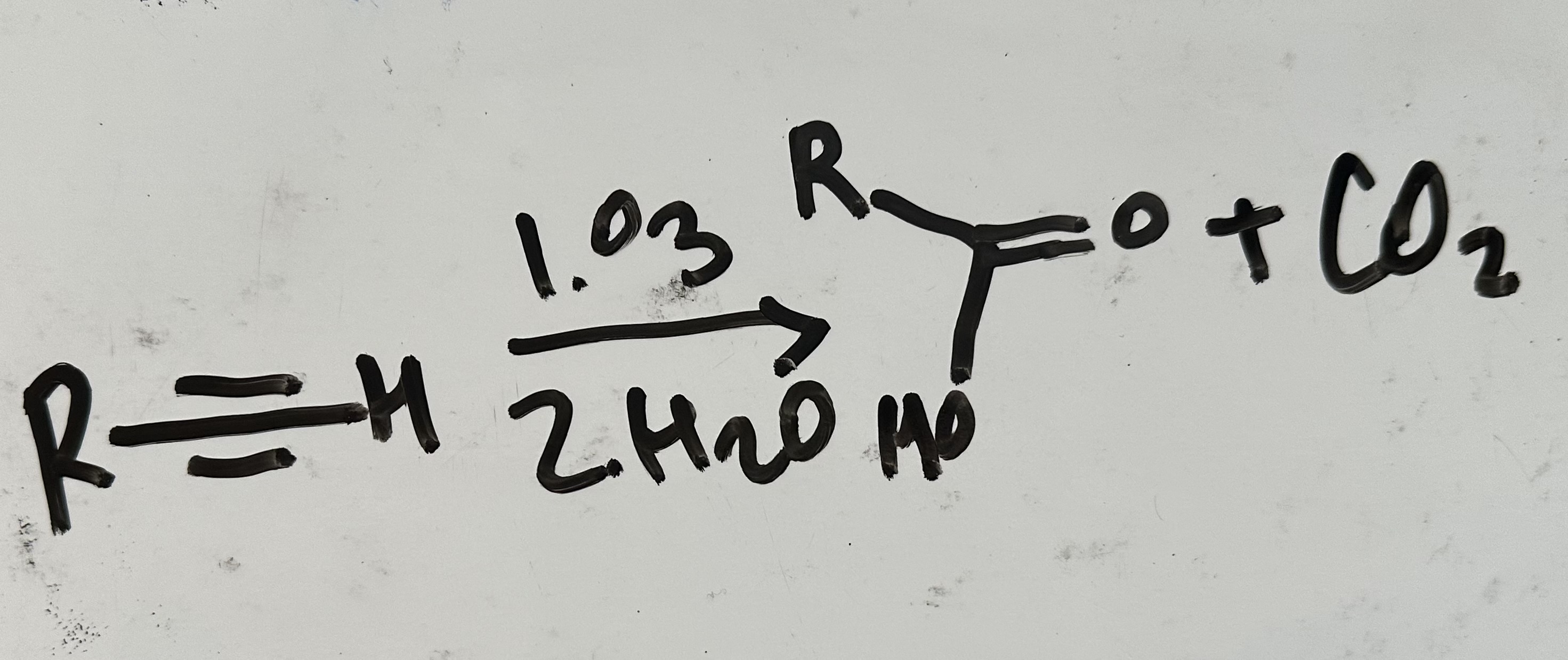
ozonolysis (terminal)
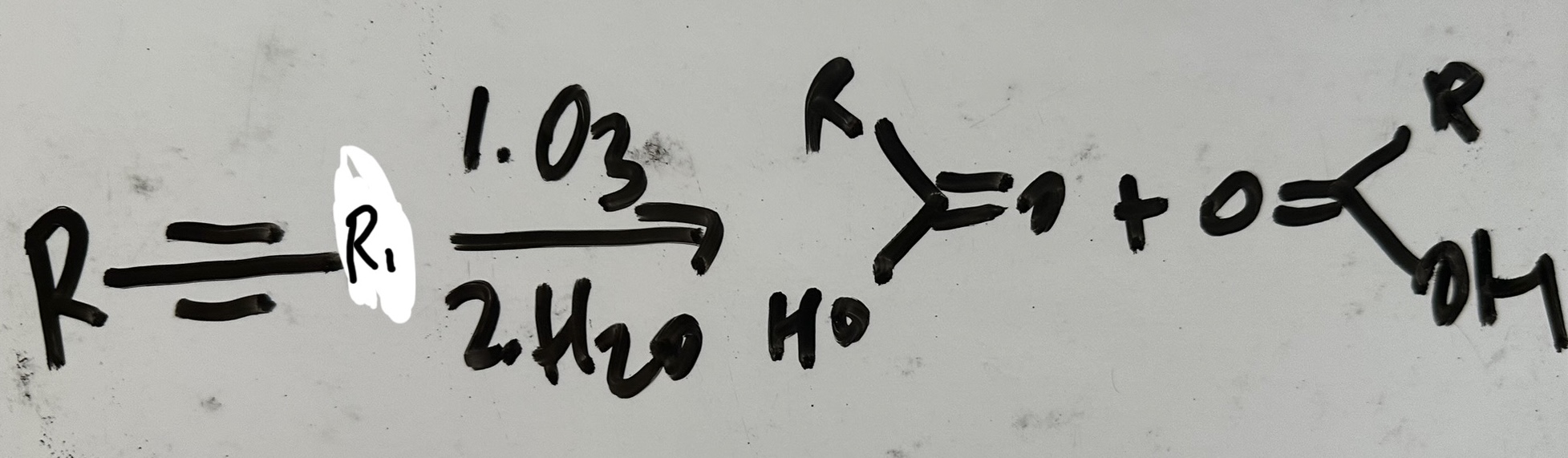
ozonolysis (internal)
What results from 1 equivalent in radical hydrohalogenation and hydrohalogenation
vinyl halide
What results from 2 equivalents in radical hydrohalogenation and hydrohalogenation
geminal halide
What isomer results from hydrogenation with Lindlar’s catalyst?
E-isomer only
What isomer results from dissolving metal reduction
Z-isomer only
What is the end result of acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkyne?
a ketone
What results from hydroboration-oxidation of an alkyne?
an aldehyde
Which reactions are Markovnikov?
hydrohalogenation
acid-catalyzed hydration
Which reactions are anti-Markovnikov?
radical hydrohalogenation
hydroboration-oxidation
Which reactions have syn stereospecificity?
hydrogenation
hydroboration-oxidation
Which reactions have anti stereospecificity?
halogenation
hydrohalogenation
radical hydrohalogenation
What is the result of ozonolysis of an internal alkyne?
2 carboxylic acids
What is the result of ozonolysis of a terminal alkyne?
a carboxylic acid and carbon dioxide
How are alkynes formed from acetylide ions?
they go from terminal to internal alkynes
What is alkylation?
Using NaNH2 to create an acetylide ion, then using a primary alkylhalide to make an internal alkyne
What mechanism is used to make an alkyne from a geminal or vicinal dihalide?
two consecutive E2 reactions
What mechanism(s) are used to make an alkyne from an alkene?
halogenation
elimination