Grade 11 Physics Chapter 7
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
proton
A positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
neutron
An uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
nucleons
Particles in the nucleus of an atom; protons and neutrons.
electron
A negatively charged particle found in the space surrounding the nucleus of an atom.
ground state
State in which all electrons are at their lowest possible energy levels
excited state
State in which one or more electrons are at higher energy levels than in the ground state.
atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus.
mass number
The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
isotope
A form of an element that has the same atomic number, but a different mass number than all other forms of that element.
radioisotope
An unstable isotope that spontaneously changes its nuclear structure and releases energy in the form of radiation.
radiation
Energy released when the nucleus of an unstable isotope undergoes a change in structure.
radioactivity
A process by which the nucleus of an atom spontaneously disintegrates.
nuclear fission
The decomposition of a large, unstable nuclei into smaller, more stable nuclei. Occurs when a highly unstable isotope splits into smaller particles. A power accelerator is used and an atom absorbs a high energy particle (like neutrons). This causes the atom to split. Total binding energy increases during the reaction. Exothermic reaction.
nuclear reaction
The process by which the nucleus of an atom sometimes changes.
electrostatic force
The force of attraction or repulsion due to electric charges.
strong nuclear force
The very strong force of attraction between nucleons.
radioactive decay
The process by which a radioactive atom's nucleus breaks apart and forms different atoms.
alpha decay
Nuclear reaction in which an alpha particle is emitted.
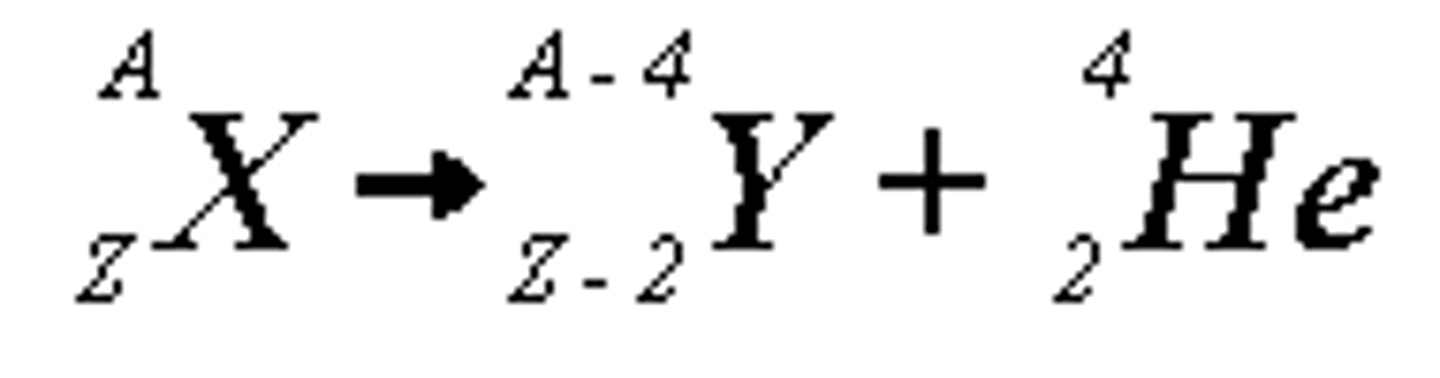
alpha particle
A particle emitted during alpha decay; composed of a helium nucleus containing two protons and two neutrons.
parent atom
The reactant atom in a nuclear reaction.
daughter atom
The product atom in a nuclear reaction.
transmutation
A nuclear decay process in which daughter atoms are different elements from parent atoms.
beta decay
Nuclear reaction in which a beta particle is emitted or captured.
beta particle
A high-energy electron or positron ejected or captured by a nucleus during beta decay.
positron
A particle with a positive charge and the same mass as an electron.
electron capture
A form of beta decay in which an electron is absorbed by a nucleus and combines with a proton to form a neutron.
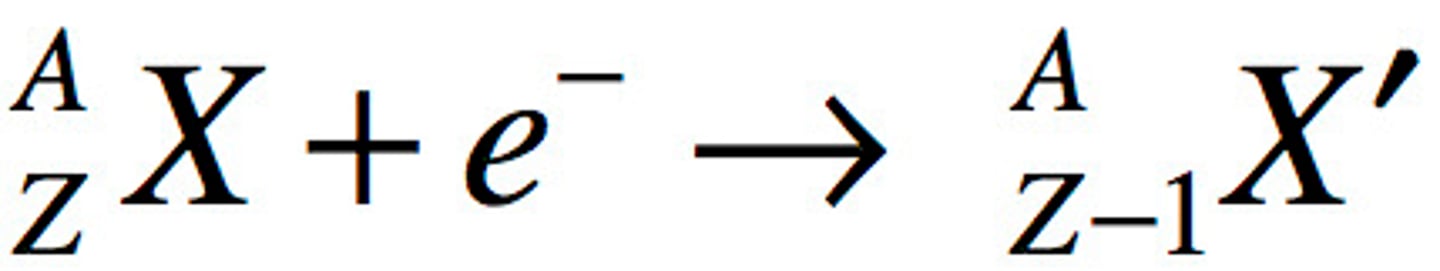
beta-negative decay
Beta decay in which electron is emitted from the nucleus of a parent atom.
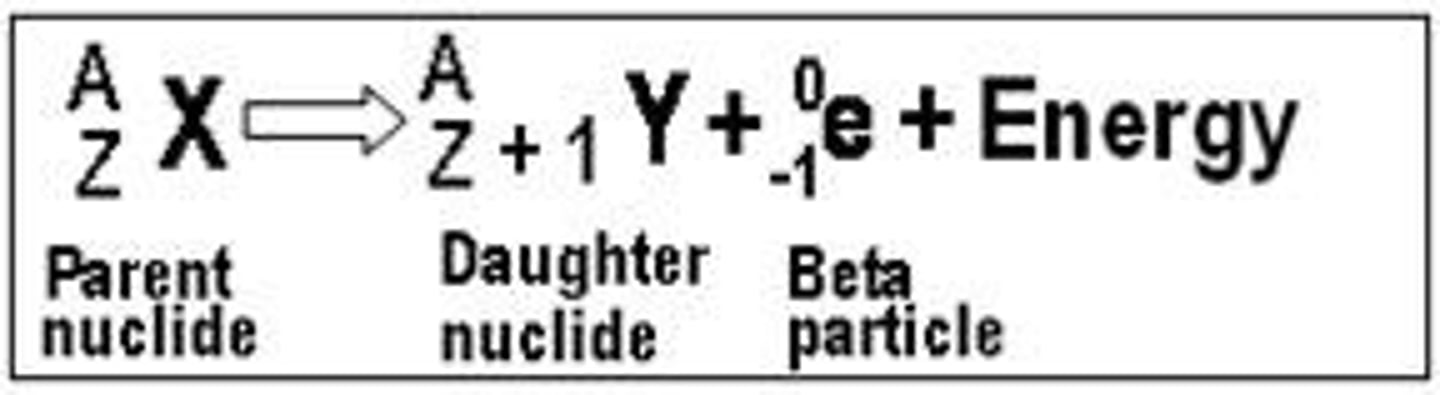
beta-positive decay
Beta decay in which a proton changes into a neutron and a positron.
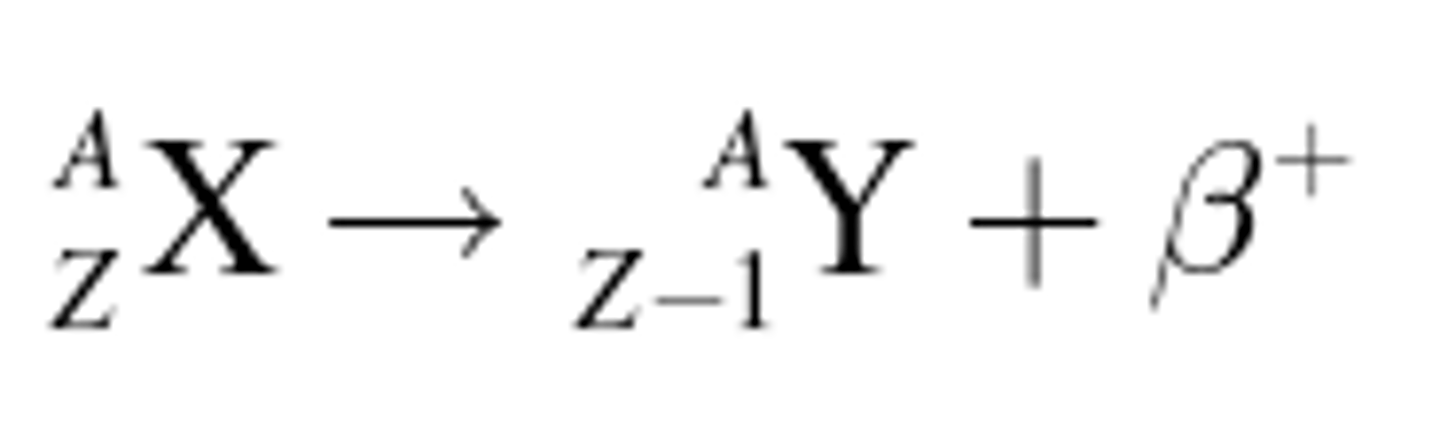
photon
A high-energy particle with no mass.
gamma decay
A reaction in which an excited nucleus returns to a lower, more stable energy state, releasing a very high-energy gamma ray in the process.
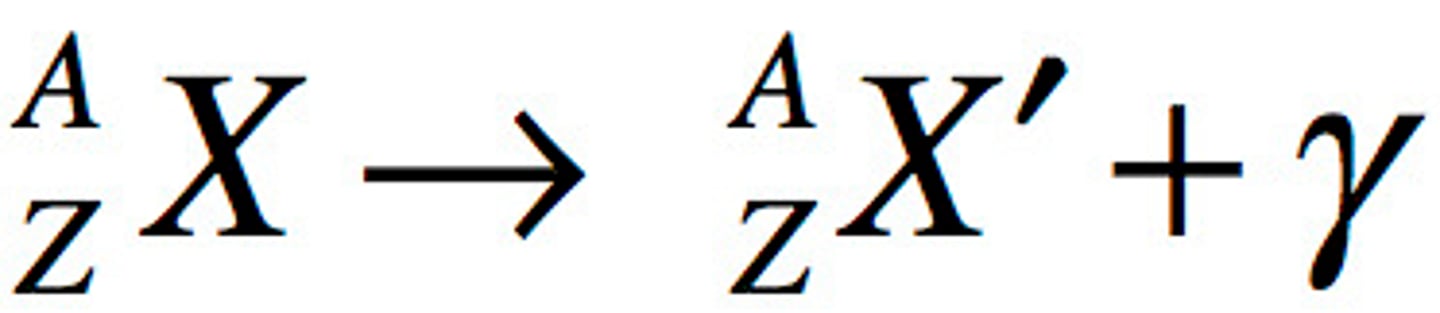
nuclear fusion
A nuclear reaction in which the nuclei of two atoms fuse together to form a larger nucleus. Lighter atoms fuse together to form heavier atoms. Occurs when a target nucleus absorbs an accelerated particle. These reactions require extremely high temperatures but they create HUGE amounts of energy. Total binding energy increases during the reaction. Exothermic reaction. Potential source of clean energy, producing little pollution or waste.
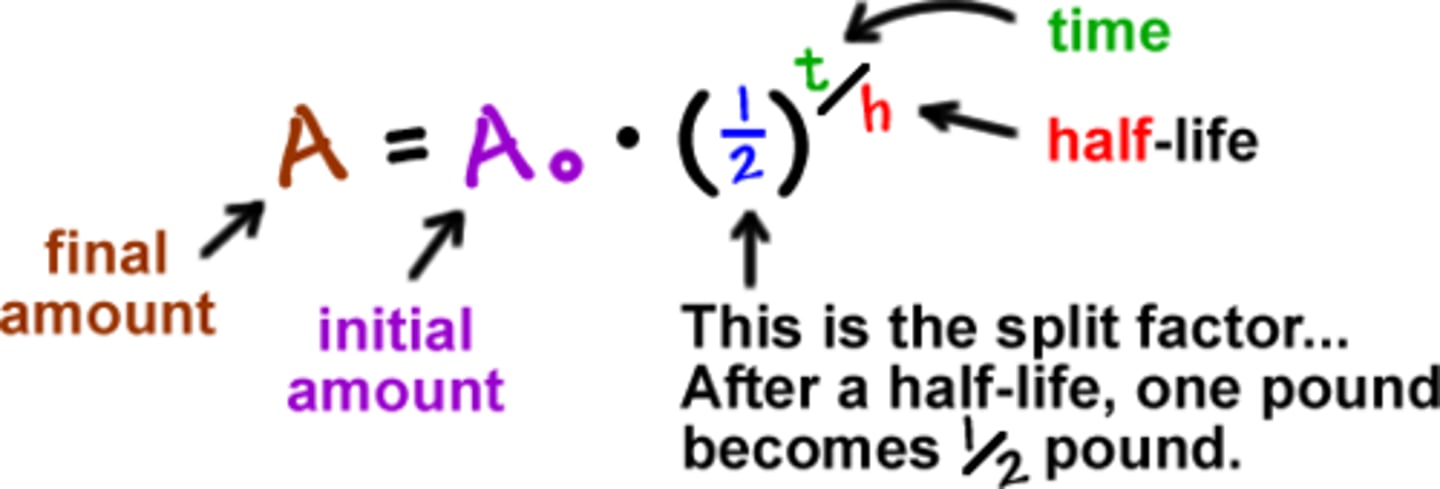
half-life
The average length of time it takes radioactive material to decay to half of its original mass.
atomic mass unit (u)
A unit of mass equal to 1.66 x 10^-27 kg.
mass defect
The difference between the calculated mass of an atom, based on the nucleons and electrons present, and the actual atomic mass.
binding energy
The energy used to hold a nucleus together.
mega-electron volt (MeV)
The energy required to accelerate an atom through a potential difference of 1 million volts.
chain reaction
The repeated series of reactions in which the products of one reaction generate subsequent reactions.
critical mass
Minimum amount of nuclear fuel required to cause chain reaction.
calandria
Core of the reactor, consisting of fuel bundles, control rods, and moderator.
fuel bundles
Fuel elements consisting of uranium pellets.
control rods
Adjustable cadmium rods used to control nuclear reaction rates.
moderator
Heavy water used to slow neutrons and absorb thermal energy.
steam generator
Absorbs thermal energy from the heavy water in the primary loop, producing steam.
primary loop
Closed loop through which heavy water flows.
secondary loop
Closed loop through which normal water, which becomes steam, flows.
CANDU reactor
Canadian made and invented nuclear power plants. Reactor where fission process occurs. Reactor surrounds high energy neutrons with heavy water (water that contains a high level of deuterium) to slow them down and they can be absorbed by another nucleus. The core can be controlled in two ways: coarsely and finely.
stellar fusion
Nuclear fusion in the core of stars due to building temperature and pressure.
proton-proton chain
A type of stellar fusion. Four protons eventually fuse to form one He-4 atom. Two of four protons each become a neutron and a positron.
carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle
A type of stellar fusion for stars significantly larger and hotter than the sun. Activates fusion of hydrogen into helium. Carbon-12 nucleus undergoes nuclear reactions involving fusion and decay. This produces large quantities of energy.
magnetic confinement fusion
Based on principle of magnetic confinement. Deuterium and tritium are placed in the core of the reactor and heated until they become plasma. To achieve plasma confinement, a superconducting electromagnet is placed around the core. When a high current is passed through the coil, a very powerful magnetic field is produced. Theoretically, fusion can occur, however none have yet sustained a chain reaction.
ITER project
First significant international attempt to create a functioning nuclear fusion research reactor. Canada pulled out due to lack of funding. Critics object due to experimental nature of facility.