Chapter 4: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Organic chemistry
the study of all molecules containing carbon
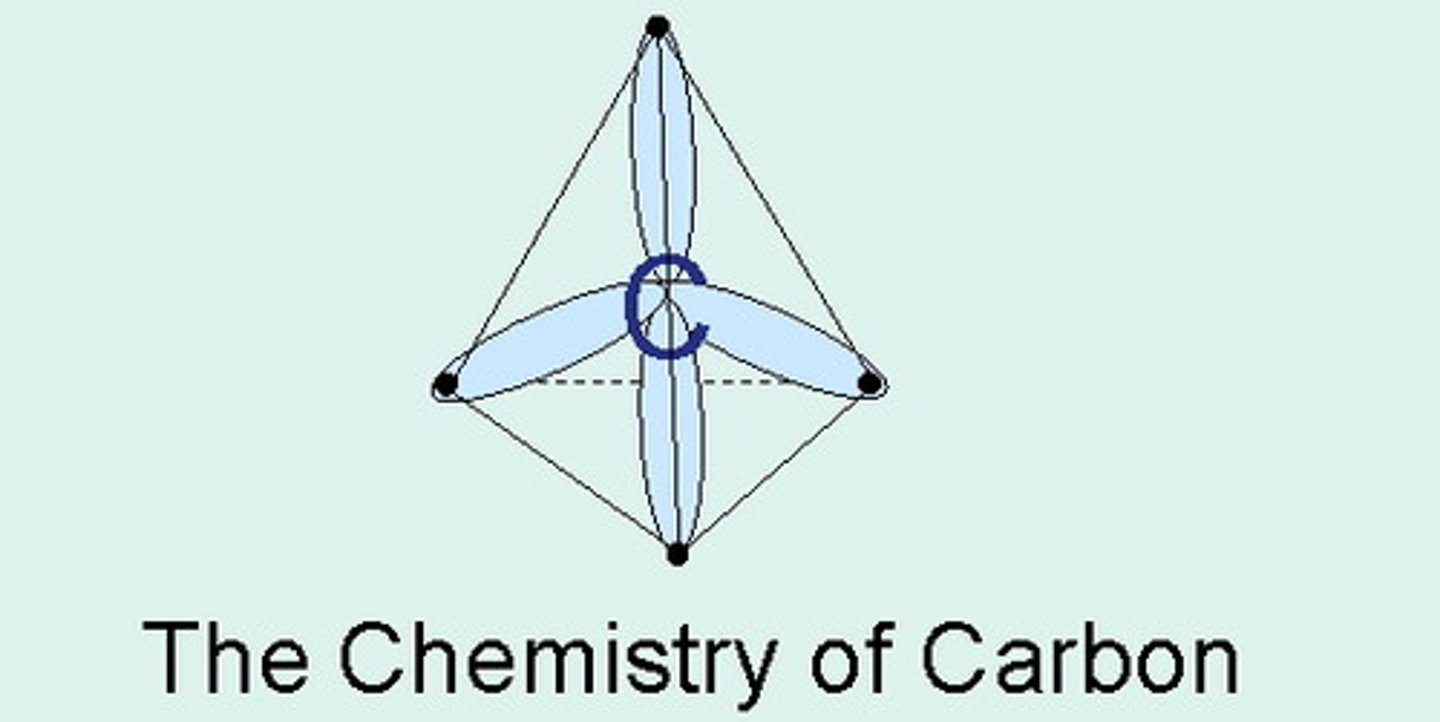
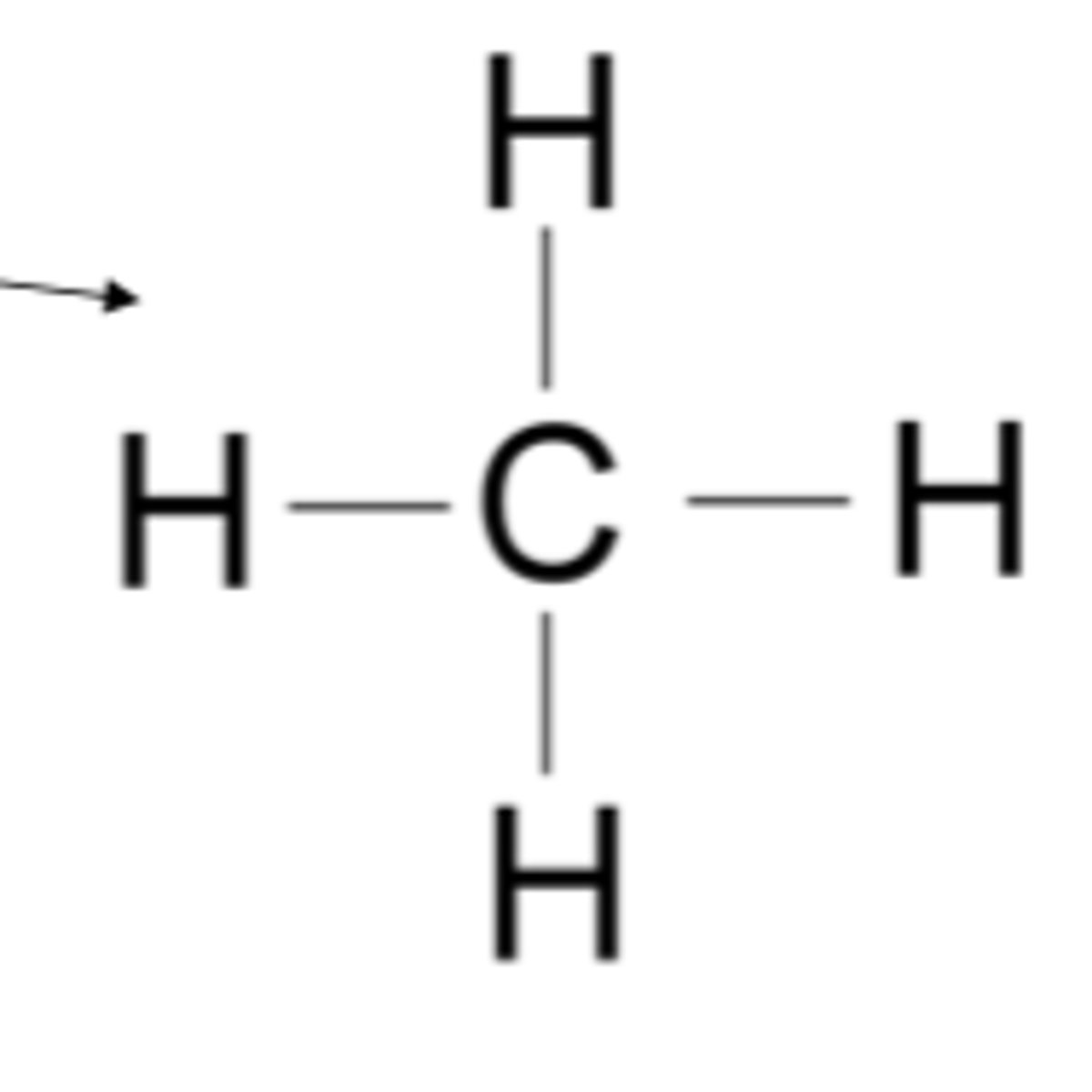
tetravalence
A molecule branching off in four directions; carbon is an example of this, a quality allowing it to be extremely versatile
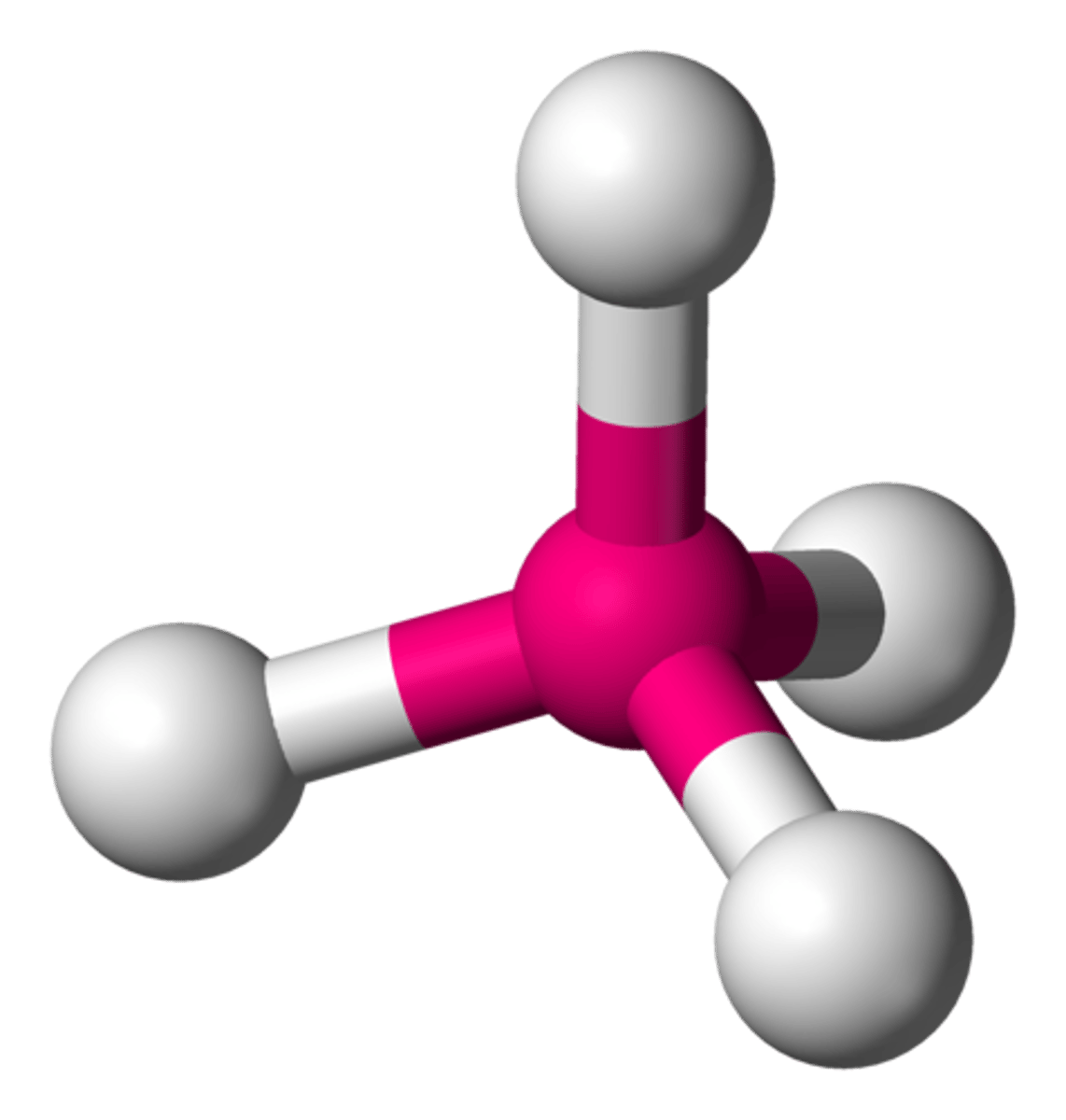
Tetrahedral
the shape of a molecule with four bonded atoms
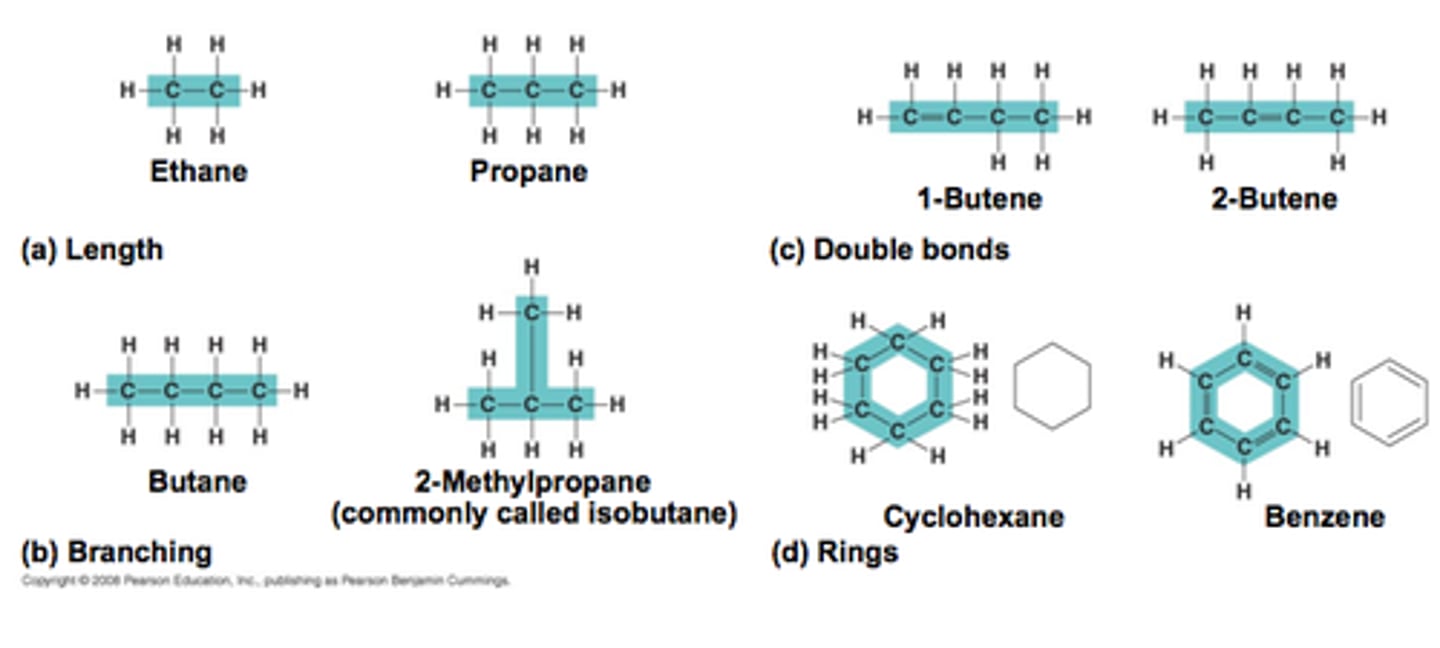
carbon skeletons
provide the basic structures for organic molecules
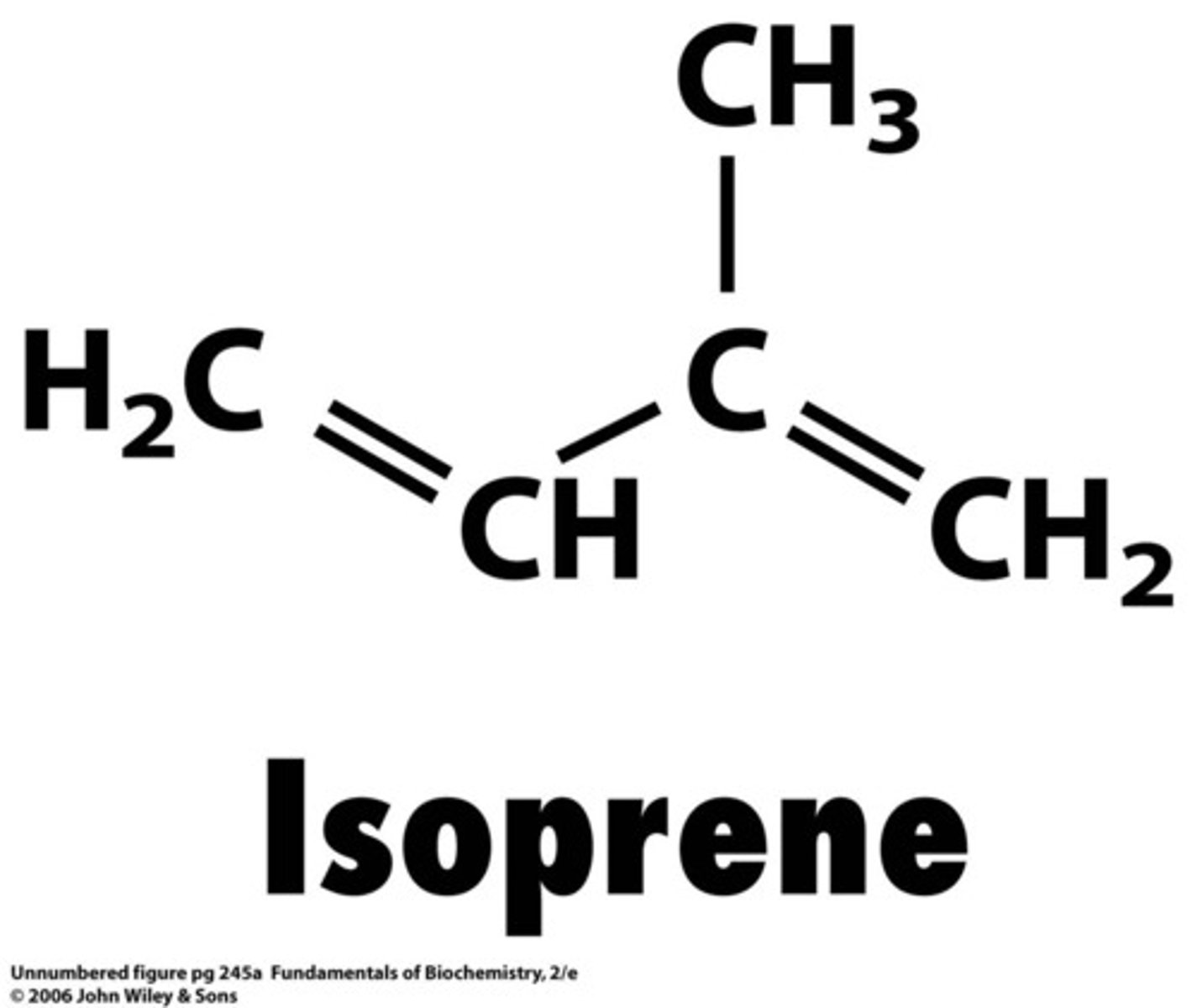
terpenoids
molecules derived from a 5 carbon precursor
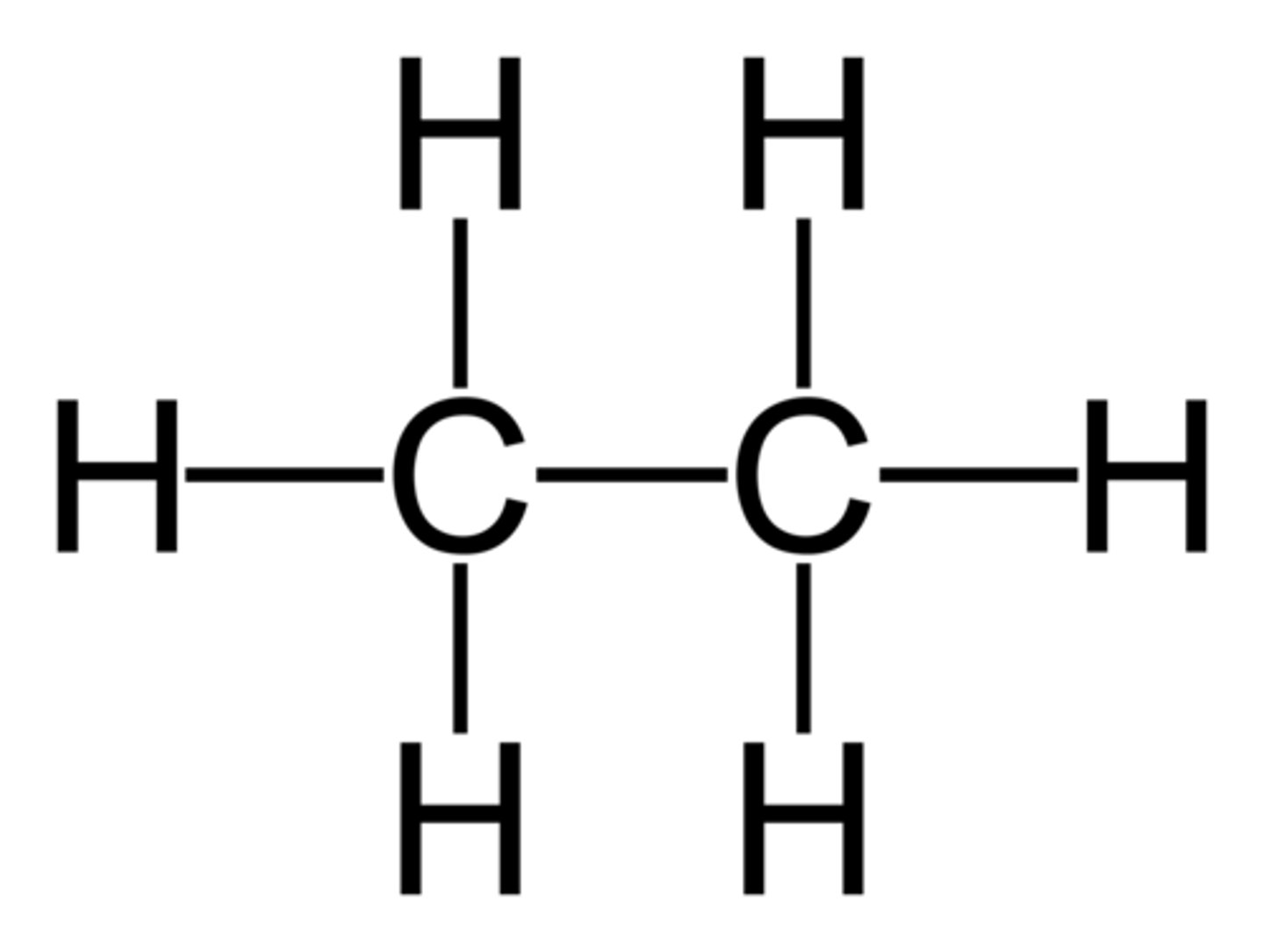
hydrocarbon
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
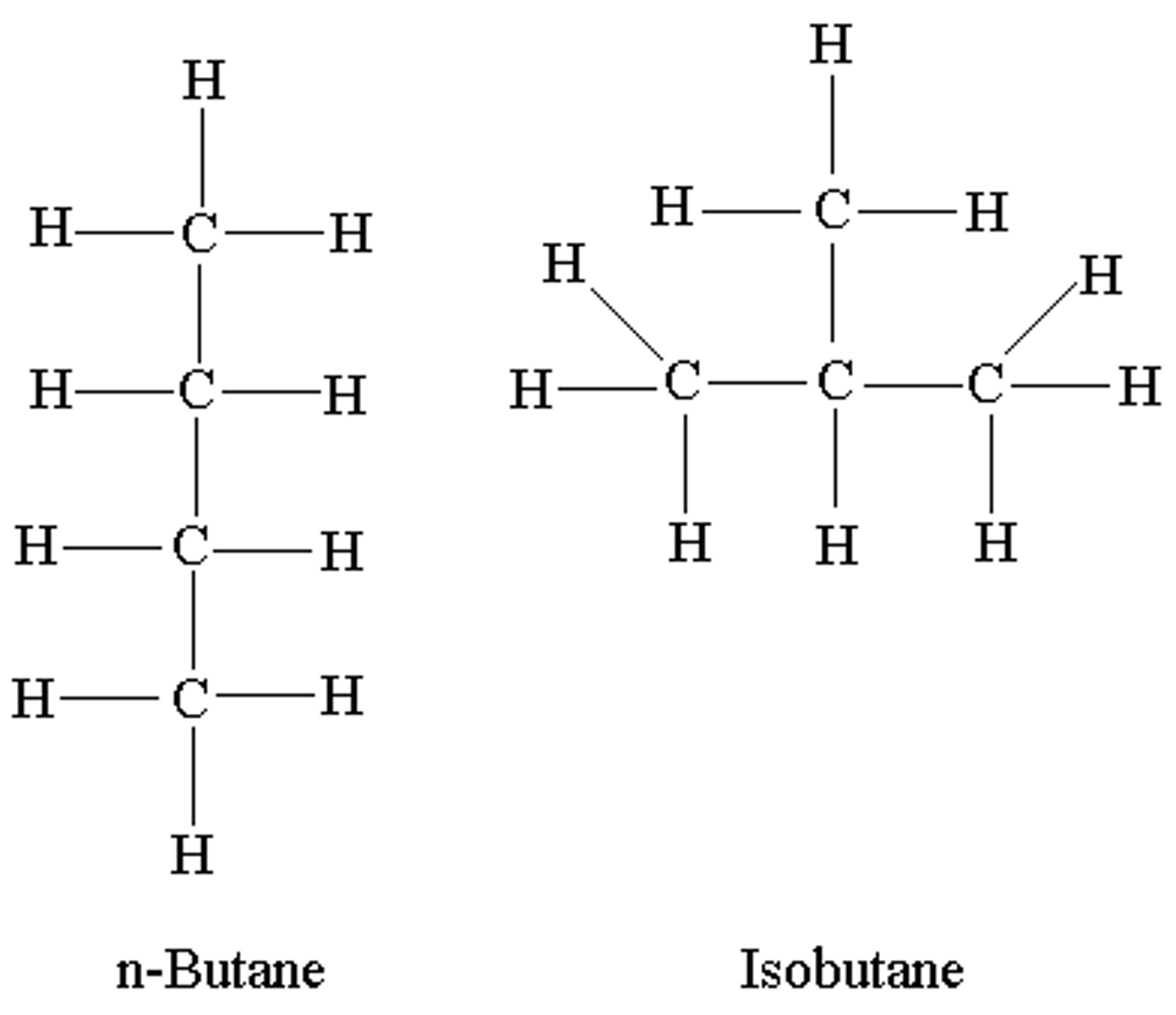
isomer
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
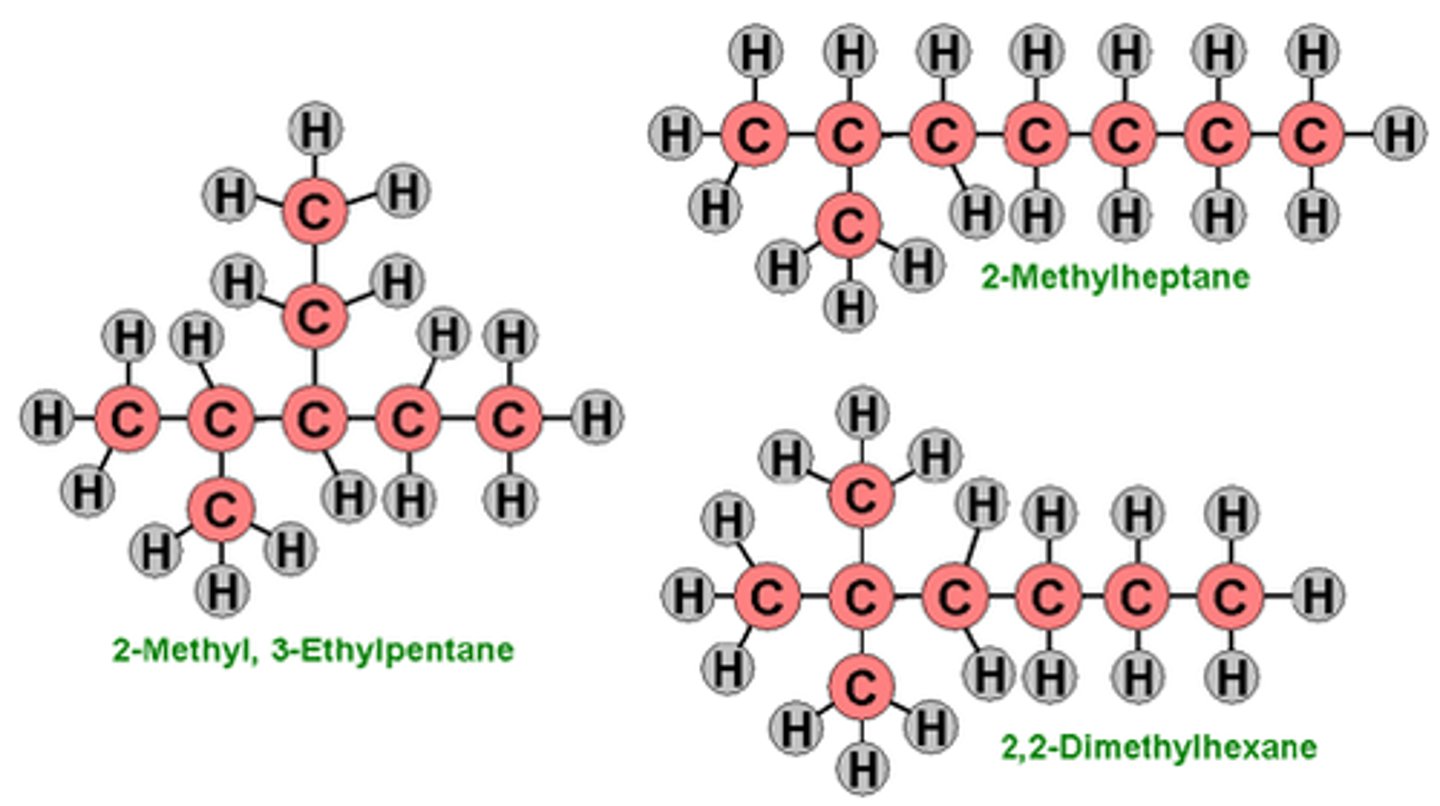
structural isomer
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms.
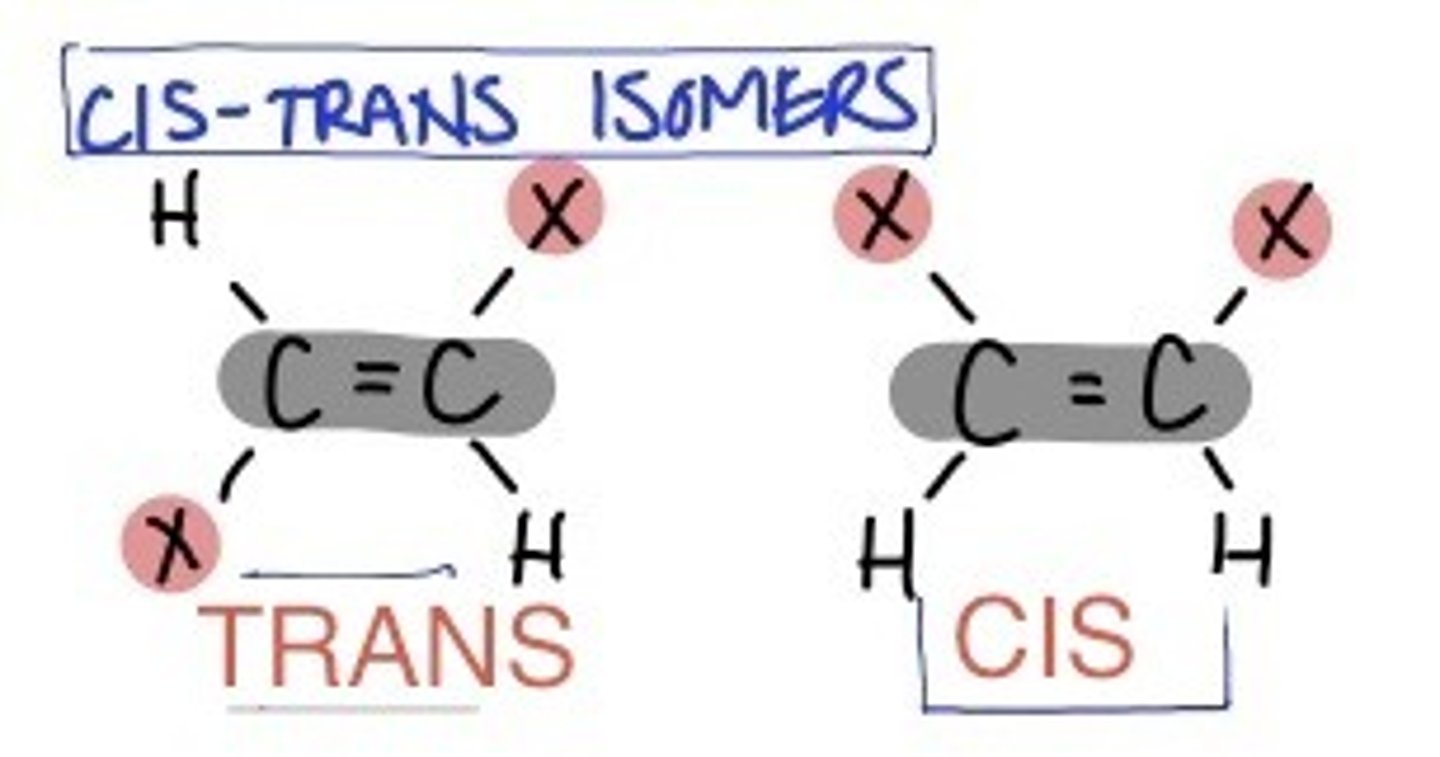
cis-trans isomers
have the same double covalent bond but differ in spatial arrangements
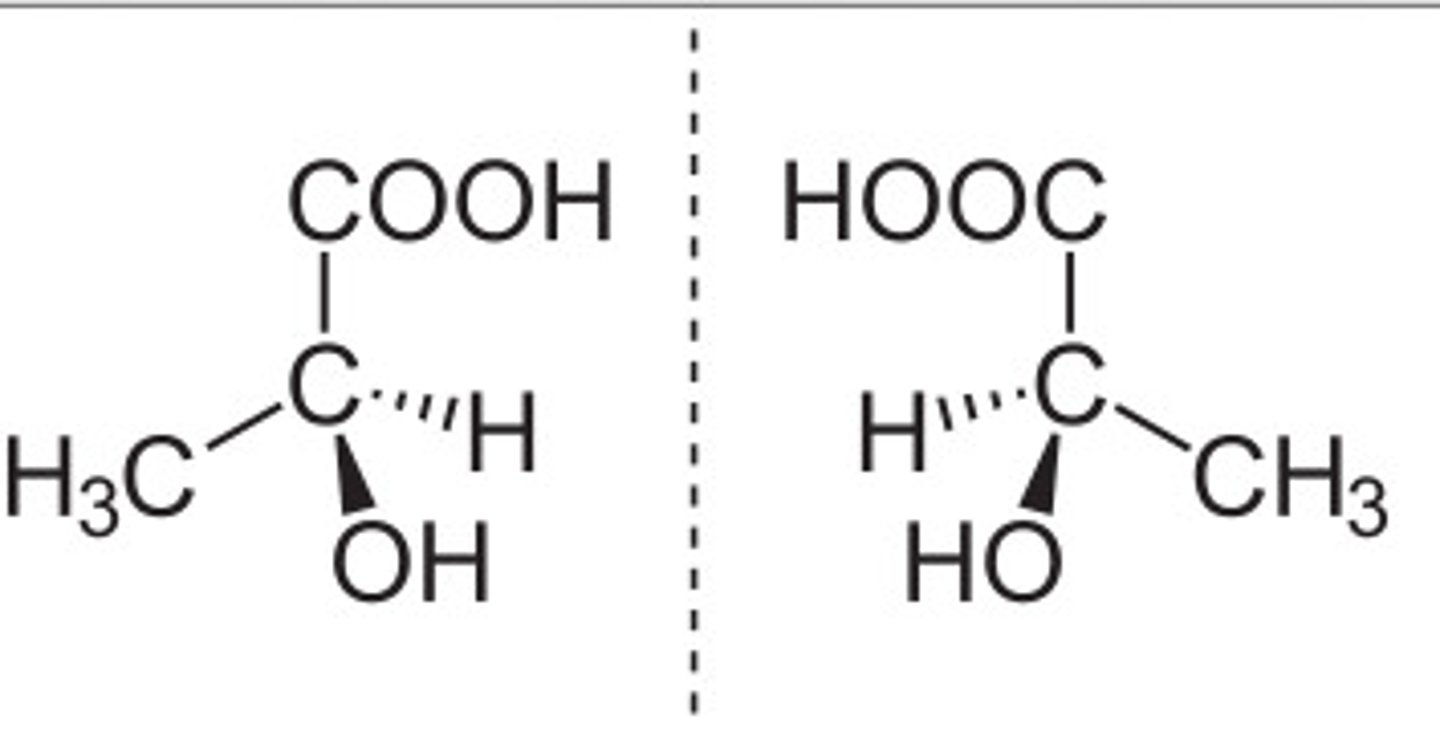
Stereoisomers
opitcal enantiomers; mirror images that cannot be superimposed on each other
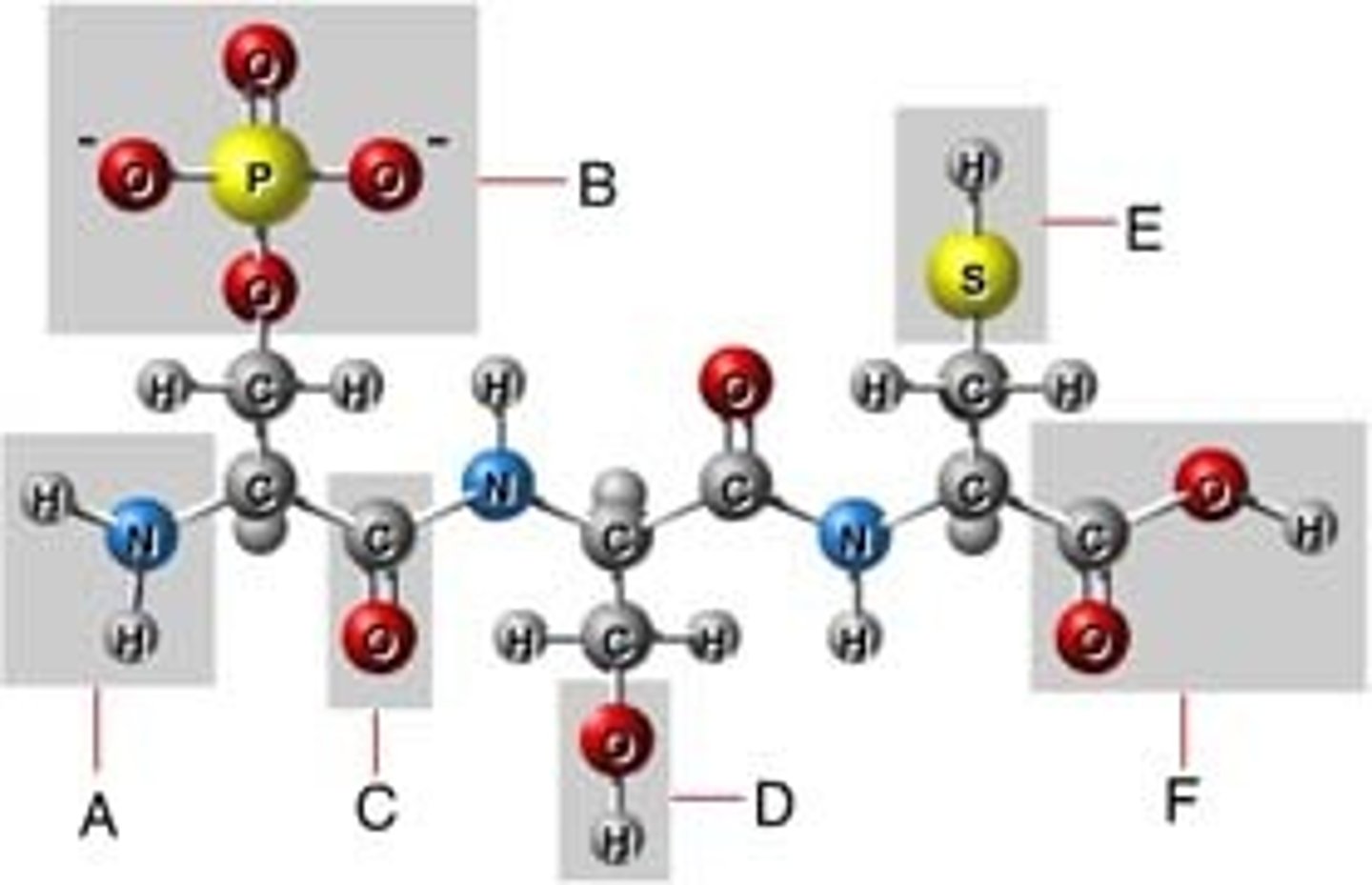
functional groups
the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
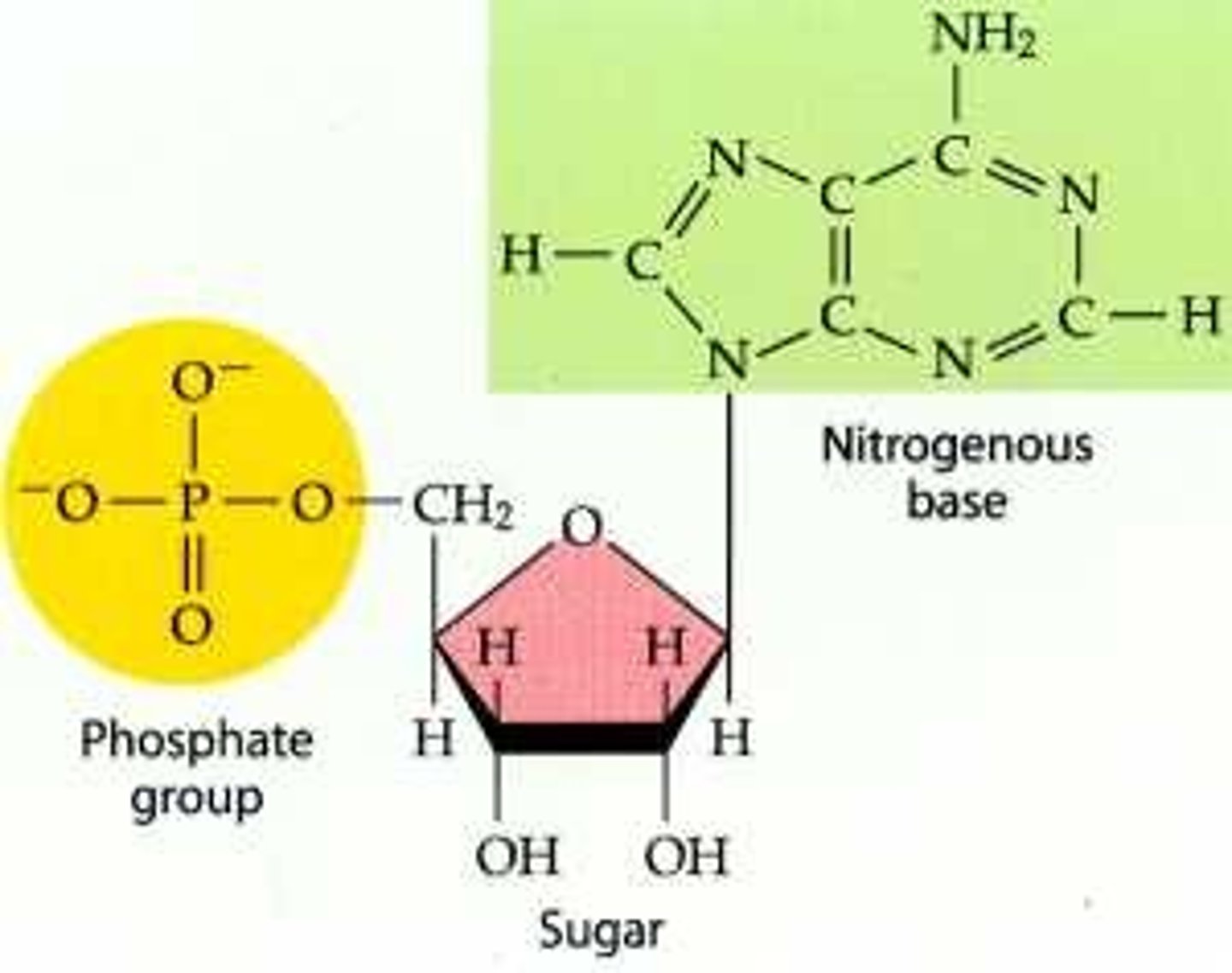
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
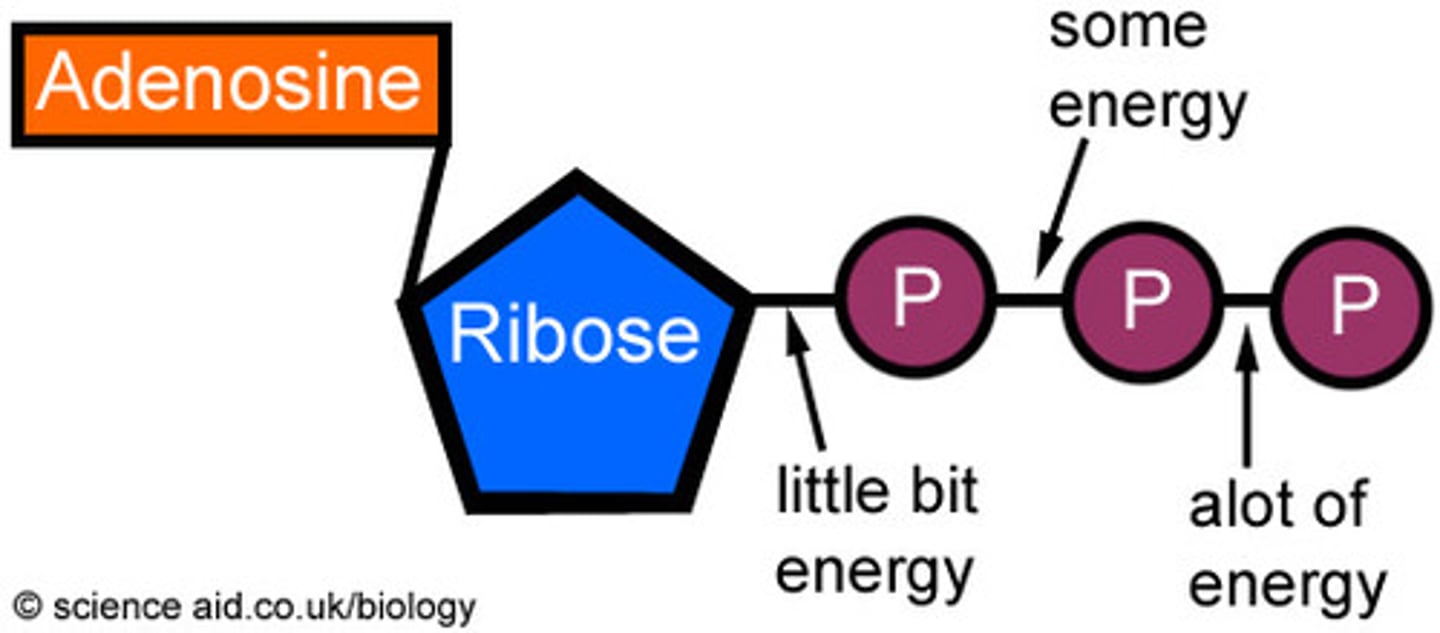
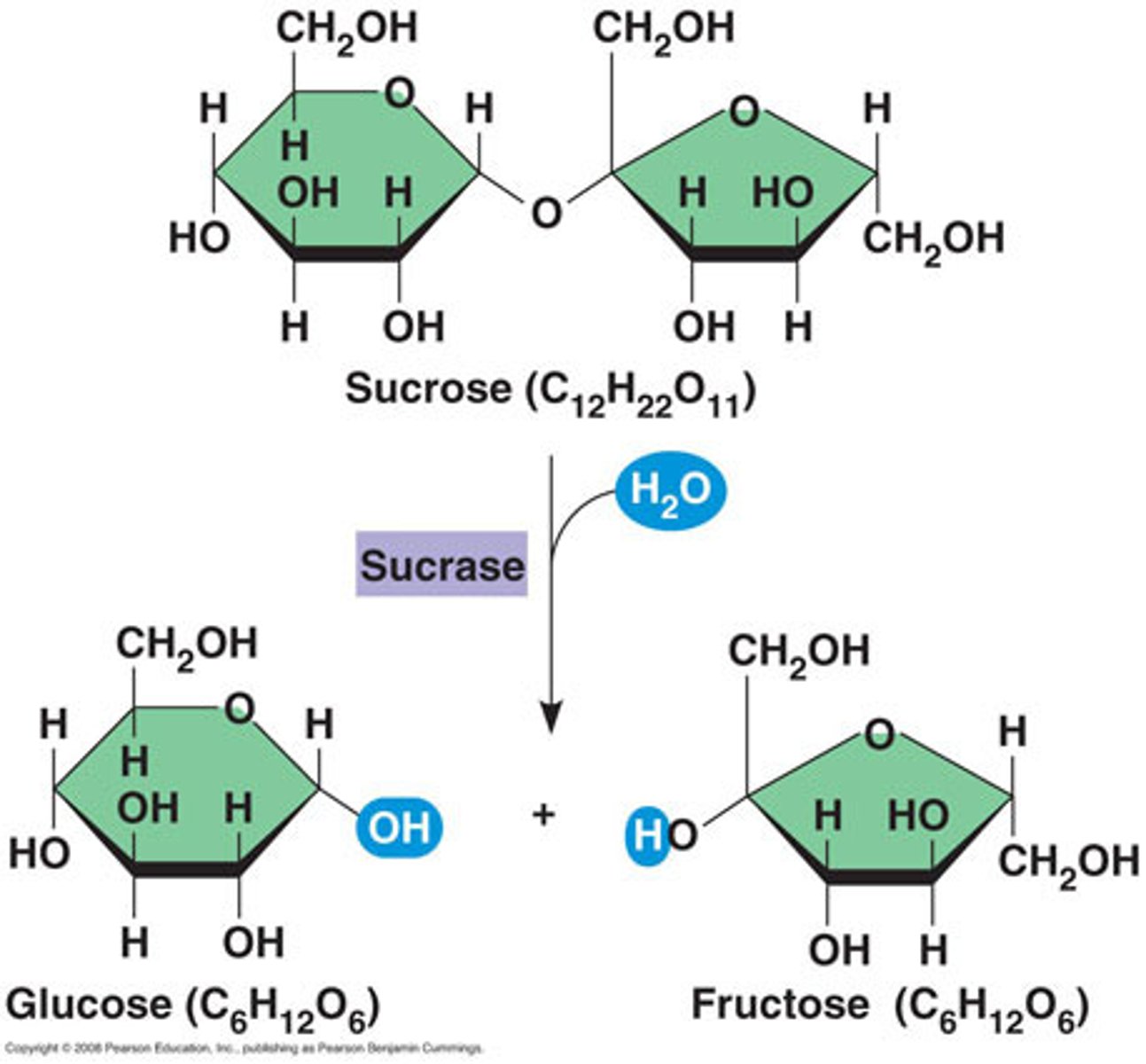
hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water; releases energy
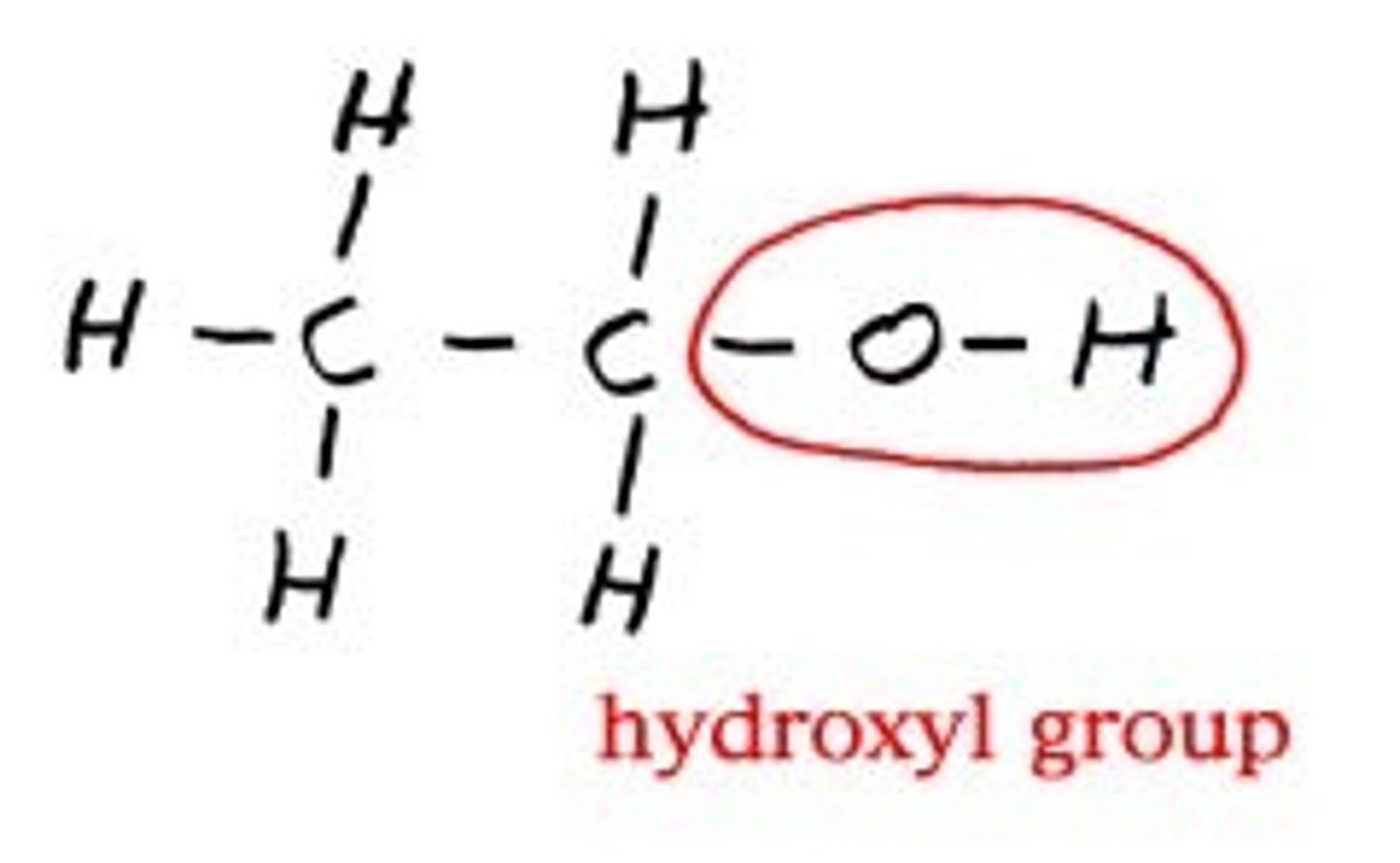
hydroxyl group
A chemical group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
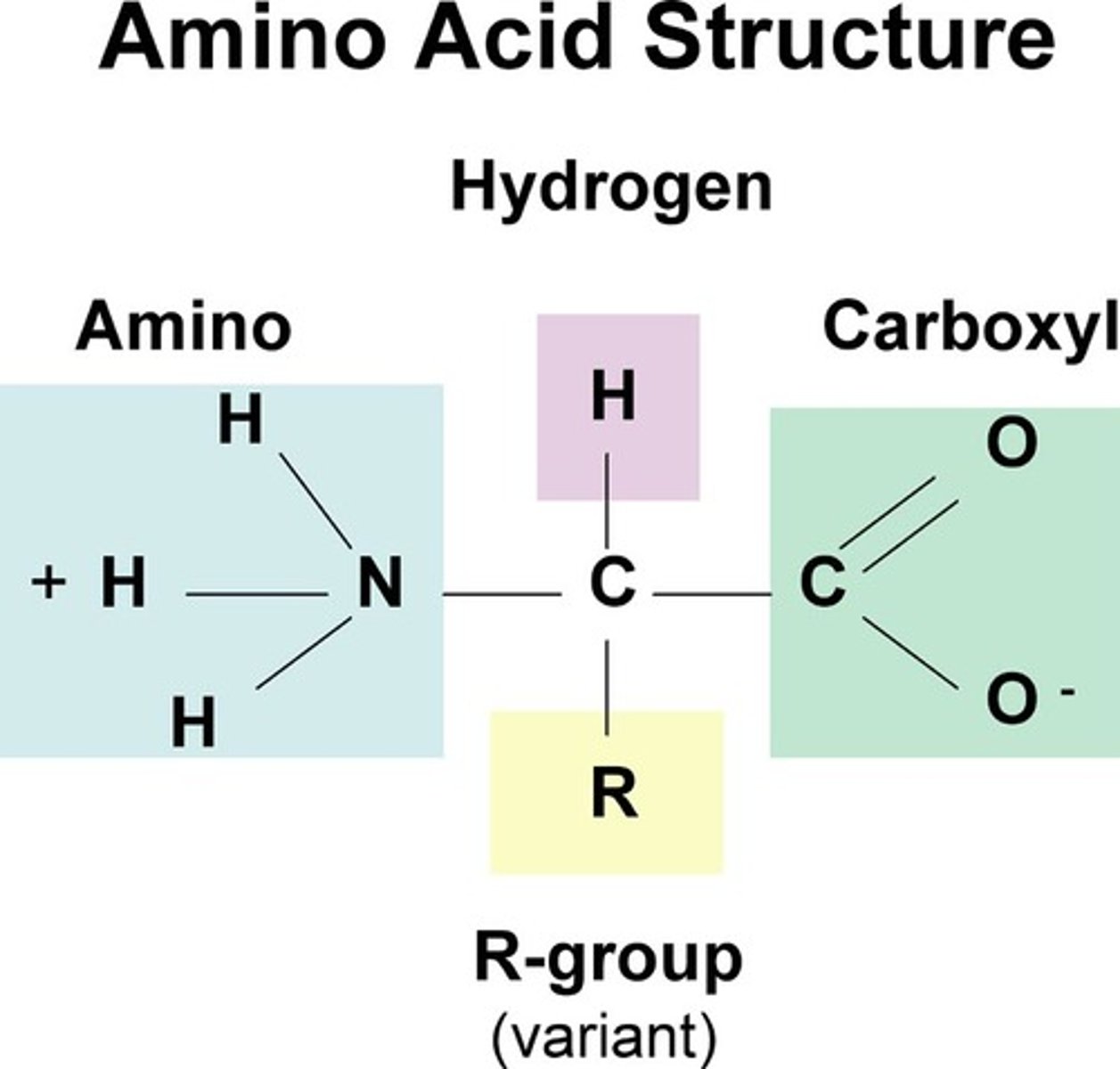
carboxyl group
A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group.
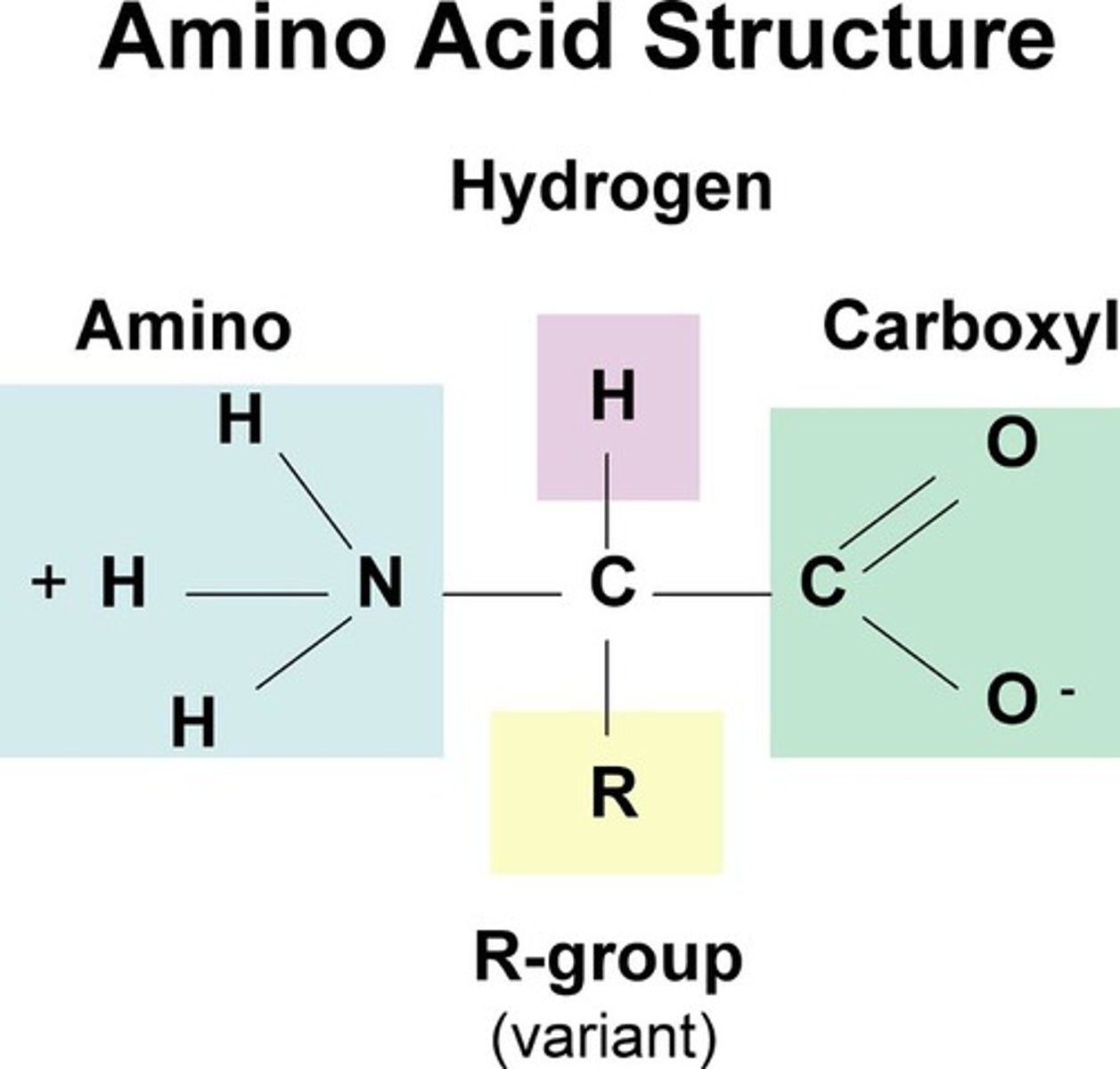
amino group
a functional group consisting of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
phosphate group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms