W6 Crystalline Lens
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
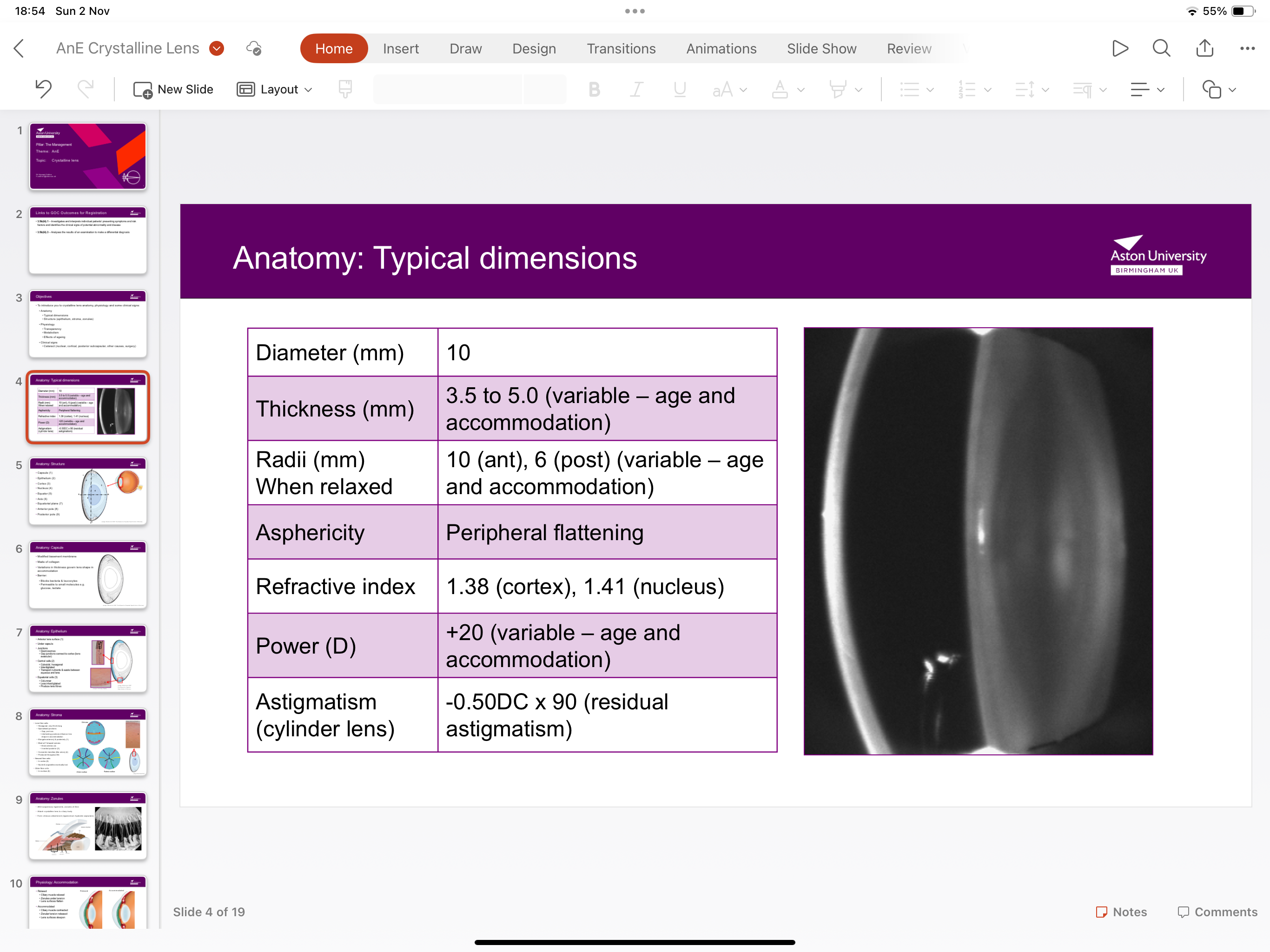
What is the anatomy of the crystalline lens?
Enclosed
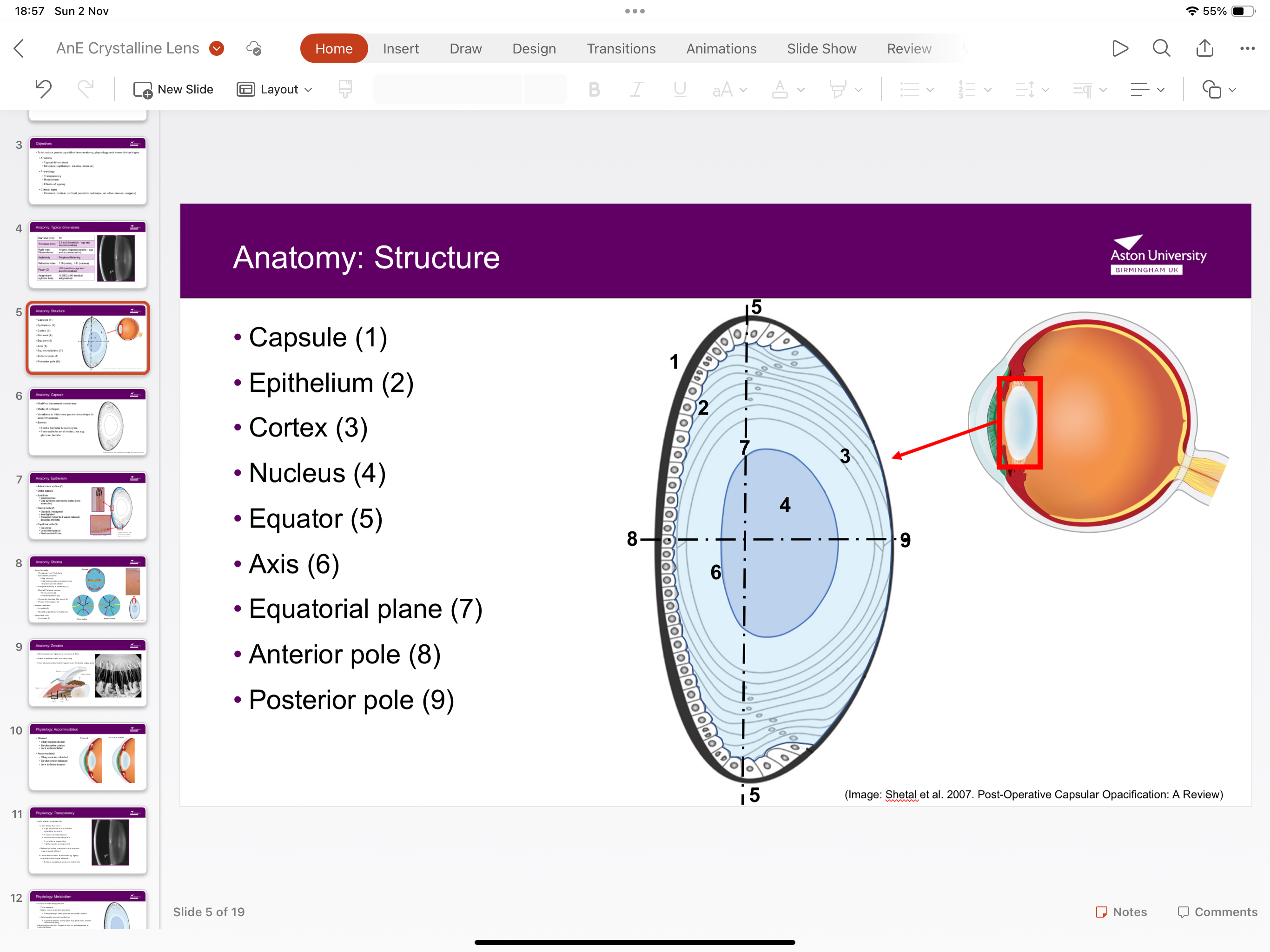
What is the structure of the crystalline lens?
Enclosed
What is the structure of the capsule?
Modified basement membrane made of collagen, thickness varies to govern lens shape in accommodation
What is the function of the capsule?
Blocks bacteria and leucocytes, permeable to small molecules such as glucose and lactate
What is the structure of the epithelium?
Anterior lens surface located under capsule, contains junctions, central cells and equatorial cells
What’s the structure of junctions in the epithelium?
Contains desmosomes, gap junctions connect to cortex
What is the structure of central cells in the epithelium?
Cuboidal, hexagonal, interdigitated, transports nutrients and waste between aqueous and lens
What is the structure of equatorial cells within the epithelium?
Columnar, less interdigiated (less finger-like projections to hold everything together) and produce less lens fibres
What happens to cells in the epithelium as they move closer to the centre?
Cells become more columnar as they move towards centre- taller than they are wider
What is the structure of the stroma?
Contains lens fibre cells, with newest fibre cells in the cortex and older fibre cells in the nucleus, concentric lamellae structure (layers), produced throughout life
What is the structure of lens fibre cells within stroma?
fibre cells are hexagonal, thin and long, elongate anteriorly and posteriorly meeting at Y shape structures,containing specialised junctions
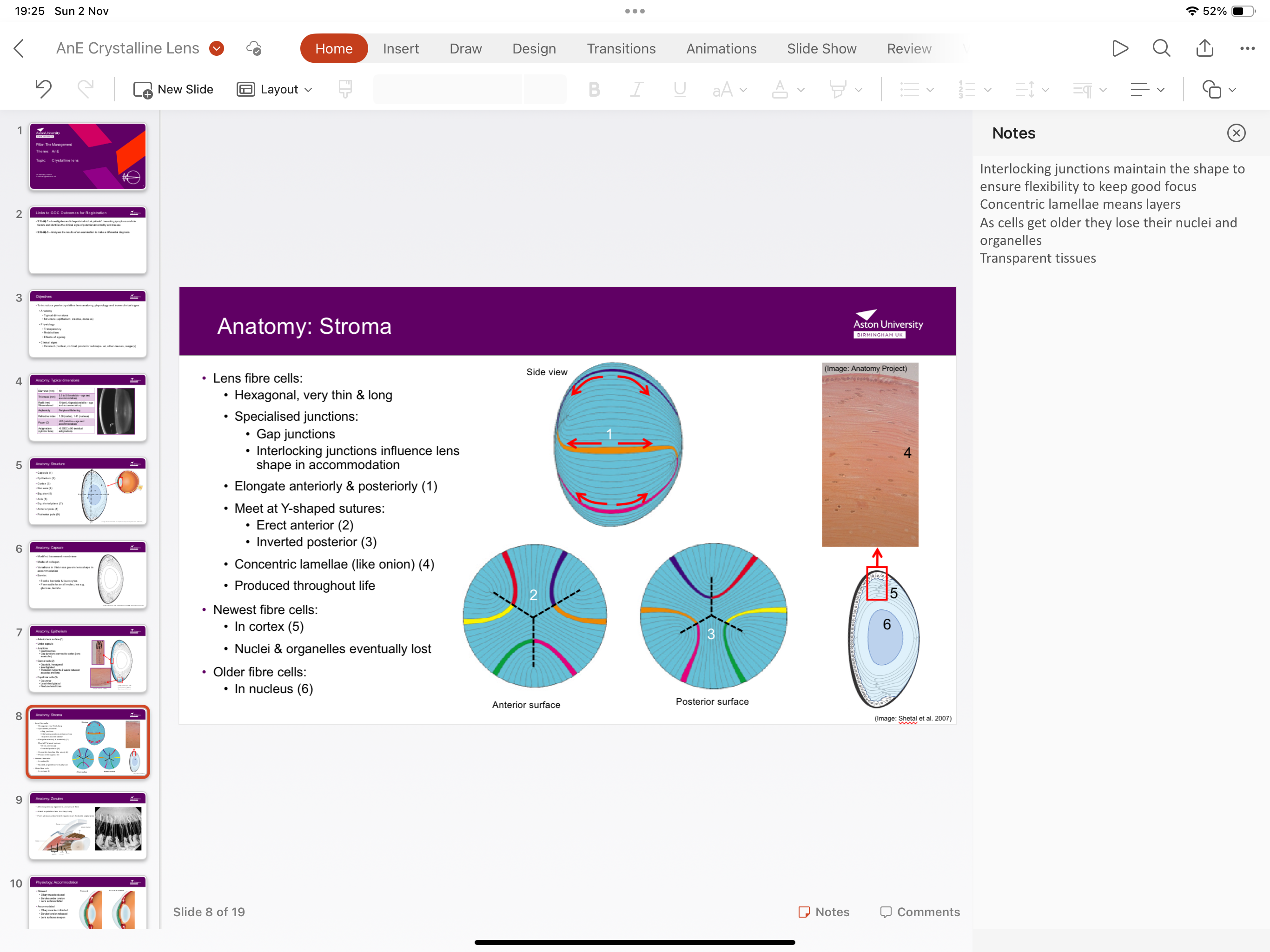
What’s the structure of specialised junctions in stroma?
Gap junctions with interlocking junctions influencing lens shape in accommodation
What is the function of interlocking junctions in stroma?
Maintains the shape to ensure flexibility to keep focus
What happens to lens fibre cells as they get older?
They lose their nuclei and organelles
What is the function of Zonules of Zinn?
Holds the lens in position and are lined around the equator
What is the structure of Zonules of Zinn?
Attaches crystalline lens to ciliary body and forms vitreous attachment
What happens accommodation occurs?
Ciliary muscles contract, Zonules slacken and lens surface steepens
What happens when there’s no accommodation occurring?
Ciliary muscles relax, Zonules are under tension and lens surface flattens
How does the structure of lens fibres minimise lens scatter?
Lens fibres have high concentration of soluble crystallins, narrow cell membranes, minimal extracellular space, no nuclei/organelles, highly regular arrangement of fibres in extracellular space
What does crystalline lens allow?
Allows light to pass through unobstructed
How is the low water content of the crystalline lens maintained and regulated?
Tightly regulated electrolyte balance by sodium potassium pump in epithelium which manages cell potential and regulates how much water is in the lens
How is oxygen obtained?
Some oxygen is obtained from aqueous which is used for high metabolic activity like the pump
What are other pathways used to obtain oxygen?
Mainly anaerobic glycolysis but alternatively pentose phosphate, sorbitol
Where does the highest metabolic activity occur?
Epithelium- te of lens fibre production, sodium potassium pump
How is oxygen harmful for tissue?
Hydrogen peroxide may form during aerobic respiration- causing damage to proteins and membrane- leading to cataract and macular degeneration
How does the crystalline lens prevent oxygen damage?
Has natural antioxidants to prevent tissue damage from ROS (free oxygen radicals) and H2O2 as well as vitamin A, C and E
What are the metabolic effects of aging?
Reduced bioactivity of anti-oxidants and hexokinase
What are the molecular effects of ageing?
ROS modify lens proteins, crystallins become insoluble, causing them to come out of solution and become opaque
What are the structural effects of ageing?
Lens fibres added throughout life, lens becomes less pilable (presbyopia), reduced sodium potassium pump activity leads to increased water intake, losing cell nuclei and organelles causes reduced metabolic activity as ROS changes structure of proteins
What are the optical effects of ageing?
Increased scatter due to insoluble crystallins and water uptake, increased brunescence (chromophores)/lens go brown
What is nuclear cataract?
Nuclear oppalescence (white scatter) due to crystallin aggregation (coming out of solution)
Nuclear brumenescnece due to chromphore aggregation
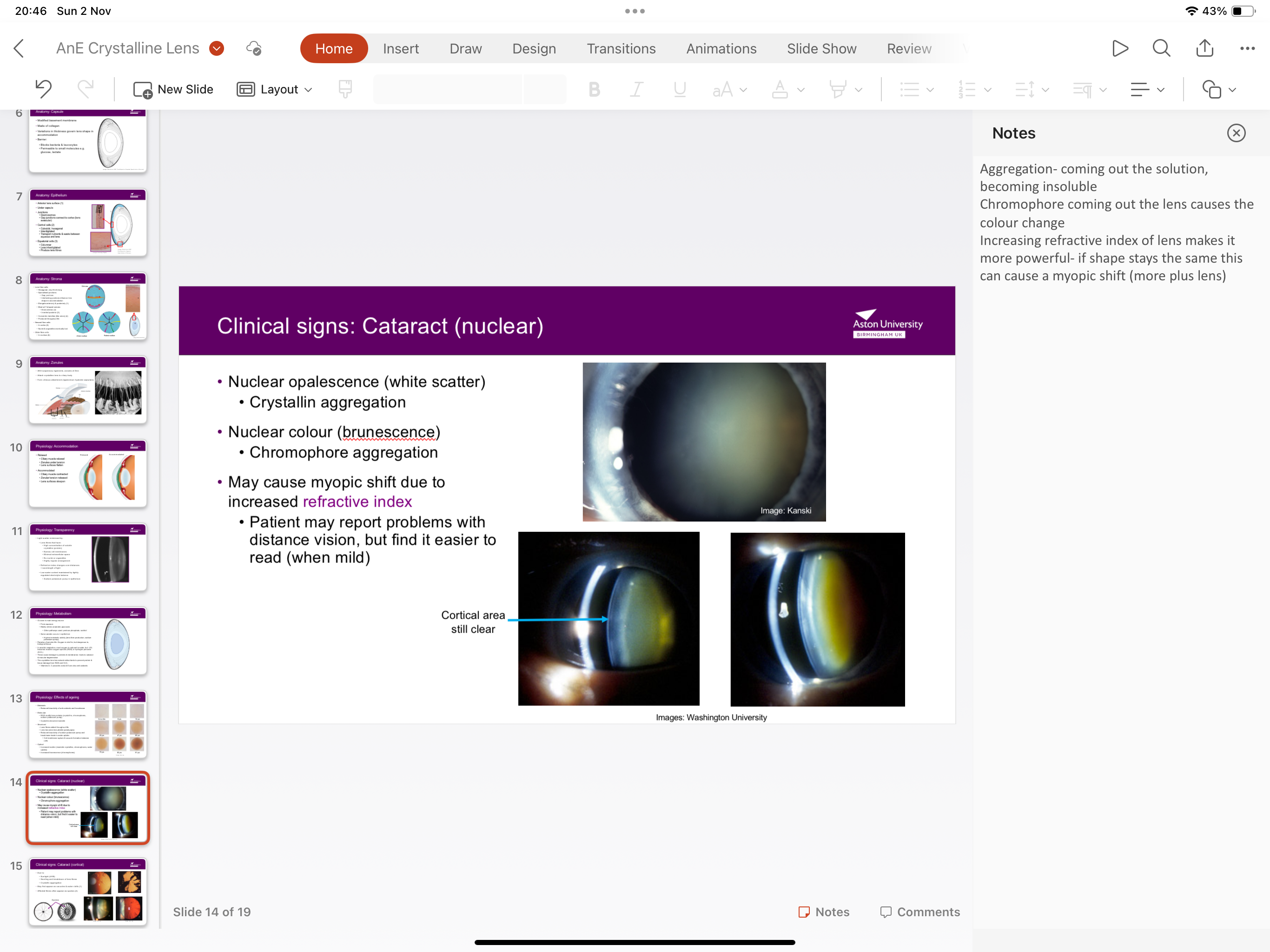
What is the effect of nuclear cataract?
May cause myopic shift due to increased refractive index of lens, making it more powerful (+ve)
What are symptoms of myopic shift?
Patients report problems with distant vision but find it easier to read (when mild)
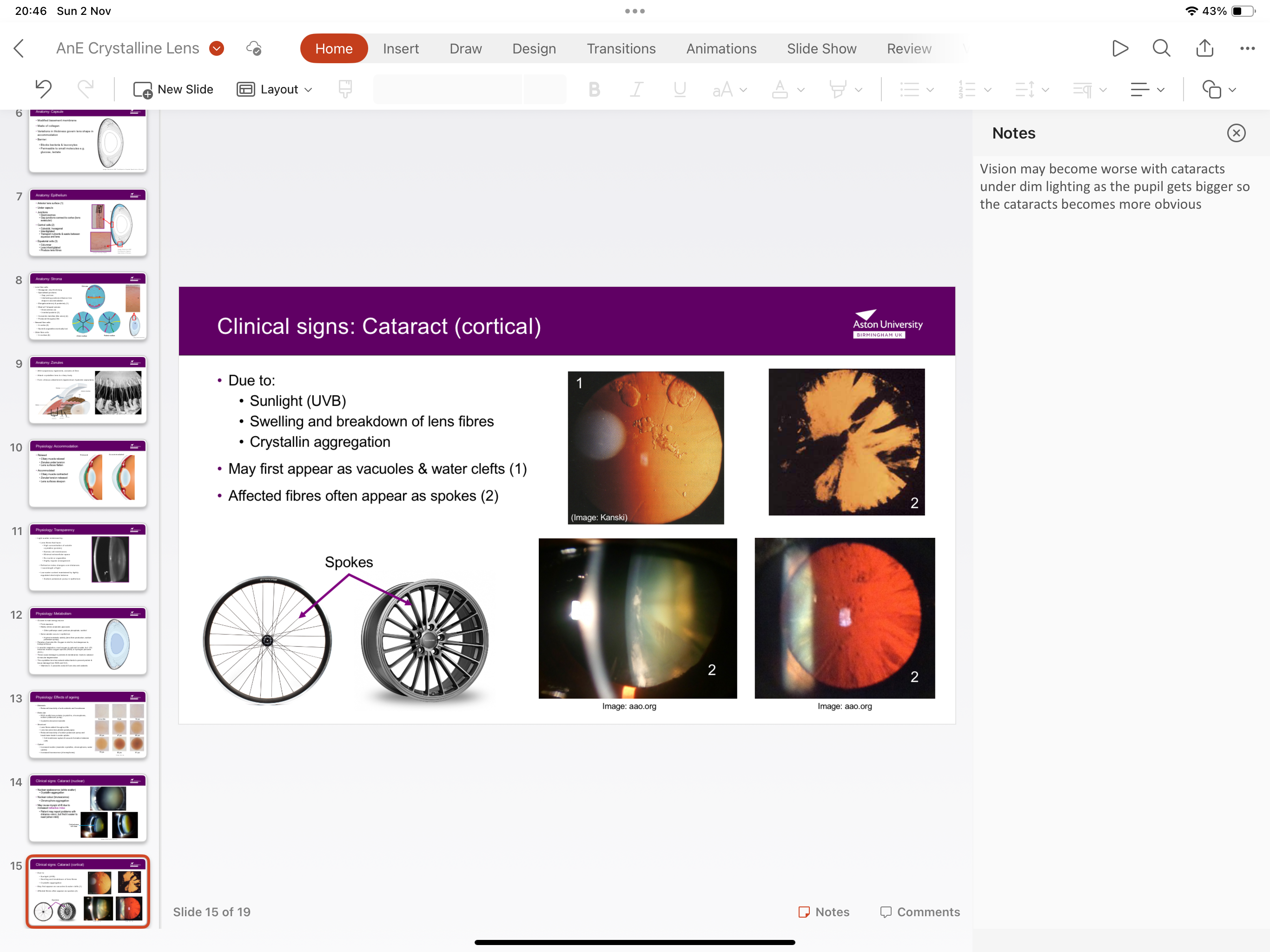
What is cortical cataract?
Due to sunlight, breakdown and swelling of lens fibres, and crystallin aggregation
What are symptoms of cortical cataract?
May first appear as vacuoles and water clefts, excited fibres often appear and stokes.
Vision becomes worse under dim lighting as pupil diabetes so cataract becomes more obvious
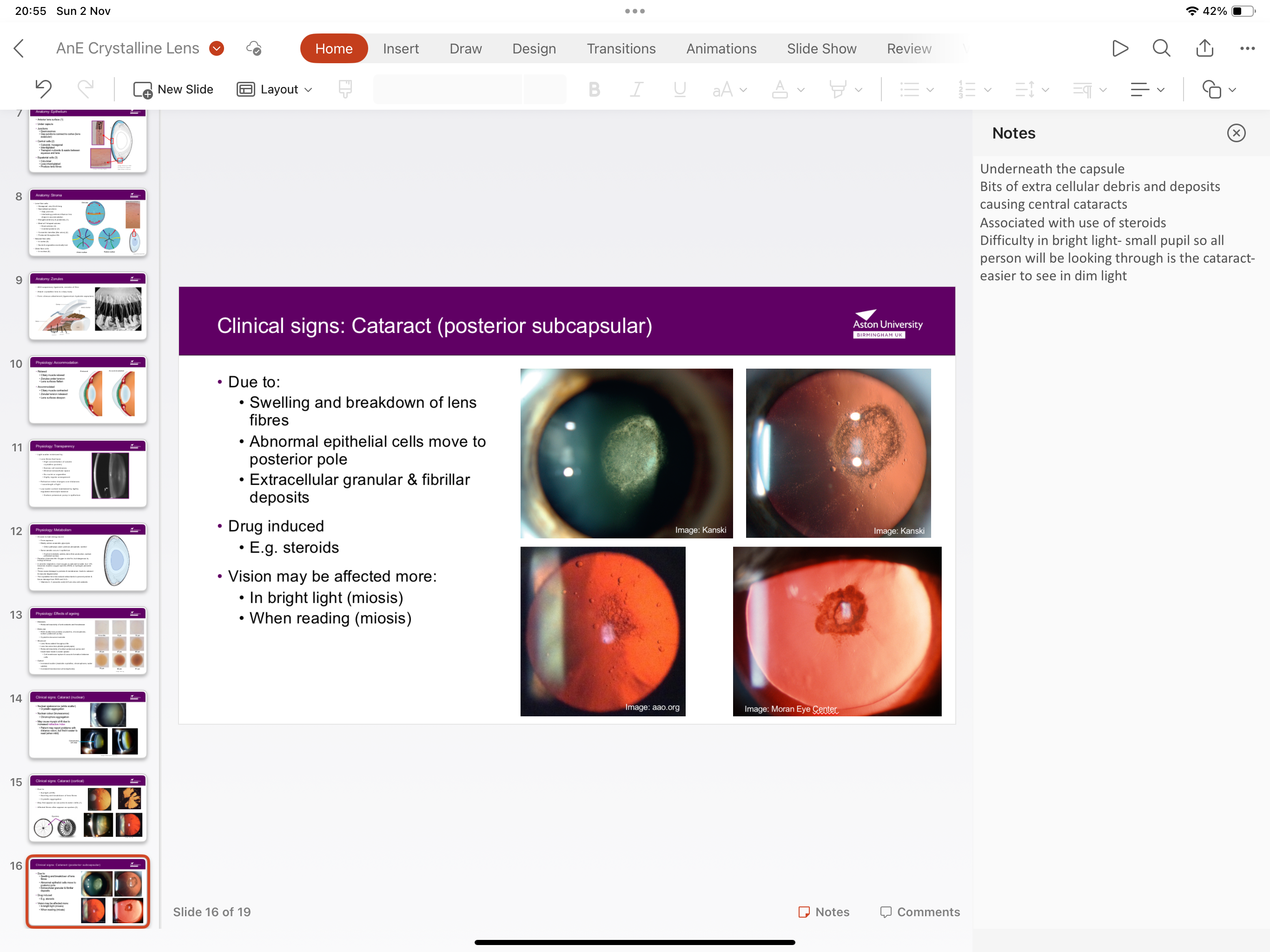
What is posterior subcapsular cataract?
Due to breakdown and swelling of lens fibres, normal epithelial cells move to posterior poles, extracellular debris and fibrillar deposits causing central cataracts, drug induced (steroids)
When is vision more affected with posterior subcapsular cataract?
Bright light- pupil constricts so patient is just looking through cataract, and when reading
What are other causes of cataract?
Diabetes- high blood glucose encourages sorbitol pathway which is too big to move back out of lens capsule eating to water uptake, increase in refractive index and myopic shift, leading to cortical vacuoles and nuclear cataract
Down’s syndrome- cataracts in late childhood
Trauma/radiation/high myopia
What does cataract surgery entail?
Small limbal incision, portion of anterior surface of capsule removed, probe breaks up and removes cloudy lens, intraocular lens inserted into capsular bag
How is cataracts generally caused?
Damage to lens proteins and fibres by reactive oxygen species (ROS)