PROTEINS PT.2
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Plasma Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What are the two most commonly measured plasma proteins
Albumin
Globulins
What are the most frequently analyzed proteins?
Plasma Proteins
What are the four different measurements typically requested by physicians from patients with LIVER Failure or KIDNEY FAILURE:
Total protein
Albumin
Globulins
Albumin/Globulin (A/G) ratio
Prealbumin is also known as?
Transthyretin (TTR)
This is a transport protein for thyroxine (T3) and triiodothyronine (T4)
Prealbumin
A protein that is a sensitive marker of poor nutritional status
Prealbumin
What is the half life of a prealbumin?
2 days
Determine whether the albumin levels will be increased or decreased in the following conditions:
Patients under steroids medication
Tissue Necrosis
Chronic Renal Failure
Hepatic Damage
Acute Phase Inflammatory Response
Alcoholism
Increased
Decreased
Increased
Decreased
Decreased
Increased
Considered to be the most abundant plasma protein.
Albumin
This plasma protein act as a water magnet to maintain osmotic pressure within blood vessels.
Albumin
Protein responsible for plasma colloidal osmotic pressure.
Albumin
TRUE OR FALSE
Albumin is a positive acute phase reactant
FALSE - it is a negative ACR
This globulin inhibits the enzyme released from leukocytes to fight infection.
⍺1-Antitrypsin (AAT)
Mutation of what gene can lead to deficiency of α1–antitrypsin protein?
SERPINA 1
A protein which is synthesized in the developing embryo and fetus and by parenchymal cells of the liver
⍺11-Fetoprotein (AFP)
The primary clinical significance of this protein is to be a tumor marker in adults, aiding in cancer detection.
⍺11-Fetoprotein (AFP)
This protein protects the fetus from immunologic attack by the mother.
⍺11-Fetoprotein (AFP)
TRUE OR FALSE:
An increased levels of AFP in mother also increases the risk for Down Syndrome.
FALSE
This protein serves as an indicator of neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
Alpha Feto Protein (AFP)
TRUE OR FALSE
Elevated AFP levels may lead to trisomy 18 or otherwise known as Edward’s syndrome.
FALSE
a tumor marker for chronic liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
AFP-L3
A protein that is useful in diagnosing neonates with bacterial infection
⍺1-Acid Glycoprotein (Orosomucoid)
What is the normal value of the protein which is used as a diagnostic tool in neonates to check the presence of bacterial infection?
50-120 mg/dL
This protein is associated in patients with Alzheimer’s disease
⍺1-Antichymotrypsin
Mutations of this protein are identified in patients with Parkinson’s disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
⍺1-Antichymotrypsin
This protein increases in heavy or chronic smokers.
⍺1-Antichymotrypsin
This protein play a role in inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Inter-⍺-trypsin Inhibitor (ITIs)
Major carrier protein of vitamin D and its metabolites in the circulation
Gc-globulin
This protein is primarily elevated in patients taking up oral contraceptive and is an indicator of survival with significant tissue injury after trauma and hepatic failure
Gc-globulin
An α2–glycoprotein which binds free hemoglobin to prevent the loss of hemoglobin and iron into the urine.
Haptoglobin
What can be the conditions associated with Increased levels of Haptoglobin?
Ulcerative Colitis
2. Acute Rheumatic Disease
3. Heart Attack
4. Burns
5. Nephrotic Syndrome
6. Severe Infection.
This protein detects and evaluate hemolytic anemia from anemia of other causes.
Haptoglobin
RBC destruction may be occurring in spleen and liver.
A. Normal Haptoglobin Count, Decreased Reticulocyte Count
B. Normal Haptoglobin levels, Normal Reticulocyte Count
C. Normal Haptoglobin Count, Increased Reticulocyte Count
C
Anemia is present but is not due to RBC breakdown
A. Normal Haptoglobin Count, Decreased Reticulocyte Count
B. Normal Haptoglobin levels, Normal Reticulocyte Count
C. Normal Haptoglobin Count, Increased Reticulocyte Count
B.
a copper containing, α2-glycoprotein enzyme
Ceruloplasmin
This protein help diagnose WILSON’S DISEASE.
Ceruloplasmin
Determine whether the ceruloplasmin levels are increased or decreased in the following conditions:
Inflammation
Malnutrition
Malabsorption
Pregnancy
Nephrotic Syndrome
Use of oral contraceptives
Cancers
Increased
Decreased
Decreased
Increased
Decreased
Increased
Increased
A condition wherein copper is deposited in the cornea.
Kayser-Fleischer ring
A tetramer of four identical subunits that inhibits proteases such as trypsin, thrombin, kallikrein and plasmin.
⍺2-Macroglobulin (A2M)
This protein is primarily increased in diabetes and liver disease
⍺2-Macroglobulin (A2M)
A glycoprotein which transports iron and prevents loss of iron in the kidney
Transferrin / Siderophilin
This protein can gauge iron metabolism and determine the iron carrying capacity of blood.
Transferrin / Siderophilin
When this protein is deficient, what type of anemia may develop within the patient?
Sideroblastic Anemia
A hereditary disorder of iron metabolism wherein iron is found in liver and pancreas
Hemochromastosis
What can be the results of a patient that has iron deficiency?
A. Iron is low, TIBC is low, Transferrin saturation is low
B. Iron is low, TIBC is high, Transferrin saturation is low
C. Iron is high, TIBC is low, Transferrin saturation is high
D. Iron is high, TIBC is high, Transferrin saturation is high
B
What can be the results of a patient that has iron overload?
A. Iron is low, TIBC is low, Transferrin saturation is low
B. Iron is low, TIBC is high, Transferrin saturation is low
C. Iron is high, TIBC is low, Transferrin saturation is high
D. Iron is high, TIBC is high, Transferrin saturation is high
C.
A light chain component of the major histocompatibility complex (HLA) and is found on surface of most nucleated cells and is present in high concentrations on lymphocytes.
β2-Microglobulin (B2M)
Determine whether the complement levels will increase in the following:
Malnutrition
Inflammation
Hemolytic Anemia
Decreased
Increased
Decreased
The most abundant complement.
C3
A protein that forms a fibrin clot when activated by thrombin,
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen is also known as?
Clotting Factor I
Proteins which are synthesized by B Cells,
immunoglobulin
In electrophoresis, a positively charged ion is called a ______ and migrates toward the _____ charged electrode, the _____
CATION; negatively; CATHODE
In electrophoresis, a negatively charged ion is called ____ and moves toward the charged electrode, the ____
ANION; positively; ANODE
What is the principle of serum protein electrophoresis?
Moving of charged biomolecules in a solution by applying an electrical field
across mixture.
What is the most common type of gel medium used for protein studies.
polyacrylamide gel
What is/are the most common stain/s used in electrophoresis to stain proteins?
Ponceau S
Amido Black
Coomassie Blue
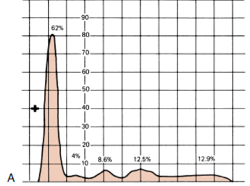
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. Monoclonal gammopathy
B. α1 –antitrypsin deficiency
C. Inflammation
D. Liver Cirrhosis
E. NOTA
E
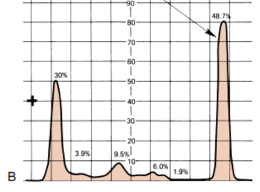
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. Nephrotic Syndrome
B. Inflammation
C. Monoclonal gammopathy
D. Liver Cirrhosis
E. NOTA
C.
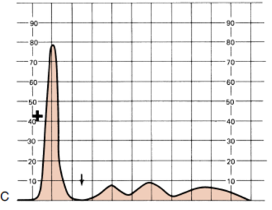
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. Monoclonal gammopathy
B. Liver Cirrhosis
C. Nephrotic Syndrome
D. α1 –antitrypsin deficiency
E. NOTA
D.
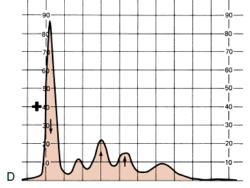
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. α1 –antitrypsin deficiency
B. Nephrotic Syndrome
C. Inflammation
D. Liver Cirrhosis
E. NOTA
B.
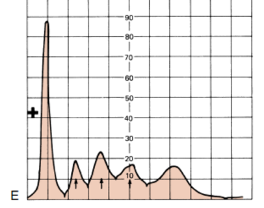
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. Inflammation
B. Liver Cirrhosis
C. Nephrotic Syndrome
D. Liver Cirrhosis
E. NOTA
A.
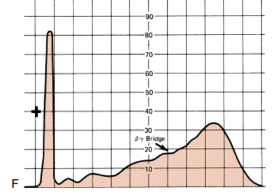
Determine the condition of the patient given the serum electrophoresis graph

A. Inflammation
B. Liver Cirrhosis
C. Nephrotic Syndrome
D. Liver Cirrhosis
E. NOTA
D.