3. Medicines Related Consultation Framework (MRCF)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is the purpose of the Medicines Related Consultation Framework (MRCF)?
To effectively communicate with patients
To demonstrate skills & behaviours of healthcare professionals
To efficiently structure the conversation
To discuss & make appropriate decisions with the patient
All within a set time!
What is the Medicines Related Consultation Framework (MRCF)?
Designed by professionals, experts, & academics
Defined by the RPS as:
"A reflective tool to support the development of consultation skills for pharmacy practitioners"
What are the 5 sections of the Medicines Related Consultation Framework (MRCF)?
Introduction
Data collection & problem identification
Actions & solutions
Closing
Consultation behaviours
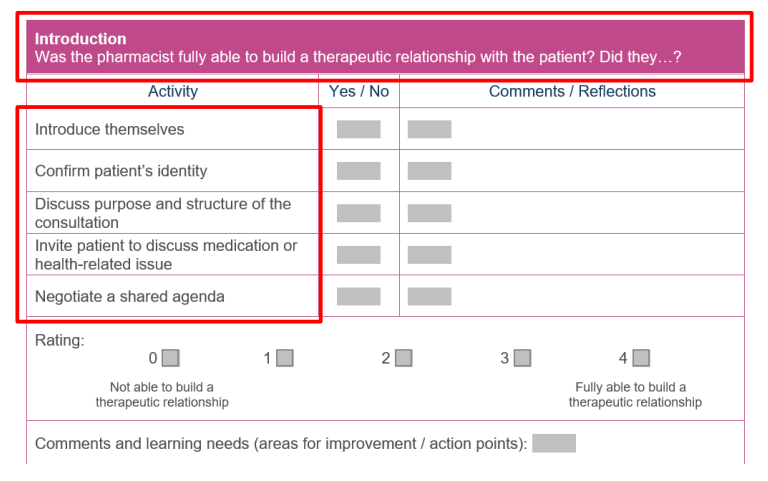
What does the intro consist of?
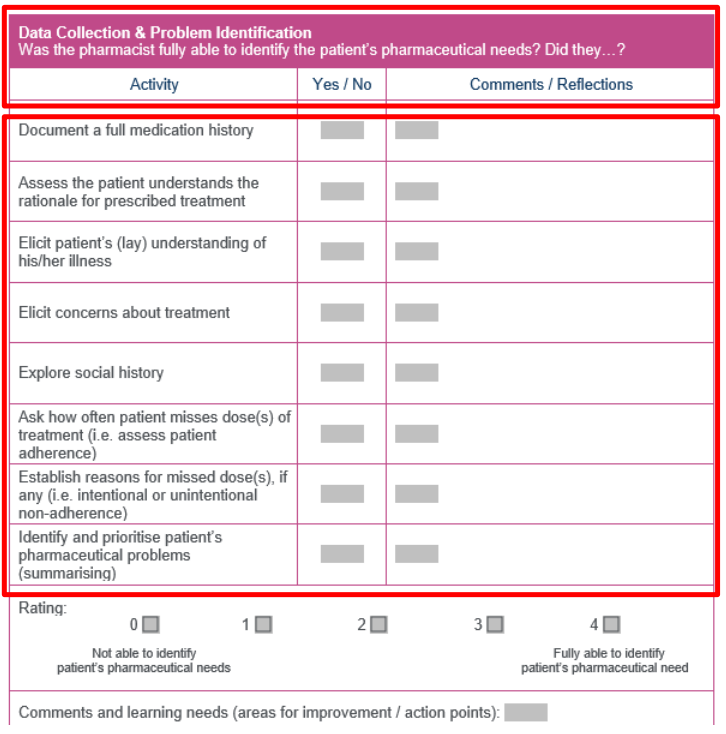
What does data collection & problem identification consist of in the MRCF?
Full medication history & patient’s understanding of prescribed drugs
Social history, including occupation & lifestyle factors
Adherence check: missed doses & reasons for non-adherence
Identifying & prioritising the patient’s pharmaceutical problems (e.g., side effects, interactions, effectiveness)
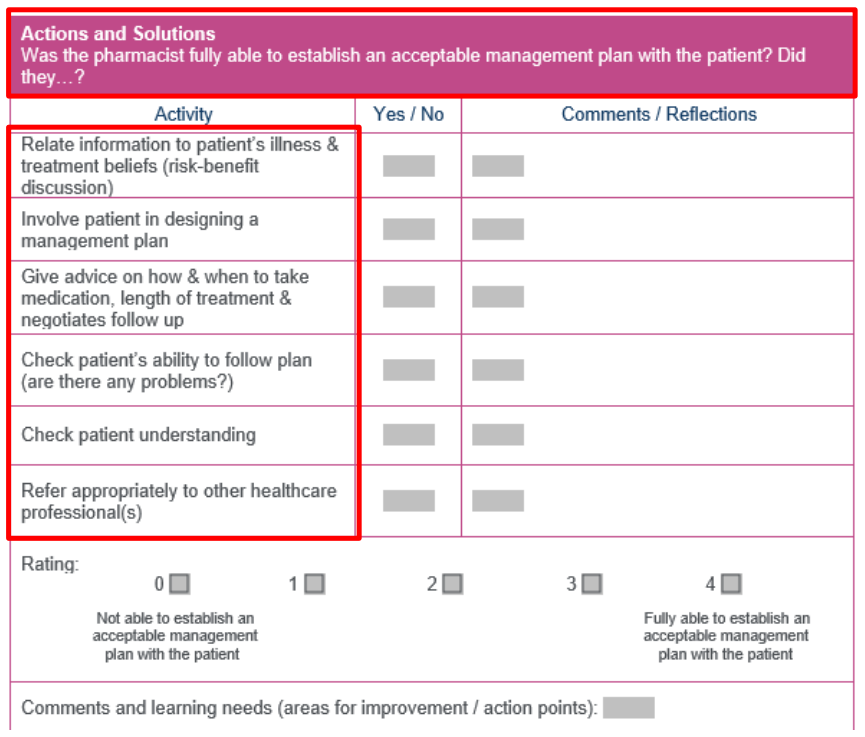
What does Section 3: Actions and Solutions involve in the MRCF?
Considering the patient's beliefs about medication & how it affects treatment choice
Involving the patient in the decision-making process
Providing medication advice: why it’s important for adherence (e.g., timing, course length)
Checking the patient’s ability to follow the plan & any potential issues (e.g., lifestyle conflicts)
Ensuring patient understanding & satisfaction with the treatment plan
Possible referrals if needed (e.g., to another healthcare professional)
What does Section 4: Closing involve in the MRCF?
Safety netting: Ensure patient knows what to do if medication doesn’t work within the expected timeframe (e.g., follow-up appointment, GP consultation, A&E visit).
Explain what to do if the patient faces difficulties and whom to contact.
Provide a clear timeframe for follow-up.
Offer an opportunity for the patient to ask further questions.
Manage patient expectations about next steps and when to follow up.

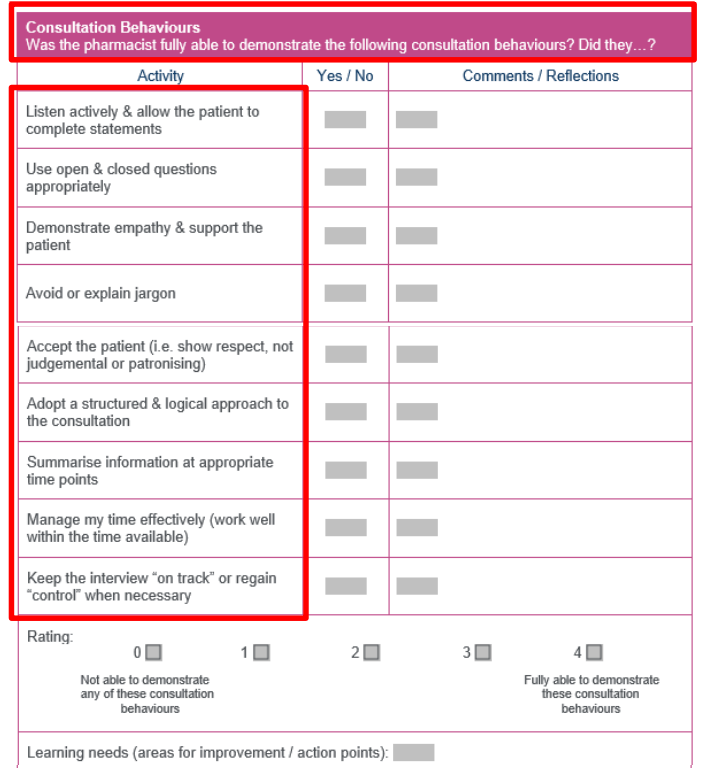
What does Section 5: Consultation Behaviours involve in the MRCF?
Skills needed: Active listening, using open/closed questions, empathy, and clear communication.
Golden Minute: Give the patient a chance to express everything they need to say at the beginning.
Empathy: Show support through tone, body language, and patient-friendly language.
Respect: Avoid judgment or patronizing behaviour.
Structured approach: Organise the consultation logically, summarise at appropriate points.
Time management: Stick to the time limit (15-20 minutes), and keep the conversation on track.
Documentation: Capture patient info accurately for effective follow-up.
How is the MRCF used in practice?
Outpatient clinics: For consultations and treatment planning.
New Medicines Service (NMS): Educating patients on new medications.
Discharge Medication Review (DMR): Reviewing discharge meds and adherence.
Emergency hormonal contraception: Assessing eligibility and safety.
Specialist pharmacist-led clinics: For conditions like anticoagulation, asthma, diabetes.
Independent prescribing: Guiding consultations and prescriptions.
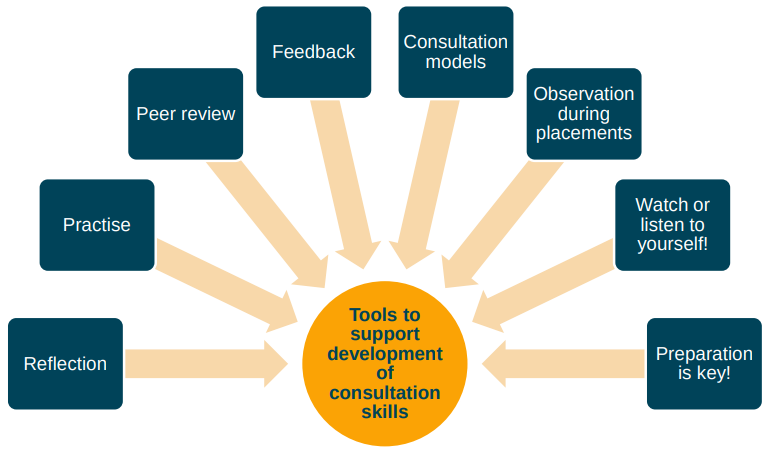
How can we develop our consultation skills?