Intro to Econ: Final Exam Study Guide
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
what are the three basic economic questions?
1.) what to produce?
2.) how to produce?
3.) for whom to produce?
what is the basic economic problem?
economics is concerned with the efficient use of limited productive resources to achieve the maximum satisfaction of economic wants
microeconomics vs. macroeconomics
micro- studies the economic behavior of individuals, particular markets, firms or industries
macro- looks at the entire economy or its major aggregates or sectors, such as households, businesses, or government
division of labor/ specialization
produce more goods
opportunity costs
the value of the next best alternative or choice that was not taken
factors of production
fixed/constant
land
anything not made by humans
water
farmland
cattle
labor
human
talent/ skills
quantity/ quality
economic interdependence
every price depends to some extent on every other place
capital goods
tools and equipment used to produce final goods and services
ex.) tractor, factory
consumer good
any good purchased for consumption and not used later to produce another consumer good
standard of living
the quantity and quality of material goods and services available to a given population
conspicuous consumption
the purchase of goods or services for the specific purpose of displaying one's wealth
wealth
an accumulation of valuable economic resources that can be measured in terms of either real goods or money value
trade-offs
when you choose one thing which causes you to have to give up, or sacrifice, another
scarcity
the demand for a good or service is greater than the availability of the good or service
strengths and weaknesses:
traditional economy
command economy
market economy
traditional
strength- the answers to what, how, and for whom to produce are determined by customs and tradition
weakness- tends to discourage new ideas and new ways of doing things
command
strength- it can be more efficient in the allocation of resources
weakness- it stifles innovation and creativity because the government leaves no room for competition
market
strength- increased efficiency, production, and innovation
weakness- monopolies, no government intervention, poor working conditions, and unemployment
adam smith and the invisible hand
the father of economics
a metaphor that describes the unseen forces of self-interest that impact the free market
what is the role of government in a market economy?
to protect property rights, ensure infrastructure and public services are adequate, and protect both consumers and the environment
capitalism
trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit
private property
the ownership of property by private parties
economic equity
the fairness and justice in the distribution of wealth, income, and other economic resources
entrepreneur
someone who organizes, manages, and assumes the risks of a business or enterprise
free enterprise
the market determines prices, products, and services rather than the government
profit motive
the intent to achieve a monetary gain in a project, transaction, or material endeavor
mixed economy
a system that combines aspects of both capitalism and socialism
change in quantity demanded vs. change in demand
change in quantity demanded- due to change in price
change in demand- due to a change in non price reason
when does the demand curve shift and in which direction?
population increases = curve to the right
population decreases = curve to the left
what factors cause a change in demand?
1.) change in taste of preferences
2.) change in consumer information
3.) change in number of consumers
4.) change in income
5.) change in price of a good related good
a.) change in price of substitute good
b.) change in price of a complementary good
6.) change in future price (expectation)
What are the determinates of demand elasticity?
1.) is there an adequate substitute?
yes - elastic no - inelastic
2.) can the purchase be delayed
yes - elastic no - inelastic
3.) does the purchase require a large amount of income?
yes - elastic no - inelastic
4.) is the price change temporary or permanent?
temporary - elastic permanent - inelastic
law of demand
as the price increases (decreases) the quantity demanded decreases (increases) inverse
diminishing marginal utility
(satisfaction) each additional unit of good is worth less and less
marginal utility
the added satisfaction a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service
demand curve
downward slopping
demand elasticity
how responsive consumers are to change in price
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantity demanded of a good or service at different price levels
complement goods
a good whose use is related to the use of an associated or paired good
substitute goods
a product or service that consumers see as essentially the same or similar-enough to another product
change in quantity supplied vs. change in supply
quantity supplied- due to increased price/ movement along
change in supply- shift/ due to change in non price
when does the supply curve shift and in what direction?
supply increase = curve to the right
supply decrease = curve to the left
what factors cause a change supply?
1.) change in input costs
2.) change in technology
3.) change in number of suppliers
4.) change in future price
5.)change in price of similar good
6.) change in government
a.) change in taxes
b.) change in subsidies
c.) change in government regulations
law of supply
as the price increases (decreases) the quantity supplied increases (decreases)
subsidy
a direct or indirect payment to individuals or firms, usually in the form of a cash payment from the government or a targeted tax cut
supply schedule
a table that shows the quantity supplied at each price
supply curve
upward slopping
price floor
government sets a minimum price, usually above the equal
price ceiling
government sets a maximum price, usually below the equilibrium
surplus
the amount of an asset or resource that exceeds the portion that's actively utilized
shortage
a condition where the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the market price
equilibrium
the state in which the market forces are balanced, where current prices stabilize between even supply and demand
equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity
equilibrium price - the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied
equilibrium quantity - the quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium price
prices
the amount of money that a buyer gives to a seller in exchange for a good or a service
natural monopoly
a type of monopoly in an industry or sector with high barriers to entry and start-up costs that prevent any rivals from competing
geographic monopoly
occur when a business is the only one offering its products or services in a particular location
laissez-faire
no taxes, regulations, or tariffs
pure competition
a marketing situation in which there are a large number of sellers of a product which cannot be differentiated and, thus, no one firm has a significant influence on price
monopoly
a market structure where a single seller or producer assumes a dominant position in an industry or a sector
monopolistic competition
a type of market structure where many companies are present in an industry, and they produce similar but differentiated products
oligopoly
a market in which the industry is dominated by a few companies that are each influential participants in the market
what are the sources of revenue for local?
intergovernmental revenues
sales taxes
interest on invested funds
property taxes
utility revenues
taxes from individuals and profits taxes from corporations
what are sources of revenue for state?
intergovernmental revenues
sales taxes
employee retirement
individual income taxes
what are sources of revenue for federal government?
individual income taxes
corporate income taxes
borrowing
excise, estate, and gift taxes
payroll taxes
progressive tax
the effective tax rate increases as a person’s income goes up
proportional tax
the effective tax rate stays the same regardless of income
regressive tax
the effective tax rate decreases as income goes up
W-4 Form
tells your employer how much money to with hold for your future tax bill
W-2 Form
get one form every employer (by Jan 31st)
needed to file tax retain
shows how much income and tax
gross pay
pay before deductions
net pay
pay after deductions
FICA
(federal insurance contribution act) federal tax used to pay for social security and medicare
excise tax
a special tax on gasoline
property taxes
real estate, buildings, and anything permanently attached to them
sales taxes
general tax levied on consumer purchases of almost all products
social security
federal program of disability and retirement
medicare
health care for the elderly
what is included and excluded when calculating GDP?
includes- all USA companies regardless of where they are located (worldwide)
excludes- any foreign companies within the US borders
GDP
a measure of the value of all the final goods and services newly produced within a period time (usually a year)
per capita GDP
a measure of the total output of a country that takes gross domestic product (GDP) and divides it by the number of people in the country
net exports
exports minus imports
real GDP
value or number not adjusted for inflation
nominal GDP
value or number that has been adjusted for inflation
underground economy
involves the exchange of goods and services which are hidden from official view
transfer payment
a payment of money for which there are no goods or services exchanged
market basket
a selected mix of goods and services that tracks the performance of a specific market or segment
intermediate product
products that are used in the production process to make other goods, which are ultimately sold to consumers
non market transaction
transactions covering goods or services that their producers supply to others free or at prices that are not economically significant
disposable income
what is left over after taxes, and is what households used for consumption of needs and wants
base year
the first of a series of years in an economic or financial index
CPI
a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a representative basket of consumer goods and services
secondhand sales
sales of used good; category of activity not included in GDP computation
Y=C+I+G+Xn
C = consumption
I = investment
G = government
Xn= net exports
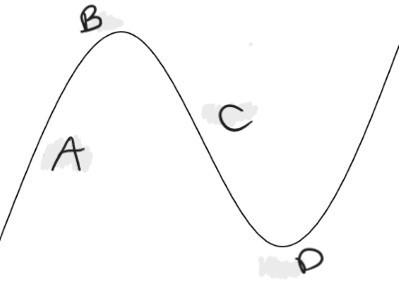
what are the phases of the business cycle?
A.) expansionary/ recovery
B.) peak/ prosperity
C.) contractionary/ recession
D.) trough
frictional unemployment
in between jobs, new graduates, new careers
structural unemployment
lack of skills, long term change in demand for job (not related to a downtown in the economy), replaced by technology
seasonal unemployment
(part of structural) farm workers, holiday help
cyclical unemployment
due to recession, a down turn in the economy. may effect only certain sectors. will get job back when economy recovers
demand pull inflation
too many dollars chasing too few goods. supply can’t keep up with demand
cost push inflation
cost of production is higher
wage-price spiral inflation
occurs as a result of demand pull and cost push happening one right after the other
hyperinflation
caused when the government or central bank of a country prints too much currency