Topic 20 - Tides, The Beach, The Desert
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What did Sir Isaac Newton state?
tides result from the gravitational attraction exerted upon Earth by the moon and to a lesser extent the Sun
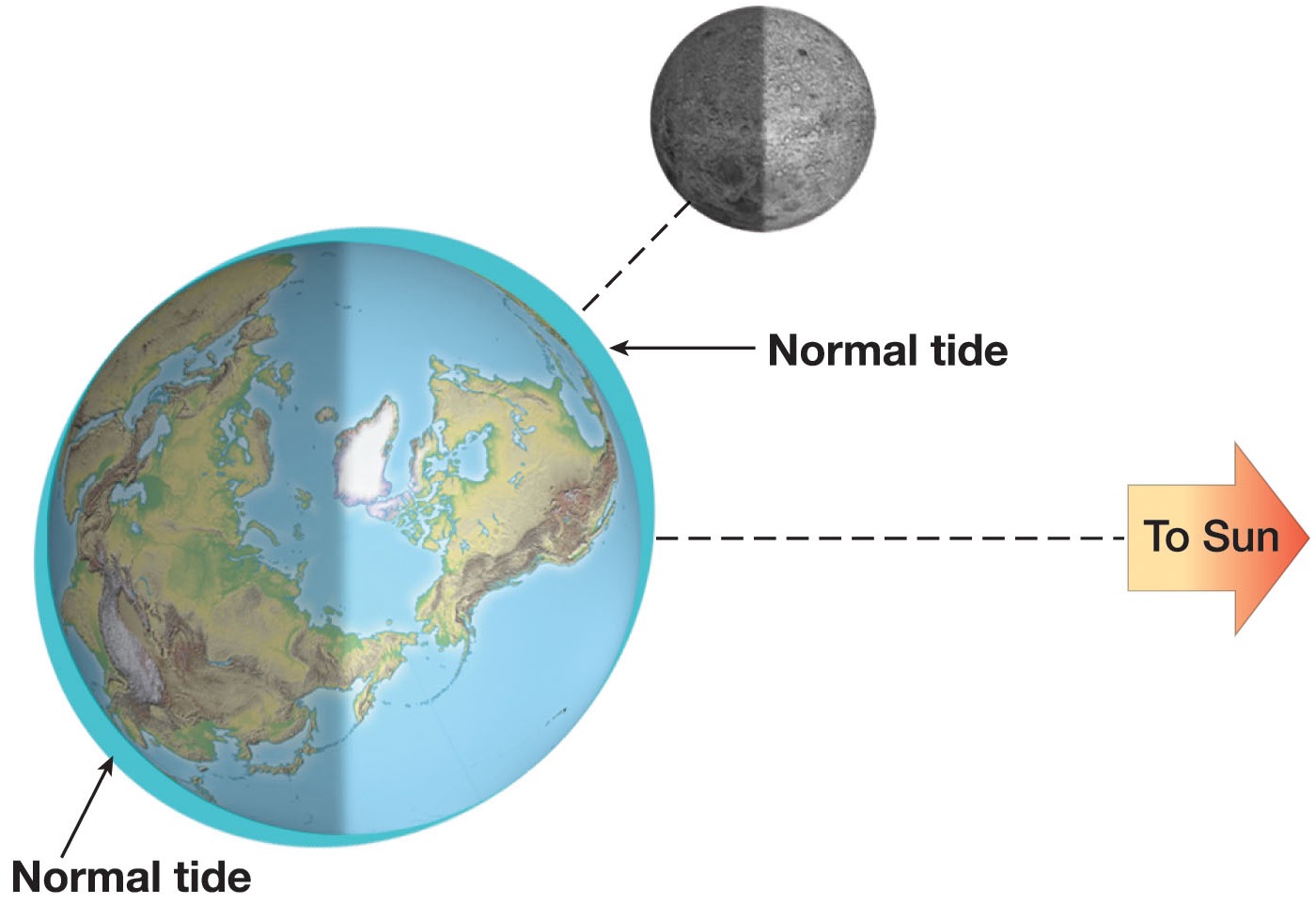
what happens during a normal tide?
high tides and low tides every day: b/c the moon adds a little more gravity and pulls the water out of the ocean basins
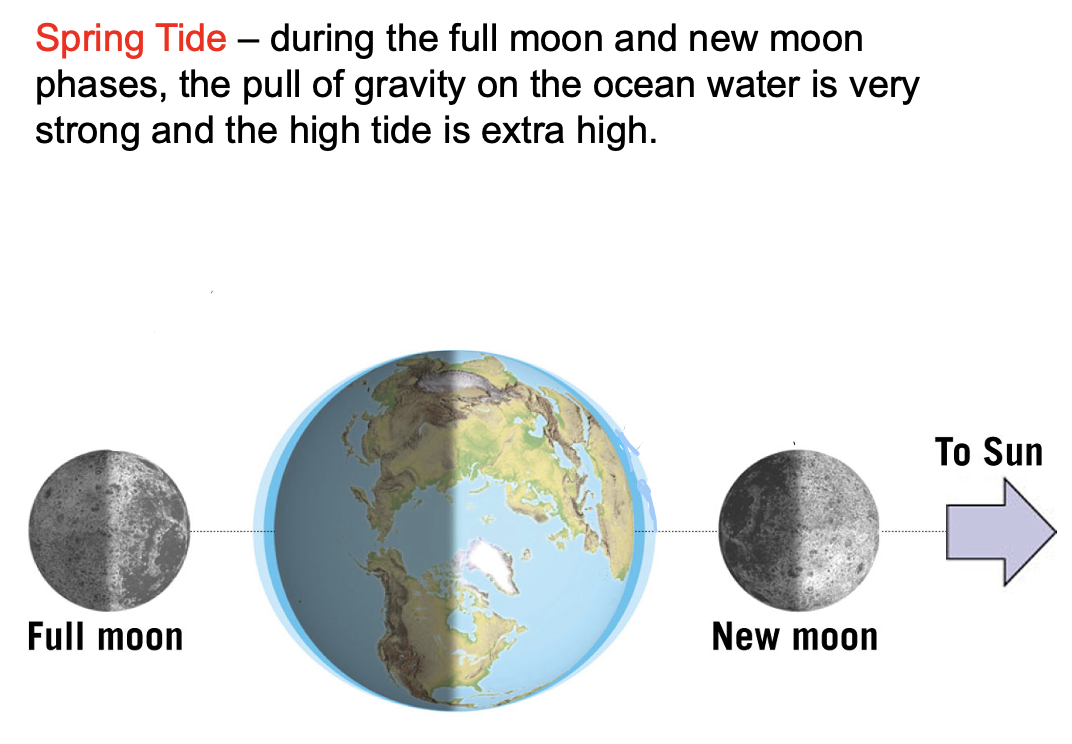
what happens during the highest high tide?
occurs when earth, the moon and the sun are all lined up - occurs during a new moon phase aka spring tide
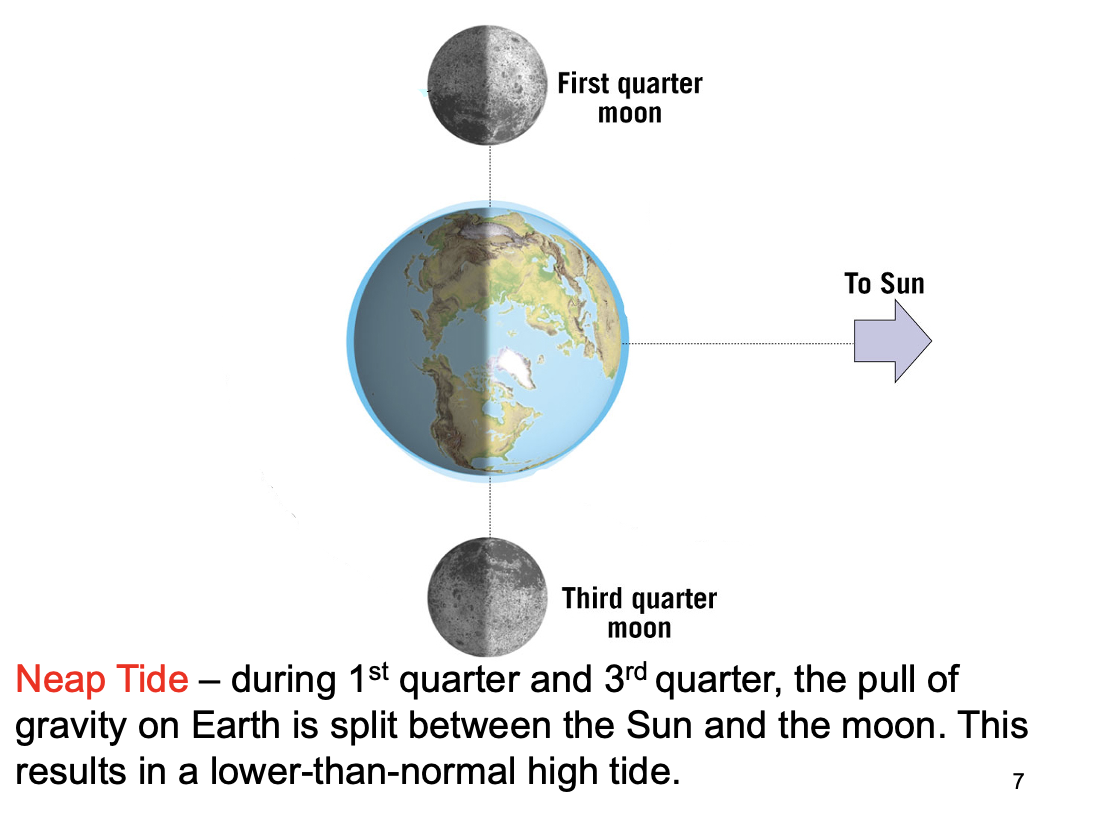
what happens during the lowest high tide?
occurs when earth, the moon and the sun are at right angles - occurs during the 1st quarter and 3rd quarter moon phases aka neap tide
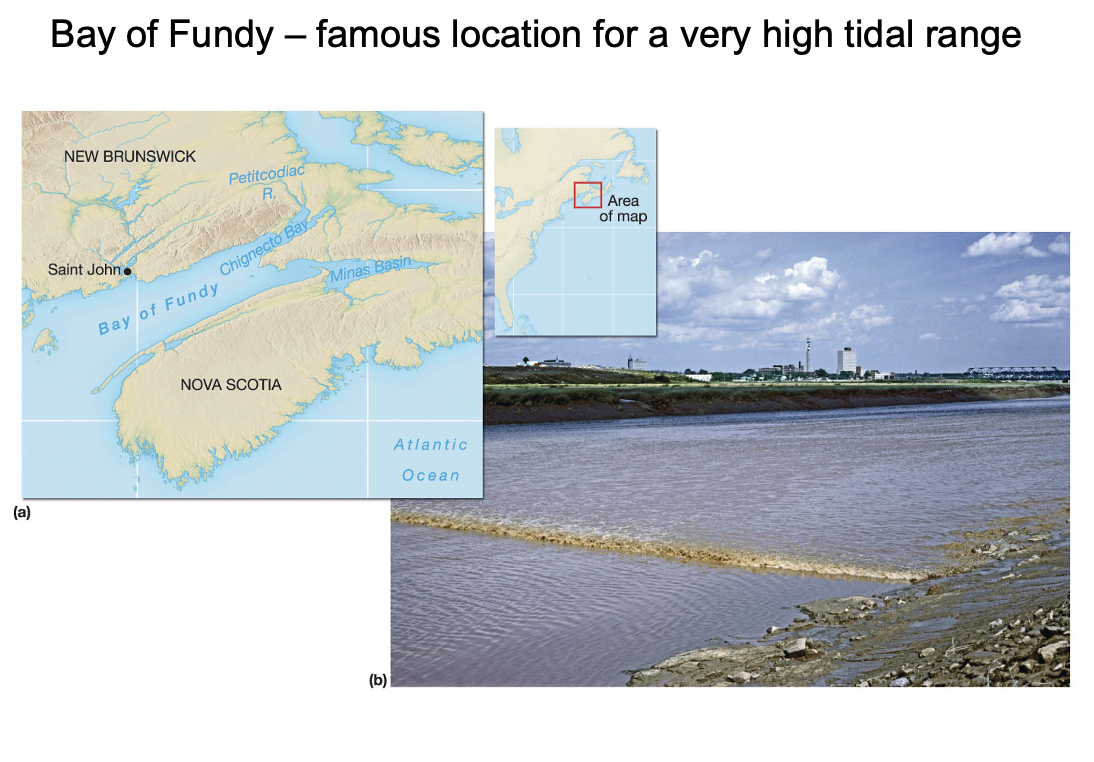
where are the highest tidal ranges in the world located?
Bay of Fundy
How do waves work? Why do they break along the shore?
As the wave form nears shore, the bottom of the wave slows down. The top keeps moving so the height builds up. (recall how an air parcel rolls along the ground during tornado formation). Eventually the wave height is too great and it topples over. This forms a white cap and a crashing wave
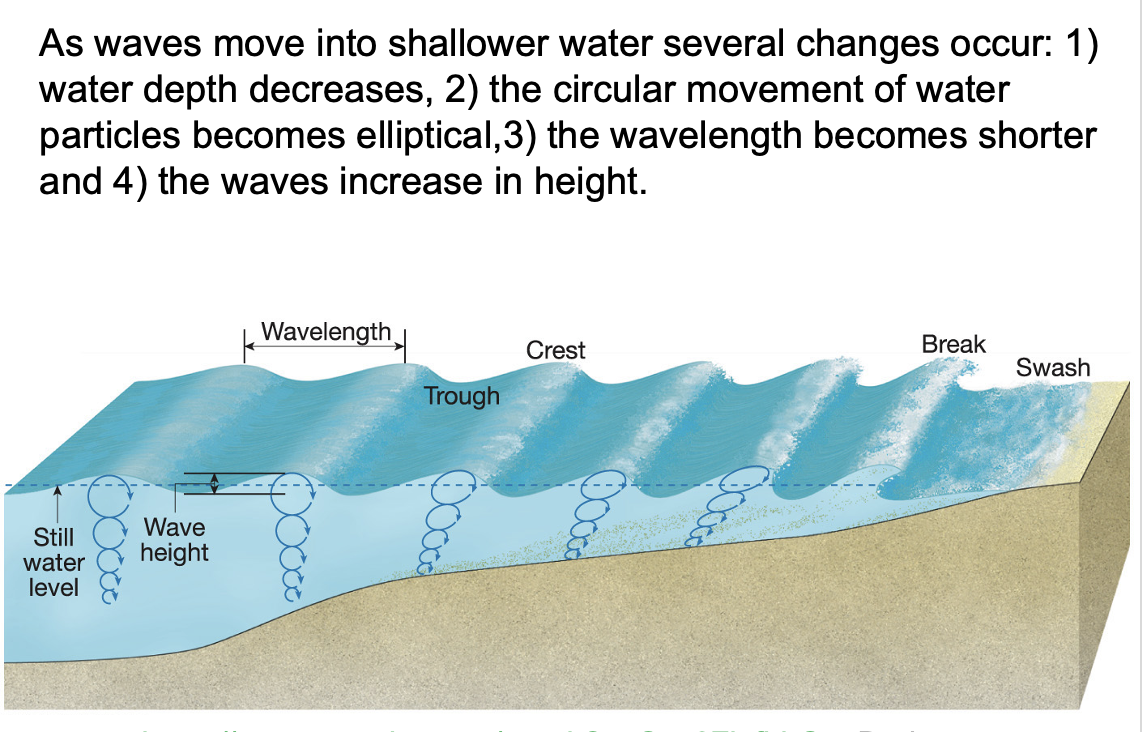
what is the result of all wave activity?
The result of all this wave activity are distinctive landforms. Beach processes are basically destructive – they break rocks down

How does sediment get transported along a beach?
Longshore drift – the process that moves sand along the beach, along the shoreline
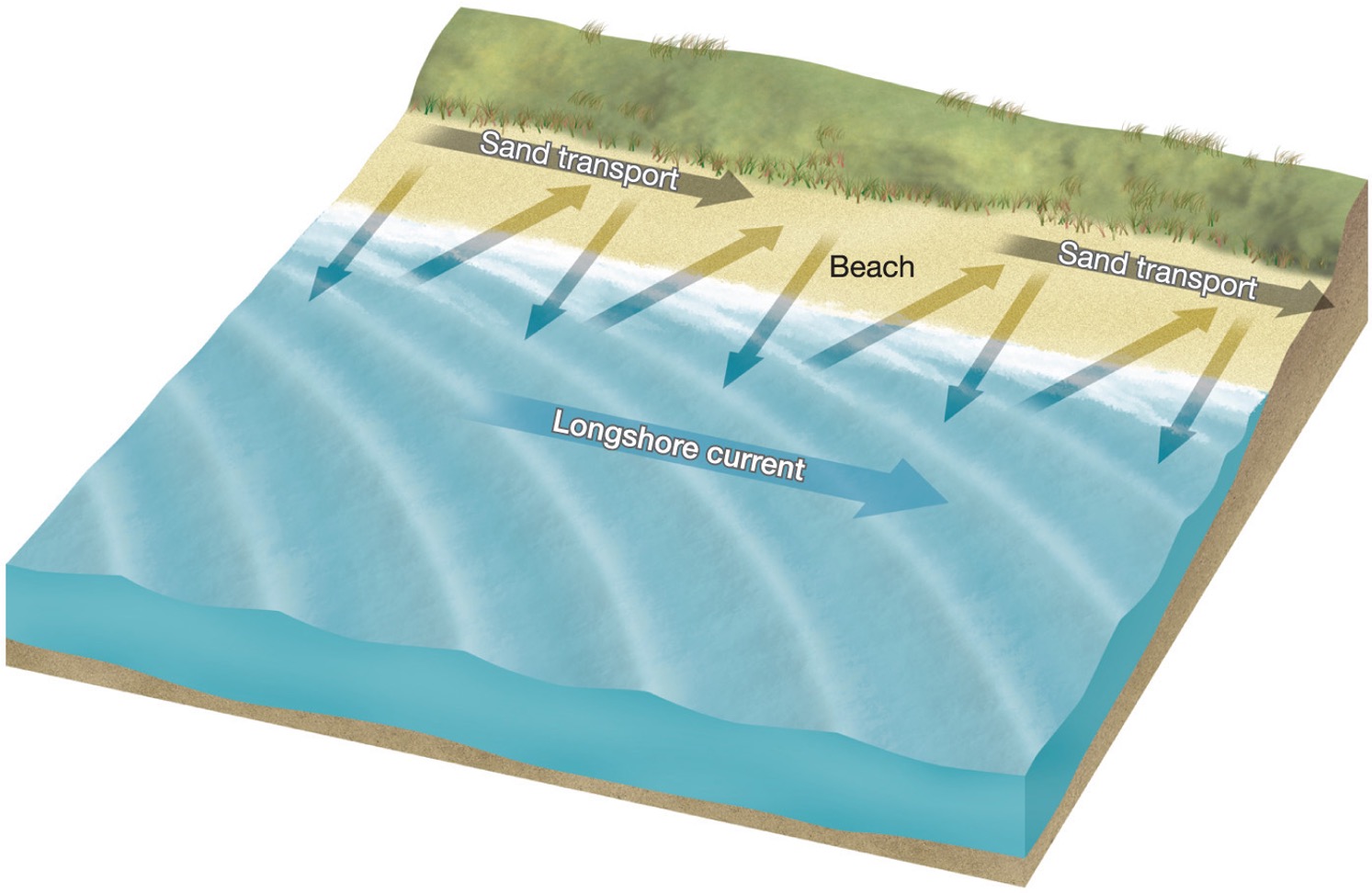

how does the process of longshore drift work?
1) The waves wash onto shore at a certain angle, and they wash sediment up onto the beach. 2) The water washes back down perpendicular to the beach, taking sediment with it. 3) The result of this angular onto the shore and the direct line back down, causes the sediment to move down beach. Great amounts of material are moved this way - so much so that the beach is often called a river of sand. 4) The movement of the water itself is called the Longshore Current

The movement of water itself is called?
the longshore current
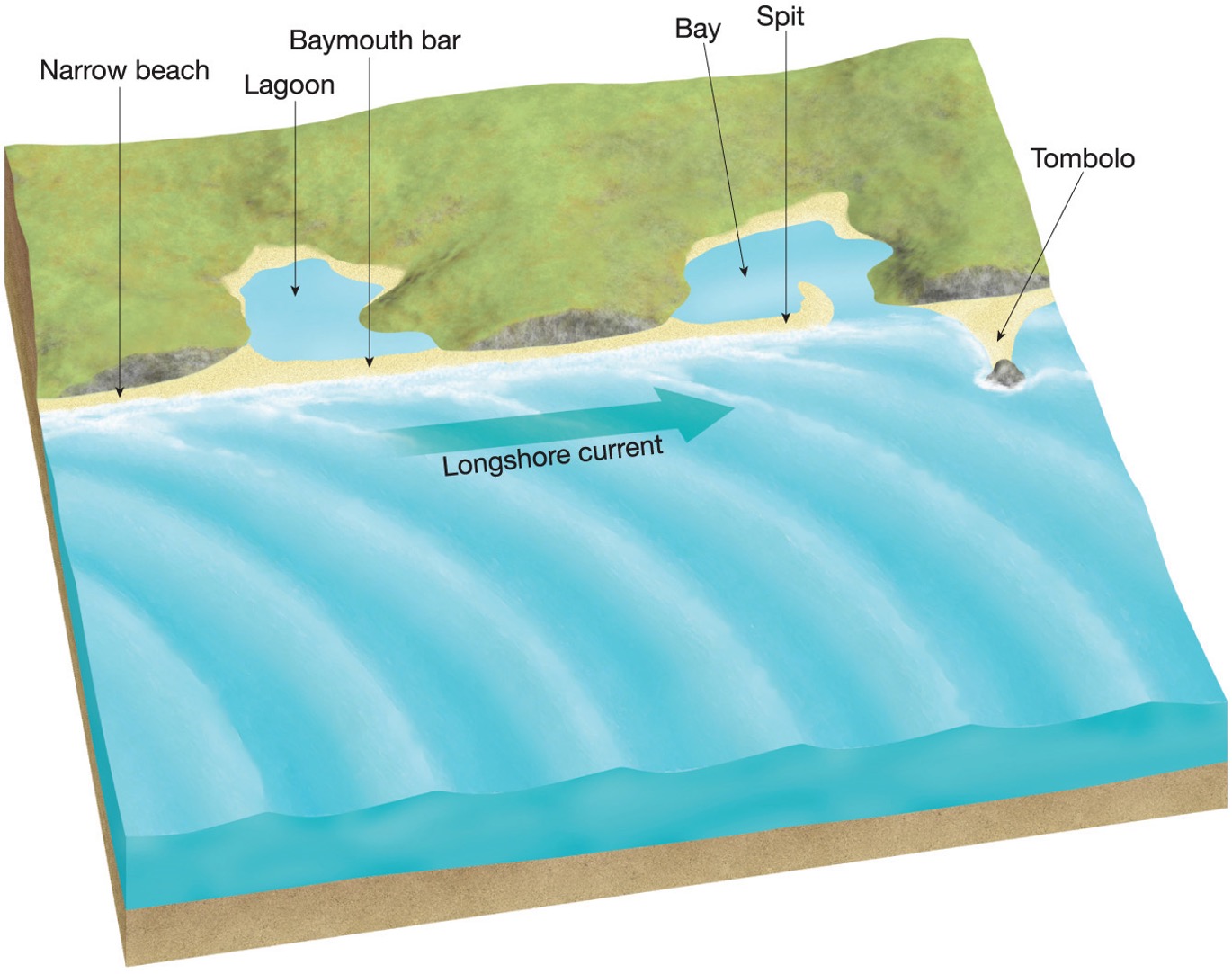
The idealized beach profile is a combination of ?
erosion and deposition
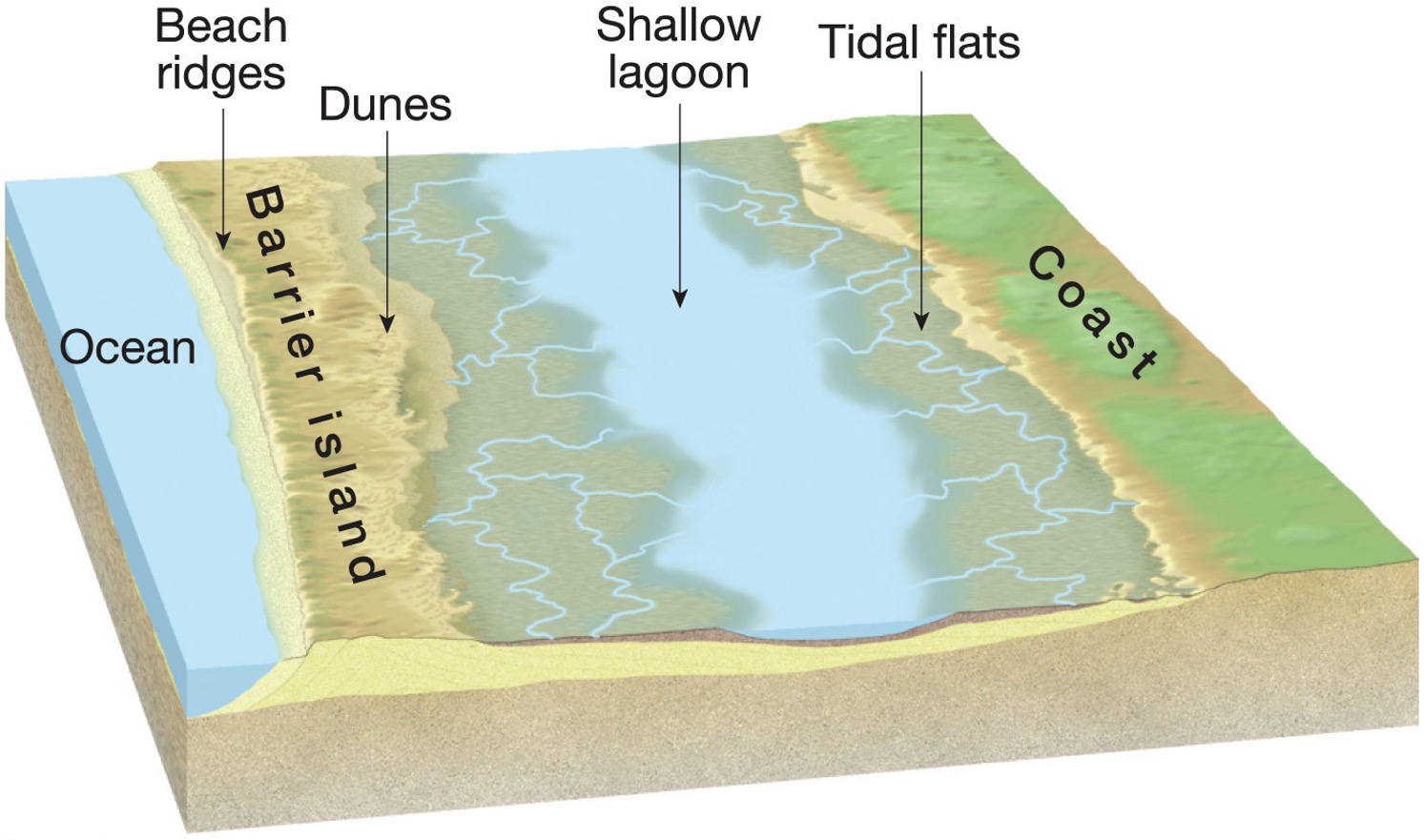
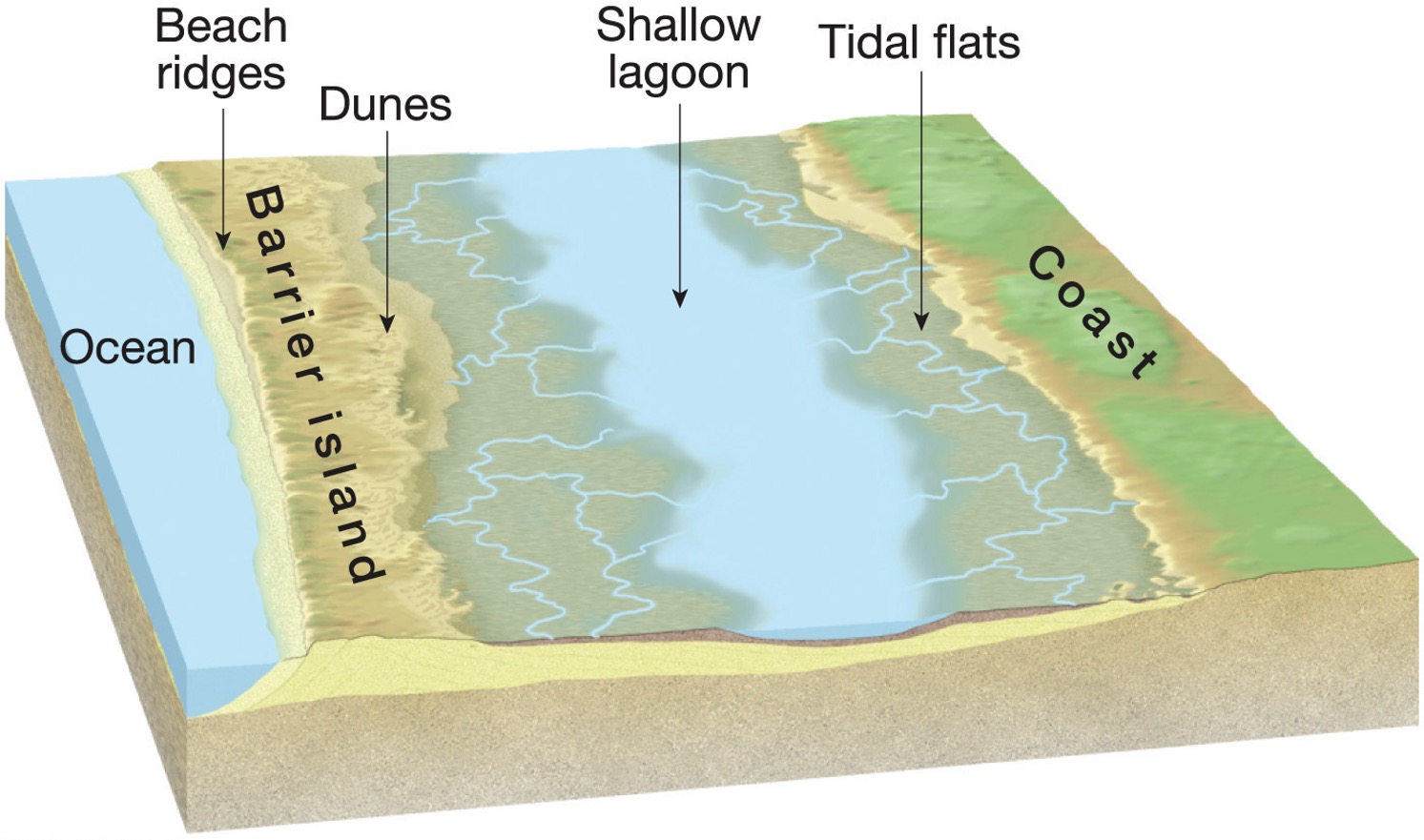
What are the features beach ridges, dunes, lagoon and tidal flat?
beach ridges - linear mounds of sand or sediment that form parallel to shorelines, dunes - mound of sand, lagoon - body of water that is separated from a larger body of water, tidal flat - low-lying coastal areas that are alternately covered and uncovered by the tides
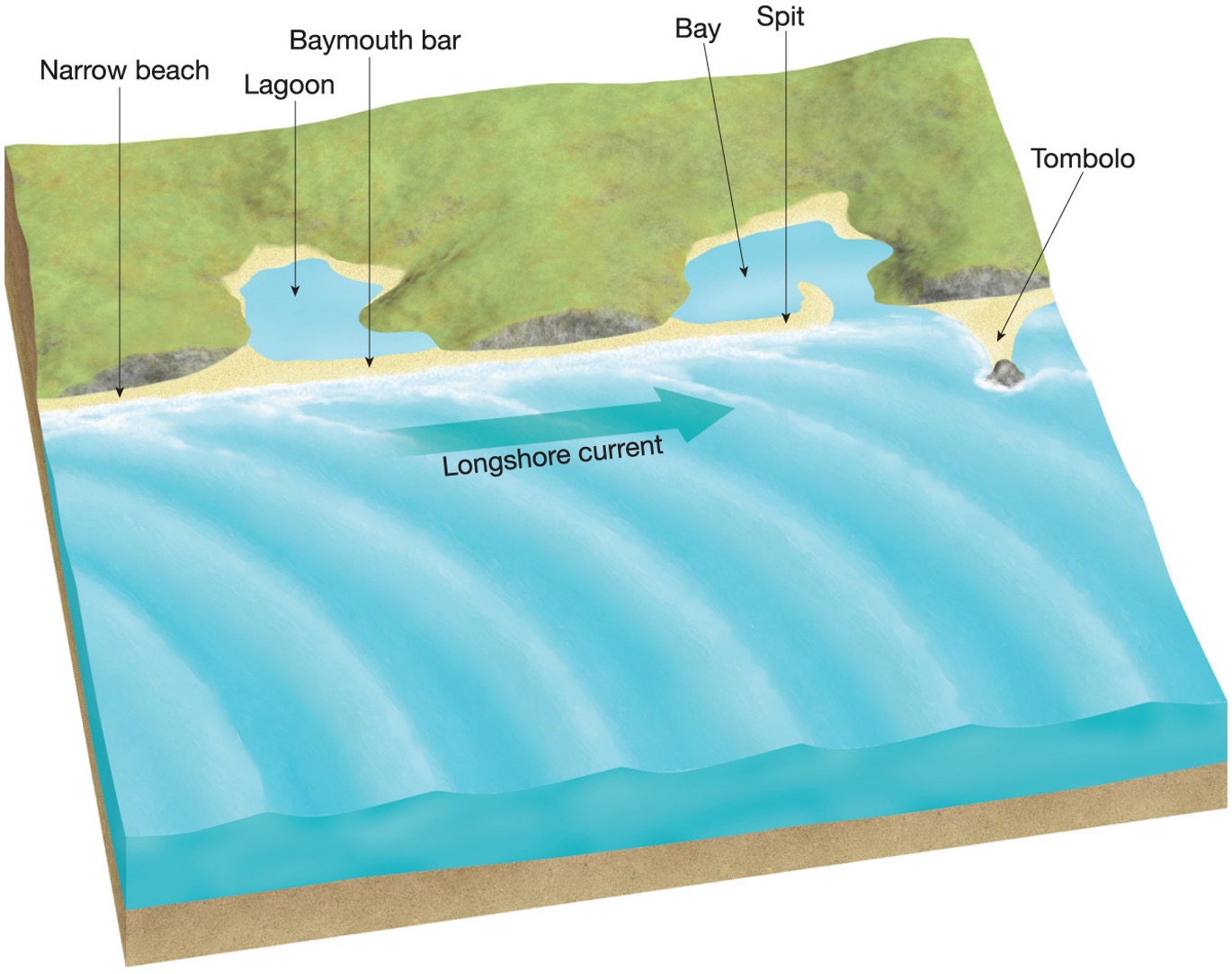
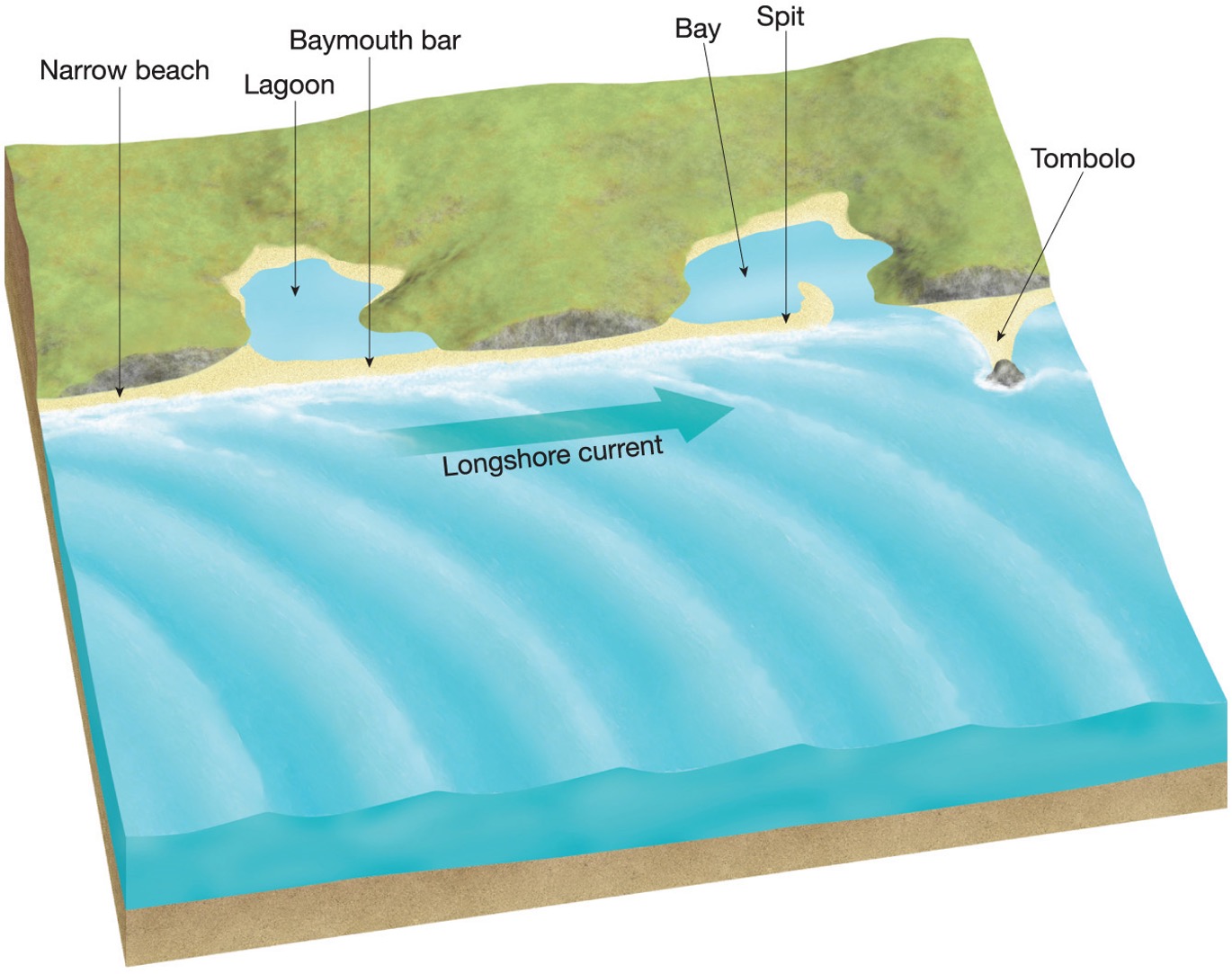
What are some bay features?
bar, lagoon, bay - body of water partially enclosed by land , spit and tombolo
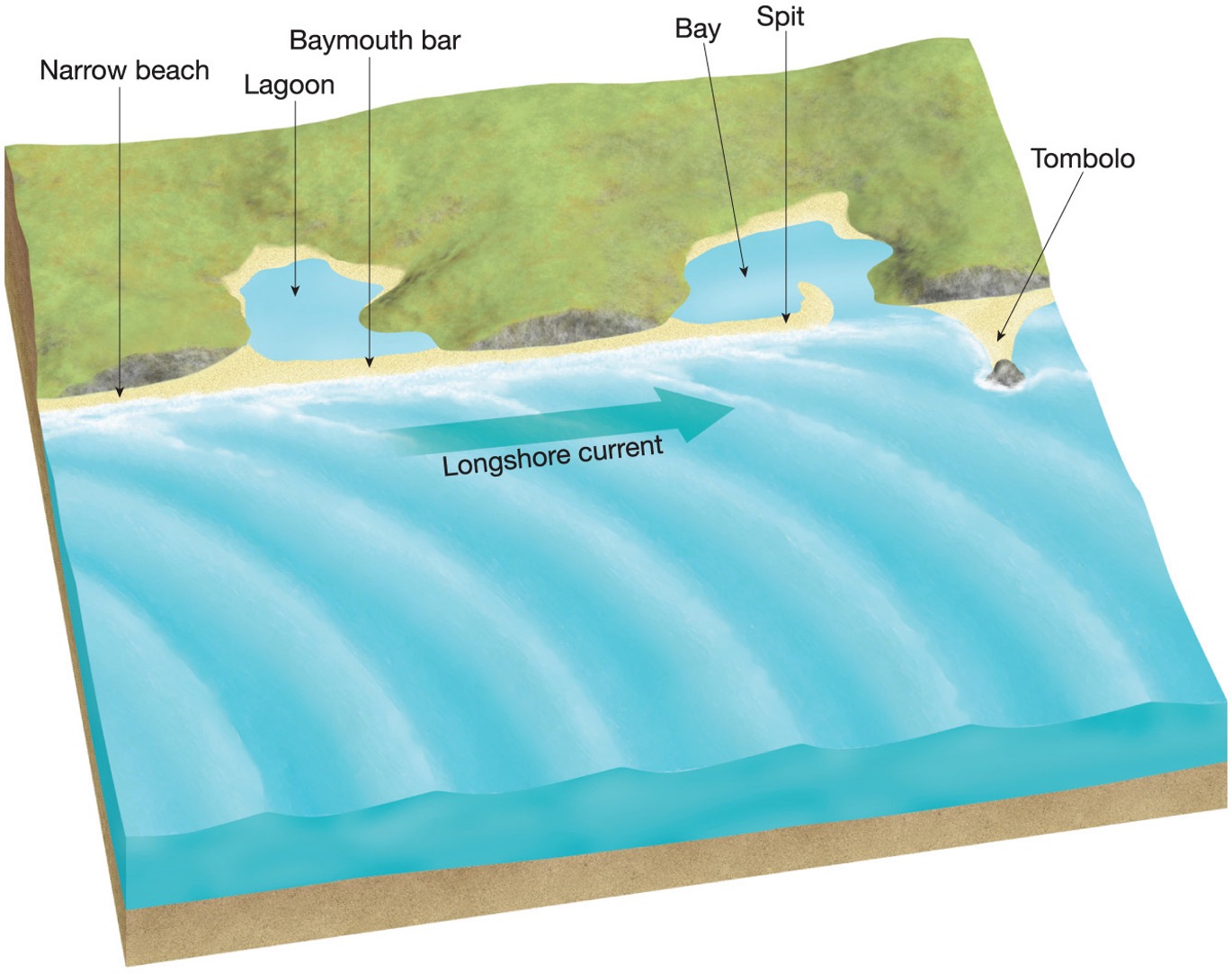
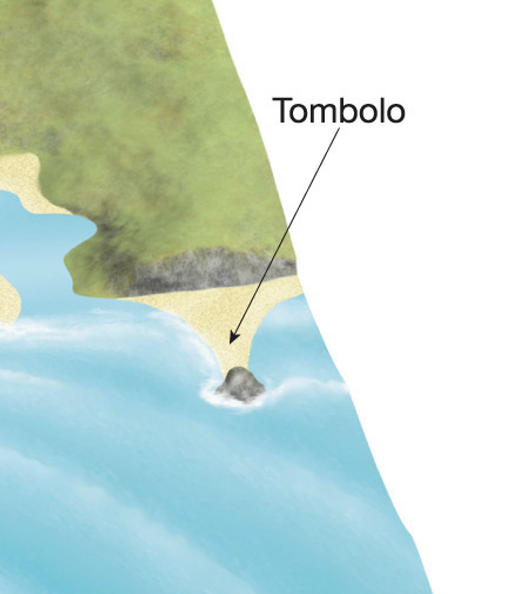
what is a tombolo?
A tombolo occurs when sediment deposits connect the shoreline with an offshore island or sea stack by accumulating on an underwater wave-built terrace
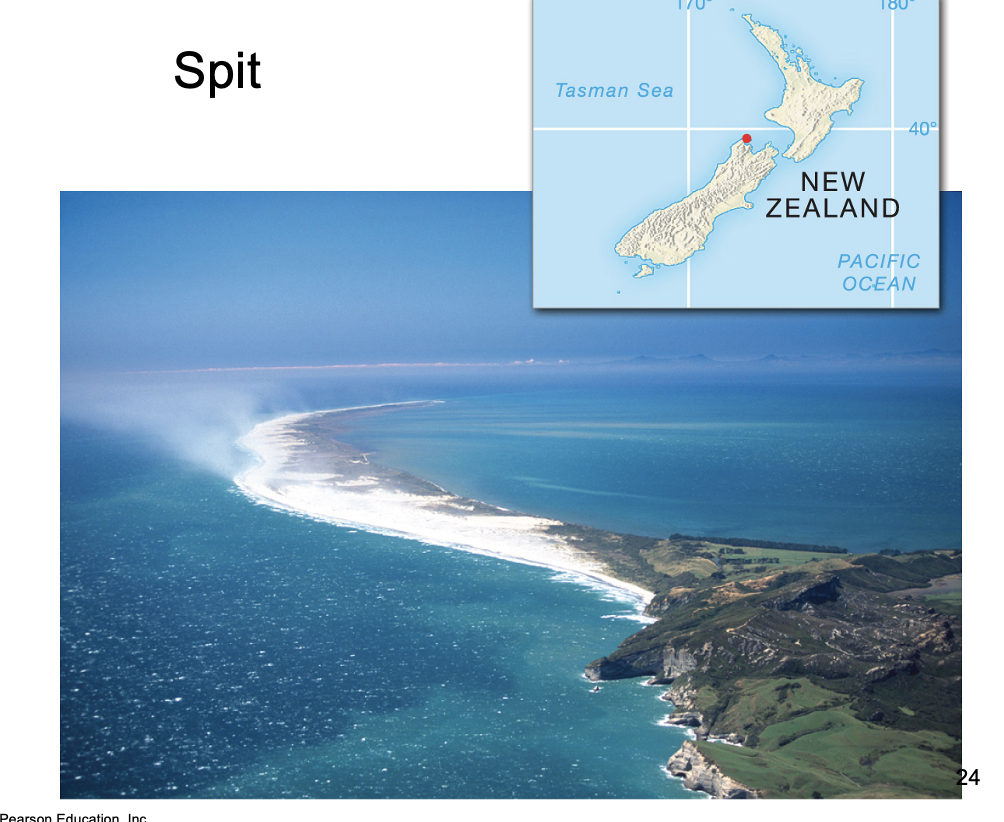
What is a spit?
Barrier spits consist of material deposited in a long ridge extending out from a coast, sometimes partially crossing and blocking the mouth of a bay
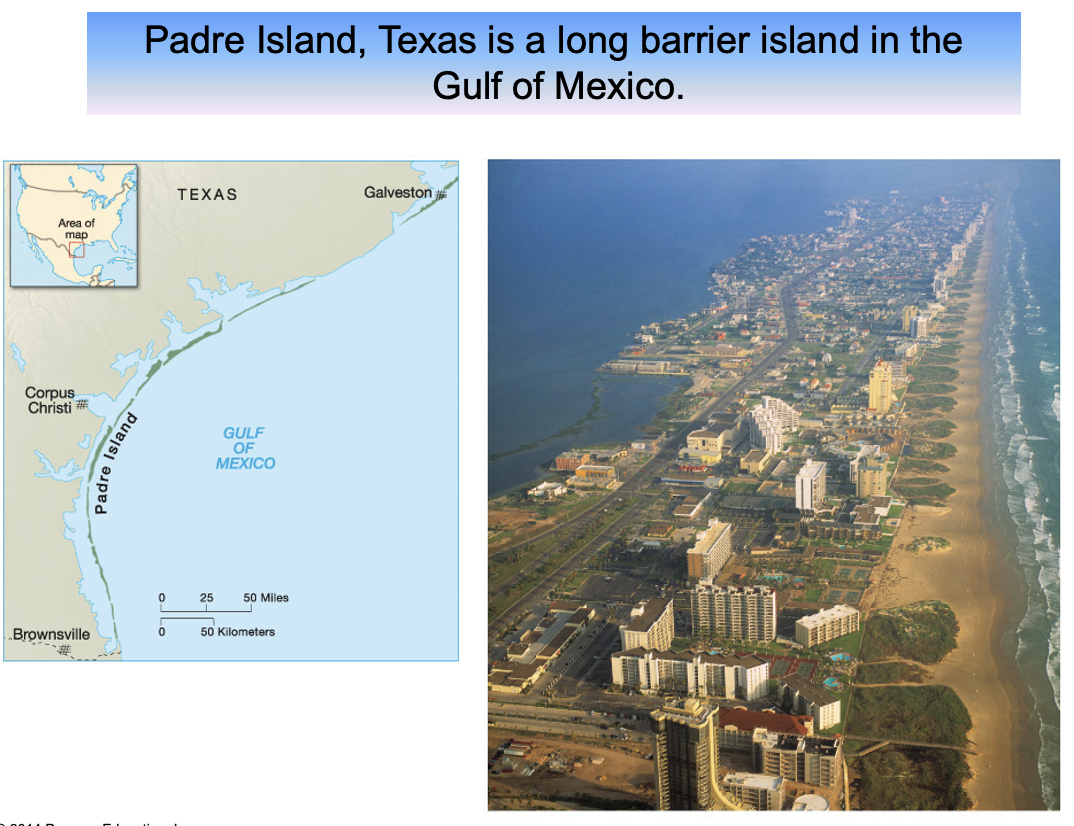
what is a barrier island?
The long, narrow depositional features, generally of sand, that form offshore roughly parallel to the coast are barrier beaches. When these features are broader and more extensive, they form barrier islands
what are wave cut cliffs?
the wave action cuts into the rock layers at the shoreline. They erode back into a cliff
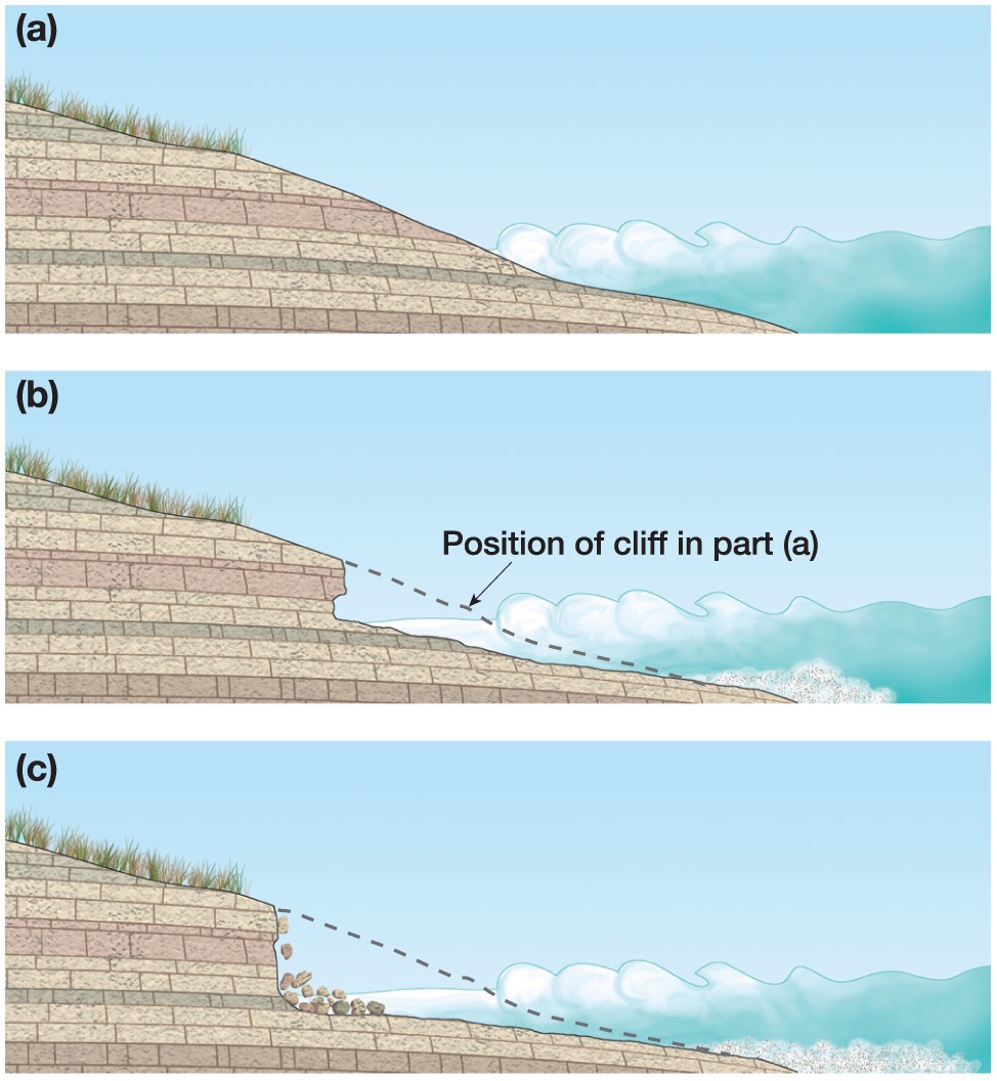
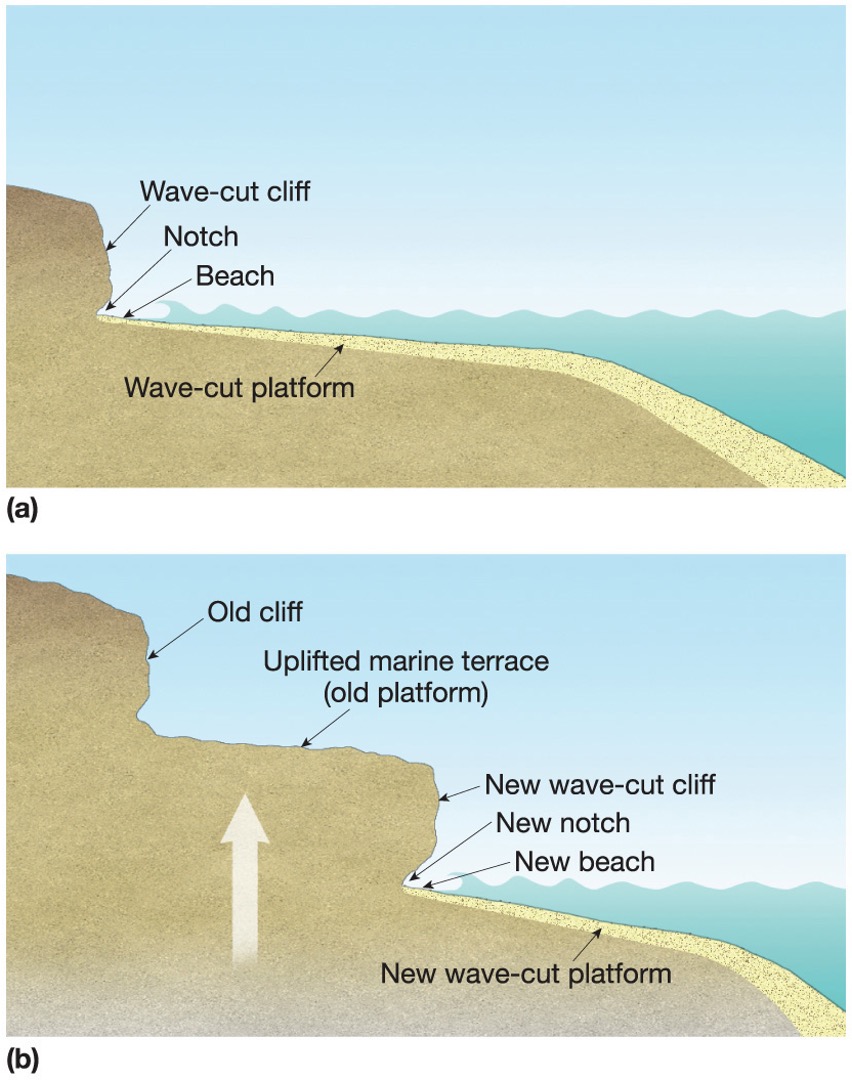
When sea level lowers, what forms?
When sea level lowers, new wave-cut cliffs form and a series of them record the changes in sea level over time

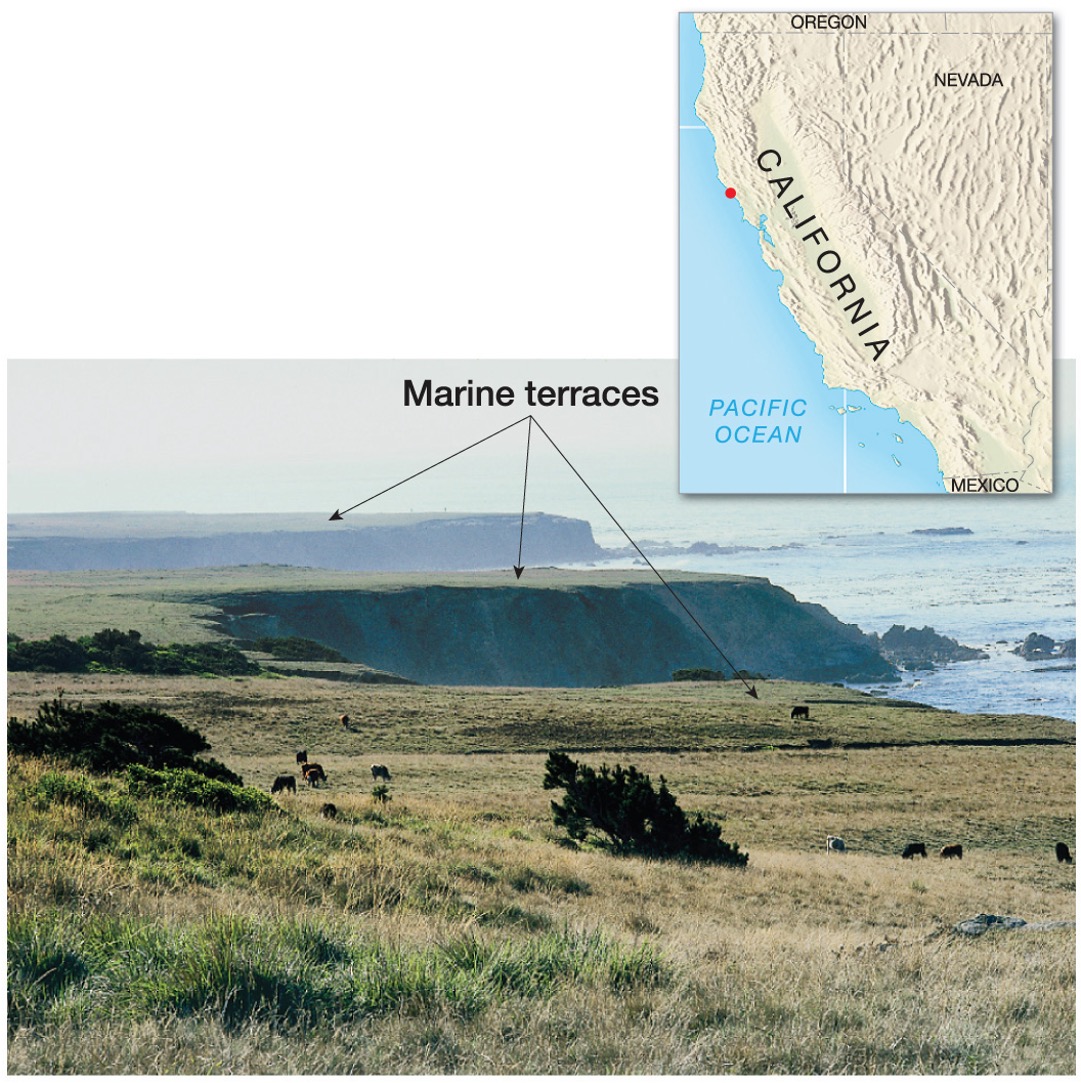
what are marine terraces?
In places where the elevation of the land relative to sea level has changed over time, wave-cut platforms may form wave-cut terraces that rise like stair steps back from the coast
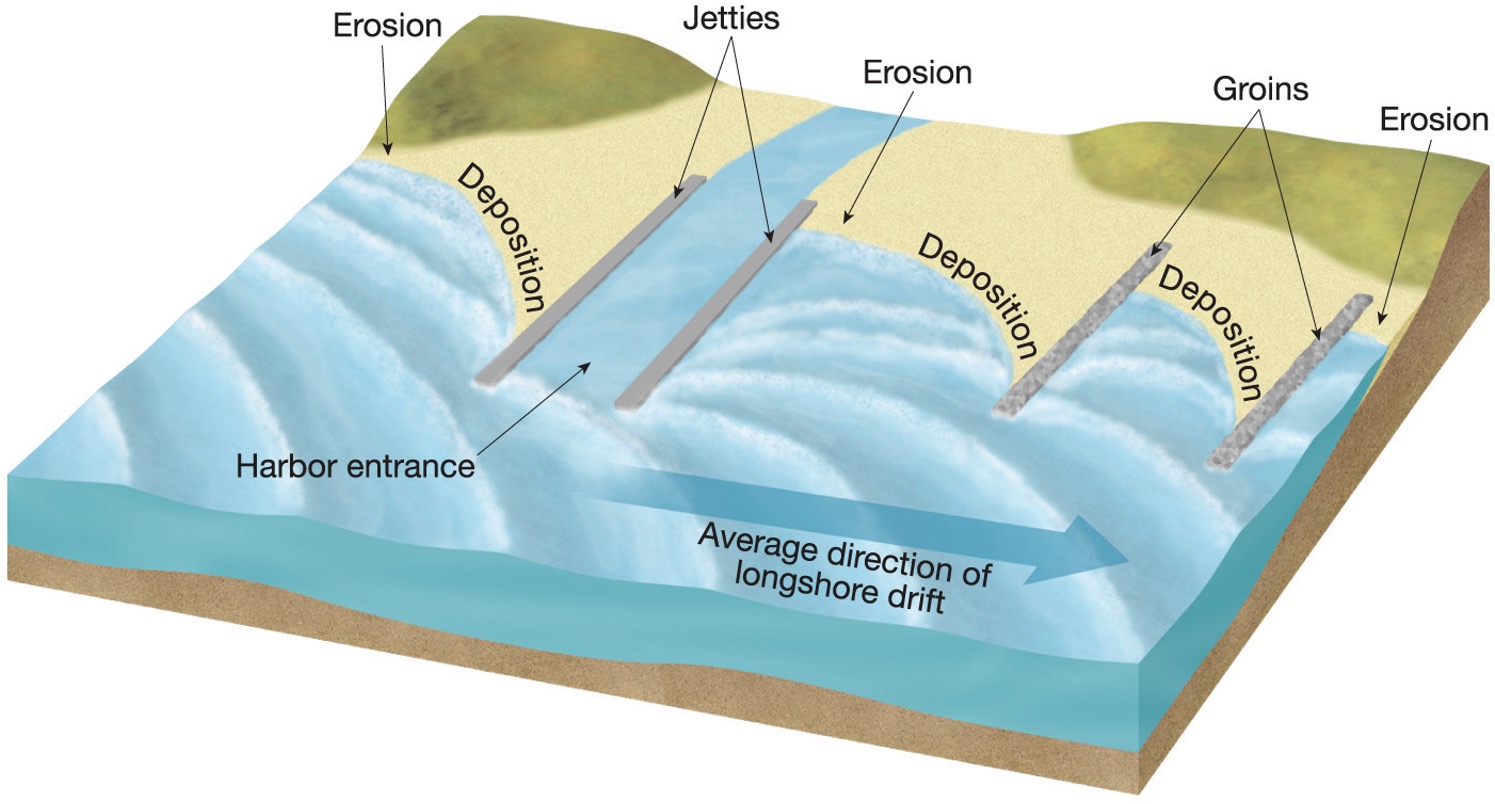
what do breakwater, groins and jetties do?
These stop the sand from eroding away, jetties keep harbors open

what is a breakwater?
to create zones of still water near the coastline, to protect from the force of waves and currents

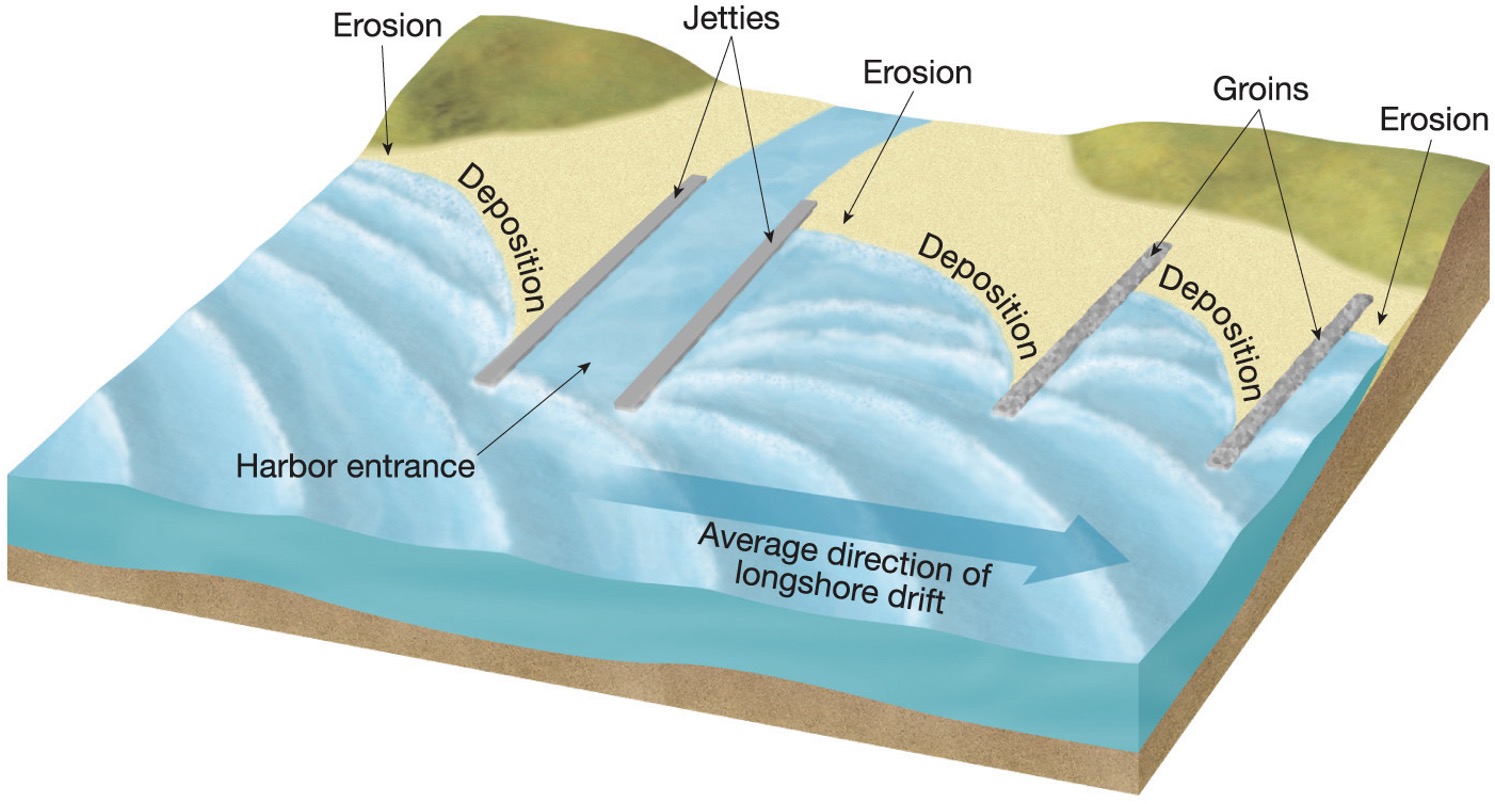
what are groins and jetties?
groins - trap sand and prevent beach erosion, jetties - help protect harbors and inlets from the damaging effects of tides, currents, and waves
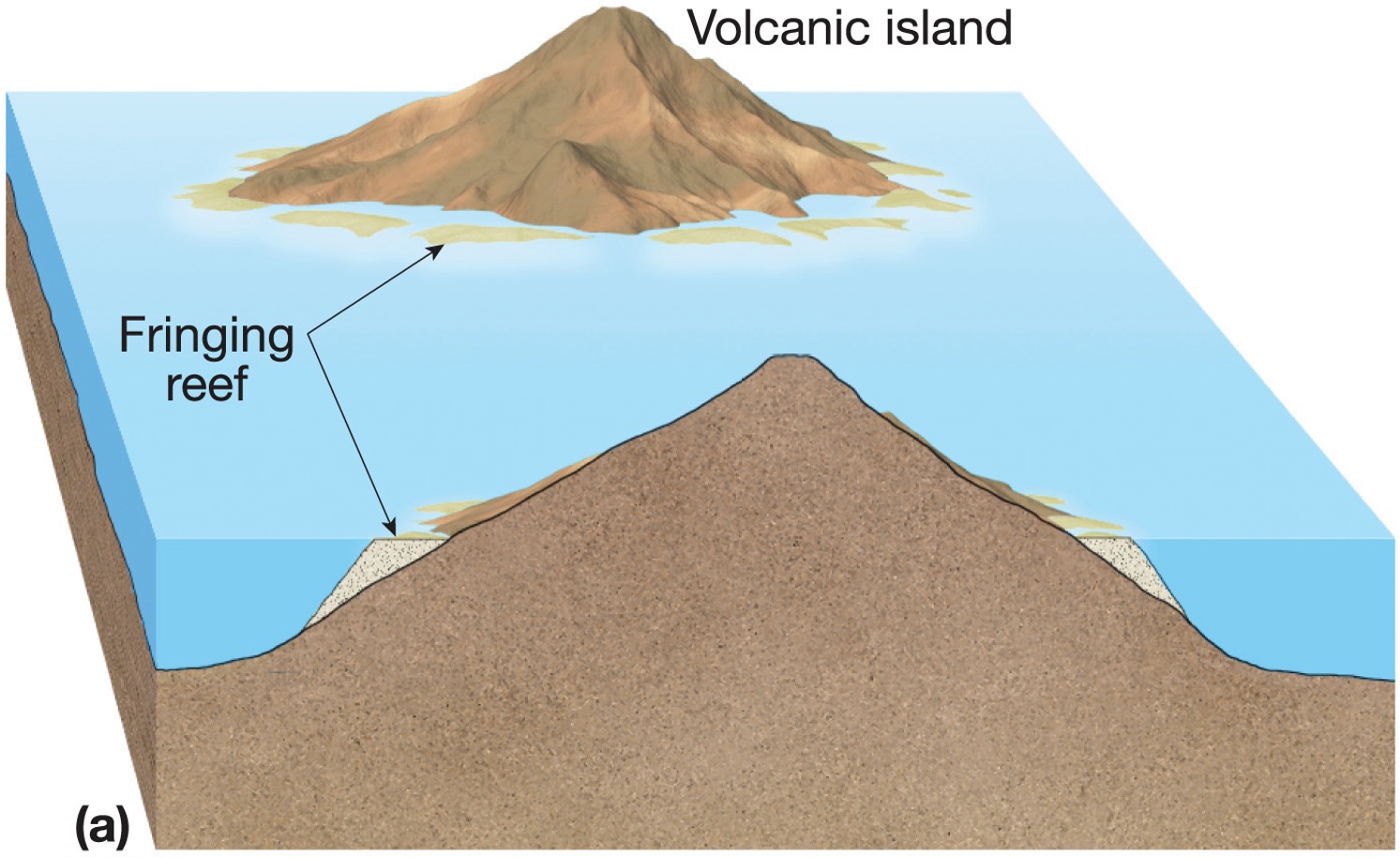
what is an atoll, barrier reef and fringing reef?
around an active volcano a fringing reef forms, as the volcano cools, it sinks down and a barrier reef forms, when the volcano sinks below the water, an atoll forms
what is a fringing reef?
around an active volcano

what is a barrier reef?
as the volcano cools, it sinks down
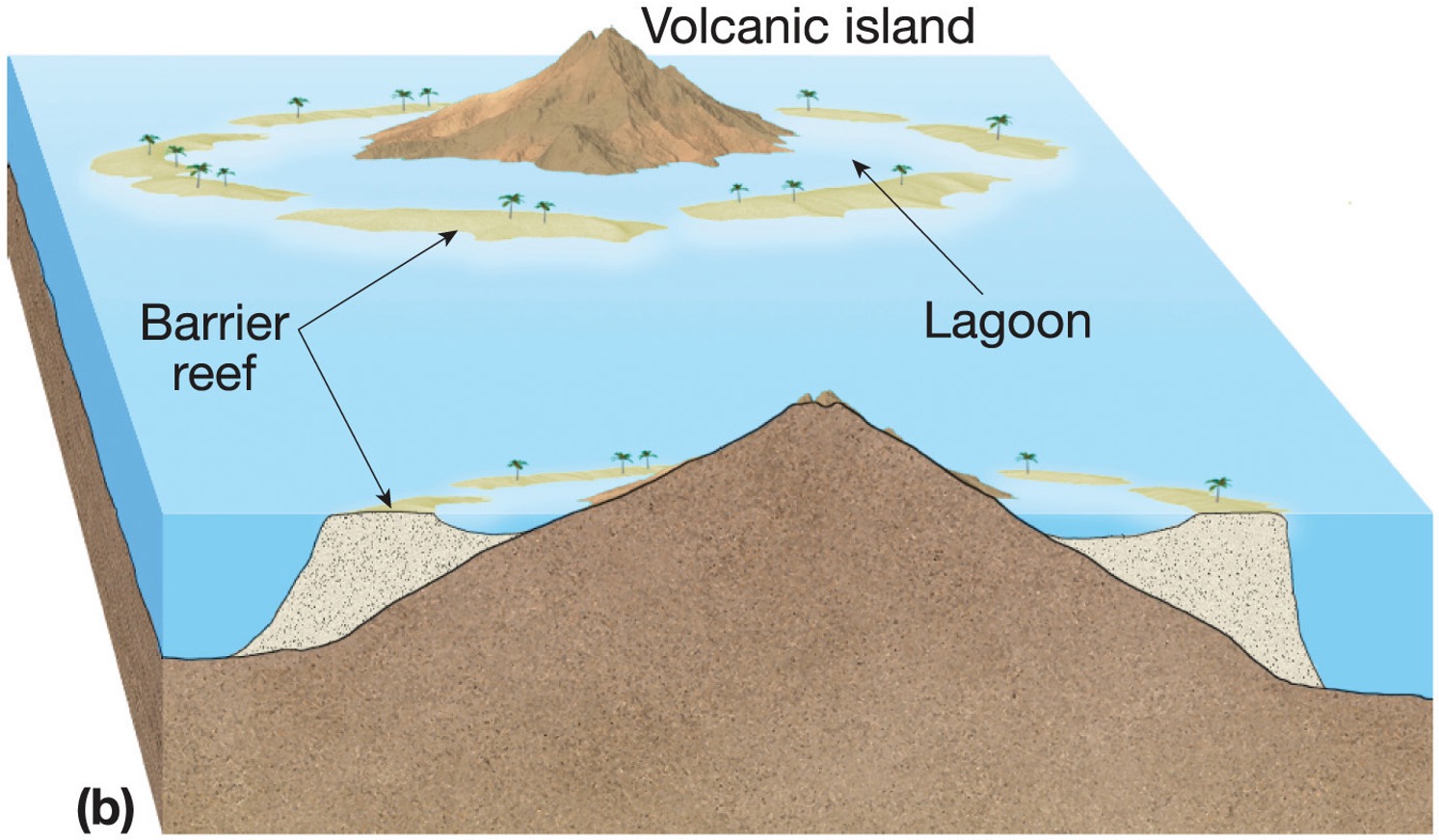
what is a atoll?
when the volcano sinks below the water

at the desert, wind is most effective …?
in exposed areas where there is no protection from it
In what type of areas is wind more effective?
Areas where there is no vegetation, arid & semi-arid regions
what is the main role of wind?
transportation and deposition of sediment
The wind behaves …?
like a fluid - it flows
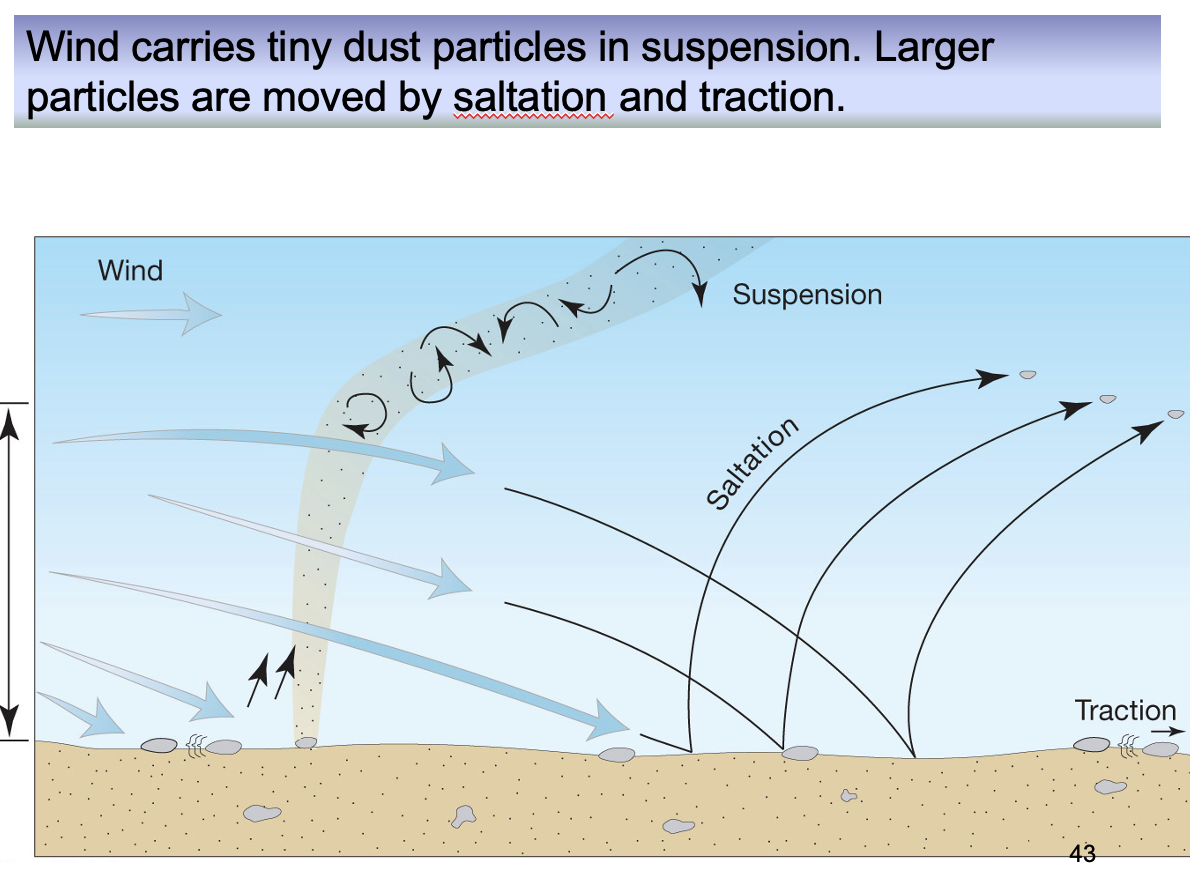
what are the two types of transportation?
bedload and suspended load
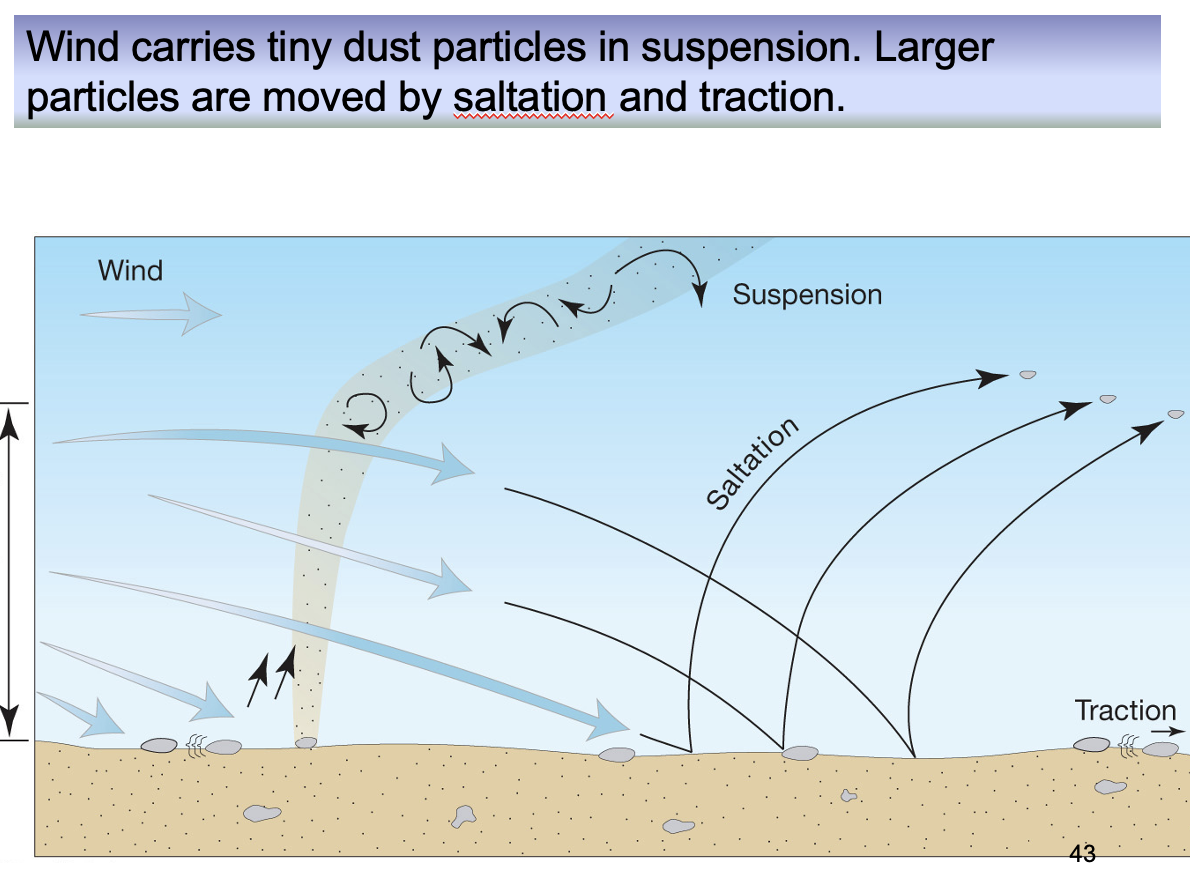
what is bedload?
material moves along the ground
what is suspended load?
material is in the air
what are the two type of storms?
sandstorm and dust storm
what is a sandstorm?
sand is in contact with the ground

what is a dust storm?
dust is in the air, too light to settle down
what type of impact does erosion have at a desert?
Erosion - insignificant agent compared to water and moving ice
what is deflation?
lowers the ground level, removes all of the fine sediment
what is a blowout?
result of deflation - wind-eroded depressions

what is a desert pavement (lag gravel)?
all of the small sediment has been blown away

what are the two types of wind depositional landforms?
two types: extensive blankets of silt, and mounds or ridges of sand

what is loess?
deposit of the suspended load, blanket/sheet like

what is loess composed of?
mostly silt sized grains, from material melting out from glaciers, and from fine grained silt blown off deserts
where does loess tend to occur?
tends to occur in vertical bluffs (Scott's Bluff, NE) - after erosion of the surrounding layers, this is left
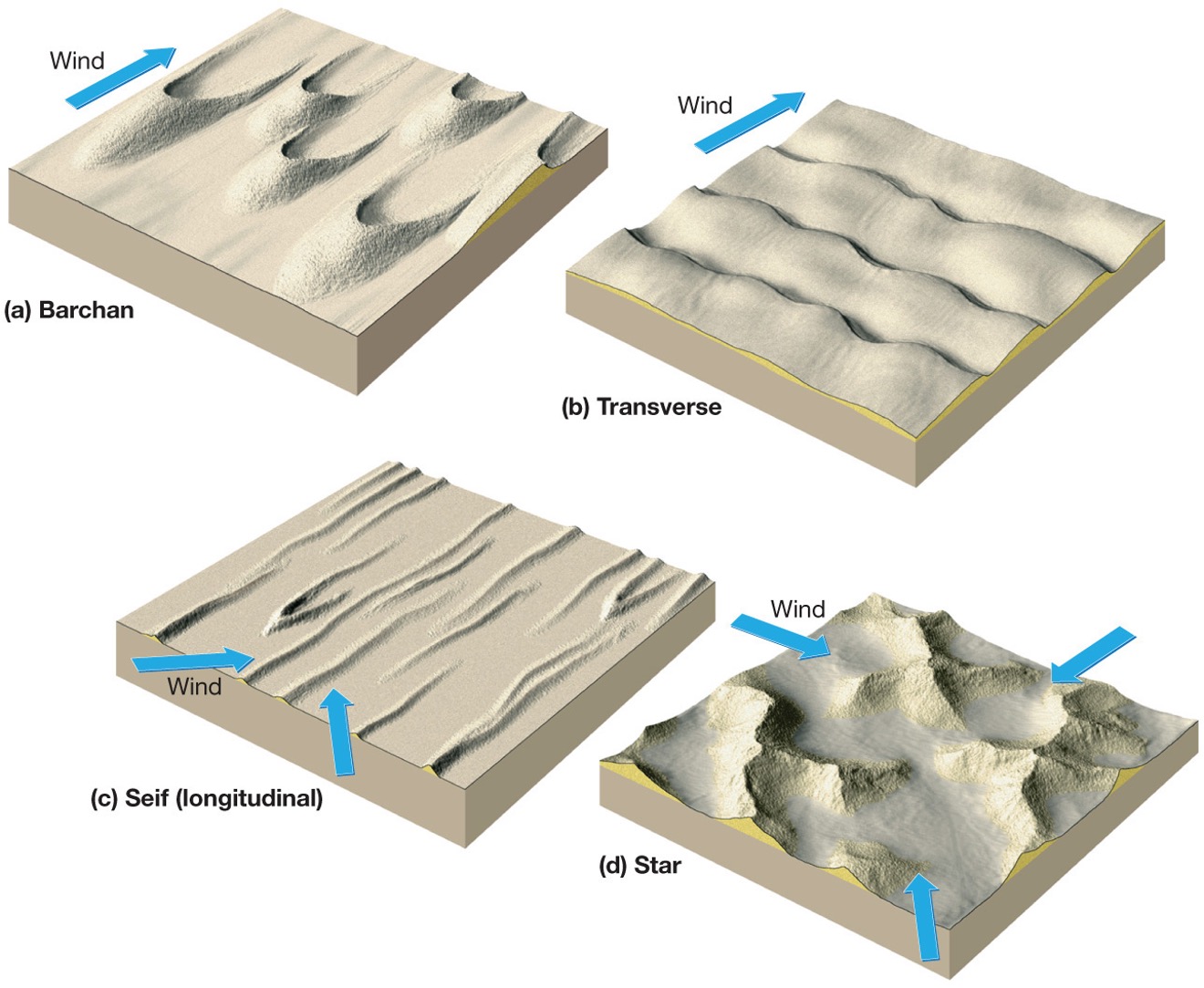
what are the several types of dunes?
barchan, transverse, longitudinal and star

a huge sand sea is called an..?
erg
What controls dune size and shape/type?
sand supply - how much is available?, vegetation - stabilizes the sand, wind strength and speed, wind direction
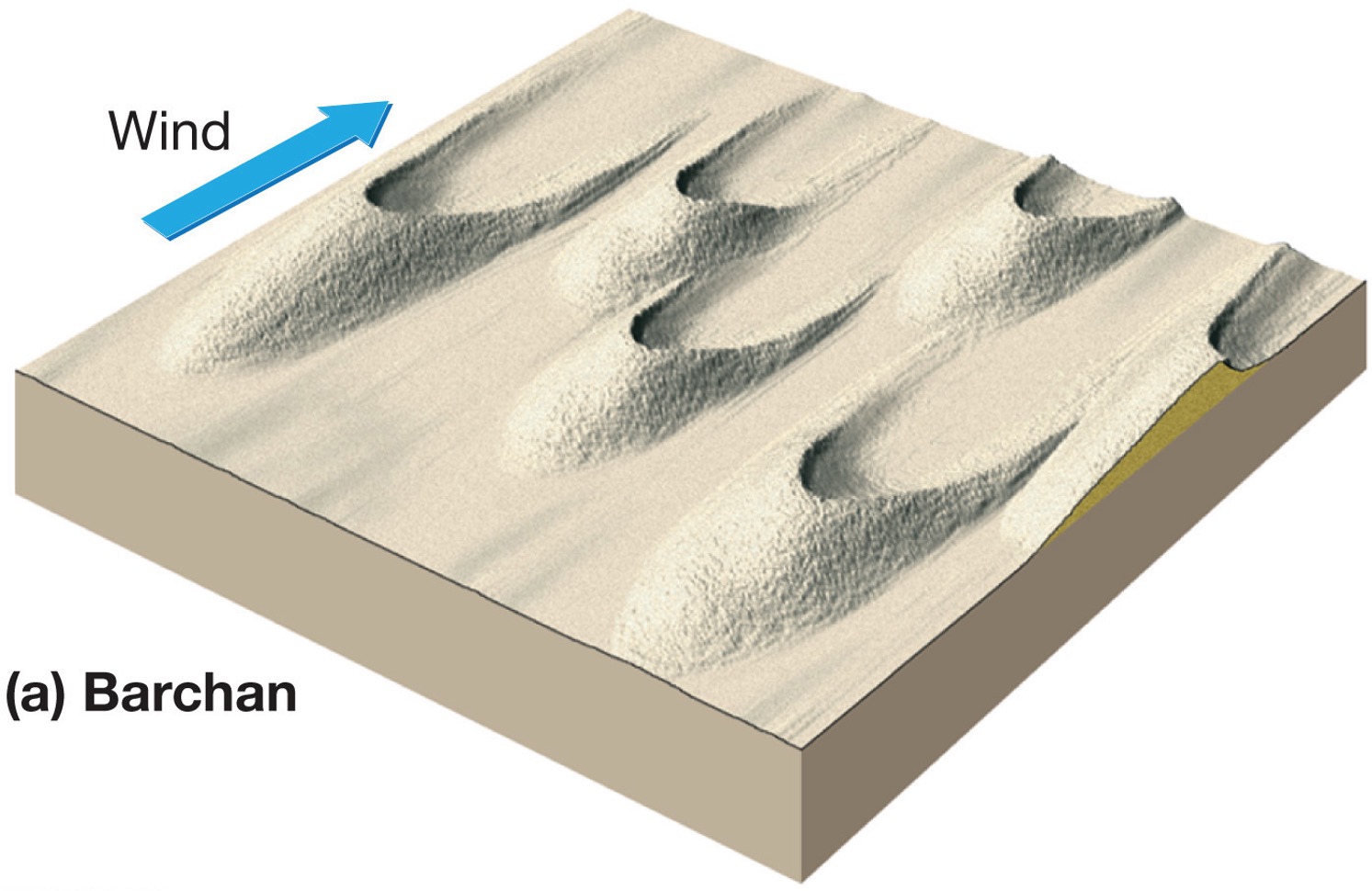
what is a barchan dune?
Most common, crescent-shaped, it points downwind
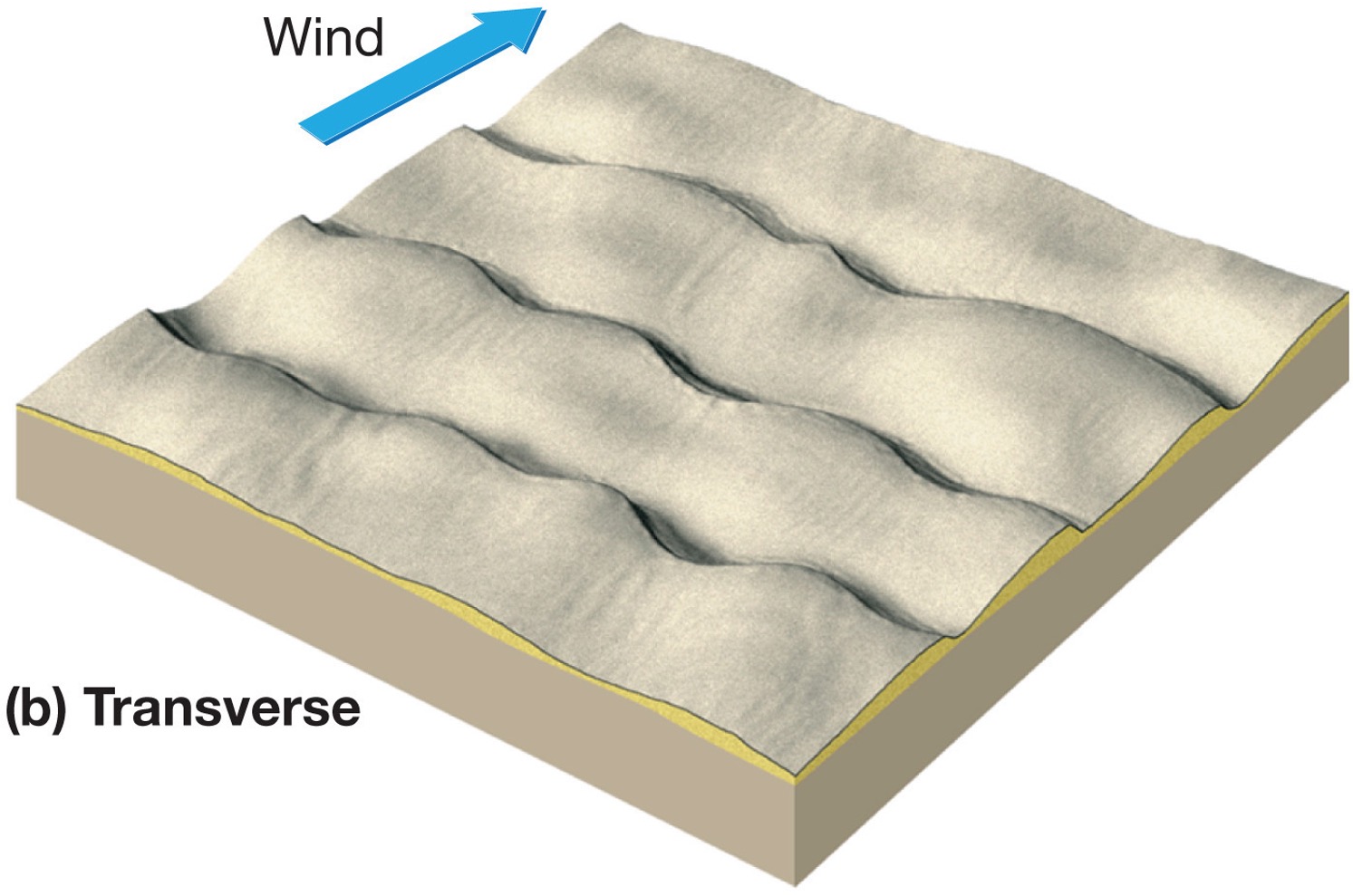
what is a transverse dune?
sand is plenty, winds are steady and vegetation is sparse or absent, wind - east to west, may form a sand sea; giant ripple(wavy) marks
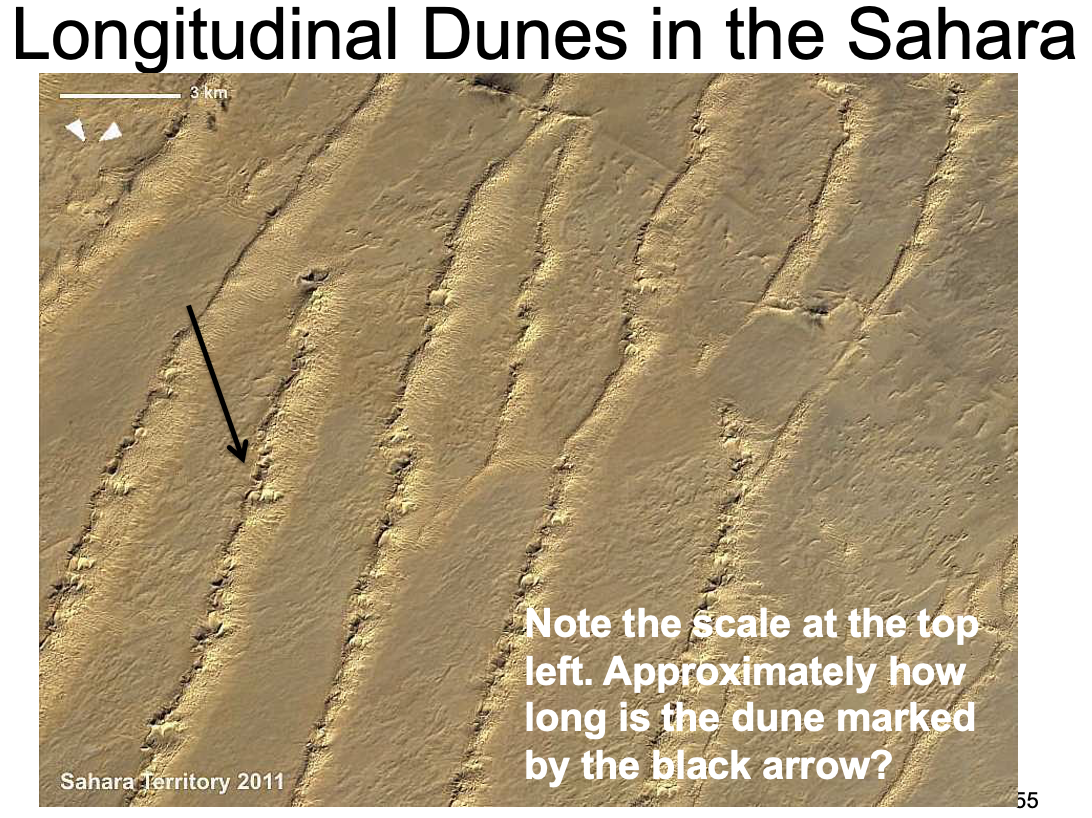
what is a longitudinal dune?
Form parallel to the wind direction, wind - north to south, limited sand supply, aka linear dunes
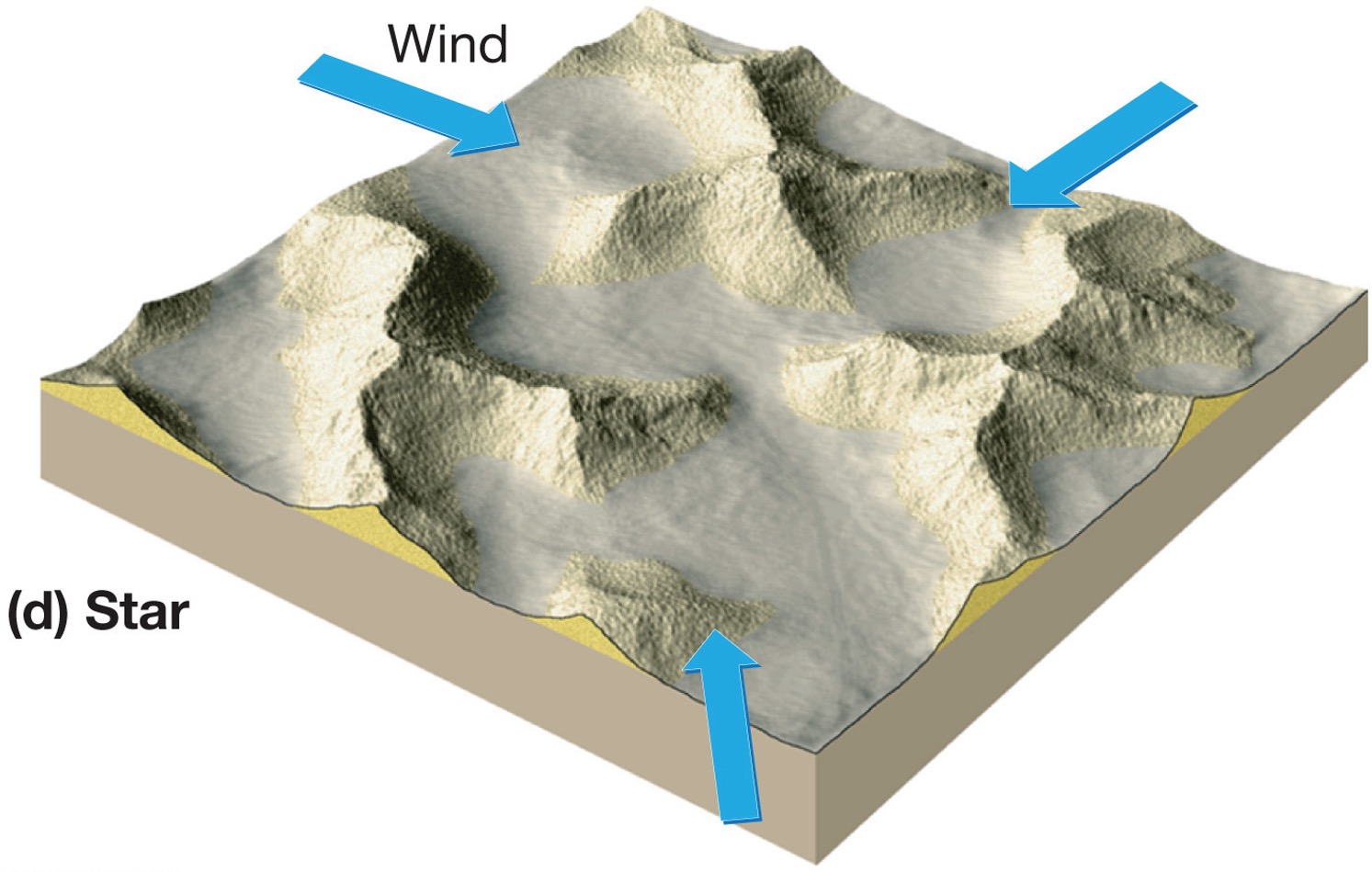
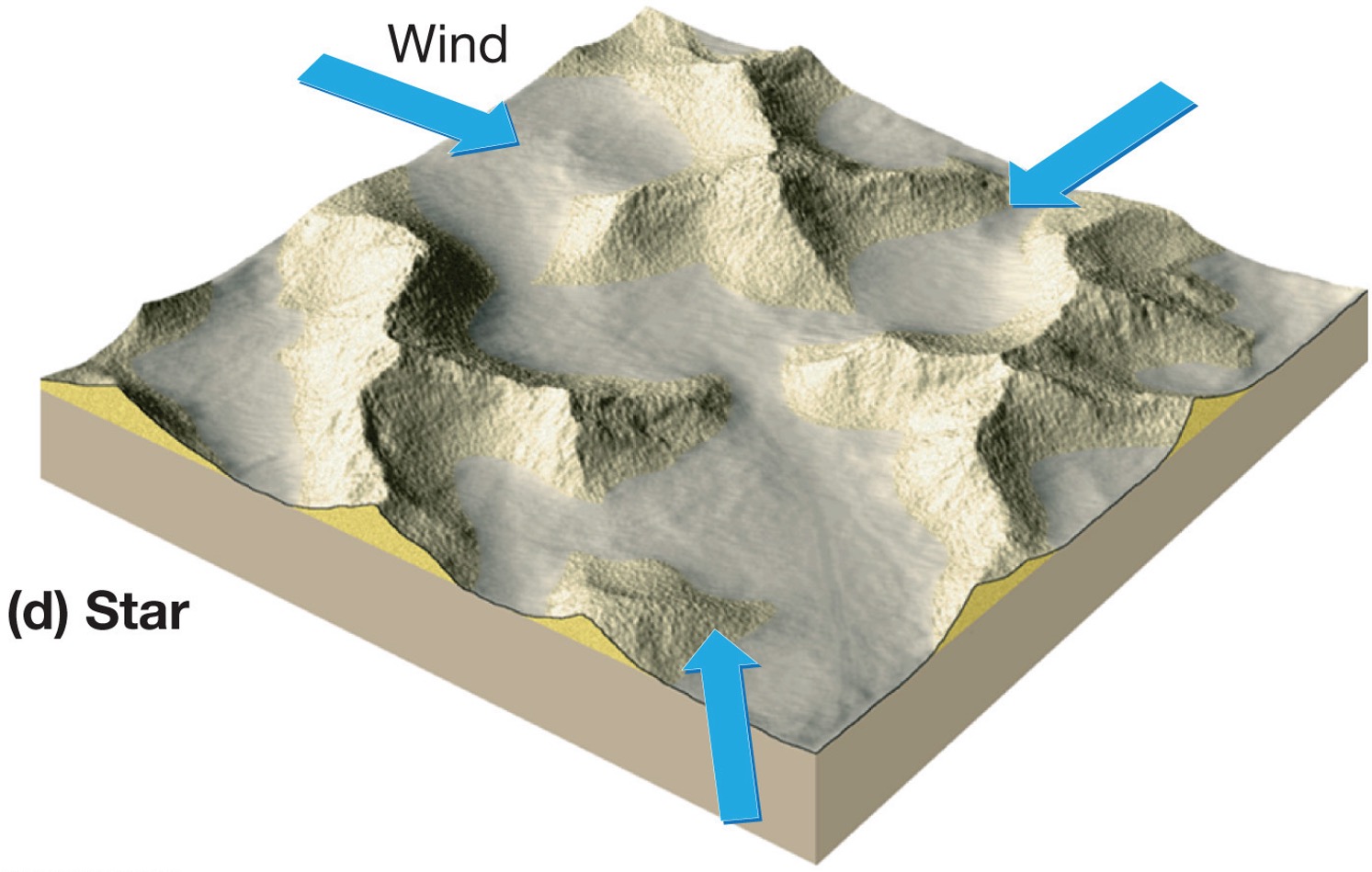
what is a star dune?
Star-shaped due to wind blowing in from all directions, form where sand is abundant and vegetation is non-existent