Endomembrane System
______ thing inside cell except for _____
cytoplasm; nucleus
______ fluid inside the cell
cytosol
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
______ thing inside cell except for _____
cytoplasm; nucleus
______ fluid inside the cell
cytosol
eukaryotic cells are _____ ____ organelles
membrane bound
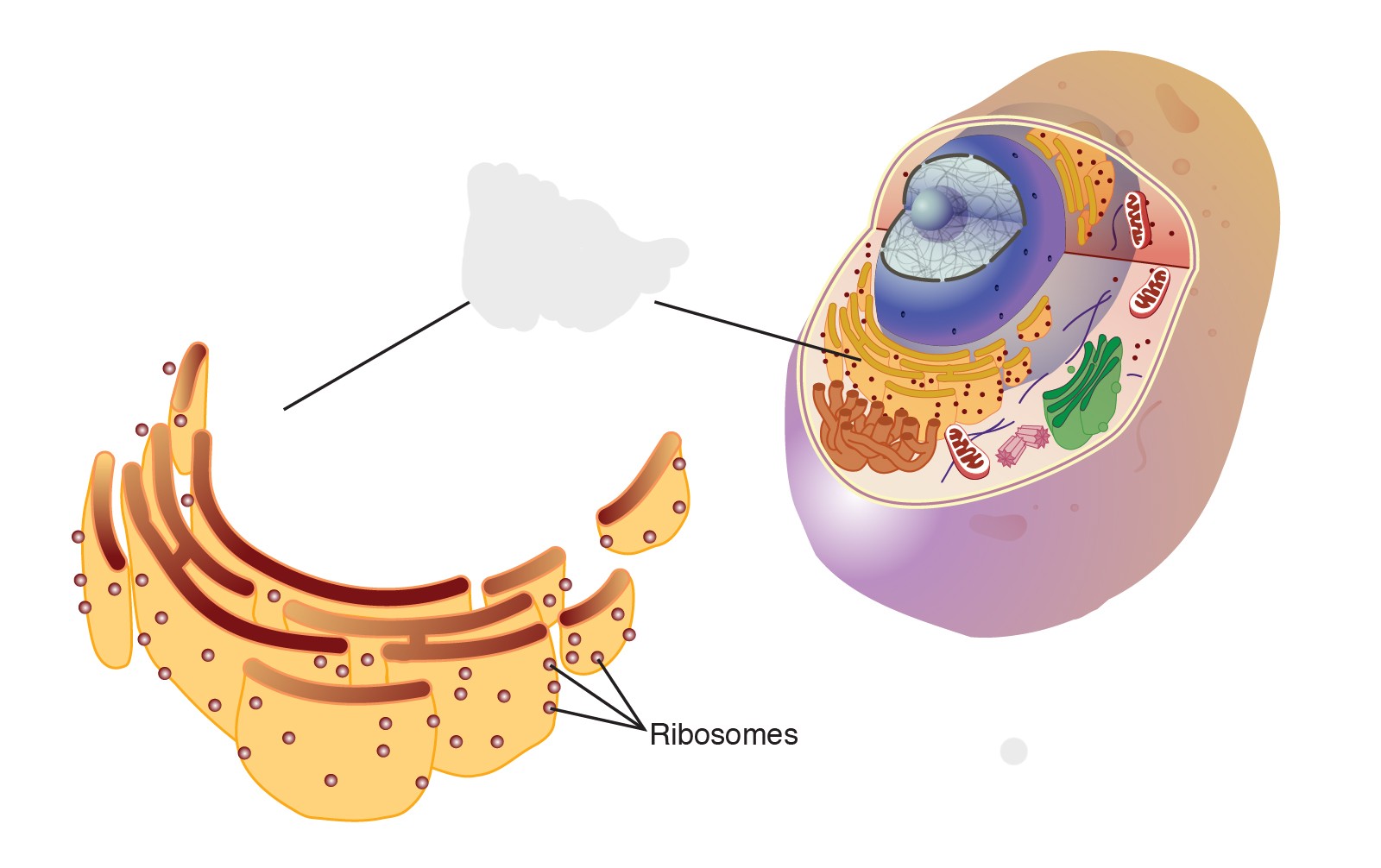
rough er is involved in protein synthesis and processing.
also makes phospholipids for membrane
if modified proteins are not needed in er, they are packaged into vesicles
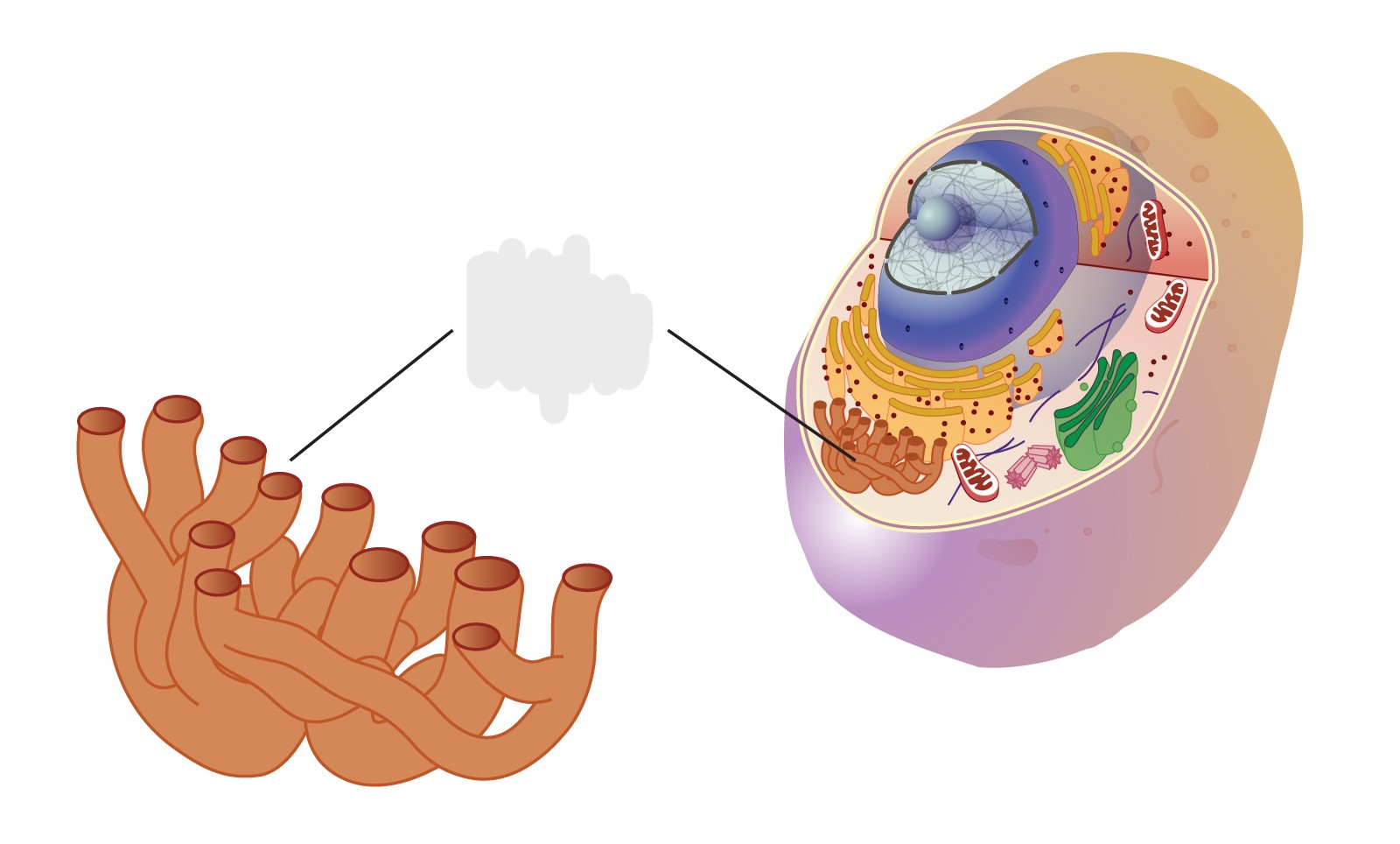
smooth er; synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates, and detoxifies the cell
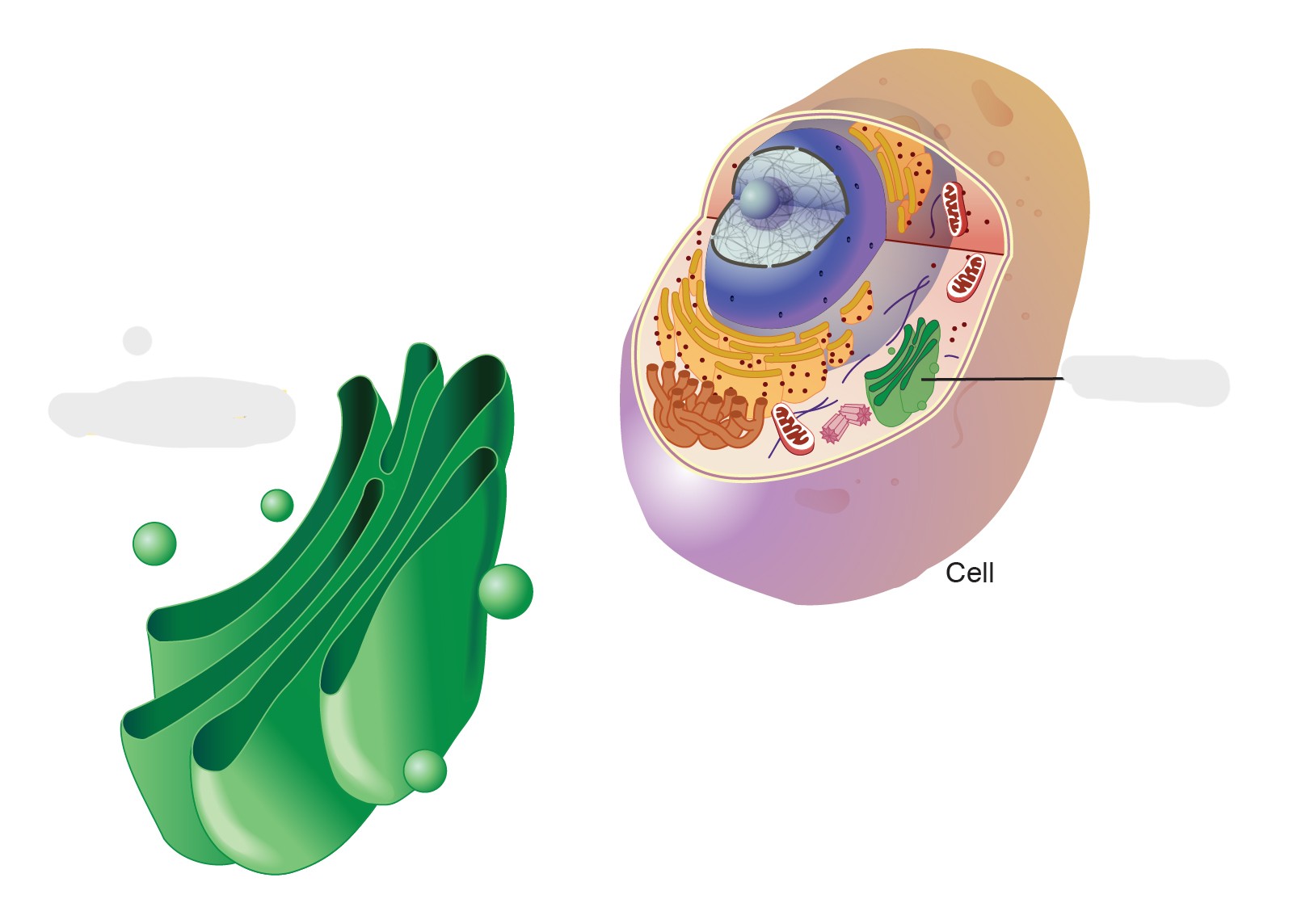
golgi complex; modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids received from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell
cis face; recieves the cell
trans face; sends vesicles back out
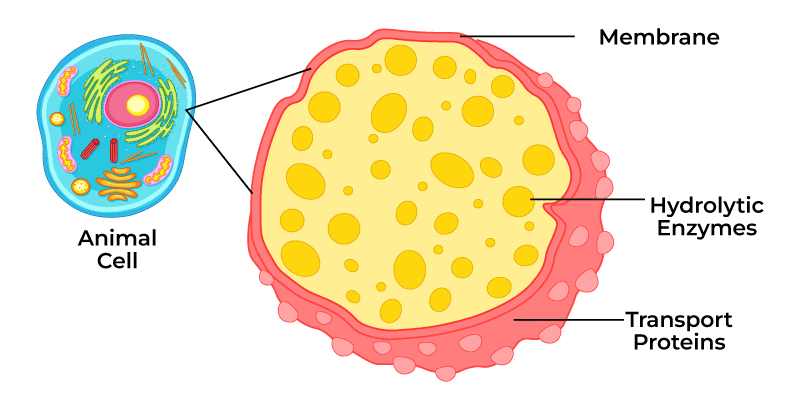
lysosome ; organelle that contains digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris. Similar to peroxisomes
use phagocytosis (fat - gocytosis, cell eating)
membranes are a _____ bilayer
lipid; phospholipid
____ are large vesicles that stem from er and golgi
vacuoles
types of vacuoles
food, contractile (water; like a contract with a plumber), central
order of endomembrane system
nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, plasma membrane.
mitochondria is the site of _____ _______
celluar respiration
mitochondria inner membrane has folds called _____
cristae
intermembrane space
space between inner and outer membrane
_______ is the area enclosed by the inner membrane
matrix
endosymbiont theory
A biological hypothesis that explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts as a result of a symbiotic relationship between early eukaryotic cells and engulfed prokaryotic cells.
_____ translate mRNA into amino acid sequences during protein synthesis
ribosome