Digestive anatomy
1/315
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
316 Terms
What is the abdominal cavity and how is it bounded?
The space containing the abdominal organs, bounded anterolaterally by musculo-aponeurotic walls and superiorly by the diaphragm at the 4th intercostal space
Which organs in the upper abdomen are protected by the rib cage?
Spleen, liver, stomach, and parts of the kidneys
What imaginary plane separates the abdominal cavity from the pelvic cavity?
The pelvic inlet, which divides the greater (false) pelvis above from the lesser (true) pelvis below
Which organs does the greater pelvis protect?
Portions of the ileum, cecum, appendix, and sigmoid colon
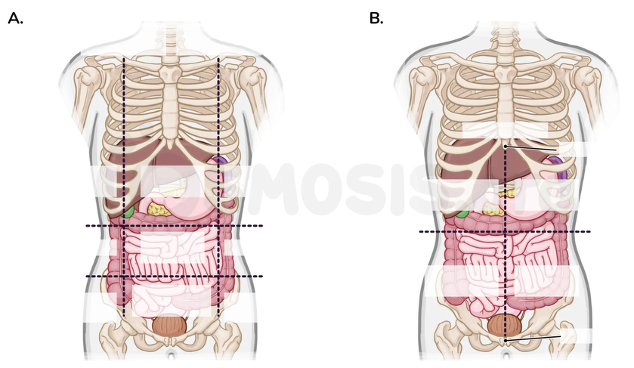
How are the four abdominal quadrants defined?
By the median plane (xiphoid to pubic symphysis) and the transumbilical plane (through the umbilicus)
Name the four abdominal quadrants.
Right upper quadrant (RUQ), left upper quadrant (LUQ), right lower quadrant (RLQ), left lower quadrant (LLQ)
Which organs are found in the right upper quadrant?
Right liver lobe, gallbladder, head of pancreas, first to third parts of duodenum, right colic (hepatic) flexure
Which organs are in the left upper quadrant?
Left liver lobe, stomach, spleen, body of pancreas, left colic (splenic) flexure
What structures are located in the right lower quadrant?
Ascending colon, cecum, appendix, and lower portion of the right kidney
What is found in the left lower quadrant?
Descending colon, sigmoid colon, and lower portion of the left kidney
Which additional structures can be present in the lower quadrants?
Ureters and internal reproductive structures (ovaries/uterus in females
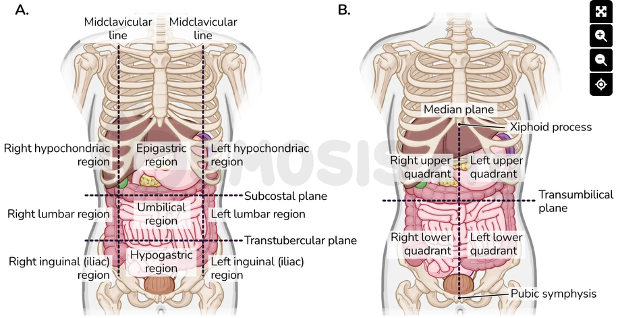
How are the nine abdominal regions defined?
By two vertical midclavicular lines and two horizontal planes (subcostal and transtubercular)
Where are the midclavicular lines drawn?
Vertically from the midpoint of each clavicle down to the groin
What is the subcostal plane?
The horizontal line just below the 10th rib costal cartilages at approximately L3
What is the transtubercular plane?
The horizontal line passing through the iliac tubercles and the body of L5
What alternative plane can define the superior boundary of the nine regions?
The transpyloric plane at L1, midway between the manubrium and pubic symphysis
Which landmark structures lie on the transpyloric plane?
Pylorus of the stomach, hila of the kidneys, fundus of the gallbladder, neck of pancreas, transverse colon, duodenojejunal junction, superior mesenteric artery, and hepatic portal vein
What organs occupy the epigastric region?
Upper portion of the stomach, parts of the esophagus, liver, pancreas, duodenum, and spleen
Which organs are in the umbilical region?
Most of the small intestine, part of the large intestine, pancreas, and parts of both kidneys
What does the hypogastric (suprapubic) region contain?
Sigmoid colon, urinary bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs (uterus/ovaries or prostate)
What is found in the right hypochondriac region?
Right liver lobe, gallbladder, parts of large and small intestine, and portions of the right kidney
Which organs lie in the left hypochondriac region?
Spleen, parts of left kidney, stomach, pancreas, and colon
What structures are located in the right lumbar region?
Lower parts of liver and gallbladder, right kidney, and ascending colon
What structures are located in the left lumbar region?
Portions of the descending colon and left kidney
What is found in the right inguinal (iliac) region?
Appendix and cecum
What is found in the left inguinal (iliac) region?
Descending colon and sigmoid colon.