Chem Basics
Week 1 (gps)
Chemistry: science of the structure, composition and properties of matter
Matter + Energy
 Mind Map: Matter
Mind Map: Matter
Central Idea: Matter
Definition: Anything w. mass + volume
Main Branches:
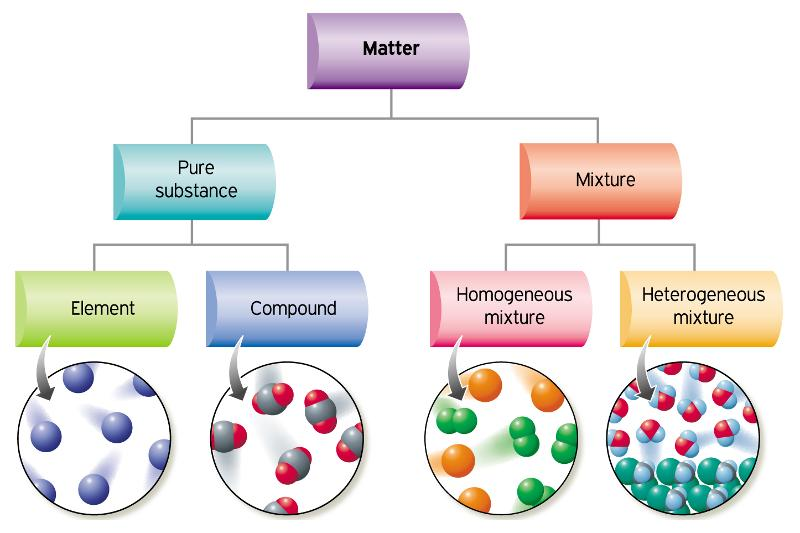
Classification of Matter
Pure Substances: any matter that is HOMOGENEOUS and has a fixed composition by mass
Elements: contain atoms of a SINGLE type and CANNOT decompose further
Compounds: 1+ type of element; compositions are FIXED
Mixtures: 2+ diff substances mixed together
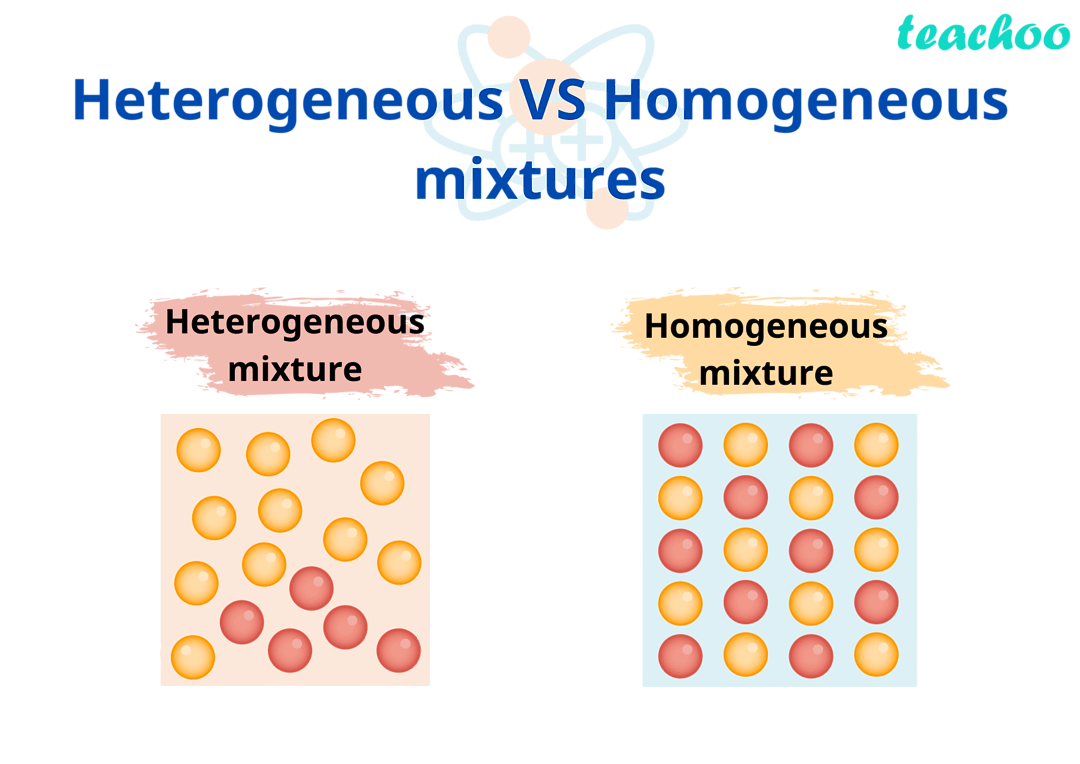
Homogeneous Mixtures: UNIFORM combo of substances at a molecular level AKA components are EVENLY mixed and visually indistinguishable.
Ex: saltwater (NaCl + H2O)
Heterogeneous Mixtures: NOT uniformly dispersed AKA scattered

Physical Properties: measured w/o changing the identity + composition of a substance
Ex: color, odor, density, melting/boiling point, solubility, texture
Chemical Properties: lead to changes in the identity + composition of a substance
Changes in Matter
Physical Changes/Rxn: changes that accompany the measurement of PHYSICAL properties
Reversible Changes
Irreversible Changes
Ex: phase changes
Chemical Changes/Rxn: changes that accompany the measurement of CHEMICAL properties
Formation of New Substances
Energy Changes
Atomic Structure
Atoms
Protons (+)
the identity of an element is determined by the atomic #/proton #
Neutrons (0)]
neutron # does NOT change an elements identity
neutrons add MASS to an atom
ISOTOPE: element w same # of protons but diff # of neutrons AKA change in neutron #
Electrons (-)
Elements
Atomic Number
atomic # = proton # = electron #
periodic table is organized by INCREASING atomic #
Atomic Mass
proton # = atomic # = electron #
atomic mass = p - n (proton # - neutron #)
Molecules: smallest identifiable sample of a substance
Monatomic Molecules: isolated atoms (do not want to interact and react w other atoms) AKA noble gases (g18)
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
Polyatomic Molecules: 2+ atoms linked (too much)
O3, P4, S8, C60
Diatomic Molecules: EXACTLY 2 atoms (paired with itself!!)
7 up aka. H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
Chemical Formulas
Bonding Types
Energy and Matter
Forms of Energy:
Heat (q)
endothermic: absorb/input heat
exothermic: release heat
Chemical
Electrical
Light
Nuclear
Mechanical Energy
Kinetic: energy associated w motion
Potential: energy associated w. position
Conservation of Energy: Energy CANNOT be created or destroyed. It can ONLY change from one form to another.
Laws and Theories
Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Definite Proportions
Atomic Theory of Matter
Sub-Branches:
Elements
Metals
Non-metals
Metalloids
Compounds
Chemical Formulas
Chemical Reactions
Homogeneous Mixtures
Solutions
Alloys
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Suspensions
Colloids
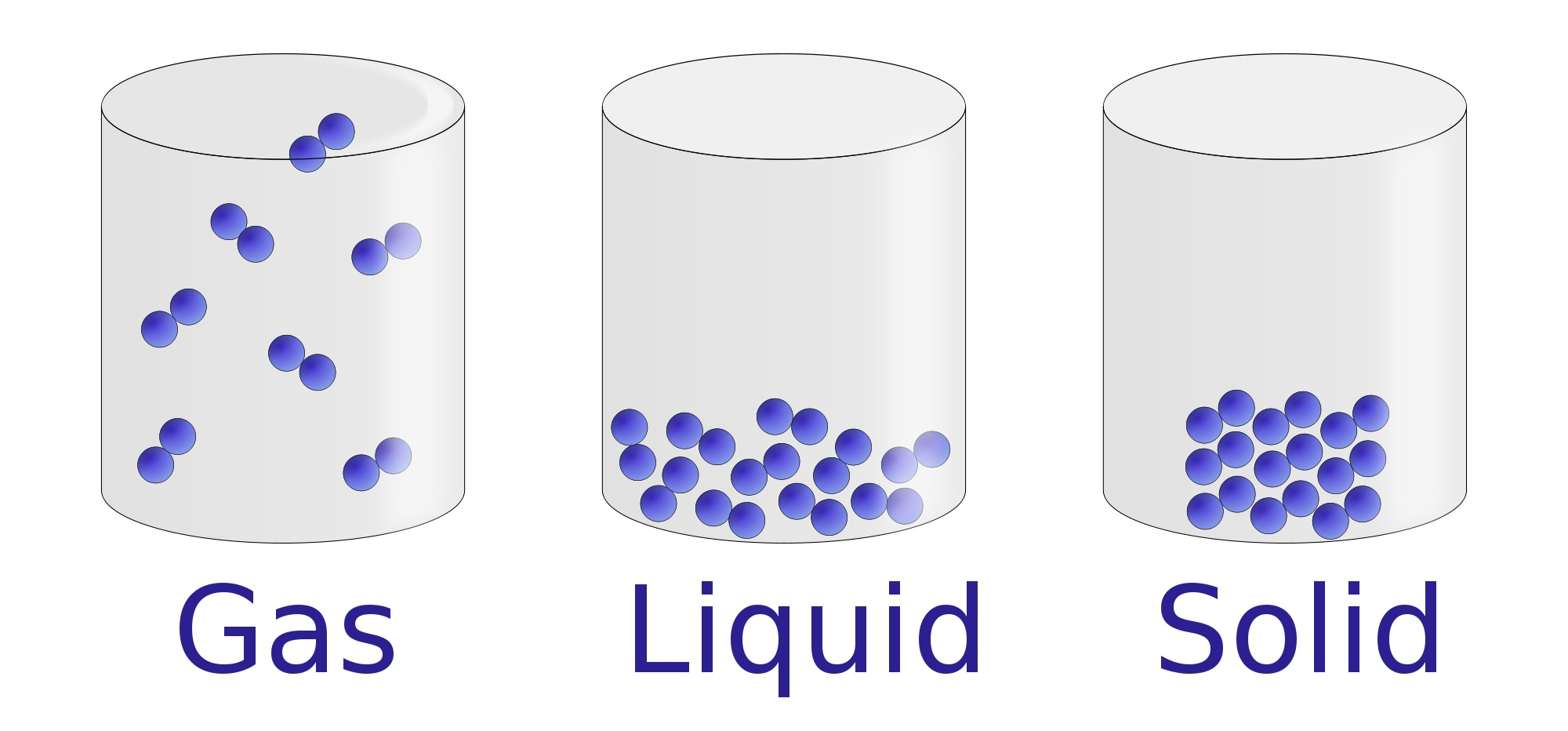
Solid
Crystalline Solids
Amorphous Solids
Liquid
Viscosity
Surface Tension
Gas
Pressure
Boyle's Law
Reversible Changes
Melting
Freezing
Irreversible Changes
Burning
Decomposition
Formation of New Substances
Combustion
Oxidation
Energy Changes
Exothermic Reactions
Endothermic Reactions