Bootcamp.com - Cell Division
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
_____ is nuclear division (karyokinesis) followed by cytokinesis
cell division
_____ is the nuclear division of cell division
karyokinesis
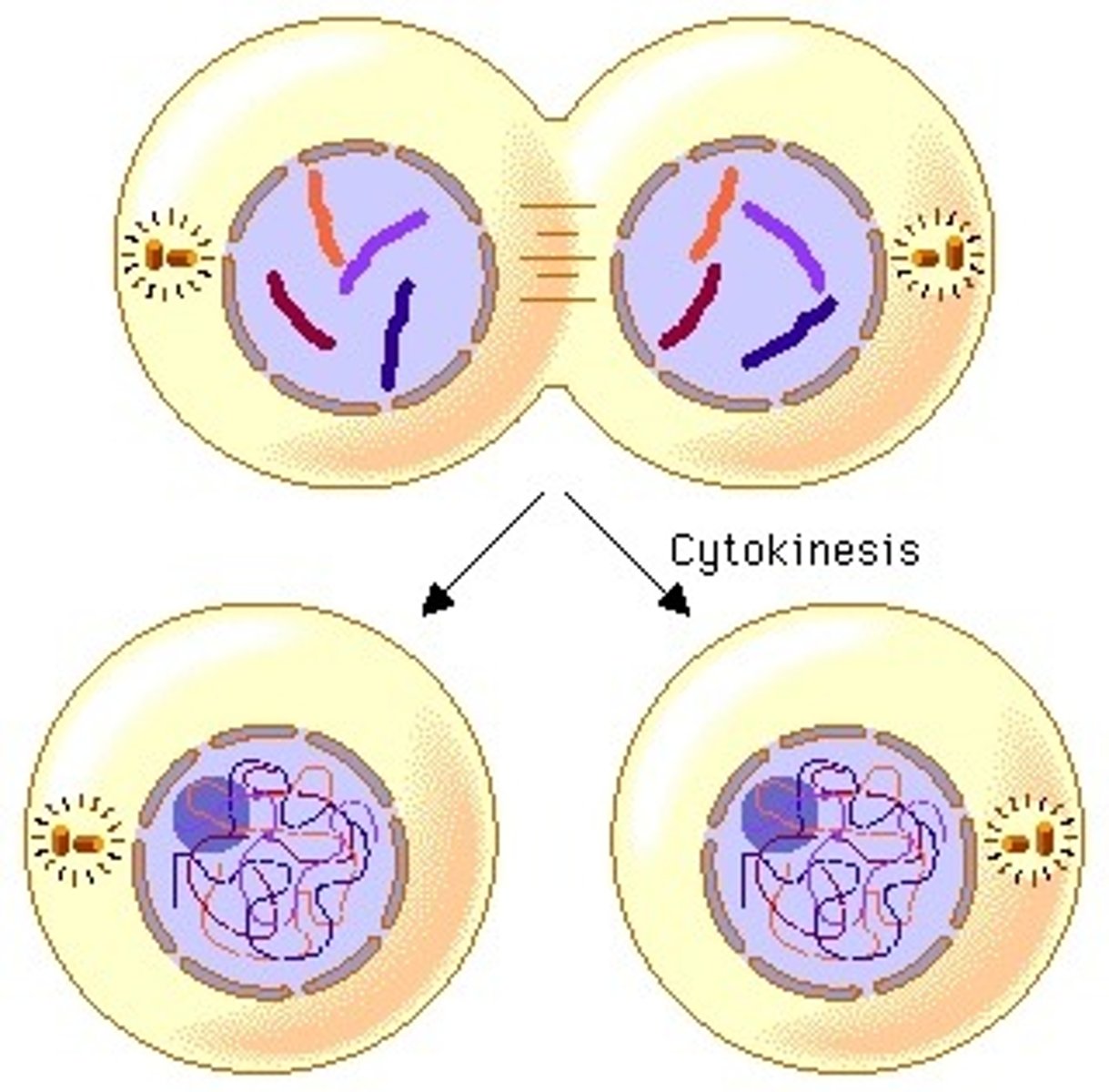
_____ is the division of the cytoplasm that happens at the end of cell division
cytokinesis
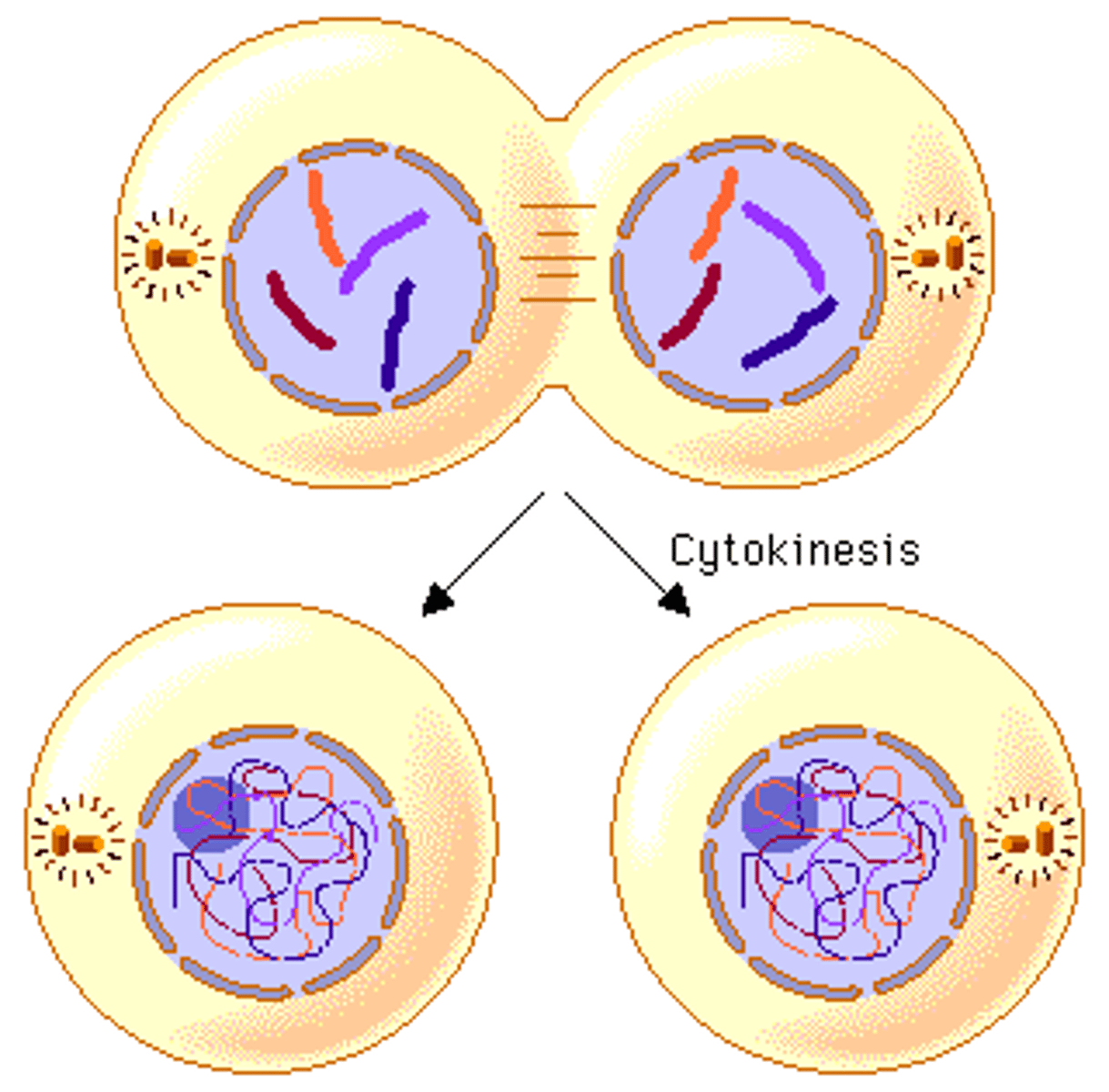
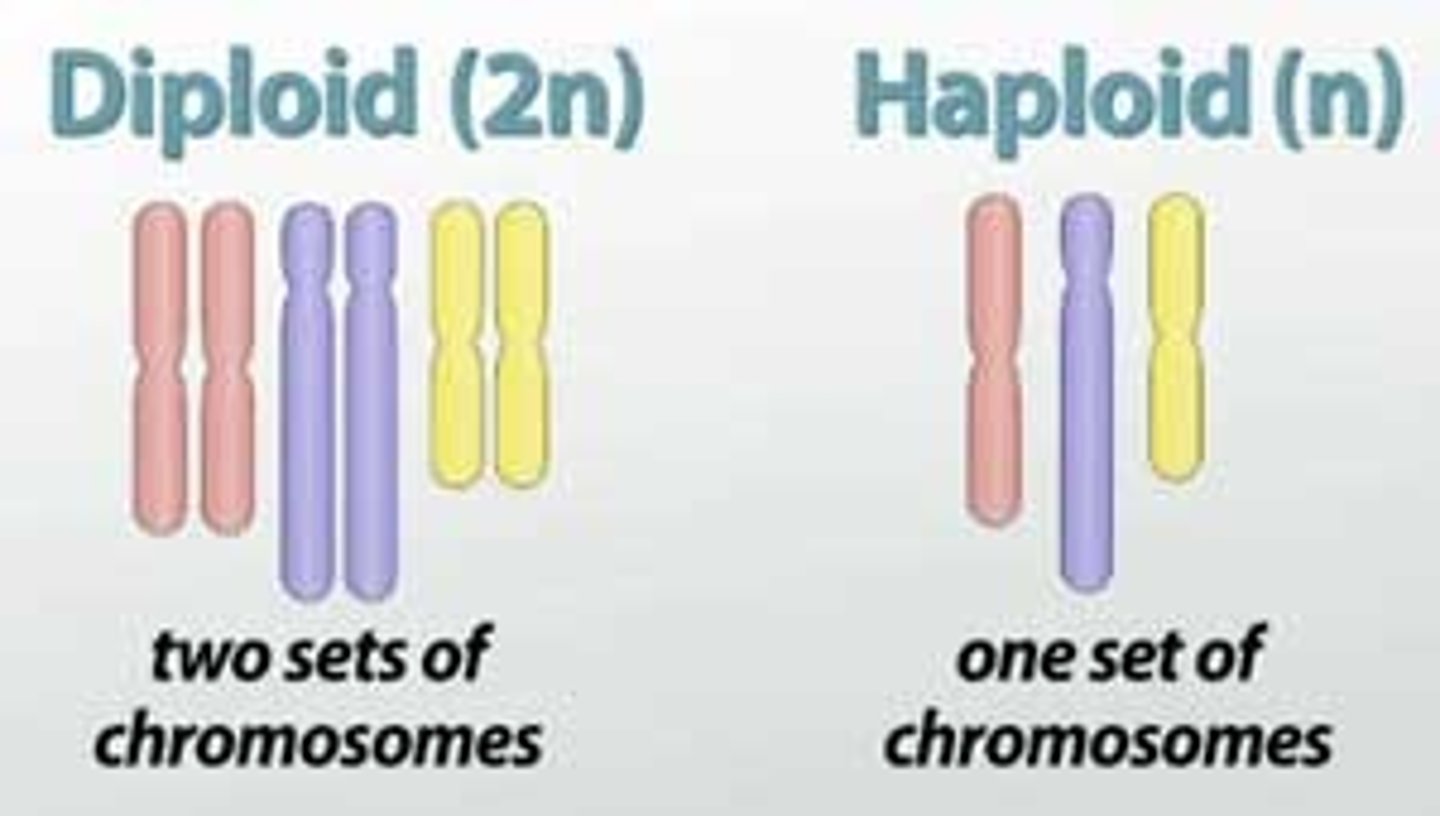
in _____ cells, there are 2 copies of every chromosome, forming a pair called _____ chromosomes
diploid; homologous
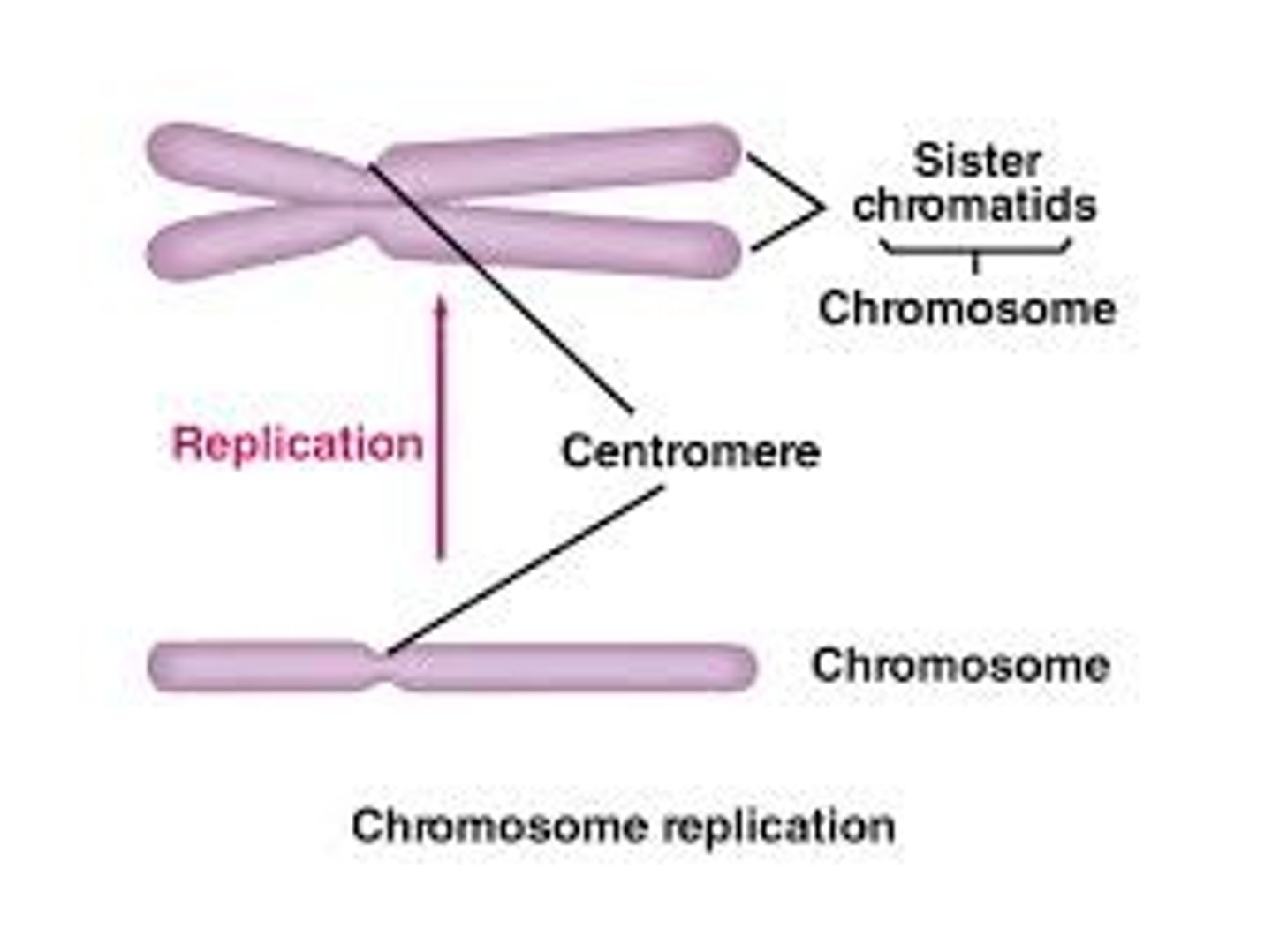
humans have _____ chromosomes, _____ homologous pairs, and a total of 92 chromatids (depending on the stage of division)
46, 23
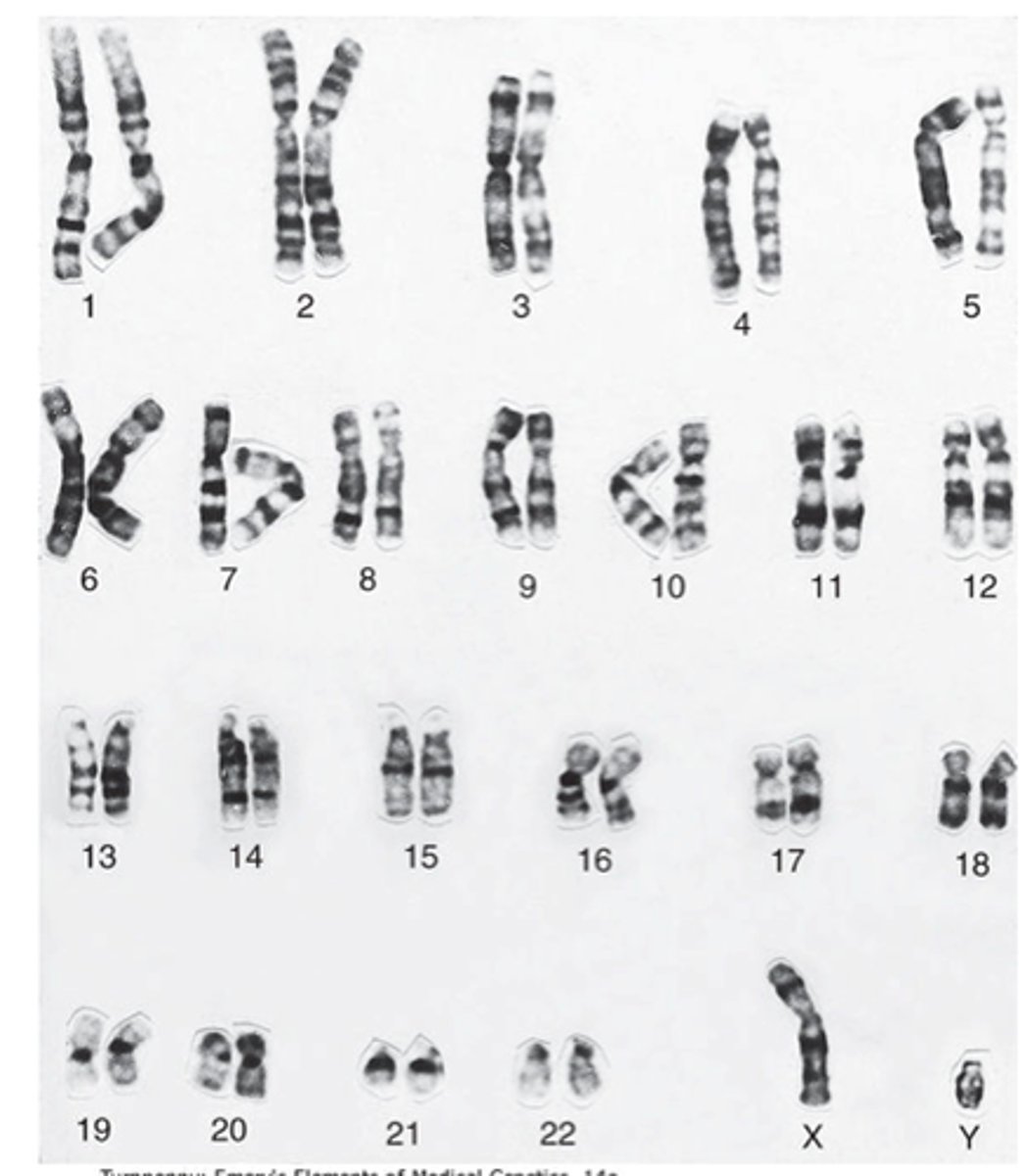
humans have 46 chromosomes, 23 homologous pairs, and a total of _____ chromatids (depending on the stage of division)
92
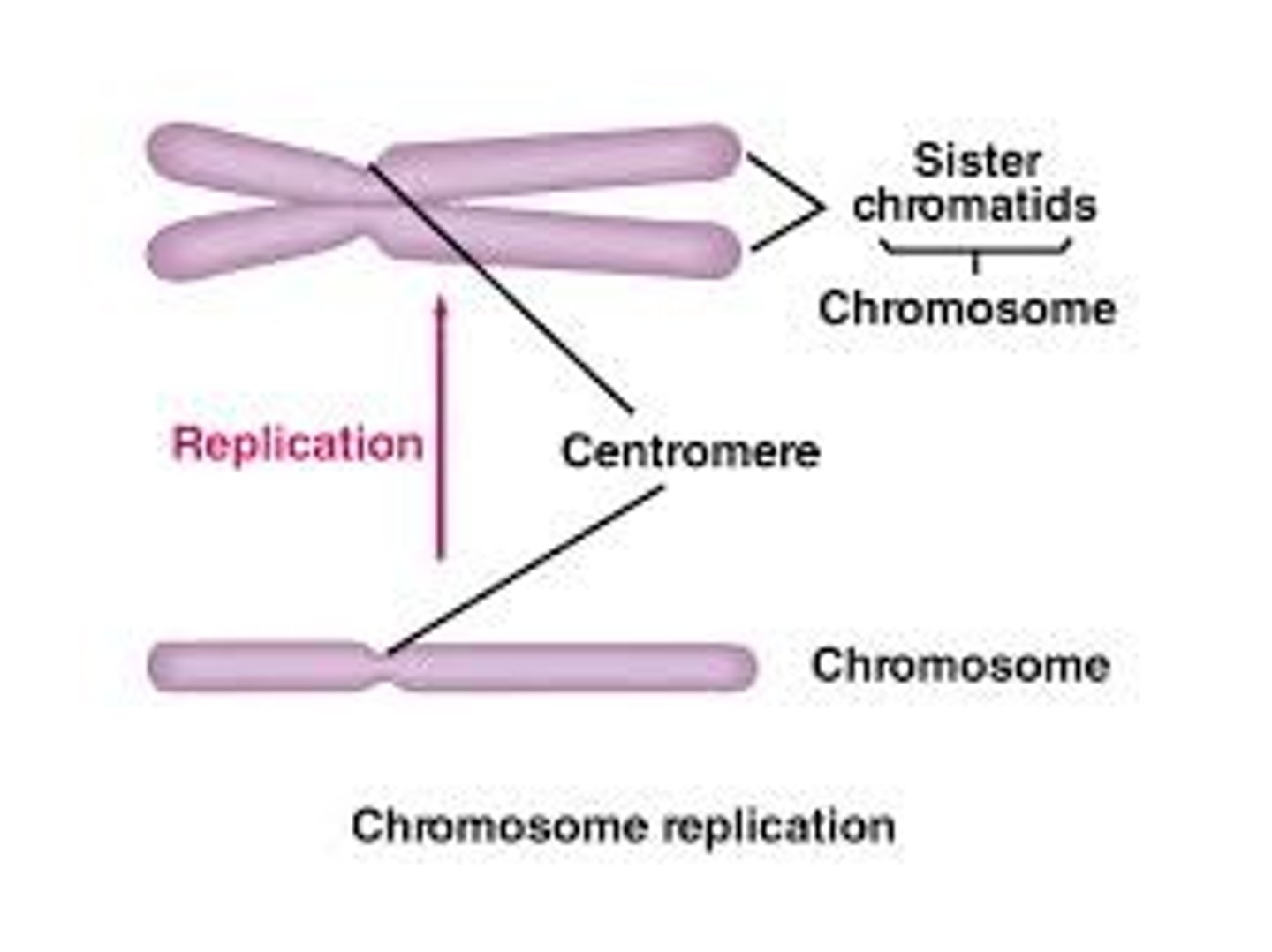
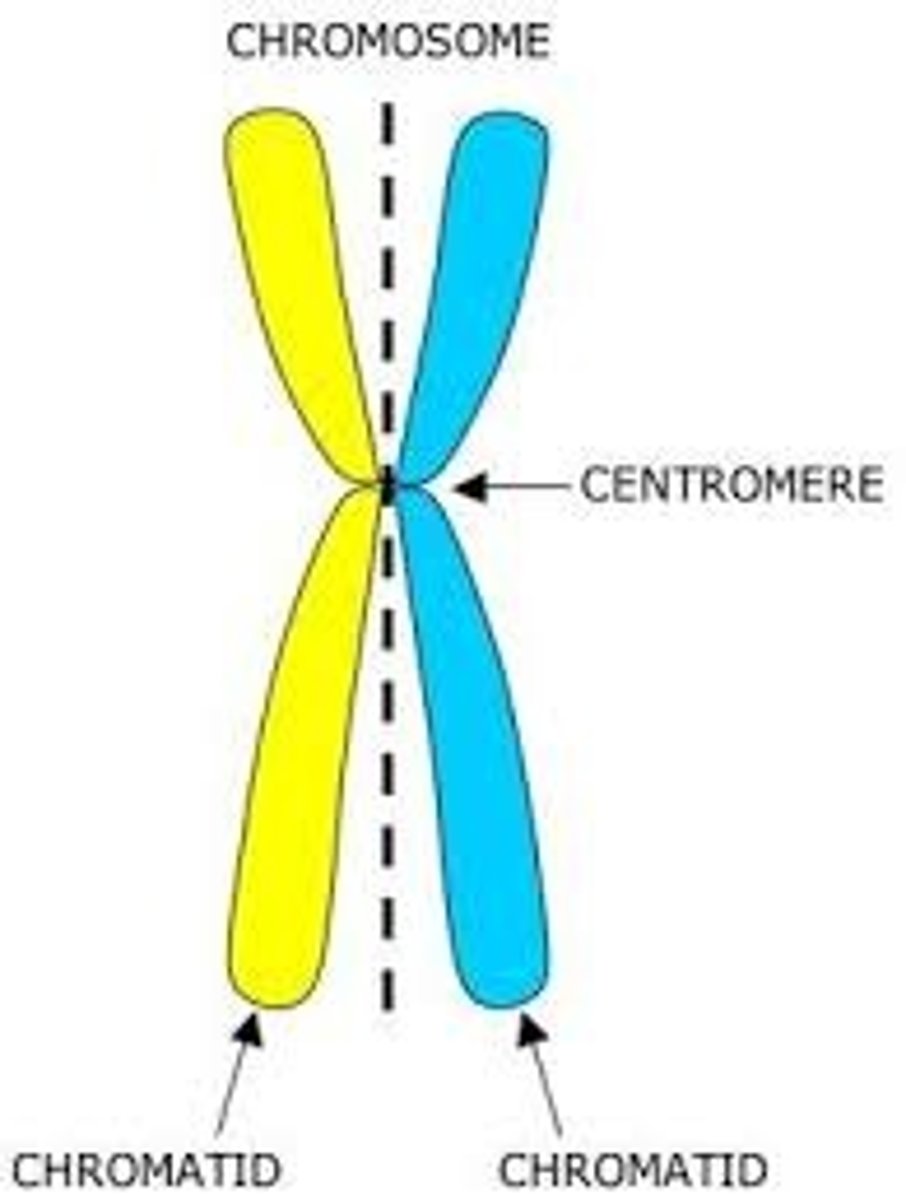
a _____ is 1 of 2 identical parts of a duplicated chromosome
chromatid
microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs) are called _____ in animal cells
centrosomes
(MTOCs are just called MTOCs in plants/fungi)
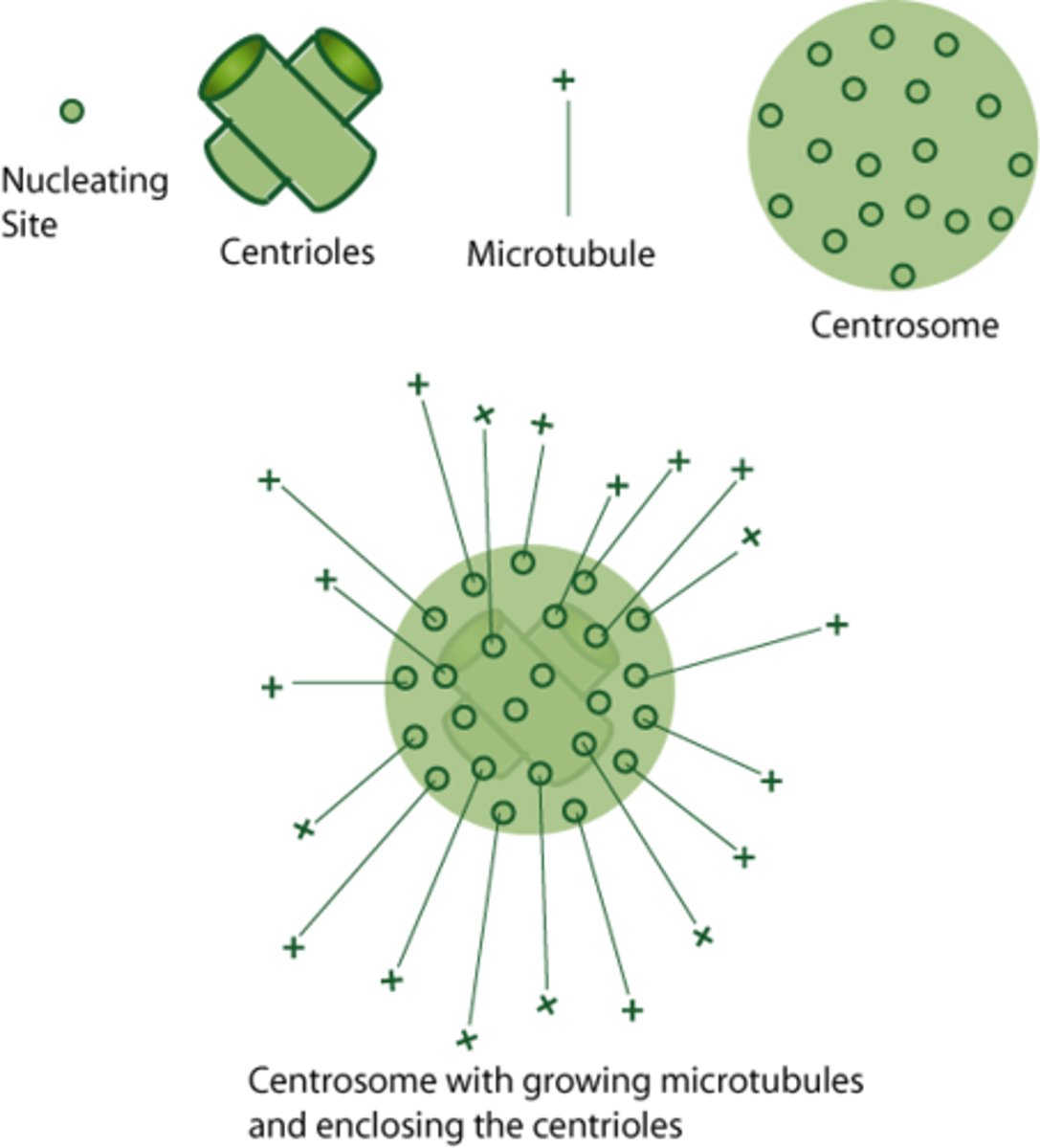
MTOCs are found outside the _____ during interphase
nucleus
centrosomes (animal cell MTOCs) contain a pair of _____
centrioles
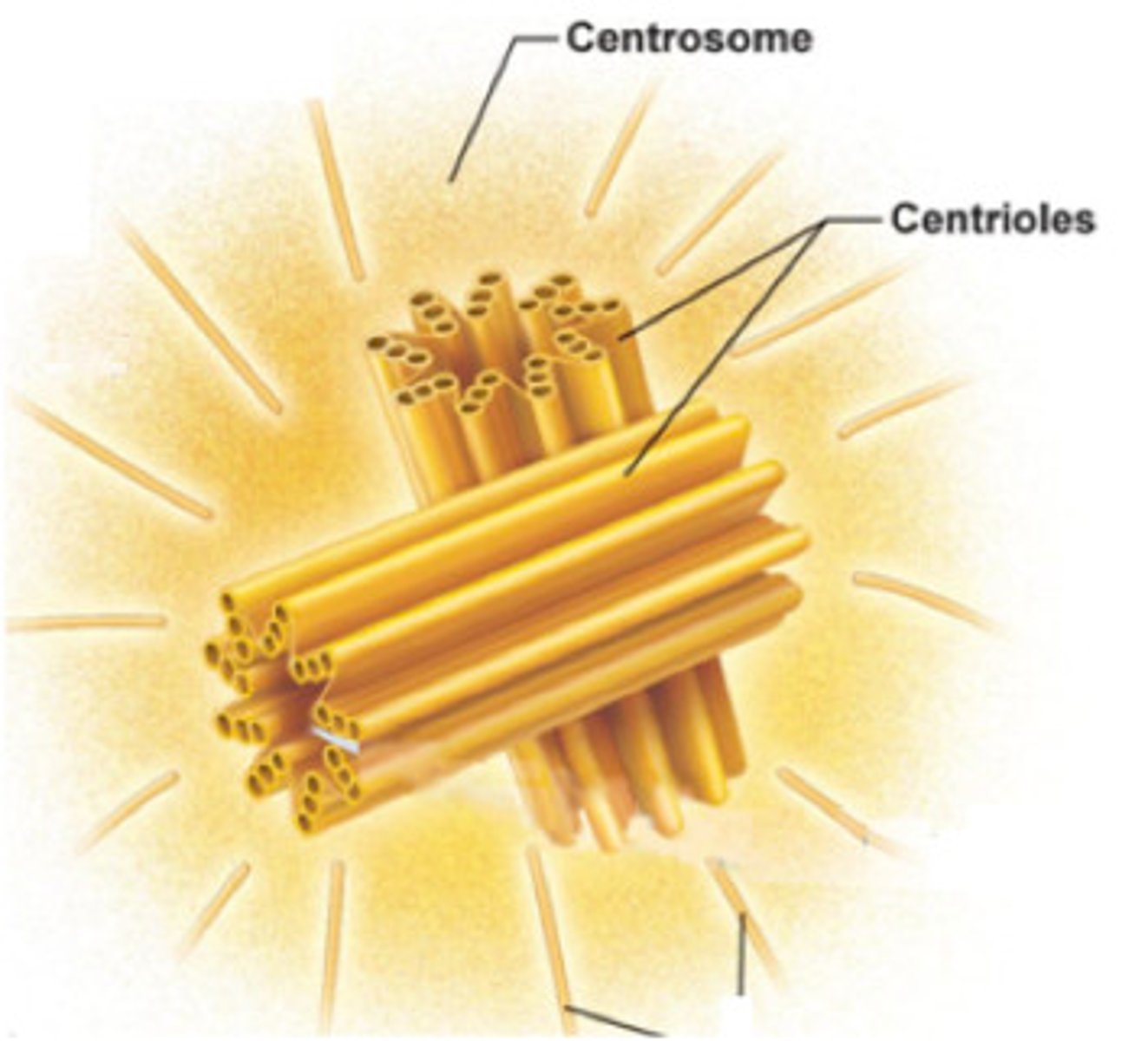
usually there is _____ MTOC per cell; however, cells replicate their MTOCs during _____
1; S phase
there are _____ MTOCs before cell division (after the S phase of interphase)
2
plants/fungi have MTOCs, but they are NOT _____
centrosomes
(plants/fungi just have "MTOCs")
_____ occurs in somatic cells and _____ occurs in gametes (egg, sperm, pollen)
mitosis; meiosis
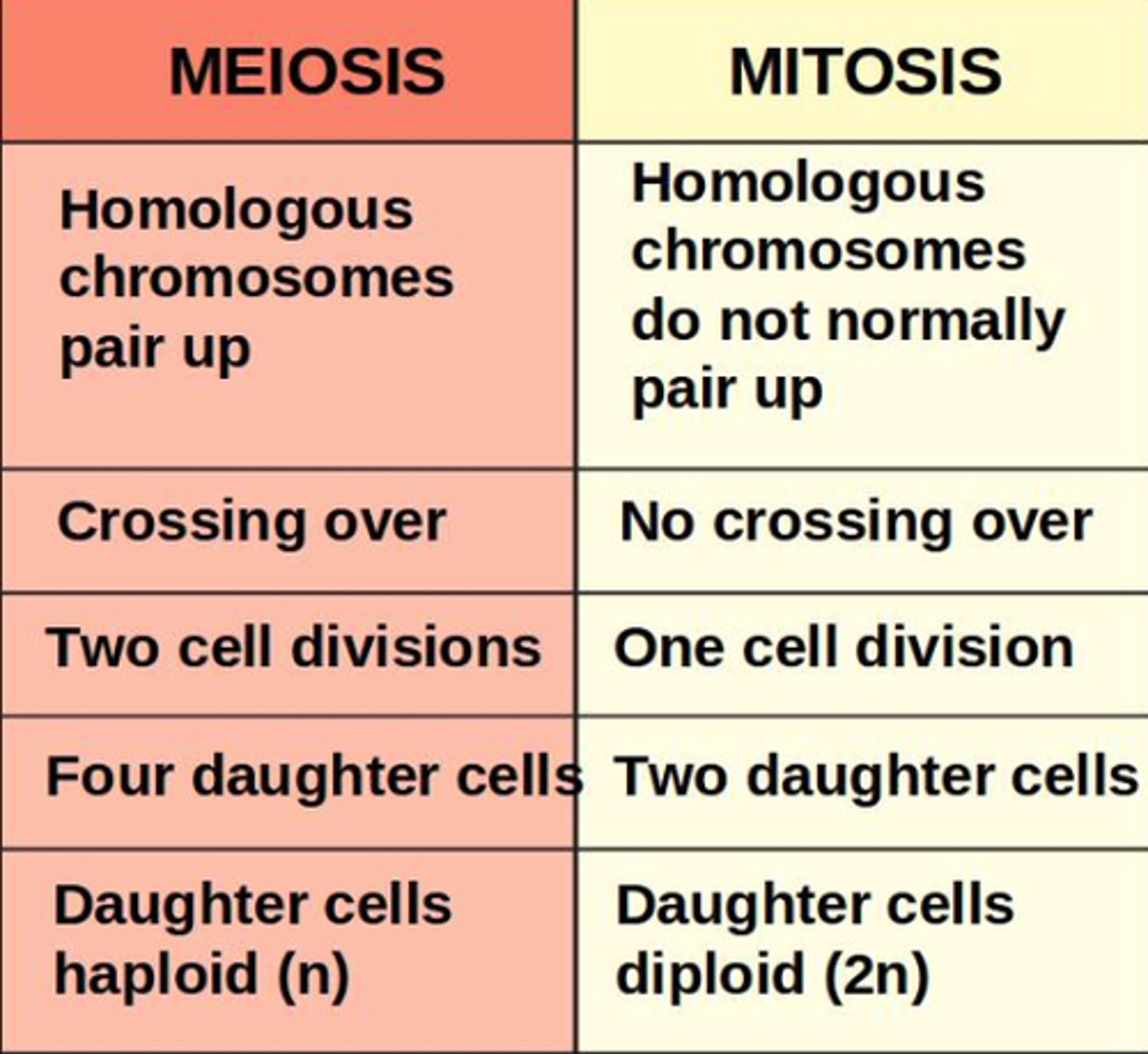
mitosis occurs in _____ cells and meiosis occurs in _____ (egg, sperm, pollen)
somatic; gametes
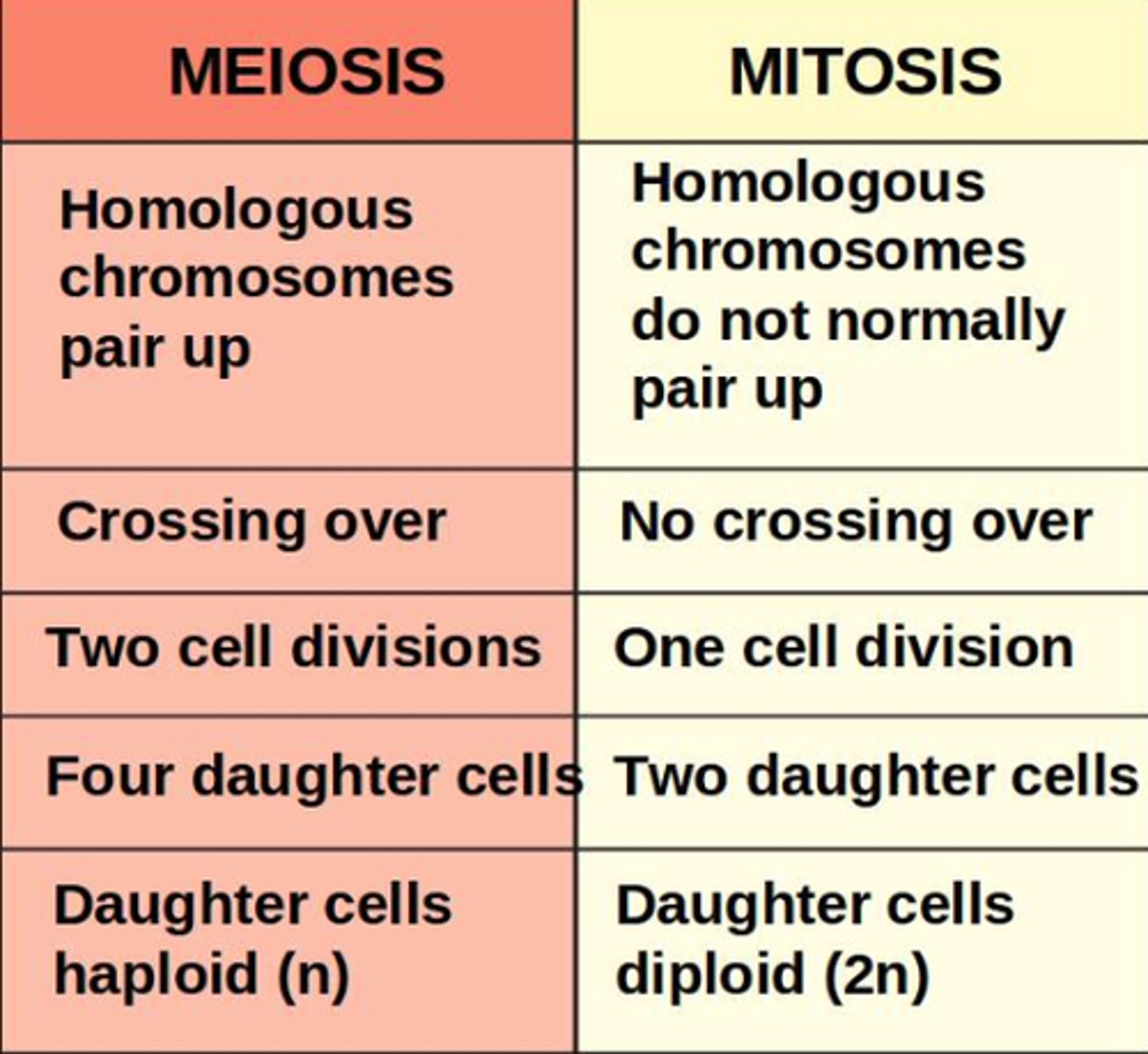
what is fertilization?
the fusion of 2 haploid gamete nuclei to make 1 diploid zygote
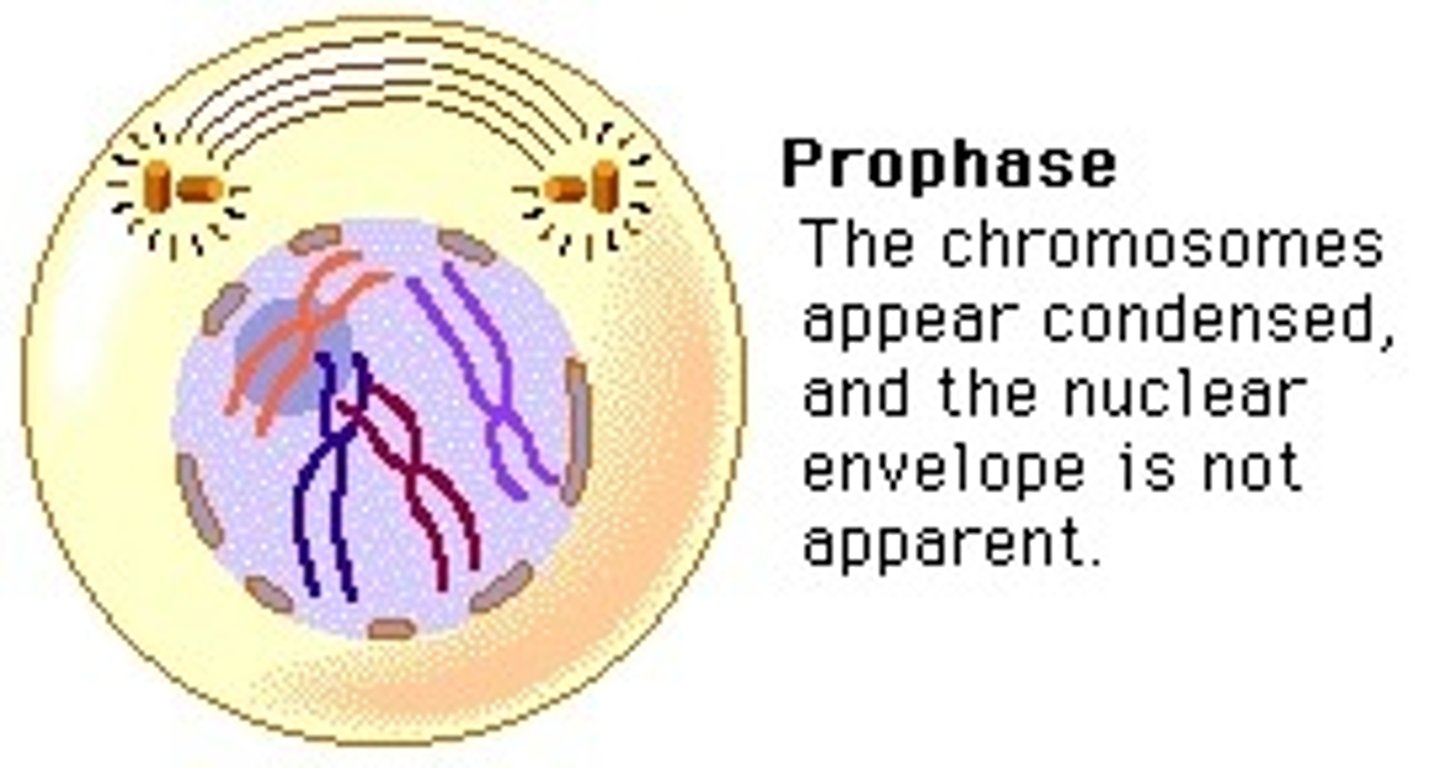
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromatin condenses into chromosomes
prophase
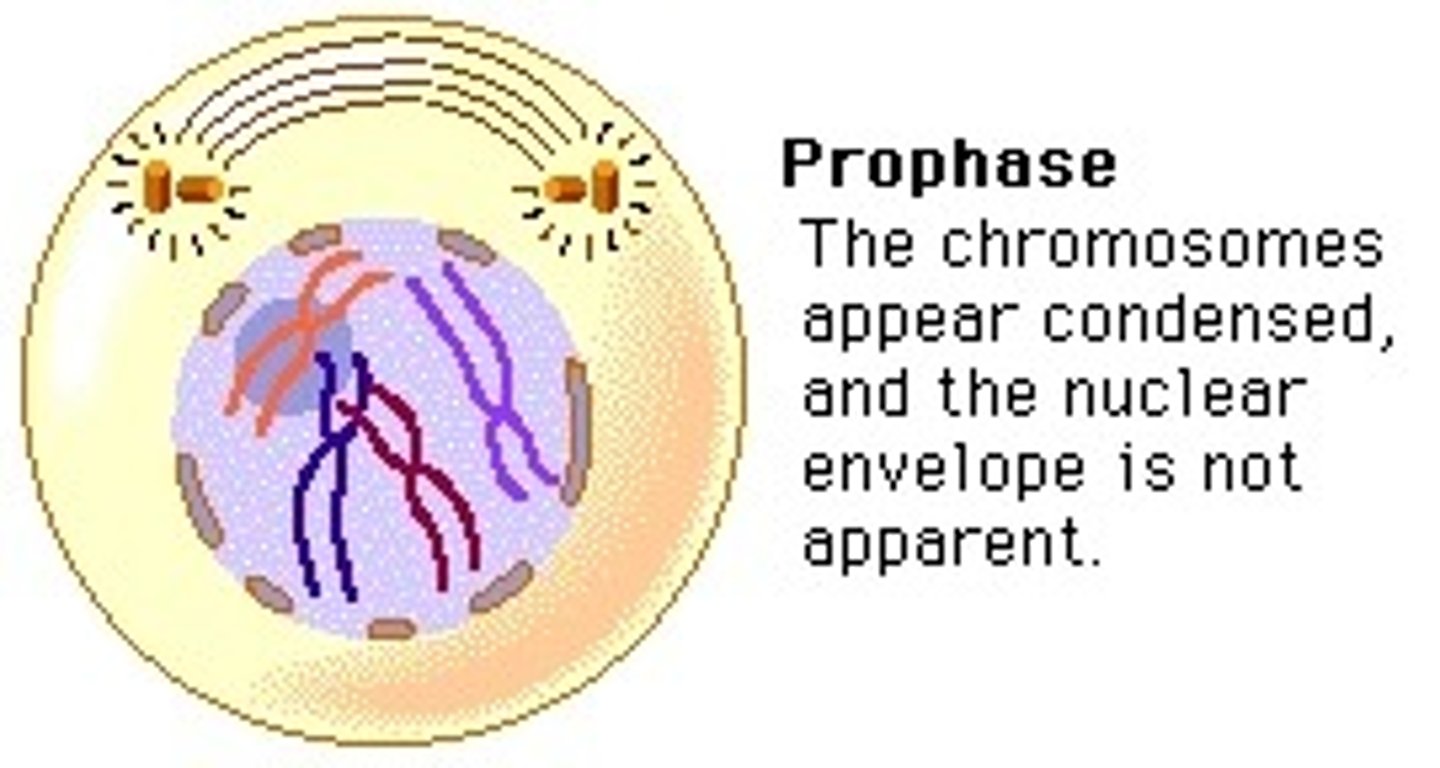
_____ is the phase of cell division, in which the nuclear envelope breaks down
prophase
_____ is the phase of cell division in which the mitotic spindle forms
prometaphase
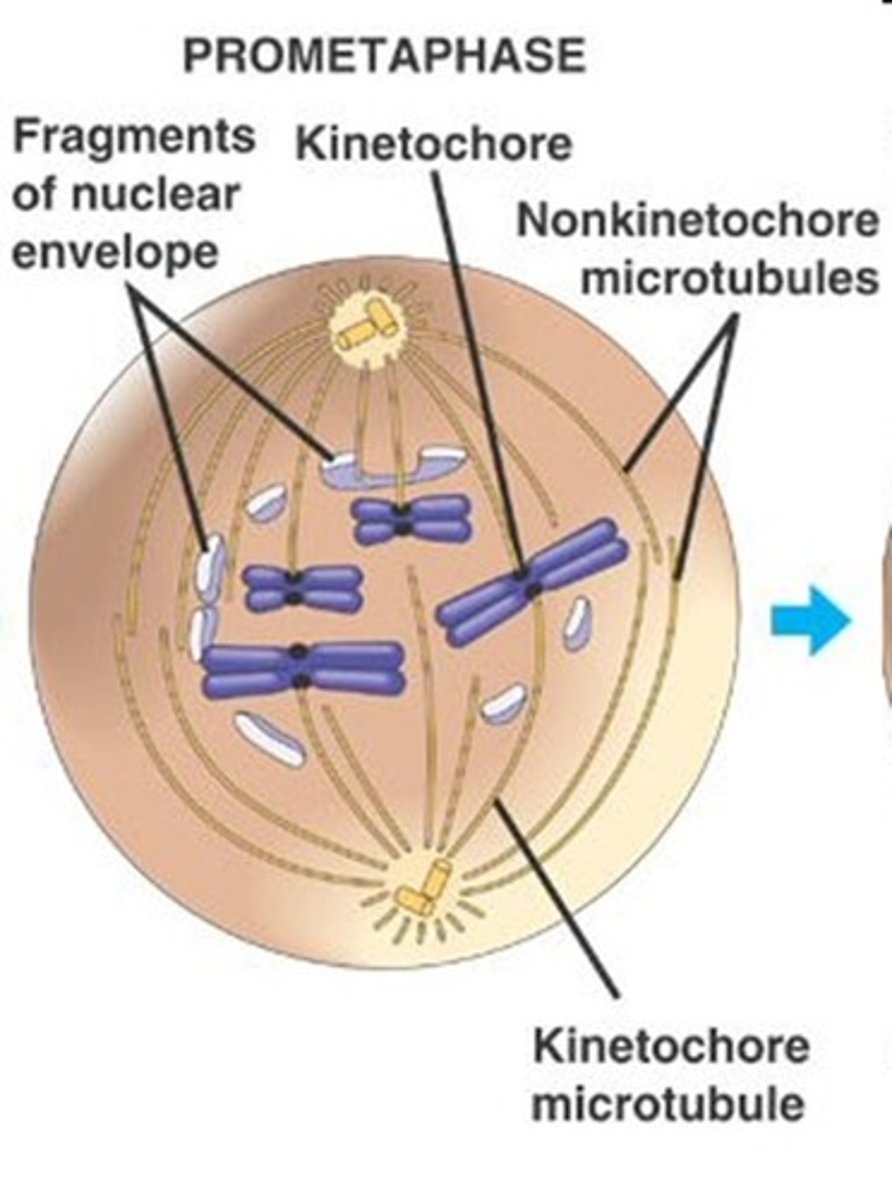
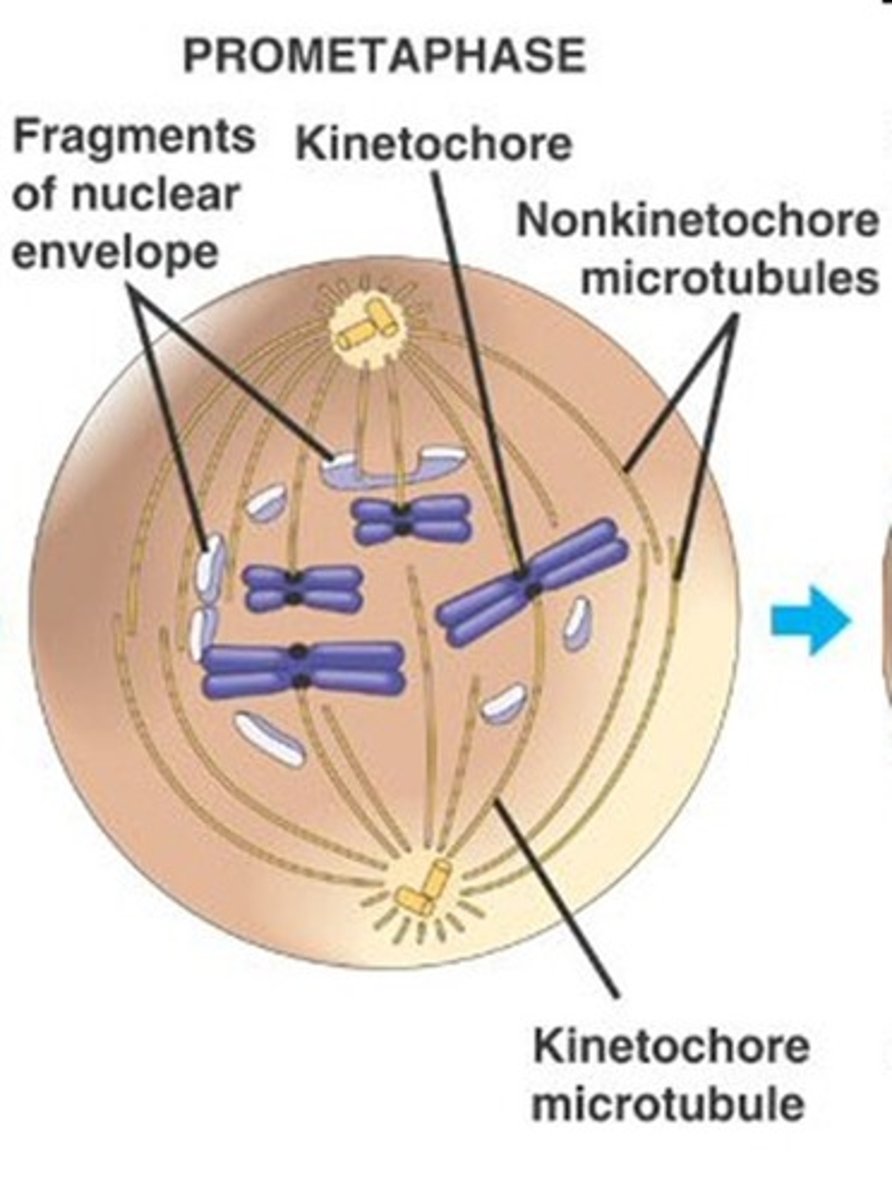
microtubules begin connecting to kinetochores during _____ of cell division
prometaphase
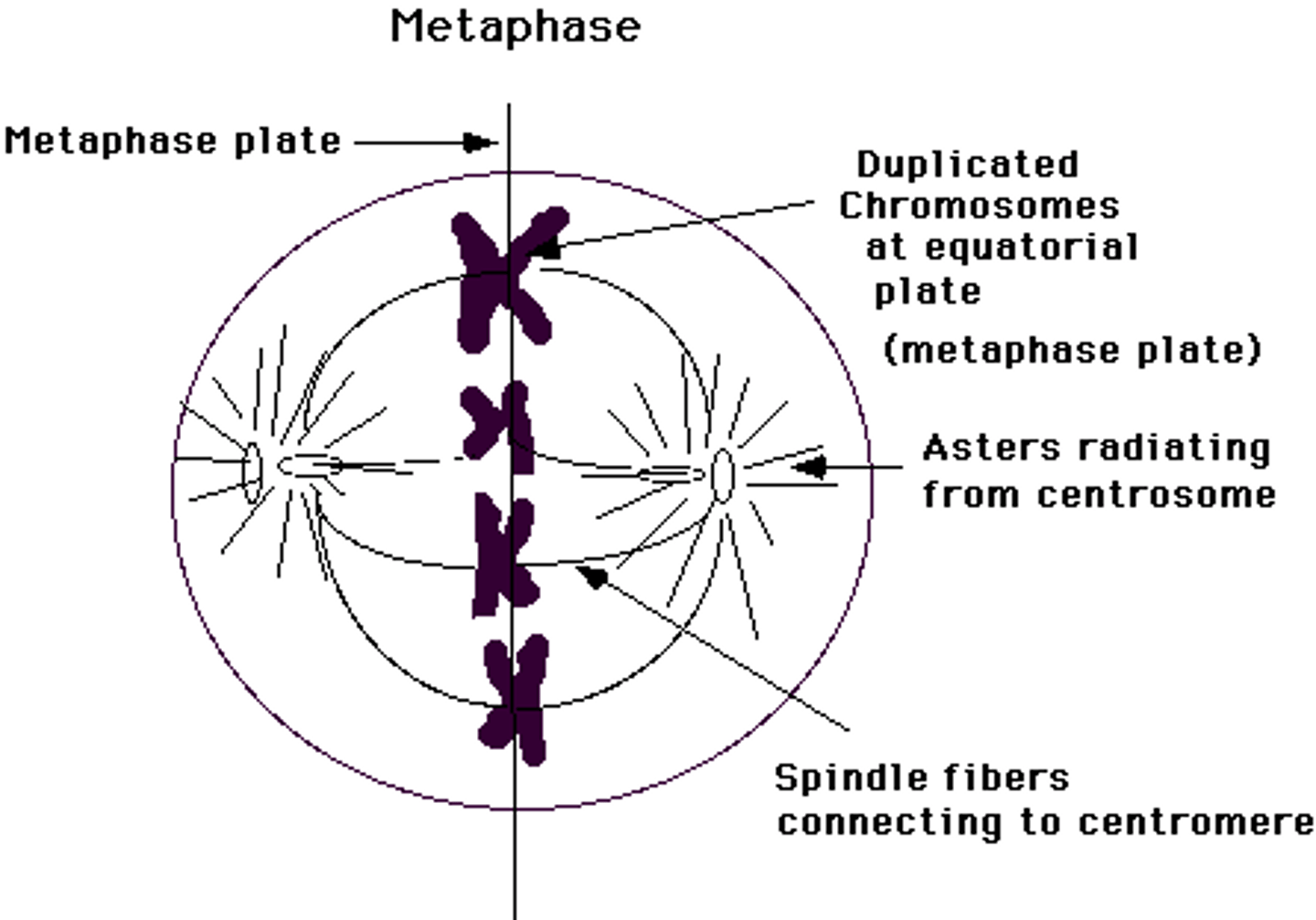
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromosomes line up in a single file in the center
metaphase
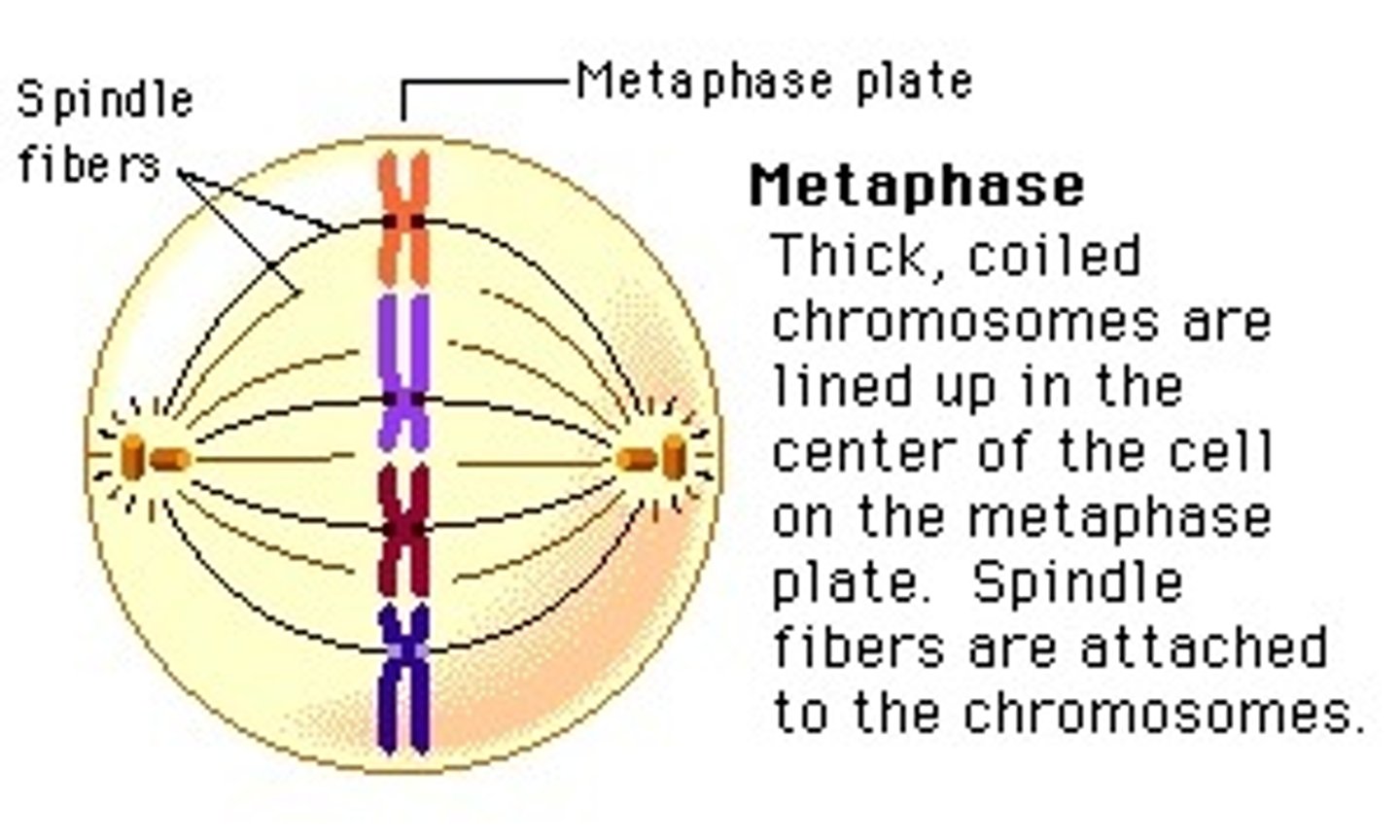
_____ is the phase of cell division in which each chromatid is complete with a centromere and attached kinetochore
metaphase
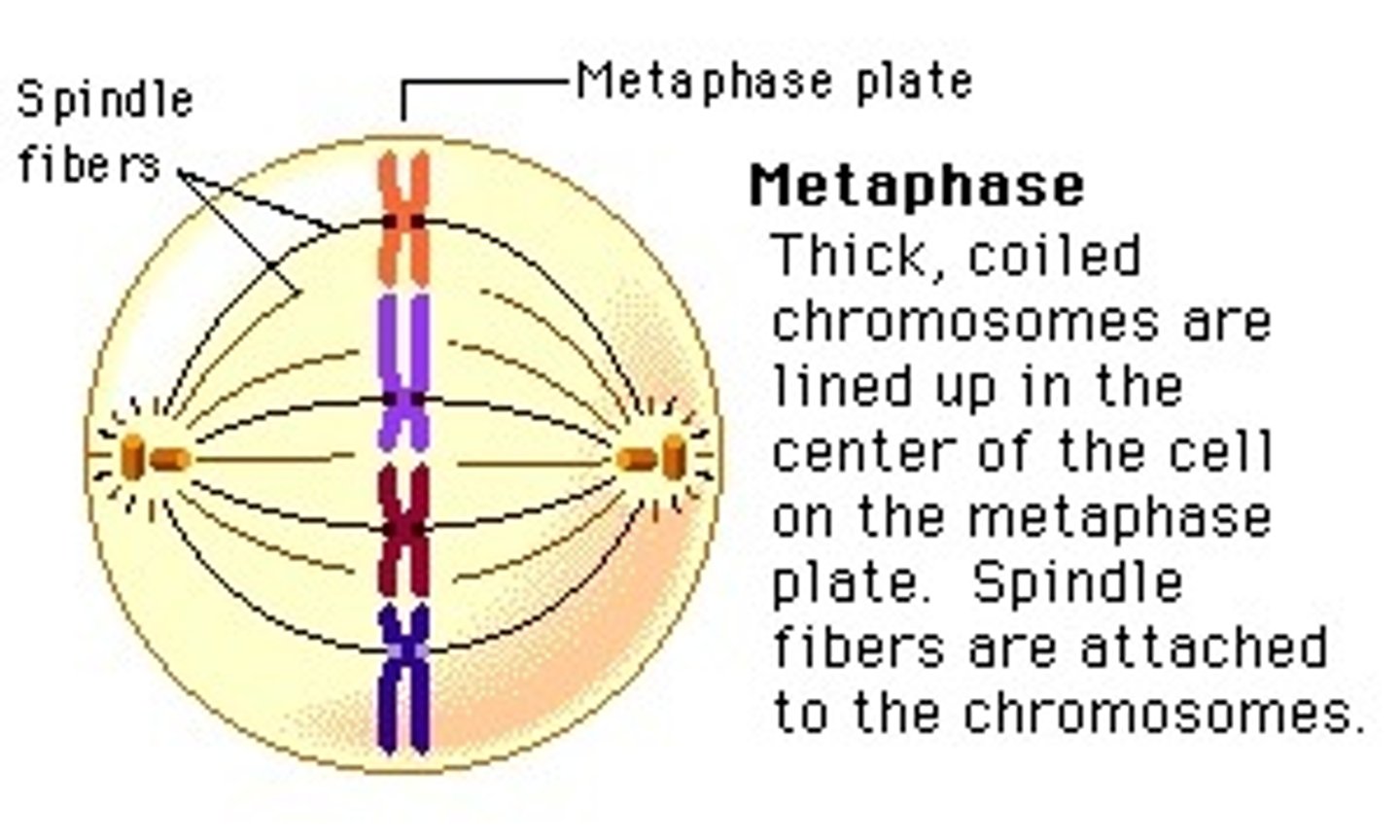
_____ is the phase of cell division in which replicated centrosomes are at opposite ends of the cell
metaphase
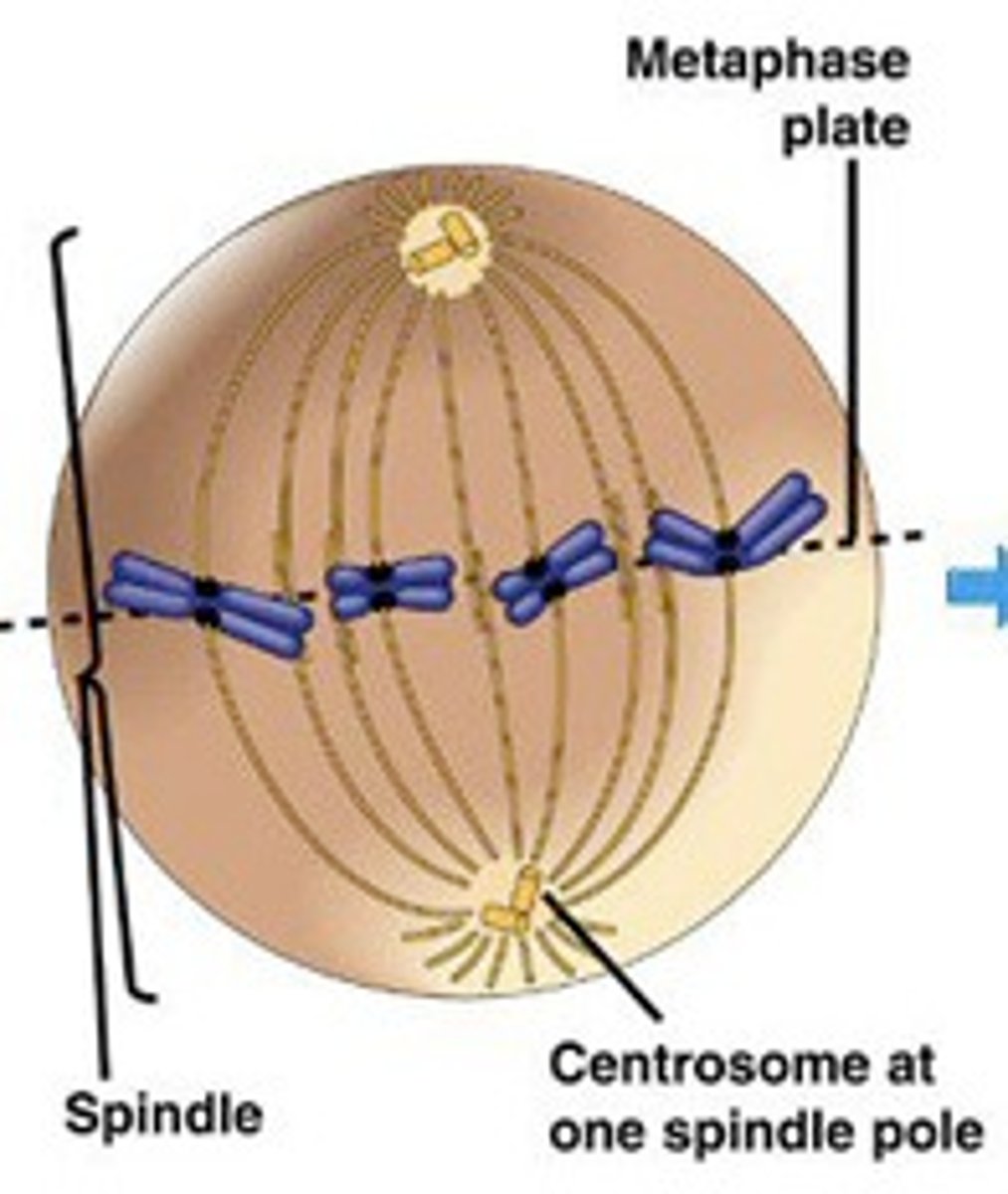
_____ is the phase of cell division in which karyotyping is performed
metaphase
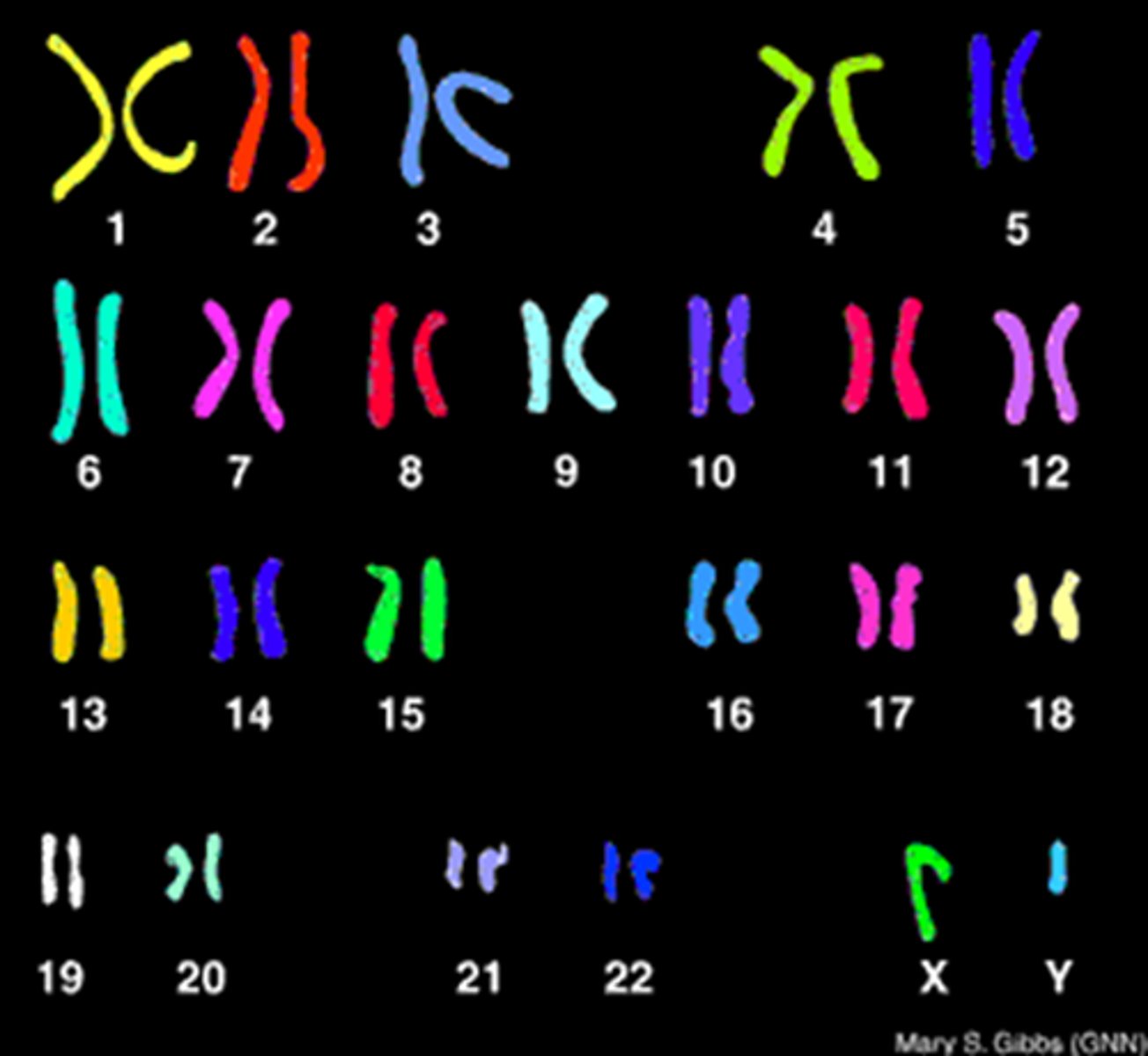
_____ is a visual depiction of one's chromosomes by homologous pairs, and it is usually performed during metaphase
karyotyping
_____ is the phase of cell division in which kinetochore microtubules shorten
anaphase
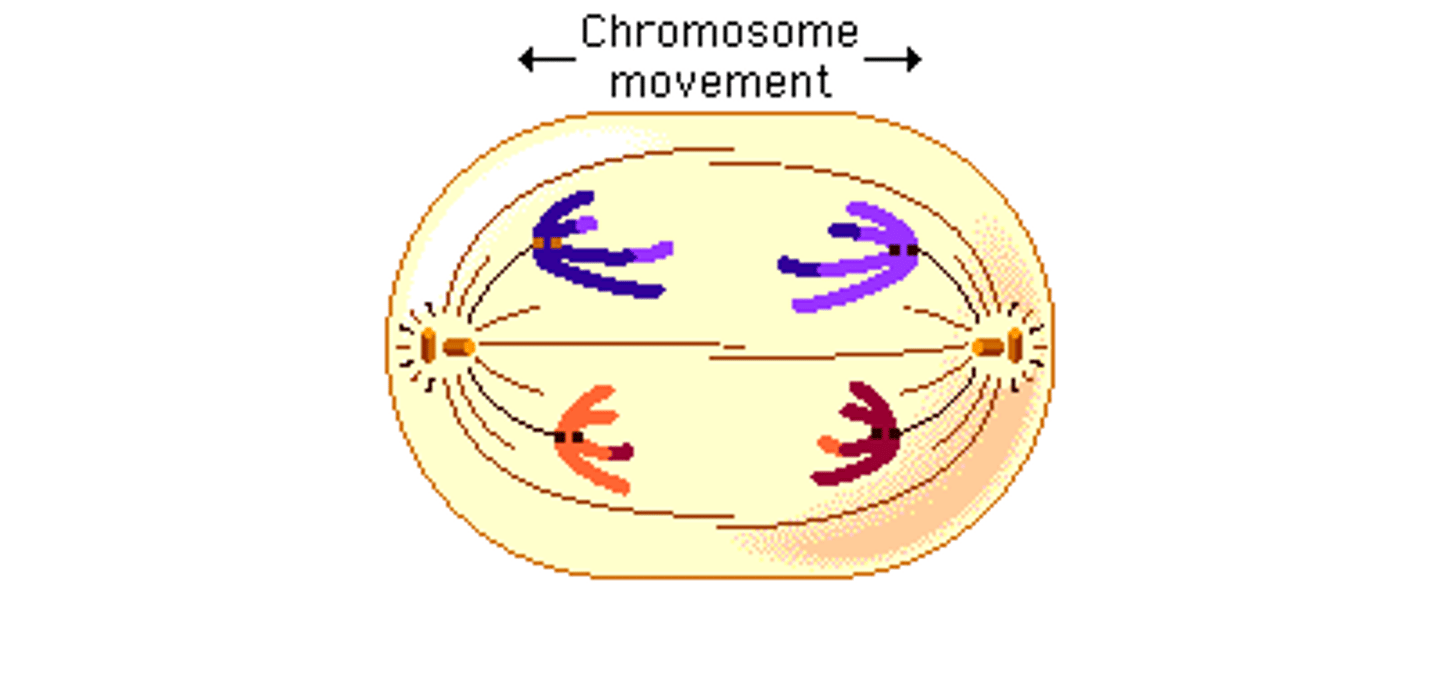
_____ is the phase of cell division in which polar microtubules lengthen
anaphase
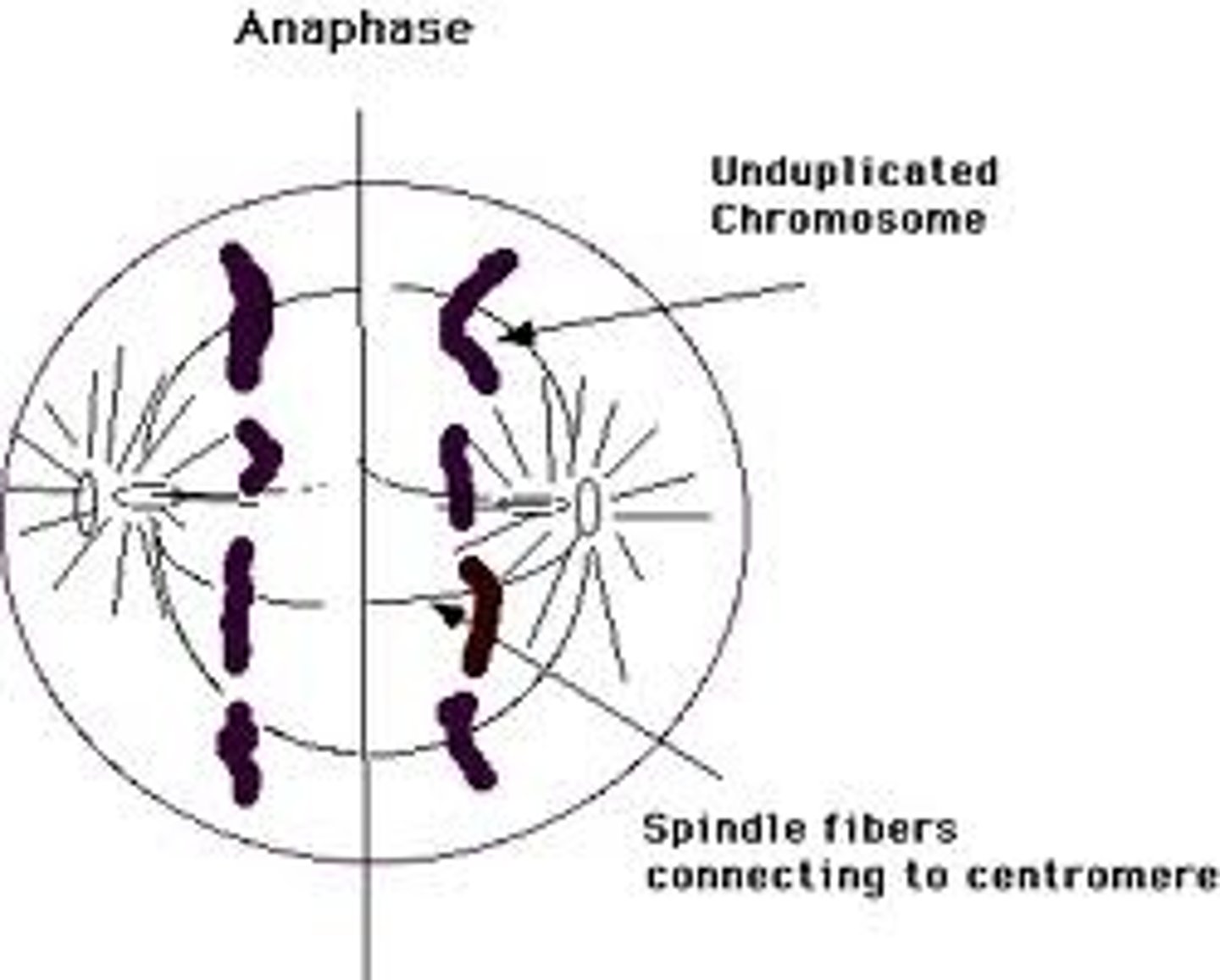
_____ is the phase of cell division in which each chromosome is pulled apart
anaphase
once separated at anaphase, each _____ is considered a _____
chromatid; chromosome
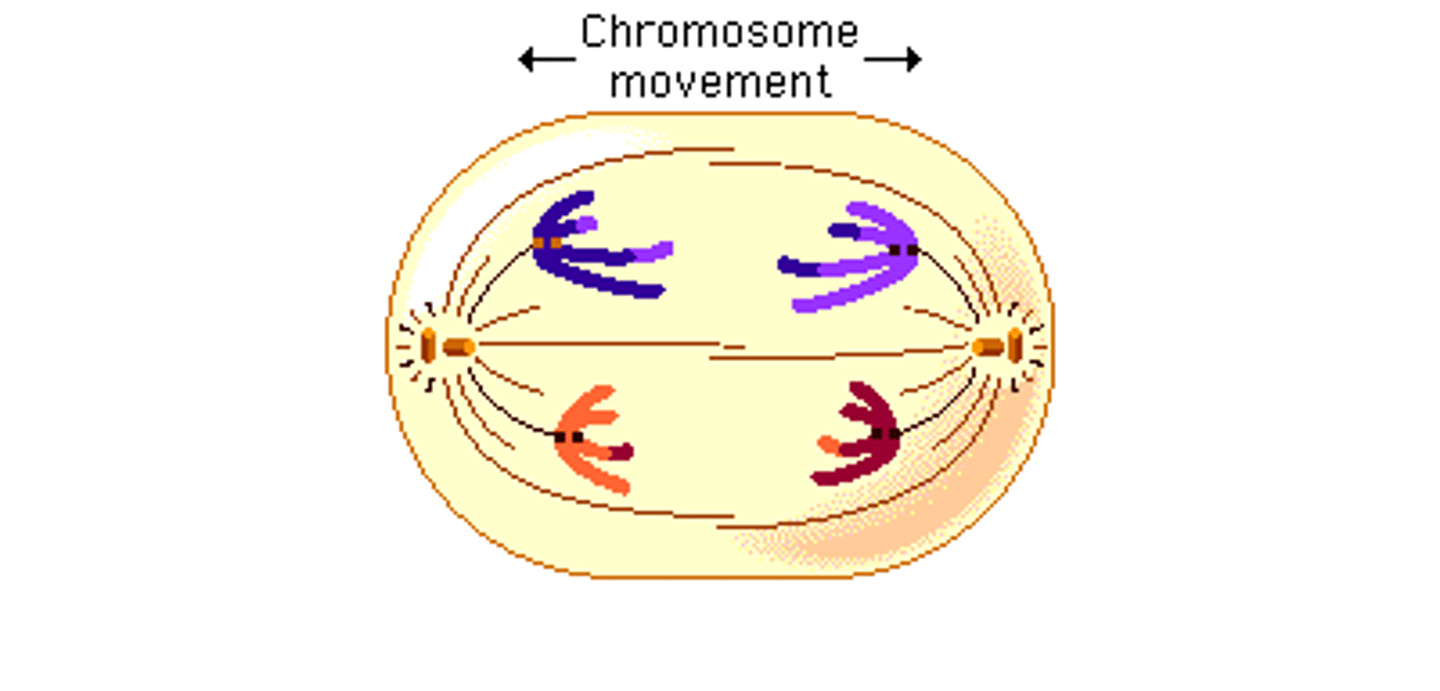
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles (disjunction)
anaphase
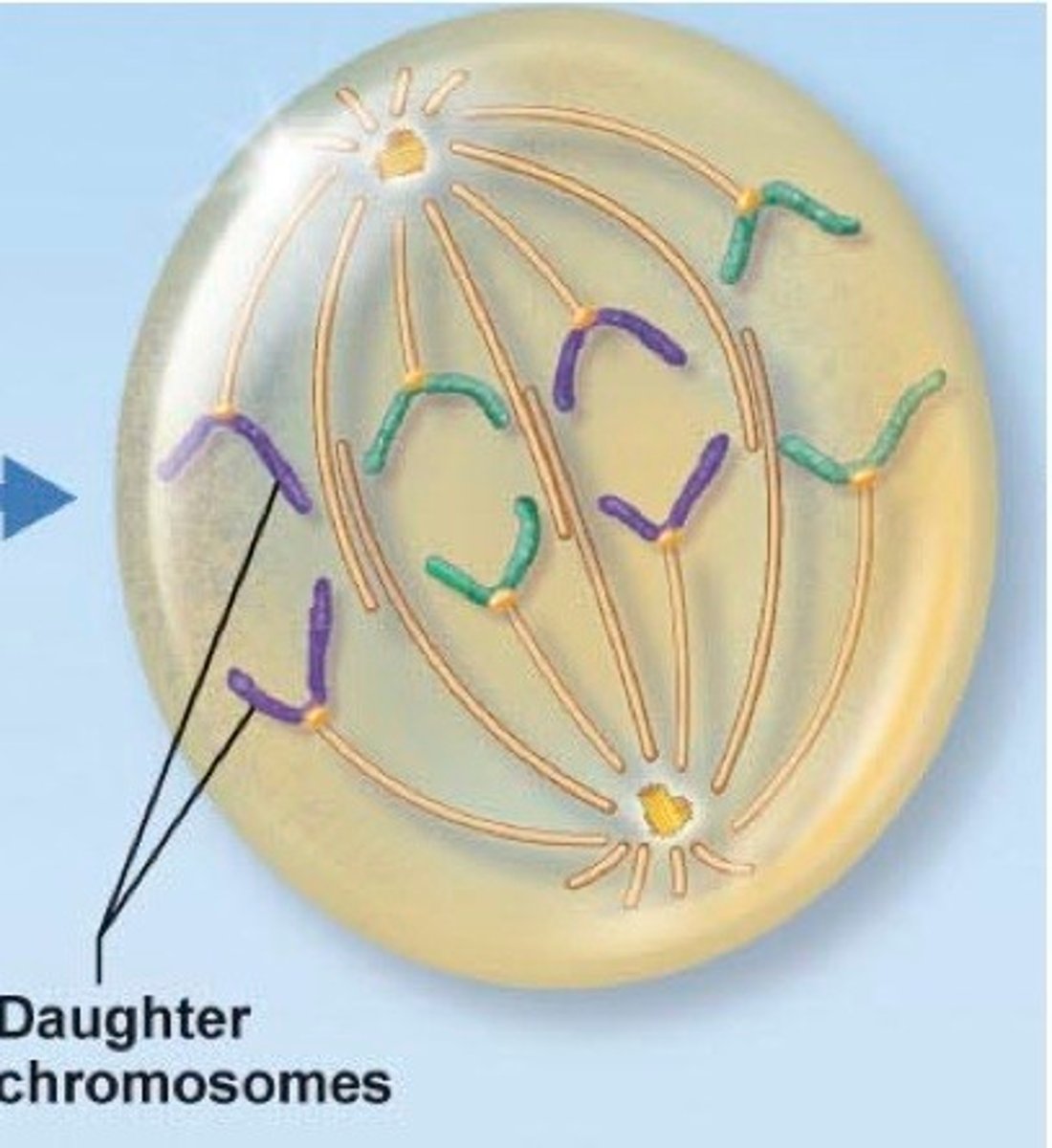
at the end of _____, each pole has a complete set of chromosomes
anaphase
what is the shortest step of cell division?
anaphase
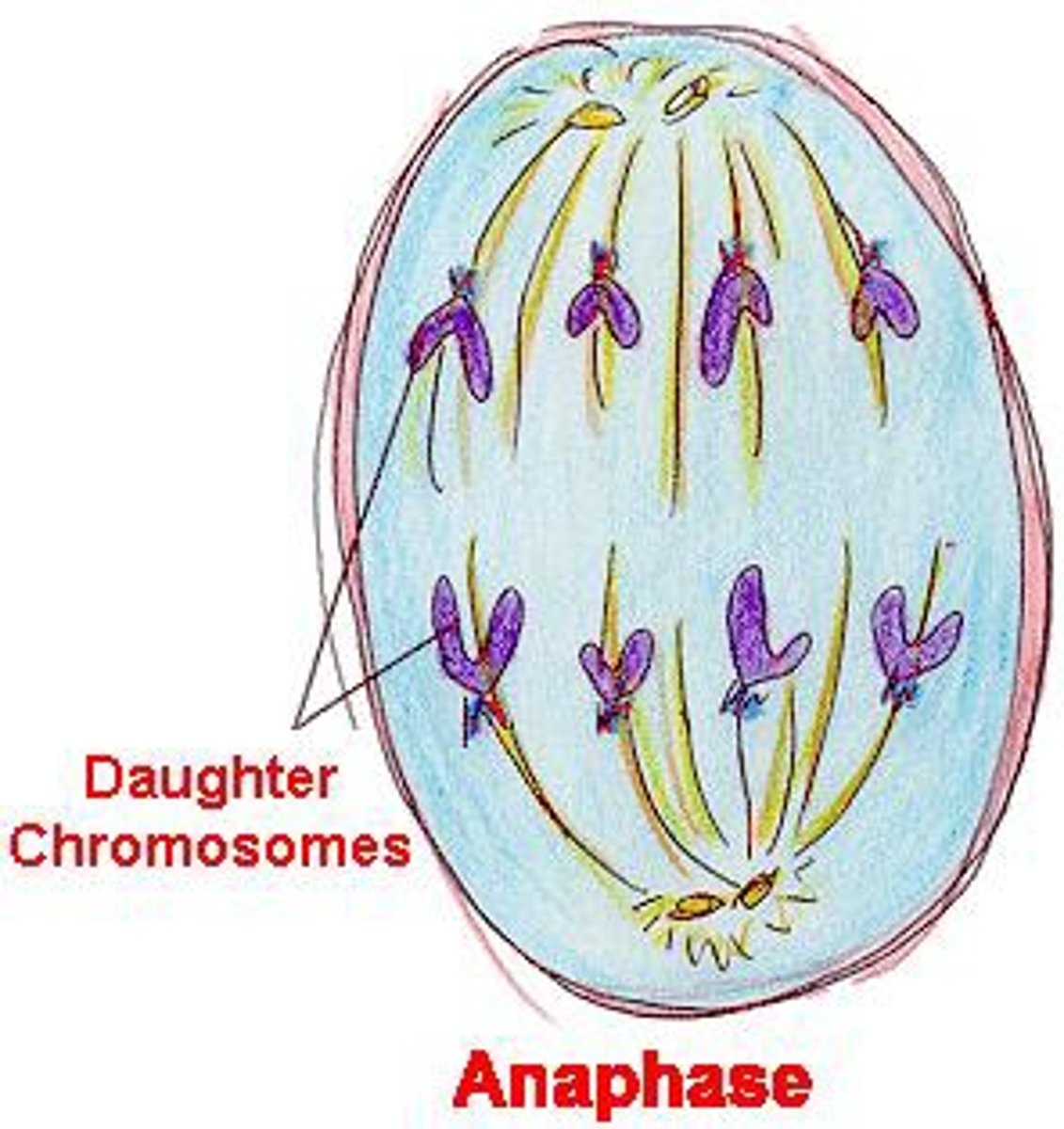
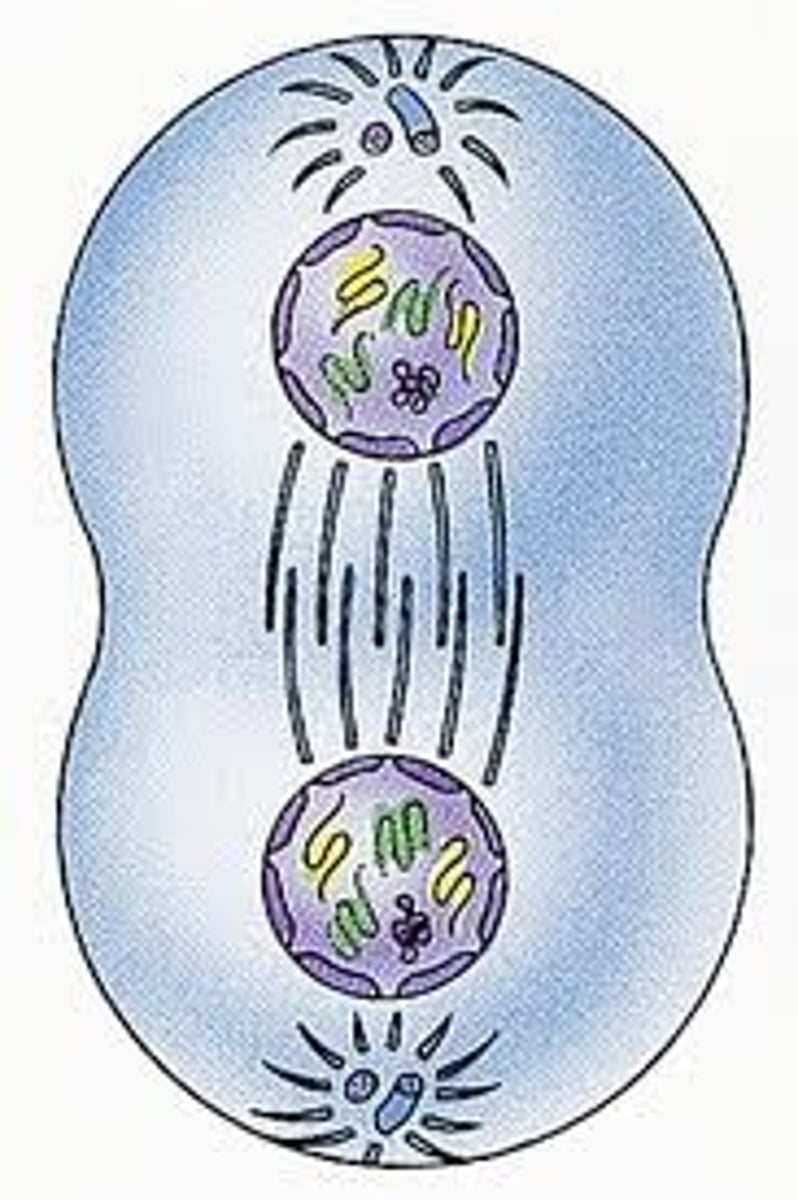
_____ is the phase of cell division when karyokinesis occurs
telophase
(karyokinesis = nuclear division - notice the formation of 2 nuclei)
_____ is the phase of cell division in which the nuclear envelopes re-develop
telophase
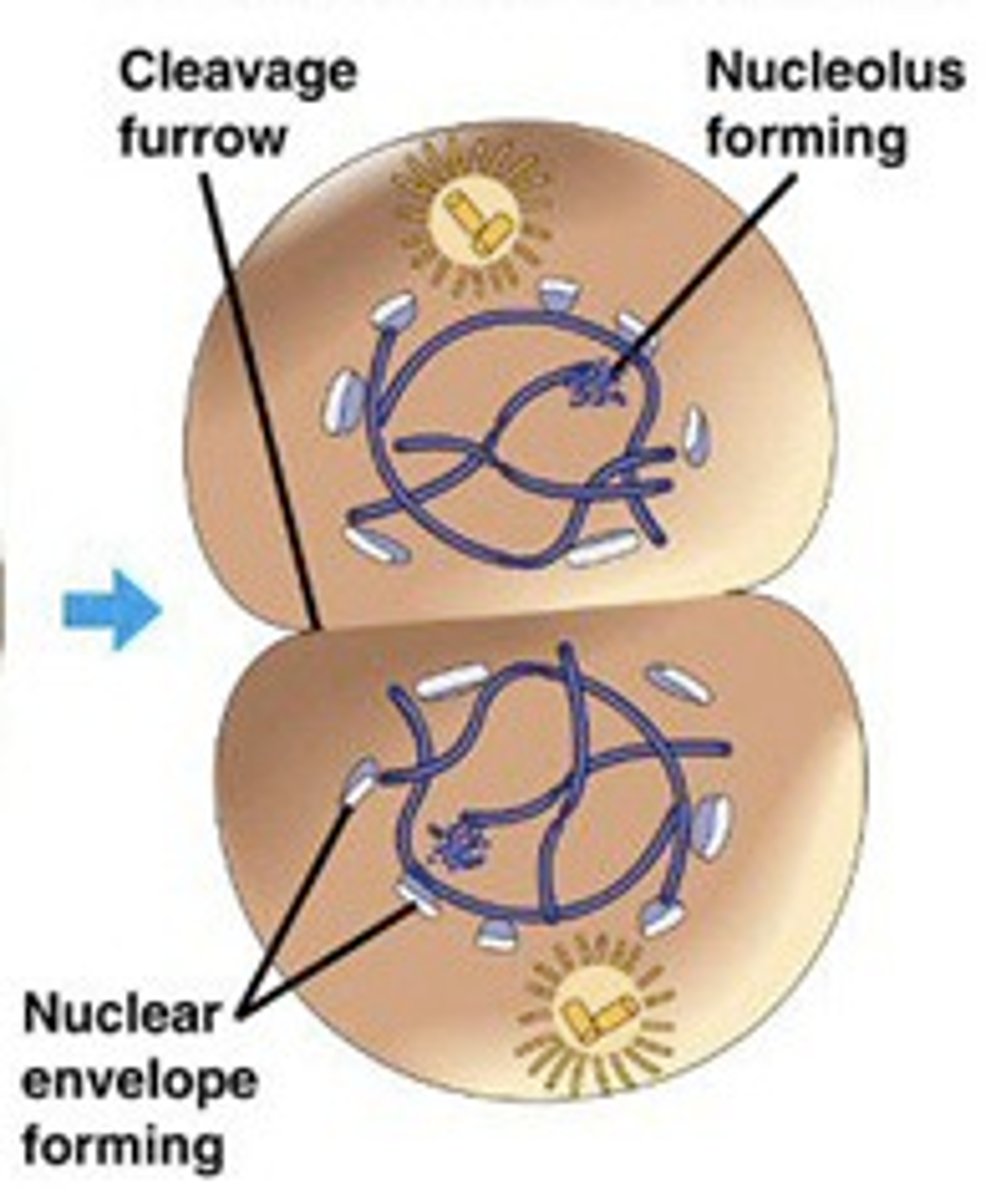
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromosomes de-condense back into chromatin
telophase
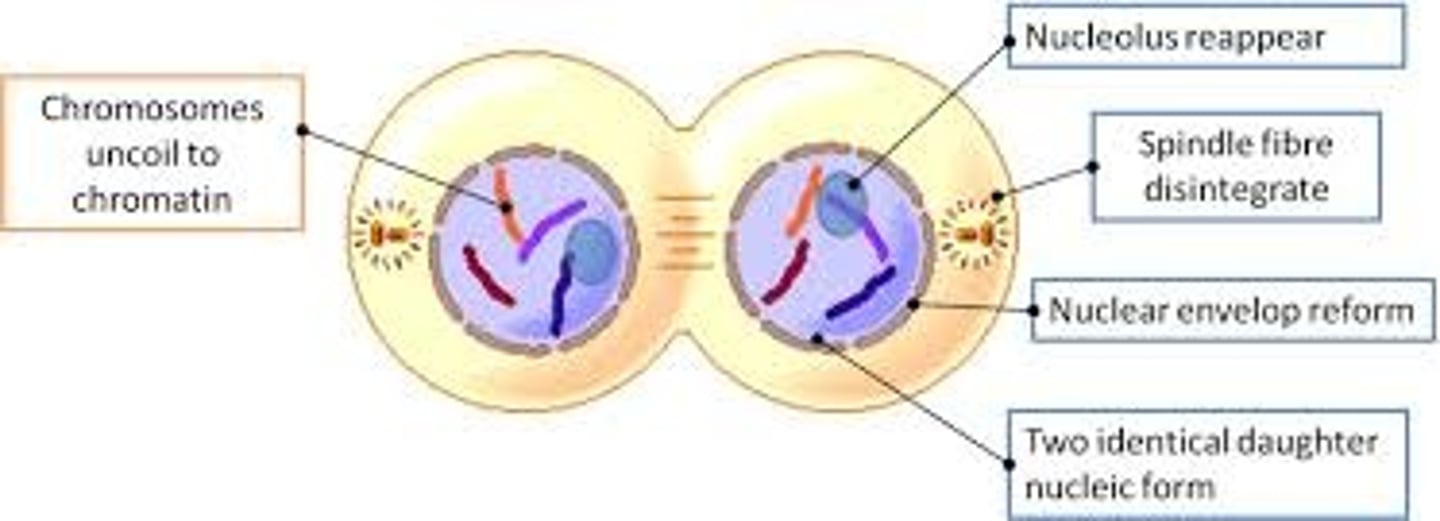
_____ is the phase of cell division in which nucleoli reappear
telophase
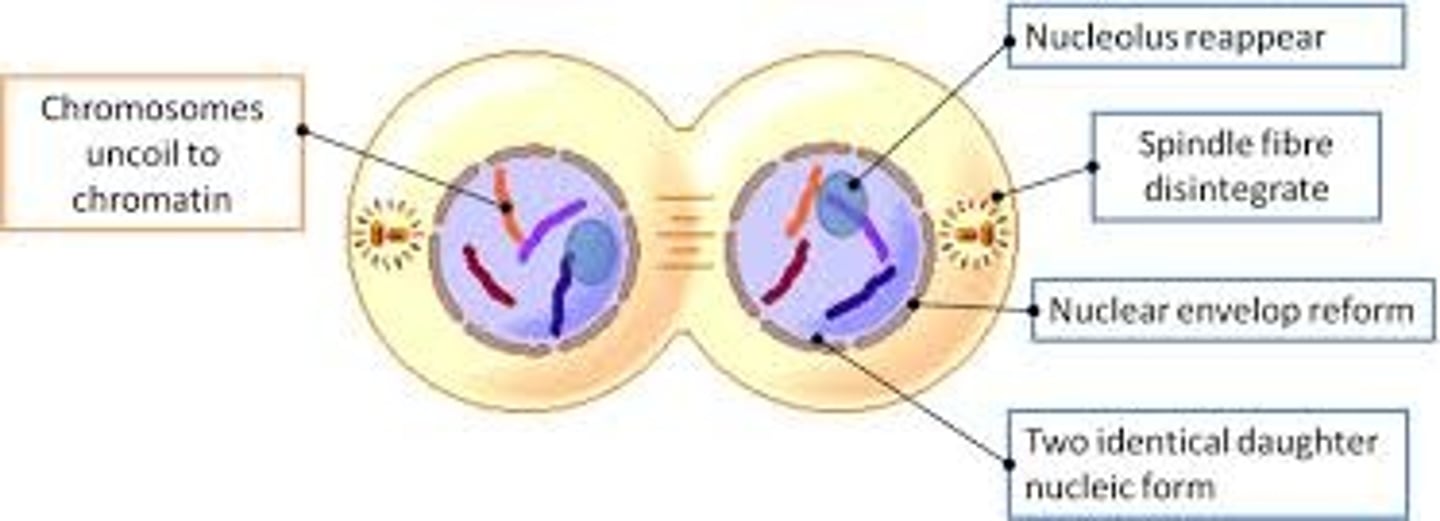
the presence of chromosomes means _____ is occurring
mitosis/meiosis
(cell division)
in metaphase, a chromosome consists of 2 closely attached _____
sister chromatids
the end of _____ is denoted by the presence of centrosomes at opposite ends of the cell
metaphase
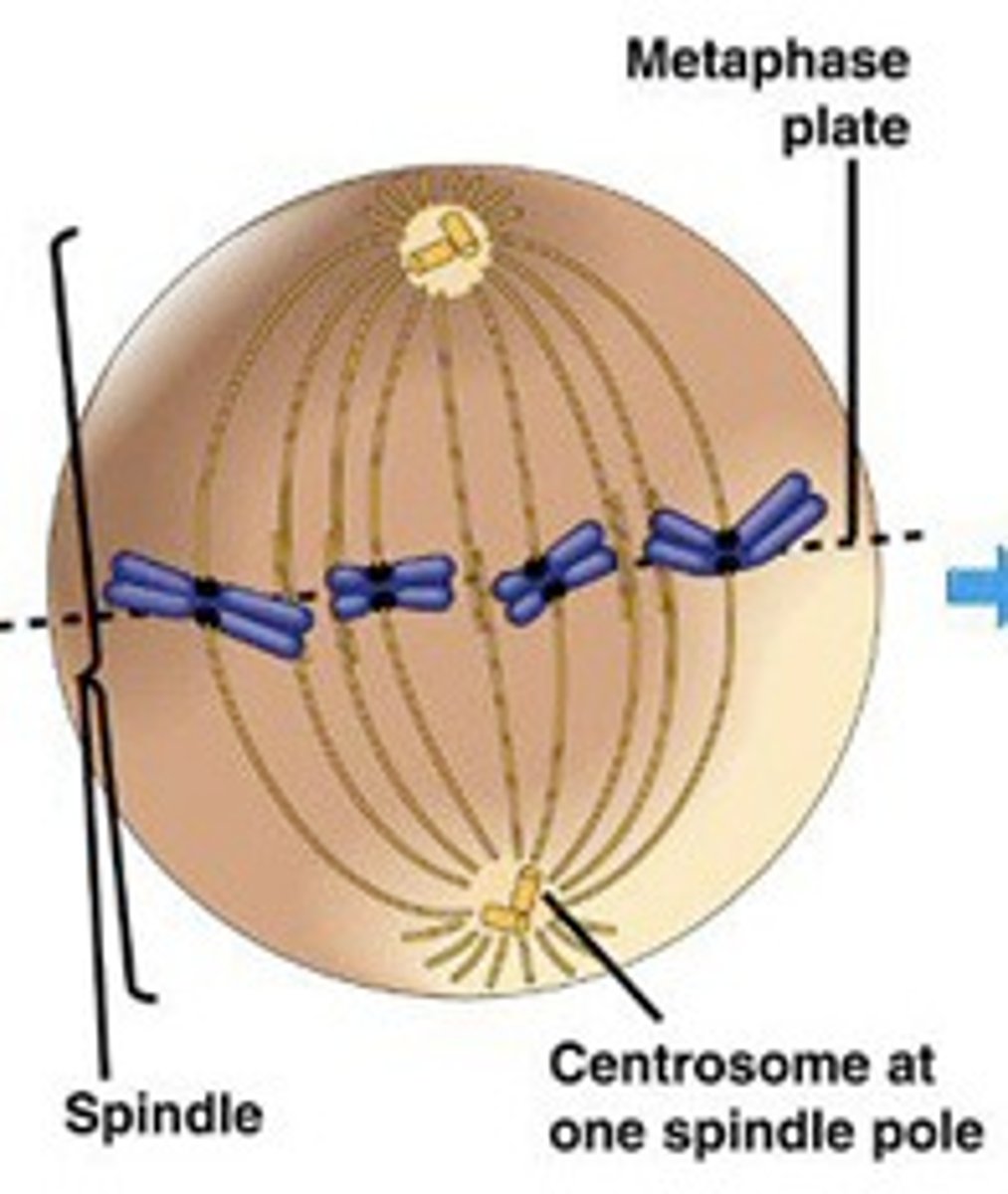
to keep track of the total number of chromosomes during cell division, count the number of _____
centromeres
in _____, the chromosome number doubles
anaphase
at the end of _____, each pole has a complete set of chromosomes, same as the original cell before replication
anaphase
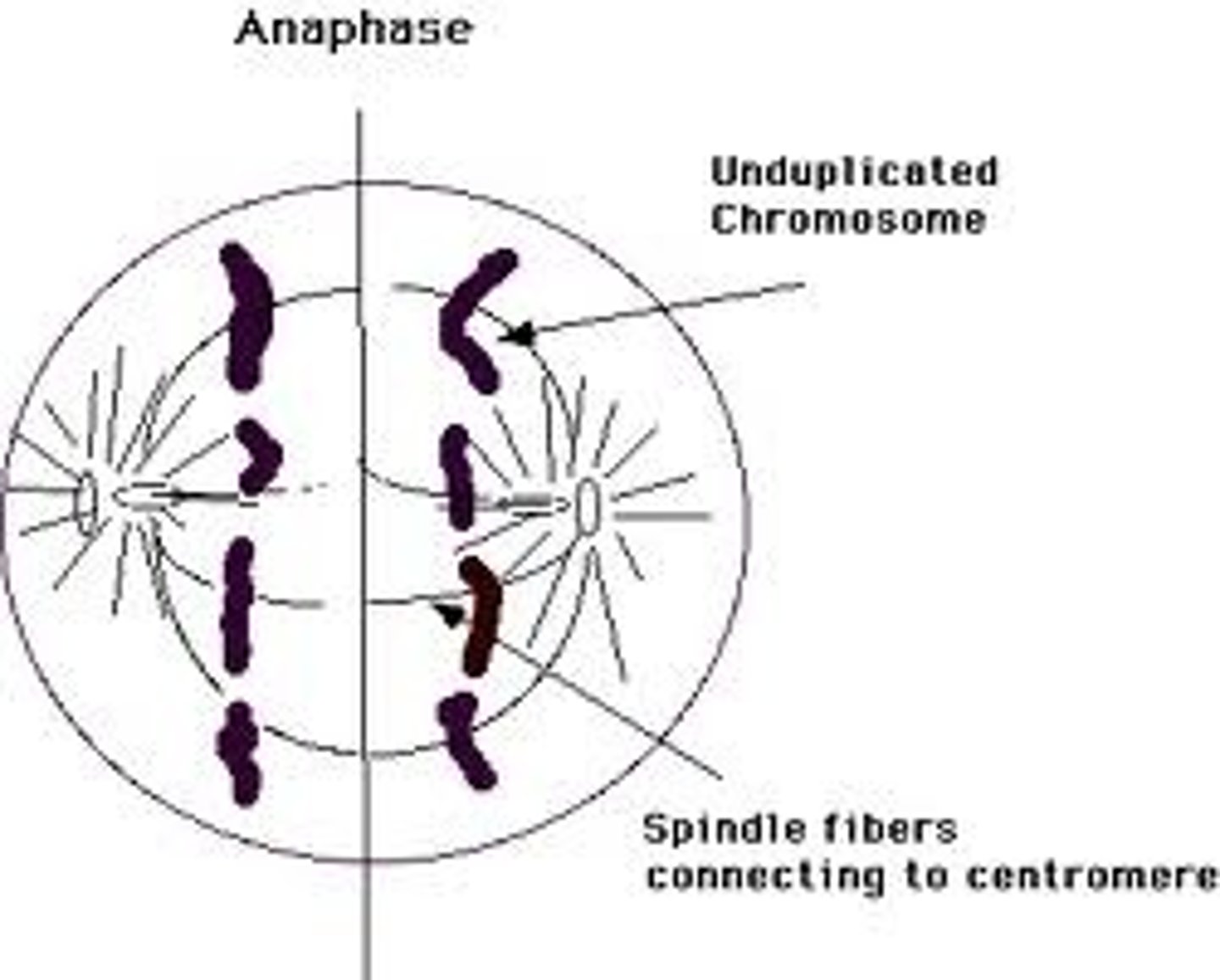
at the end of anaphase, there would be a total of _____ chromosomes (separated chromatids) if a cell has 46 chromosomes at the beginning
92
genetic variation occurs in _____, but not in mitosis
meiosis
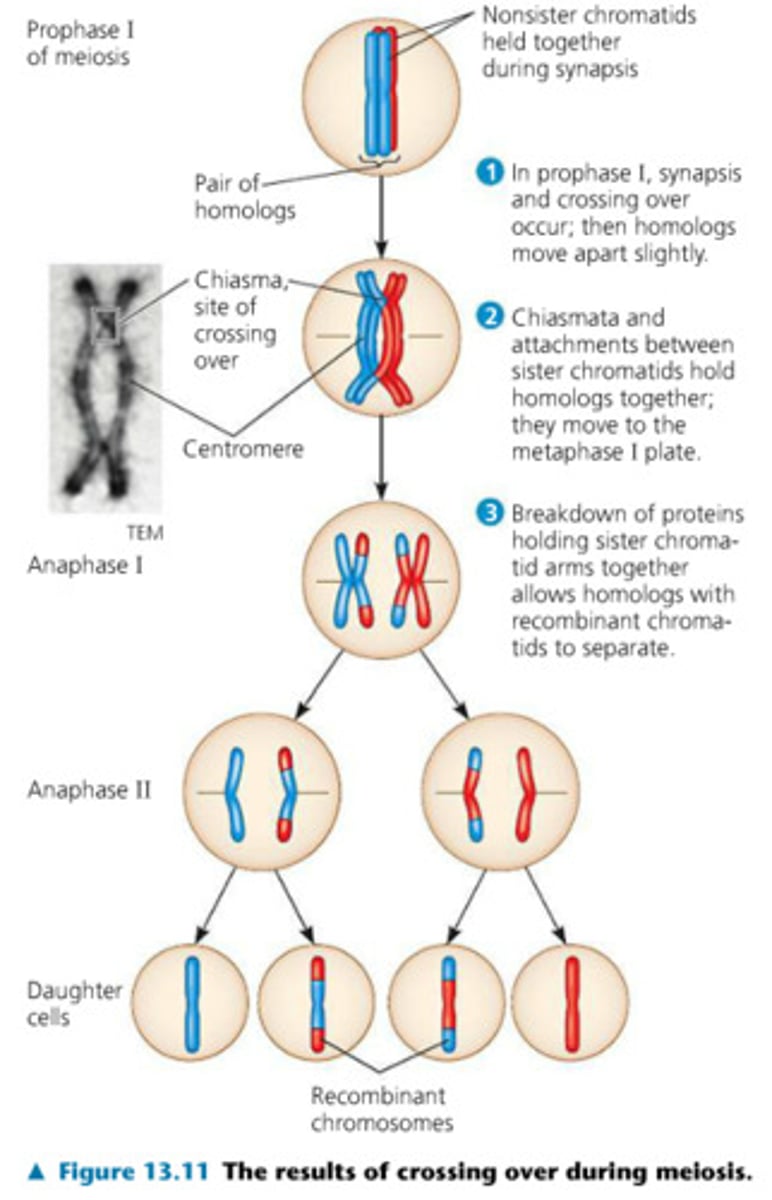
unlike meiosis, NO _____ occurs in mitosis
genetic variation
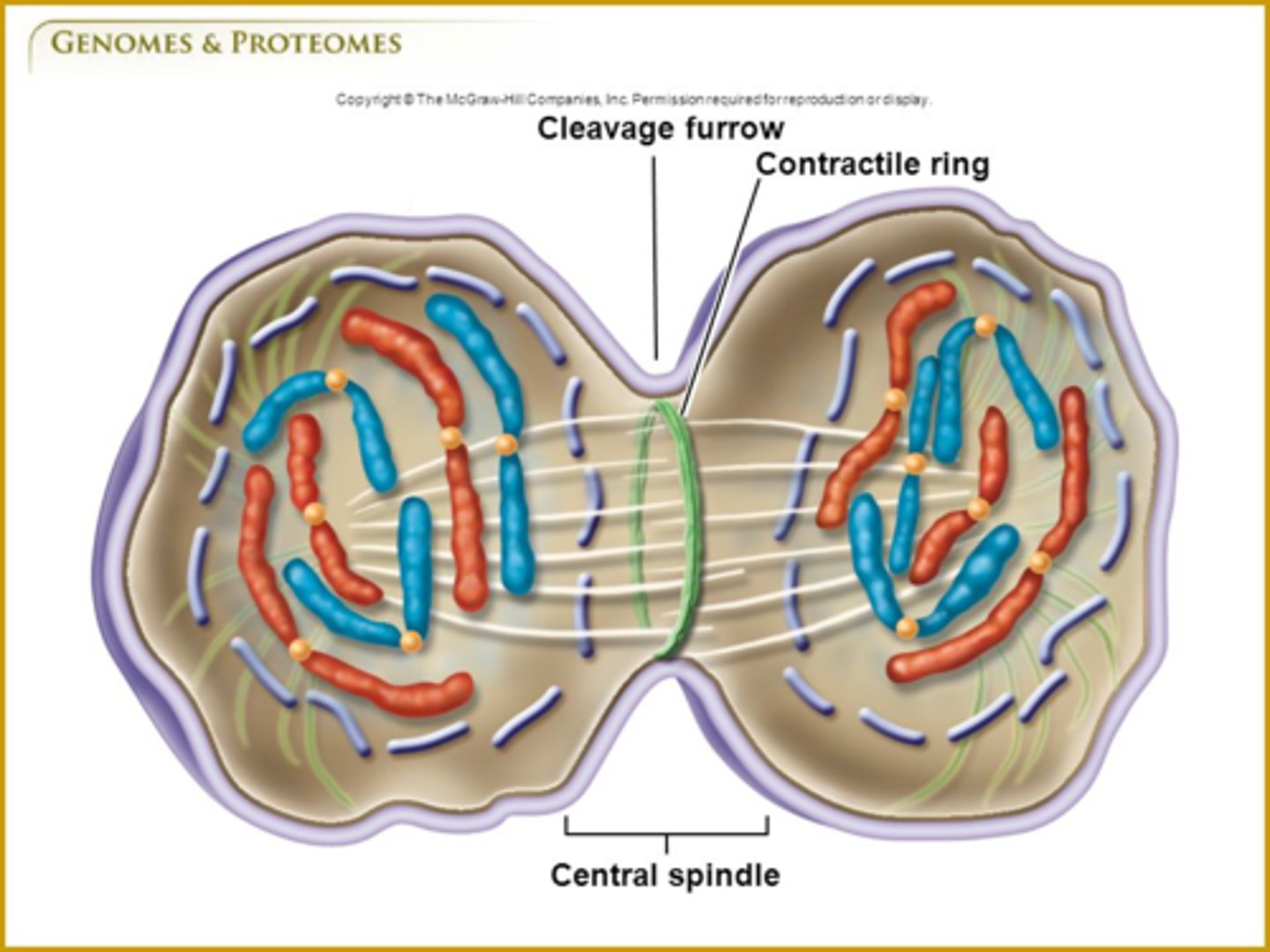
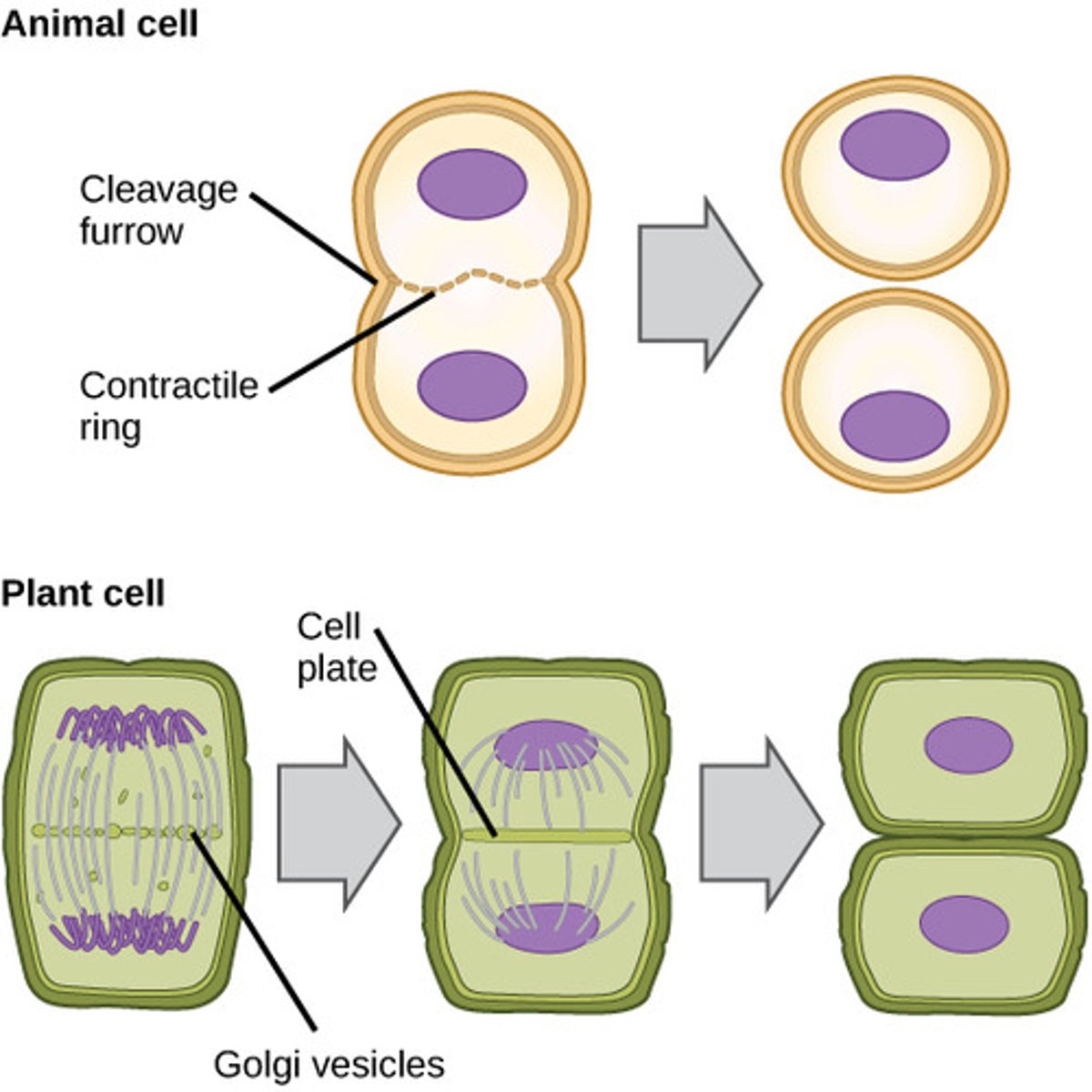
during cytokinesis, animal cells separate via creation of the _____
cleavage furrow
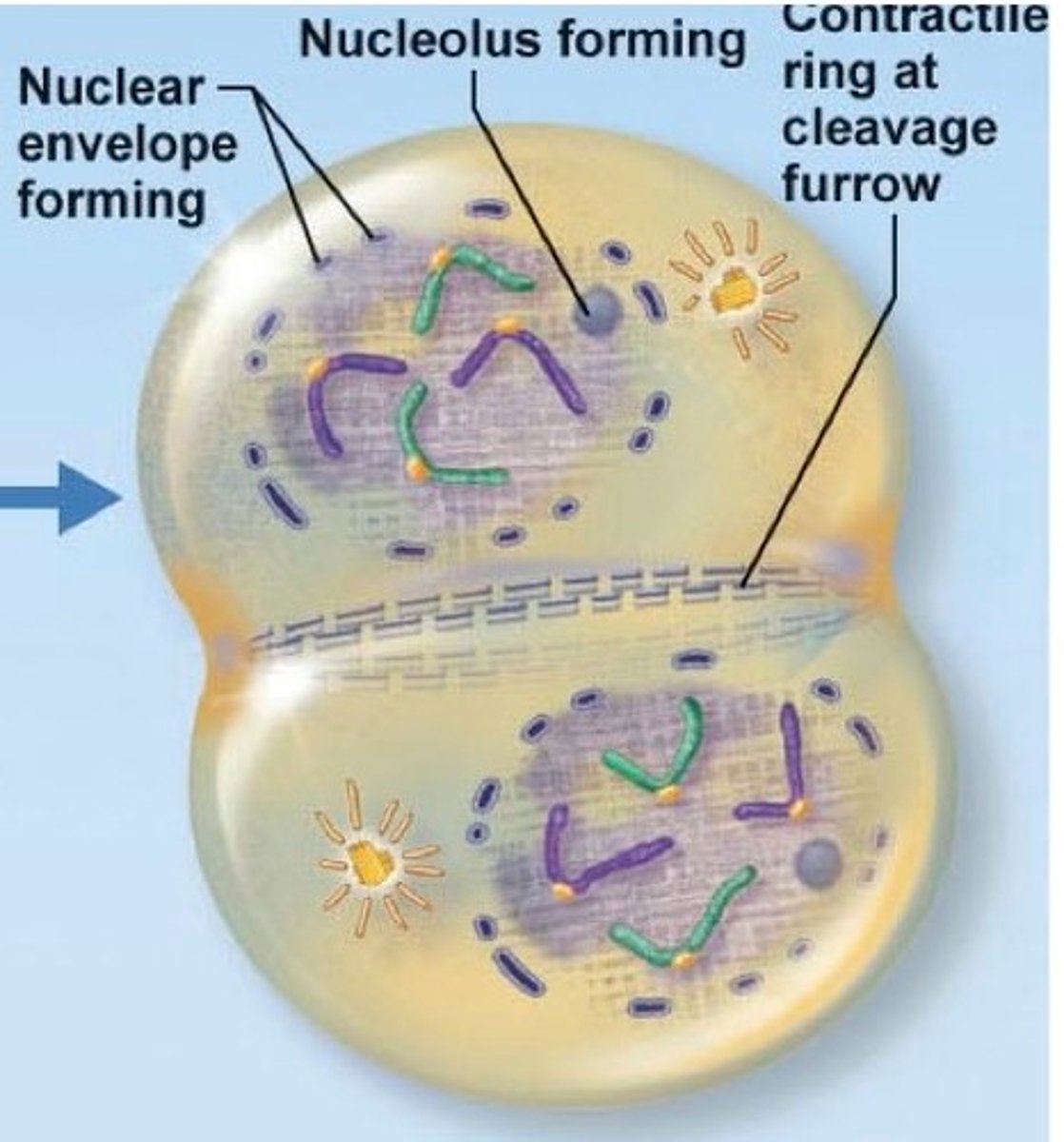
during _____ in animals, actin and myosin microfilaments shorten and the plasma membrane is pulled into the center, creating a _____
cytokinesis; contractile ring/cleavage furrow
plant cells undergo cytokinesis via formation of a _____
cell plate
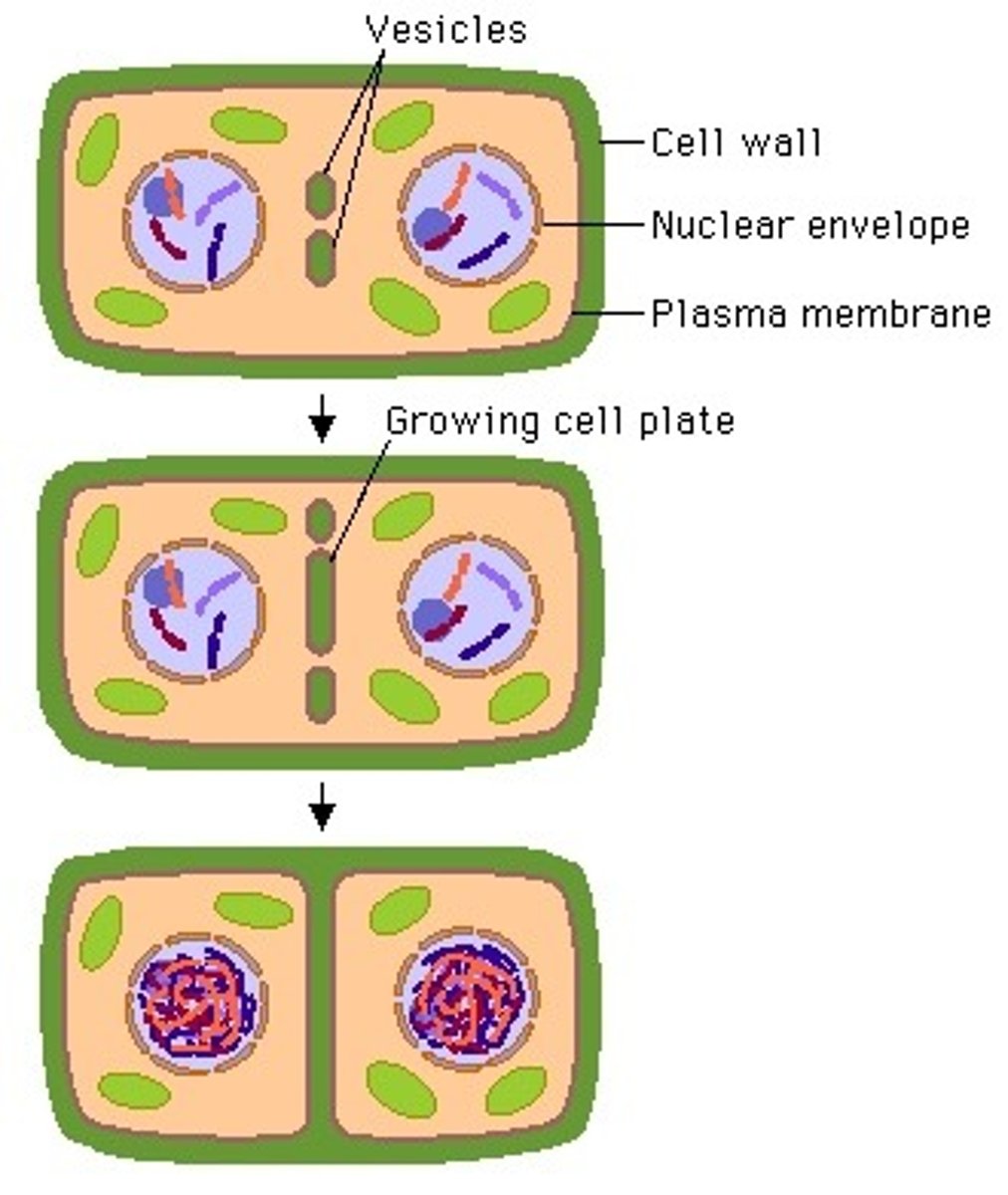
as plant cells undergo cytokinesis, vesicles from _____ migrate and fuse to form a cell plate
golgi bodies
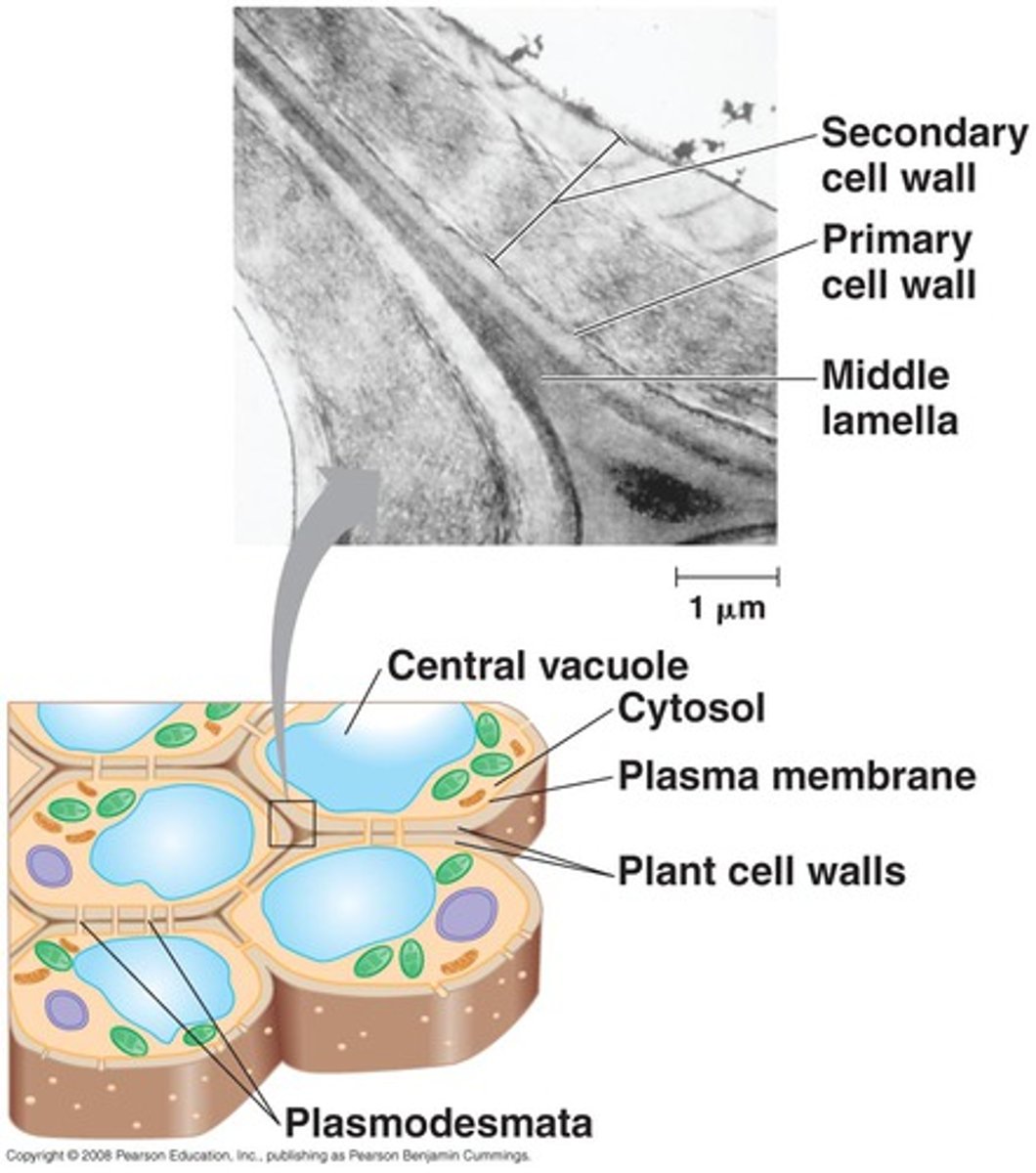
during plant cell division, the cells don't actually separate from each other because the _____ cements adjacent cells together
middle lamella
_____ begins after mitosis and cytokinesis complete
interphase
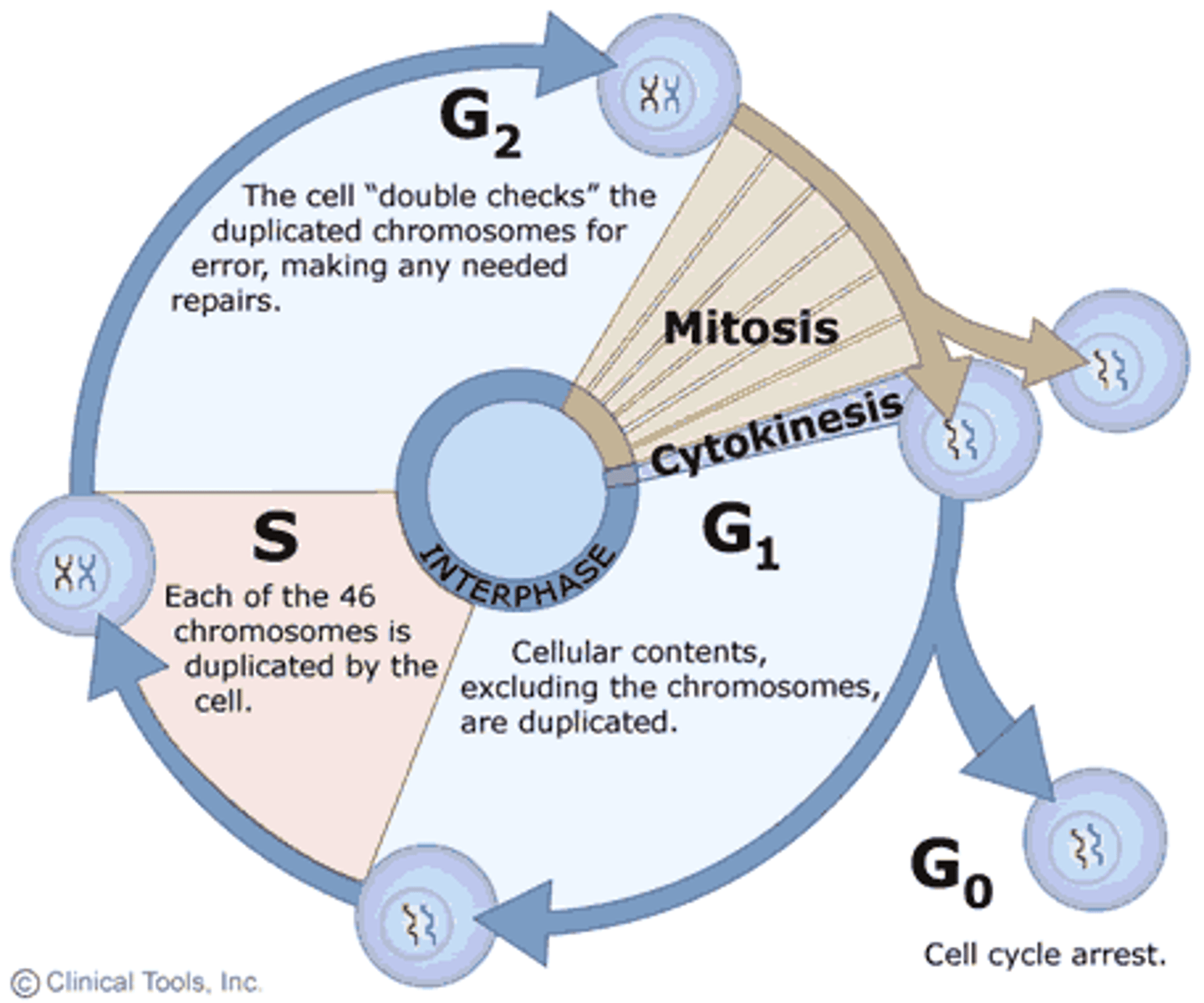
only the somatic cells that divide by _____ undergo interphase
mitotic
gametes do undergo _____ after they are made
interphase
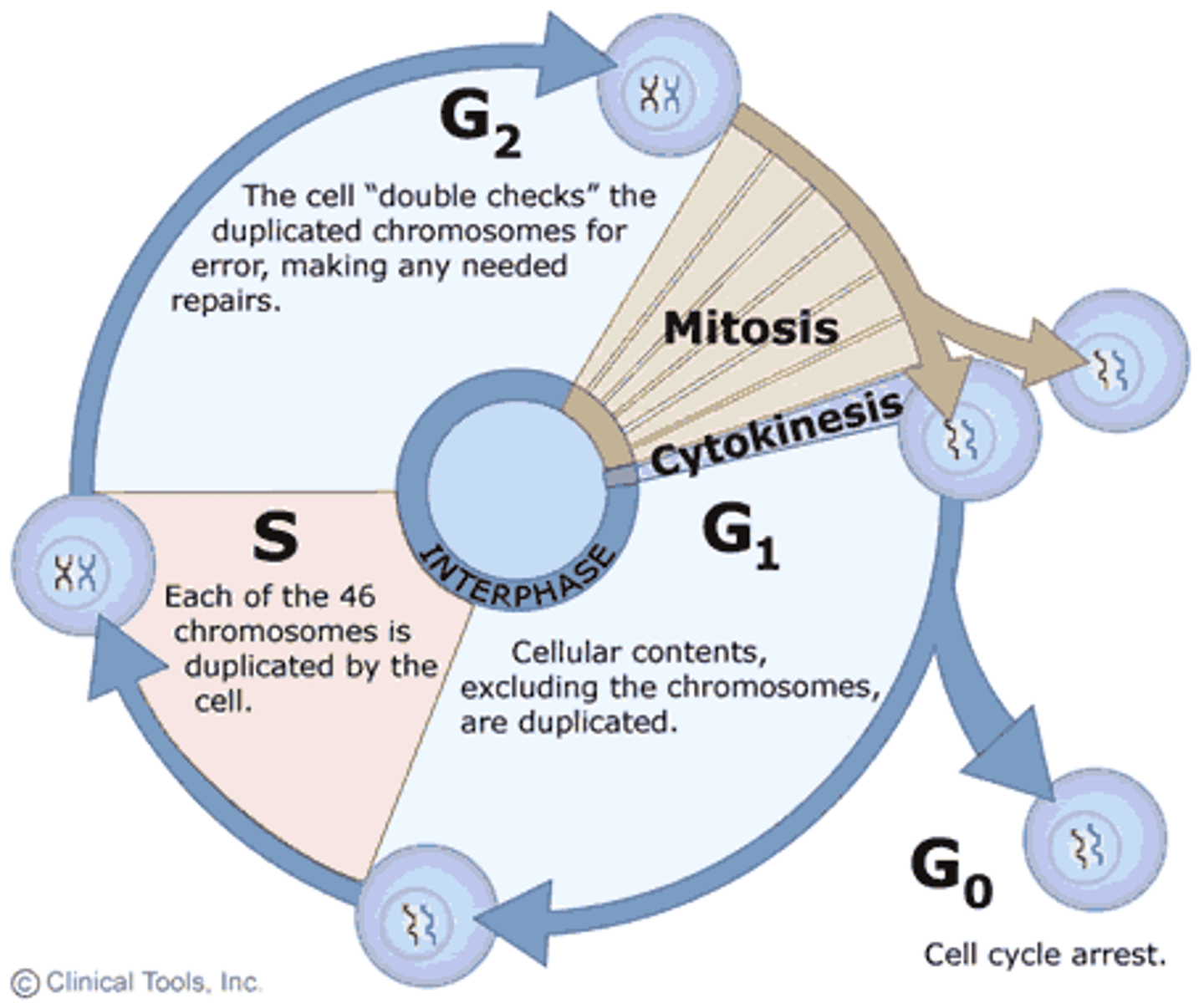
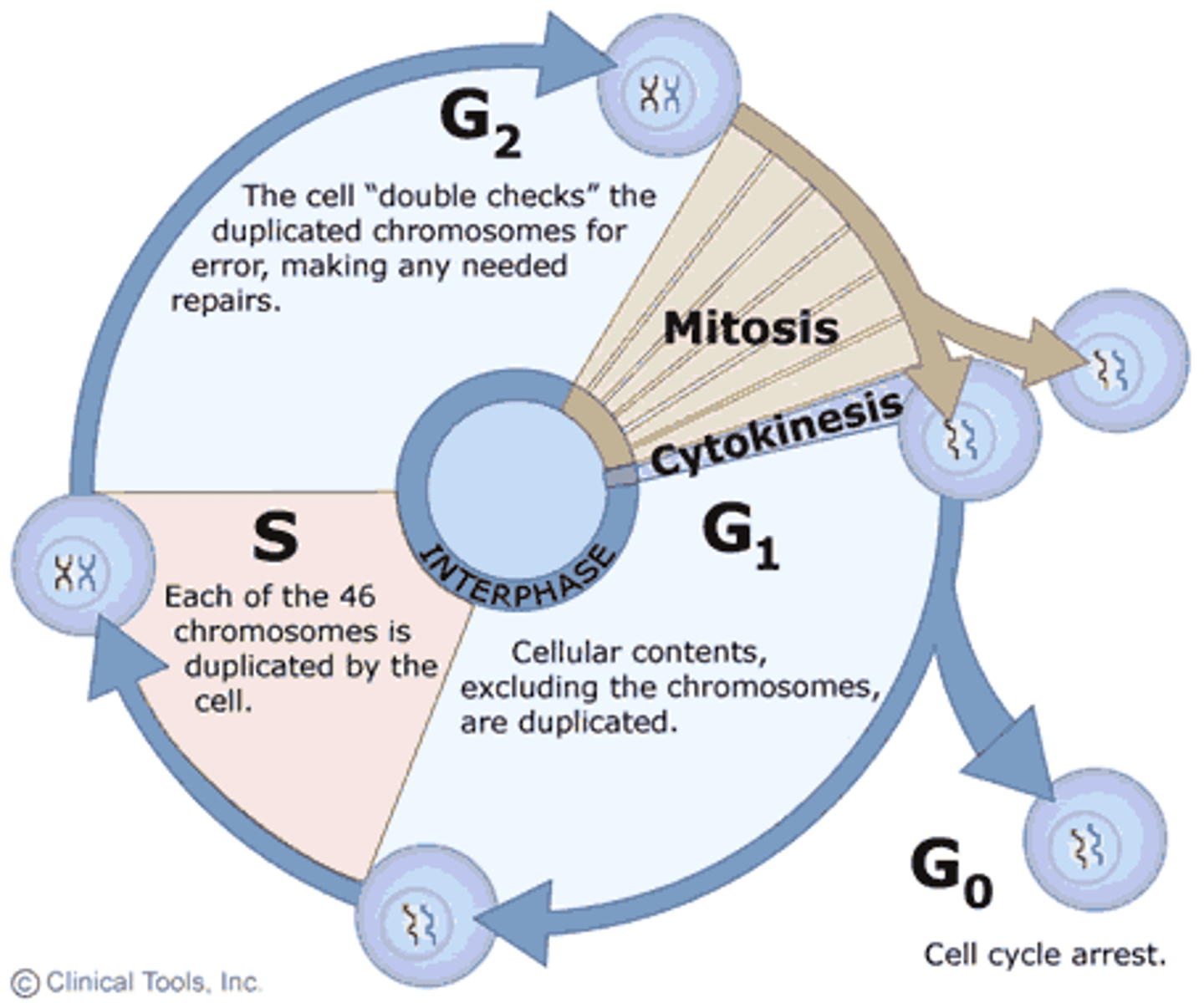
what are the phases of interphase?
G1 (possibly G0), S, and G2 phase
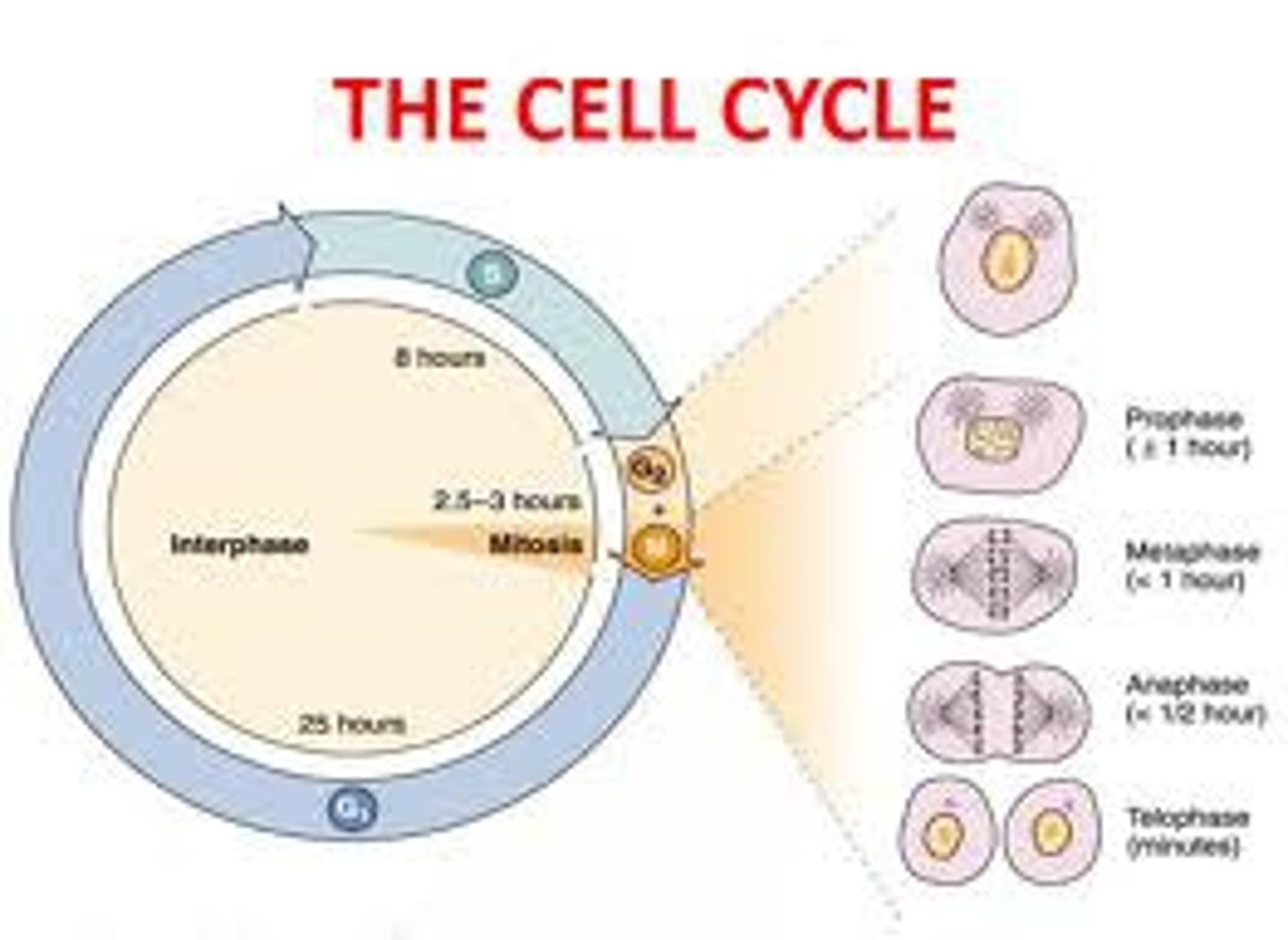
what are the 3 *main* phases of the cell cycle?
mitosis, cytokinesis, interphase
90% of the cell cycle is spent in _____
interphase
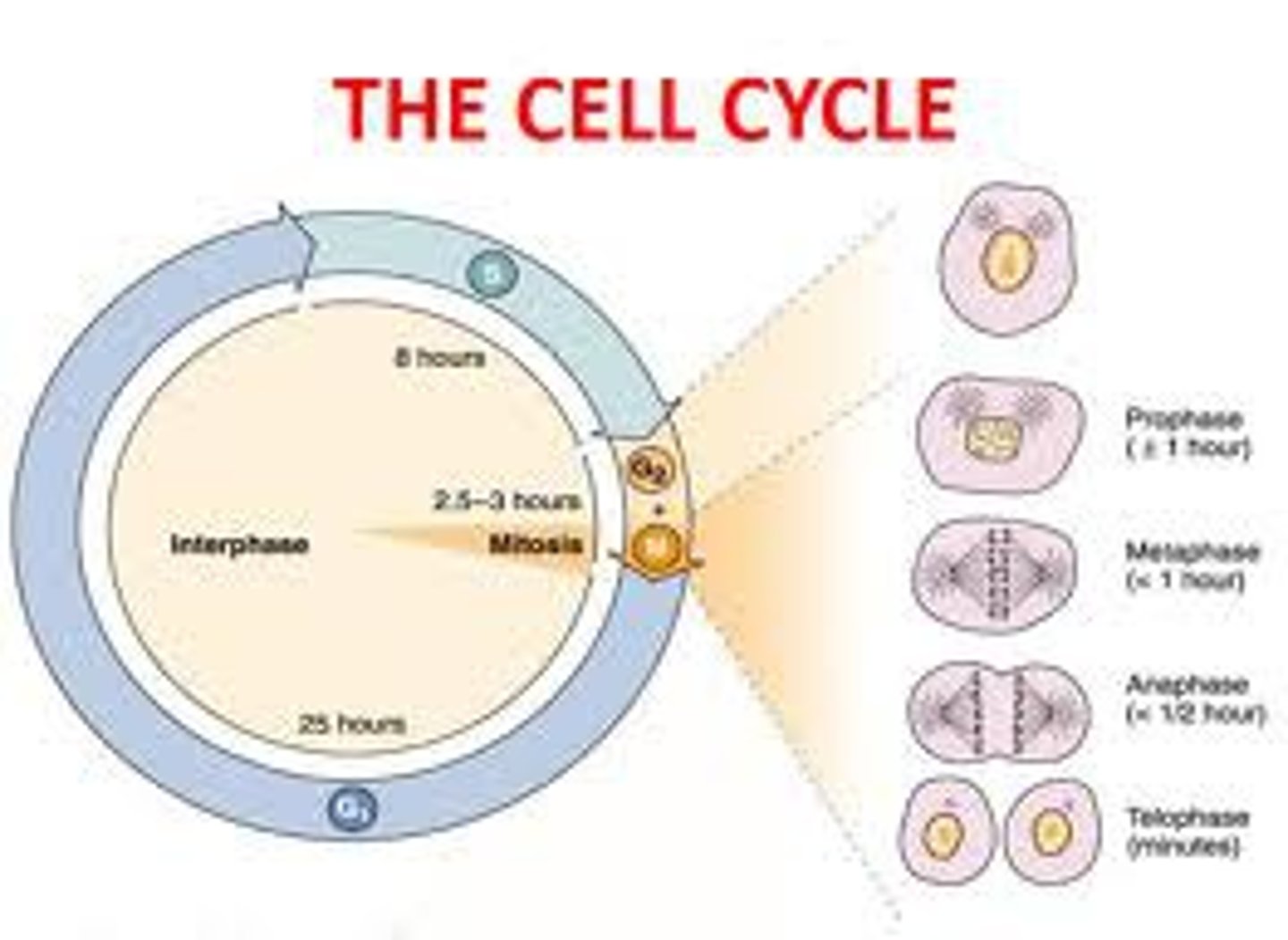
the phase of interphase in which a checkpoint ensures everything is ready for DNA synthesis
G1
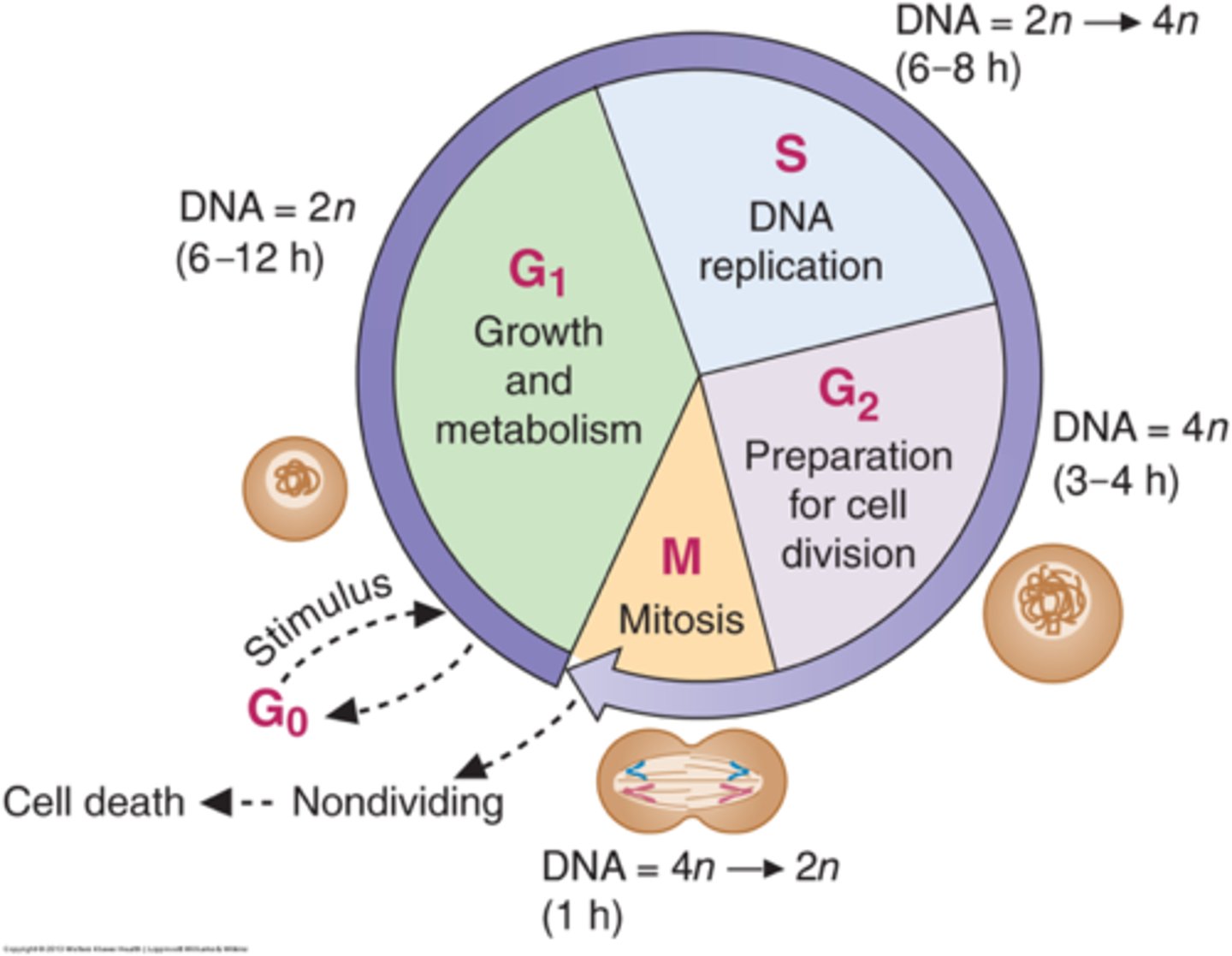
in what phase of the cell cycle will DNA synthesis occur?
the S phase of interphase
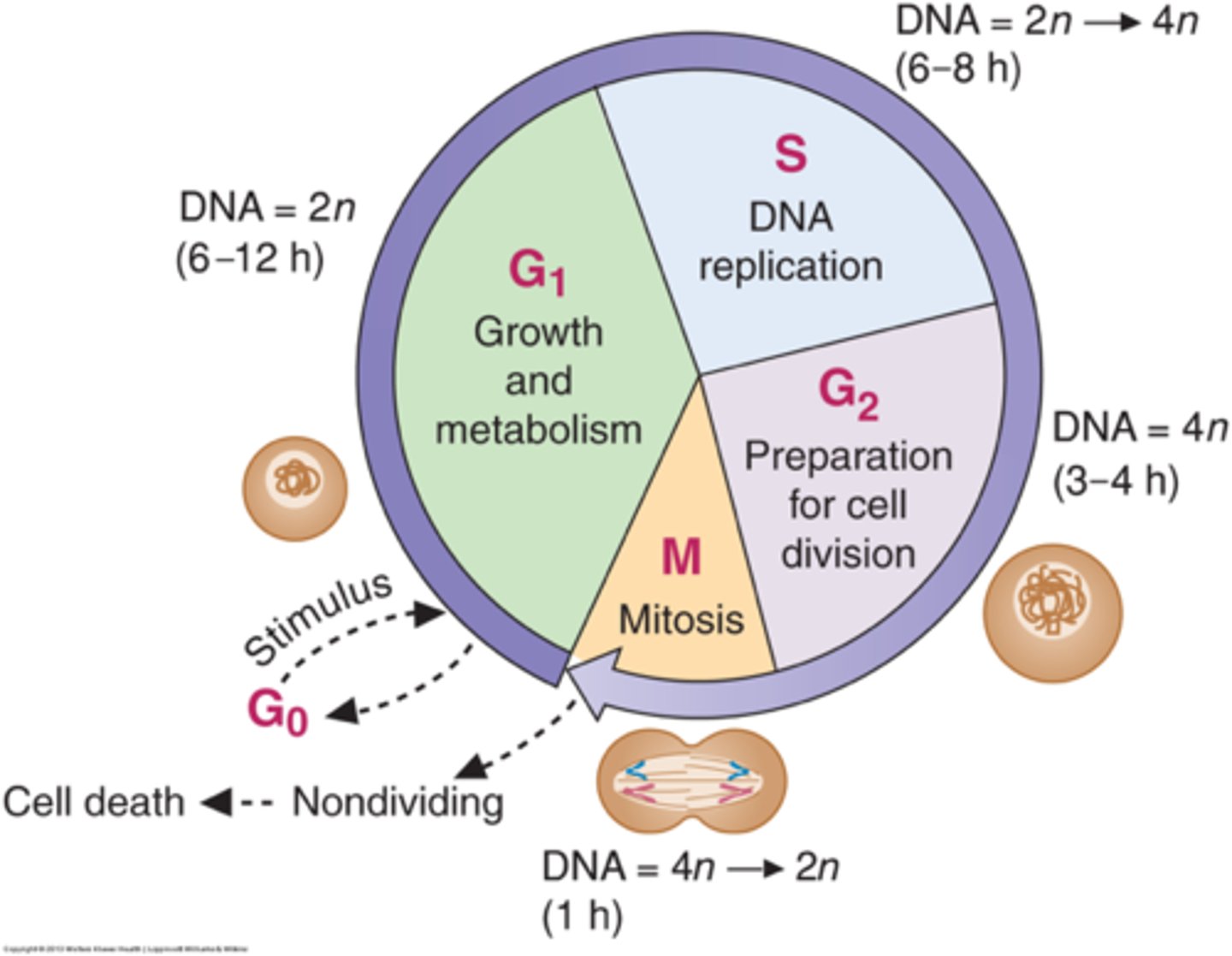
a second molecule of DNA is replicated from the first to provide sister chromatids in the _____ of interphase
S phase
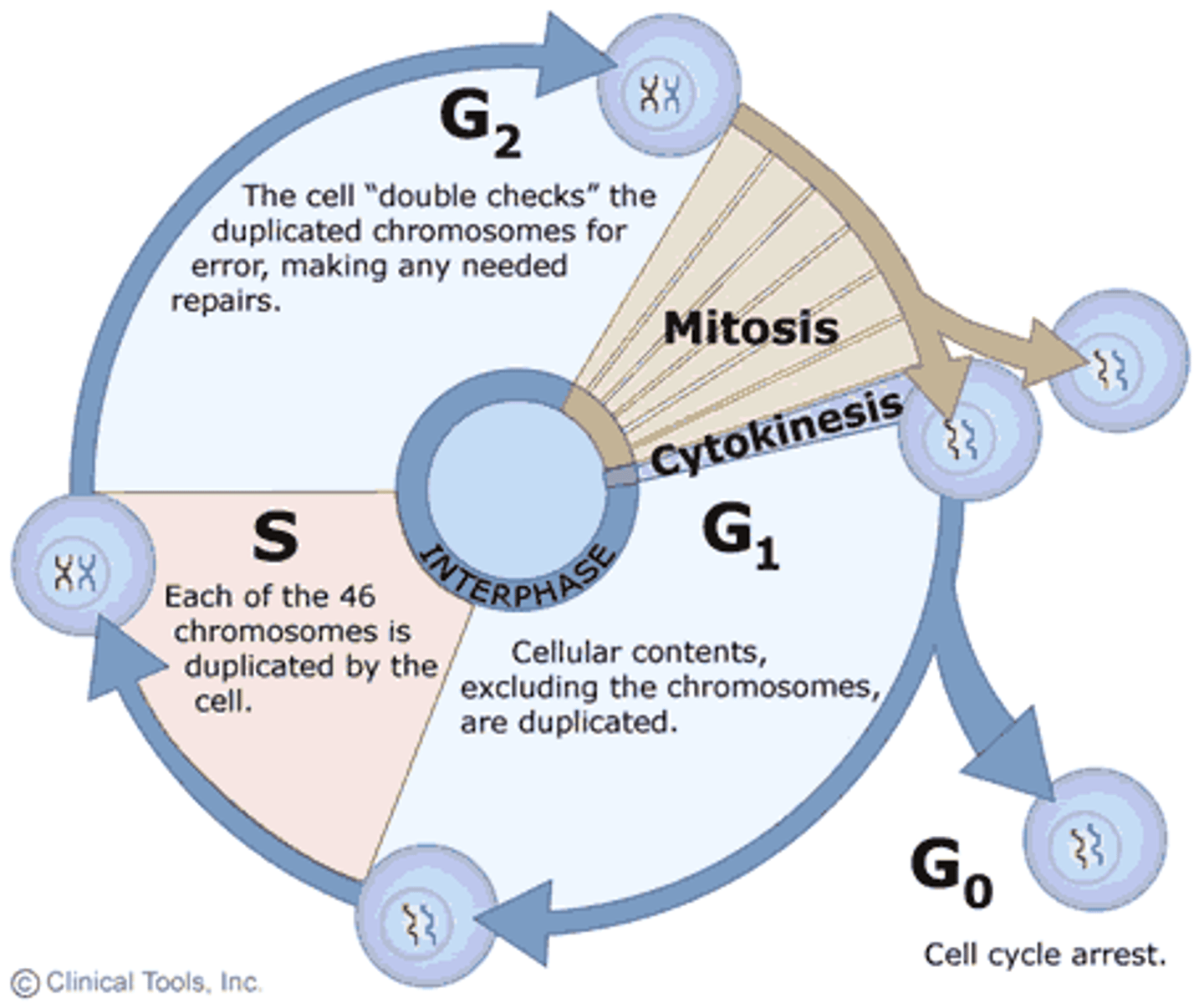
the phase of interphase in which rapid cell growth occurs
G2
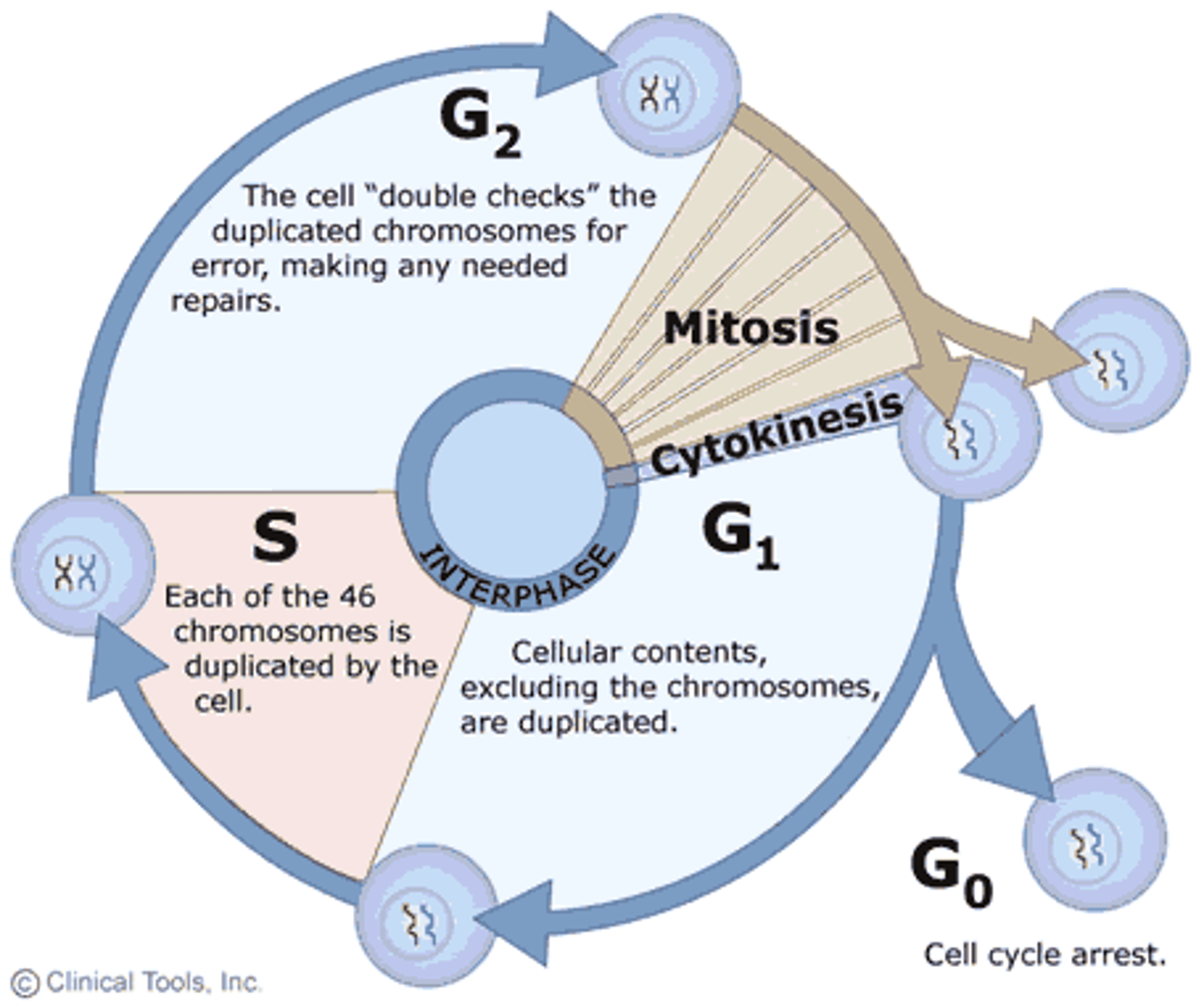
the cell prepares its genetic material for cellular division during the _____ of interphase
G2 phase
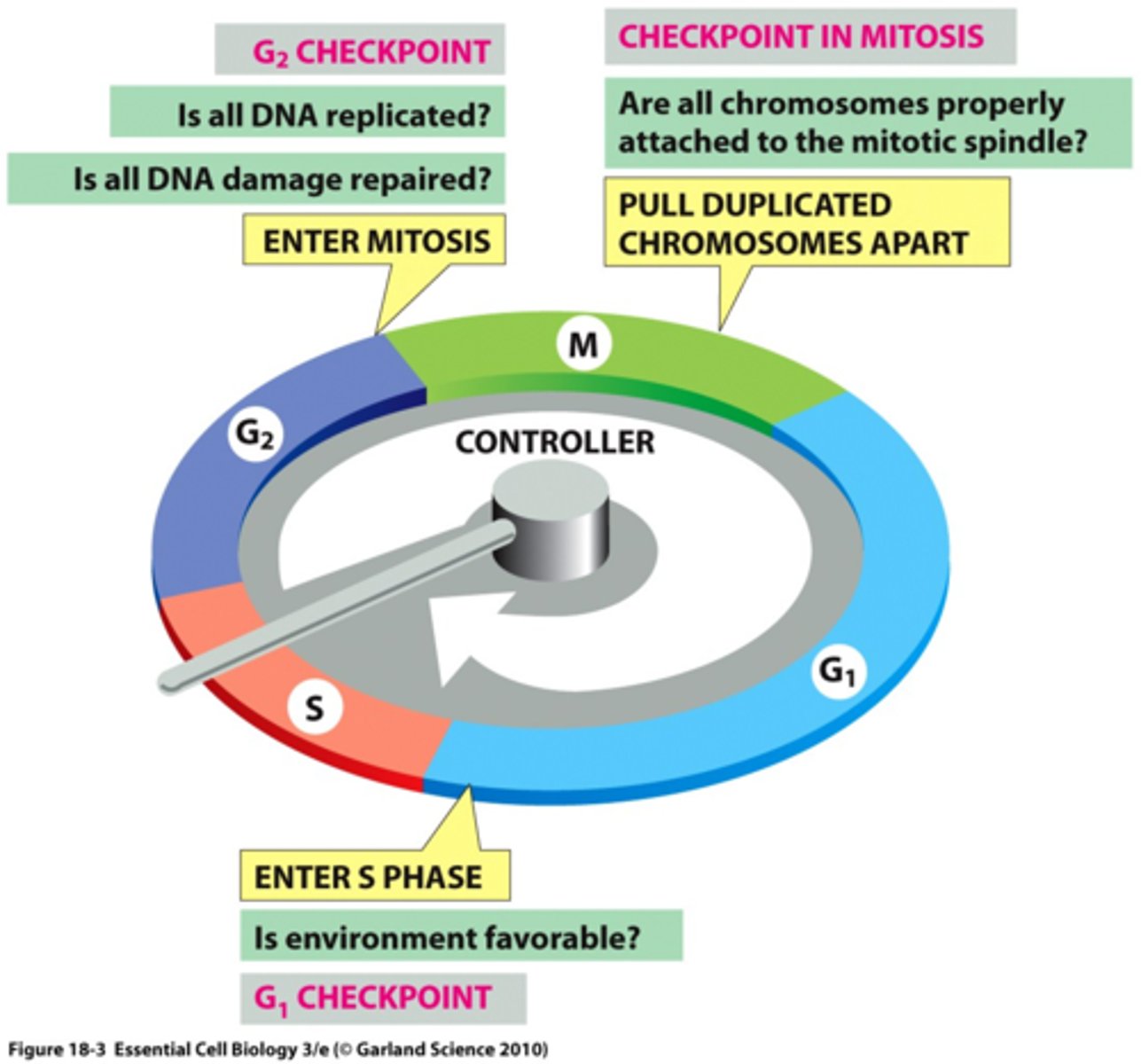
cells replicate their organelles during the _____ phase
gap 2 (G2)
when surface/volume ratio is _____, cellular exchange becomes easier
large
when surface/volume ratio is _____, cellular exchange is hard, and leads to cell death or cell division to increase surface area
small
what happens as the genome/volume ratio decreases (volume gets bigger)?
the cell exceeds the ability of its genome to produce sufficient amounts of regulation for cellular activities
some large cells (paramecium, human skeletal muscle) are _____ to deal with problems associated with ever decreasing genome/volume ratios
multinucleated
what is the most important checkpoint of the cell cycle?
the G1 checkpoint
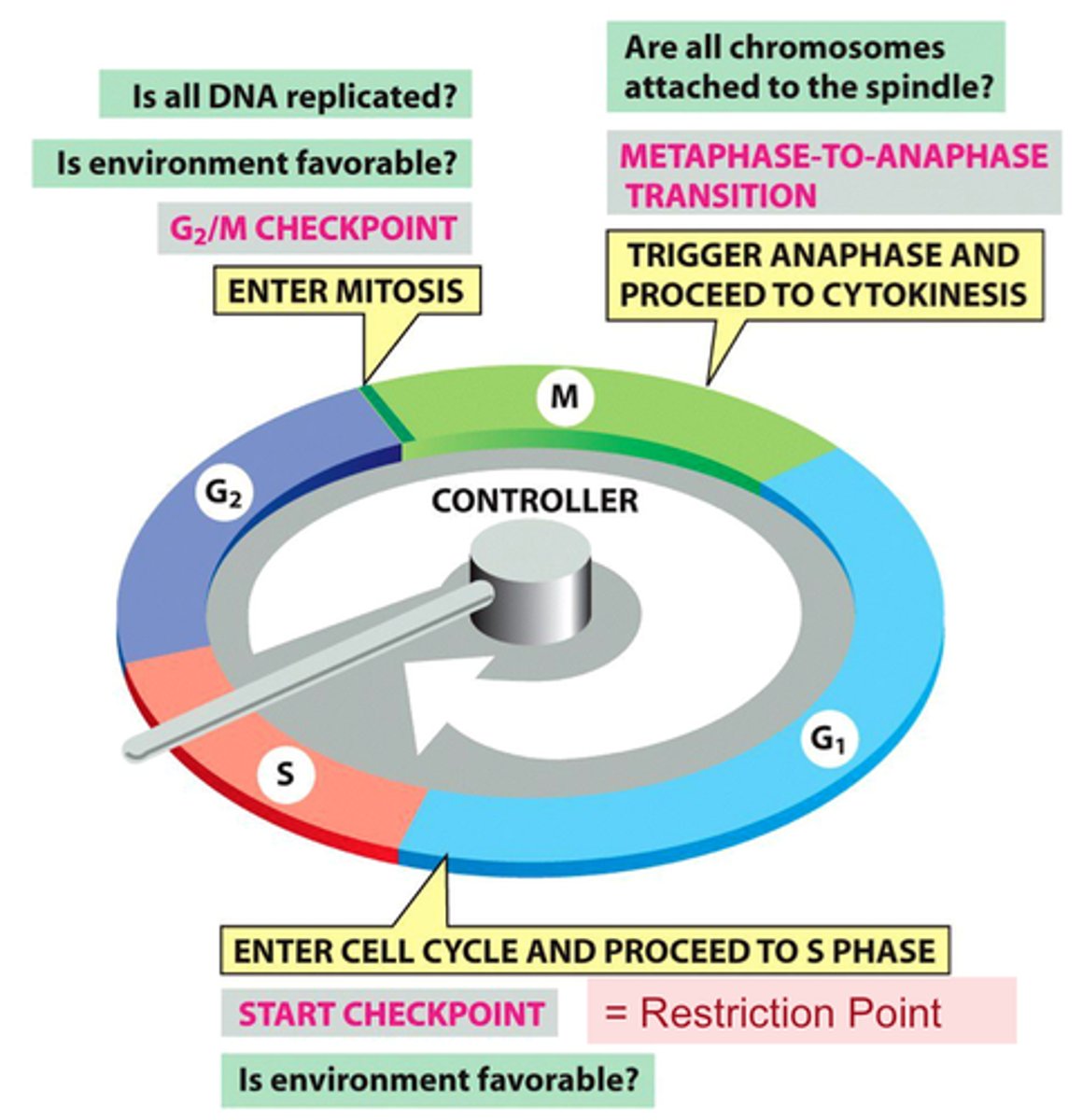
_____ is assessed and _____ conditions are checked during the G1 checkpoint
cell growth; favorable
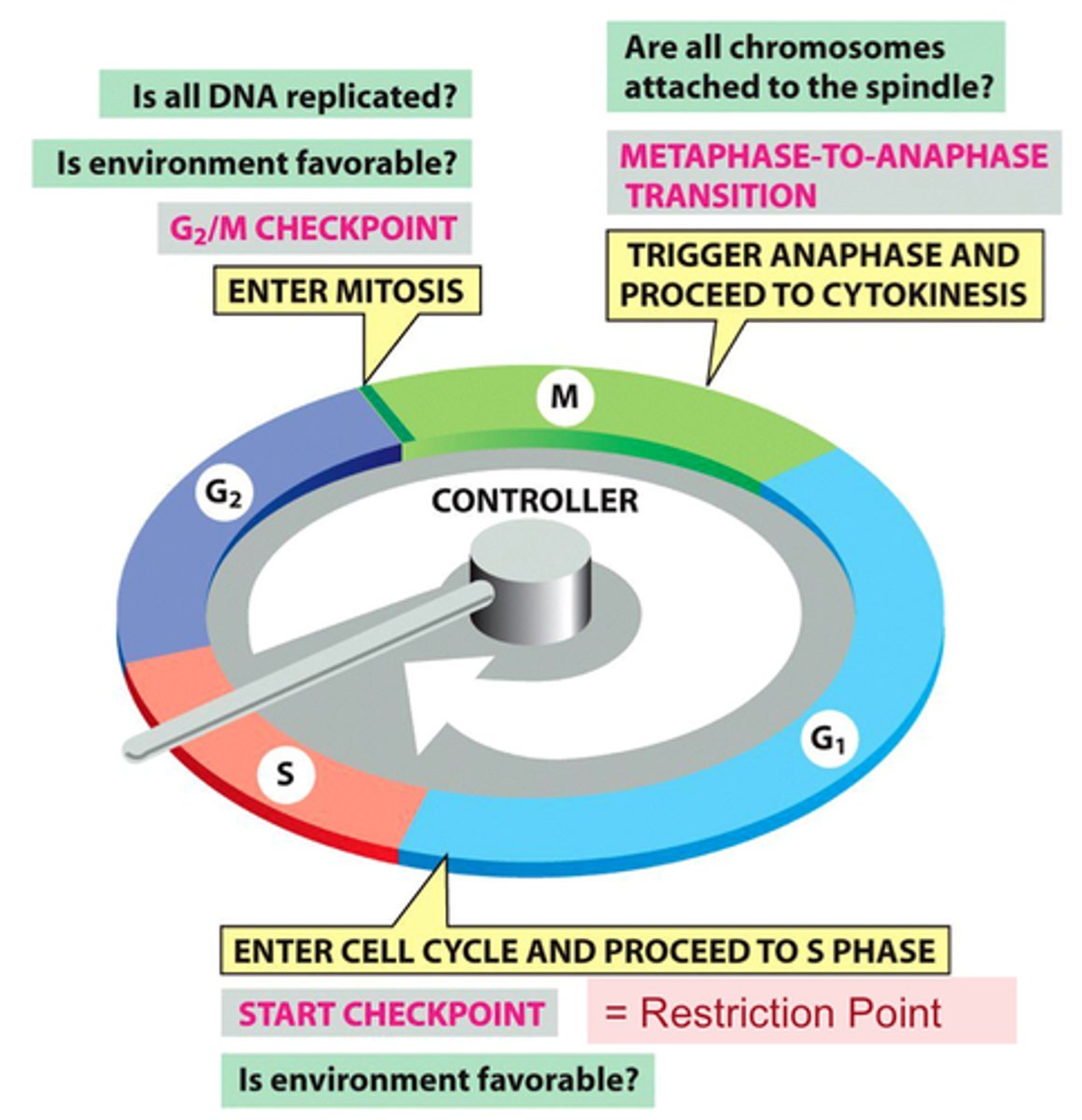
what happens if the G1 checkpoint fails?
the cell enters G0
; ; if checkpoint fails, ; some cells (liver, kidney) can be induced out of G0, some stay permanently (nerve and muscle cells); cells can either never proceed or wait until the cell is ready
G₁
at the end of _____, the cell evaluates the accuracy of DNA replication and signals whether to begin mitosis; the cell checks for sufficient mitosis promoting factor (MPF) levels to proceed.
G₂
at the end of G₂, the cell evaluates the accuracy of DNA replication and signals whether to begin mitosis; the cell checks for sufficient _____ levels to proceed.
mitosis promoting factor (MPF)
_____ checkpoint occurs during metaphase; division stops if the chromosomes are not attached to spindle fibers; if all are attached, cell is allowed to proceed with anaphase.
M
_____ are enzymes that activate proteins, which regulate the cell cycle by phosphorylation.
cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk)
_____ is a protein that activates cyclin-dependent kinases
cyclin
the plasma membrane has receptors for _____ that stimulate cells for division (such as damaged cell).
growth factors
cells stop dividing when surrounding cell density reaches a maximum - this is called _____.
density-dependent inhibition
most cells only divide when attached to an external surface, such as neighboring cells or a side of culture dish - this is called _____.
anchorage dependence
cancer cells defy the five cell-specific regulations in place. Such cells are called _____ cells.
transformed
cancer drugs that inhibit mitosis do so by disrupting the ability of _____ to separate chromosomes during anaphase, thus stopping replication.
microtubules
cancerous cells are a manifestation of defective cell _____.
differentiation
in meiosis, crossing-over occurs during _____
prophase I
during meiosis, _____ is when the homologous chromosomes pair up. These pairs are referred to as tetrads (groups of 4 chromosomes) or bivalents.
synapsis
during meiosis, synapsis is when the homologous chromosomes pair up. These pairs are referred to as _____ (groups of 4 chromosomes) or _____.
tetrads, bivalents
during meiosis, the _____ is the region where crossing over occurs of non-sister chromatids.
chiasmata
in meiosis, the _____ is a protein structure that temporarily forms between homologous chromosomes. This gives rise to the tetrad with chiasmata and crossing over
synaptonemal complex
in meiosis, disjunction of homologues occurs during _____
anaphase I
the phase of meiosis in which each pole forms a new nucleus that now has half the number of chromosomes - chromosome reduction phase to haploid
telophase I
phase of meiosis in which nuclear envelope disappears, spindle develops, etc.
• no chiasmata
• no crossing over
prophase II
phase of meiosis in which chromosomes align on middle plate like in mitosis, but there are now half the number of chromosomes
metaphase II
phase of meiosis in which sister chromatids separate
anaphase II
phase of meiosis in which nuclear envelope develops and cytokinesis occurs to produce 4 haploid cells
telophase II
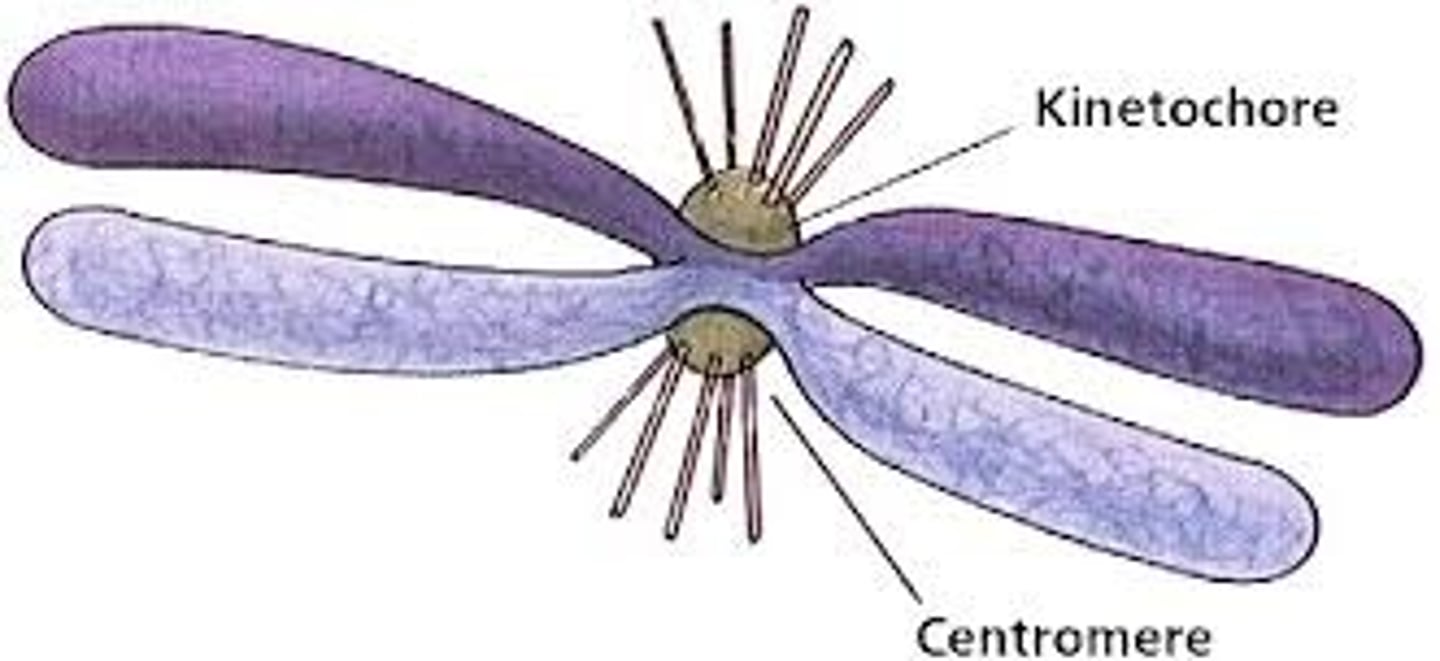
Dyads
Replicated chromosomes containing two sister chromatids that look like an "x"
Centromeres
Regions of DNA that connect sister chromatids in a dyad
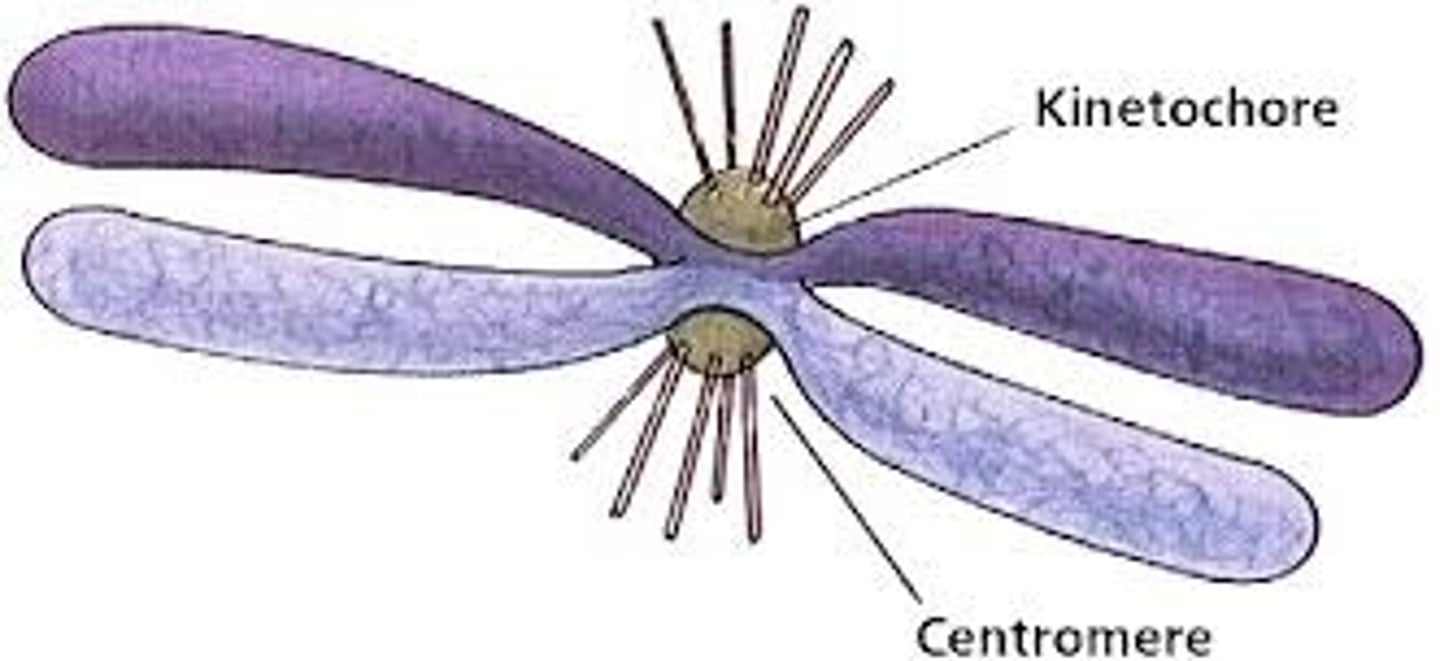
Kinetochores
Proteins on the sides of centromeres that help microtubules pull sister chromatids apart during cell division
Humans are _____ because they contain two sets of chromosomes
diploid (46 chromosomes, 23 pairs)
Gametes are _____ cells
haploid (only contain one chromosome set (23 chromosomes))
Gametocyte
Eukaryotic germ cells that can either divide to form more gametocytes or produce gametes
Kinetochore microtubules
Extend from centrosomes and attach to kinetochores on chromosomes
Astral microtubules
Extend from centrosomes to the cell membrane to orient the spindle apparatus