Lecture 23 - Type 1 Diabetes Clinical Presentation & Rationale for Insulin Administration
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is the initial presentation for type 1 diabetes
usually developed before 20 years old
hyperglycemia but little glucose used for cellular energy
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia
weight loss (can be sudden), lean body composition
20-40% present with diabetic ketoacidosis
when can diabetic ketoacidosis present
initial presentation for type 1 diabetes
acute illness
when insulin doses are missed
what are s/s of diabetic ketoacidosis
high blood glucose (>14)
dehydration
metabolic acidosis (pH<7.4, low HCO3-, anion gap)
electrolyte imbalances (Na/K)
increased respiratory rate
acetone (fruity) odor to breath (from ketones)
abdominal pain
decreased consciousness
what are general emergency treatments for diabetic ketoacidosis
fluid replacement, insulin therapy, electrolyte monitoring
what are the risk factors for type 1 diabetes
family history (immediate family), especially age of onset
genetic markers
autoantibodies
environmental factors
what is the rate of beta cell destruction dependent on
genetic predisposition
immunogenic abnormalities
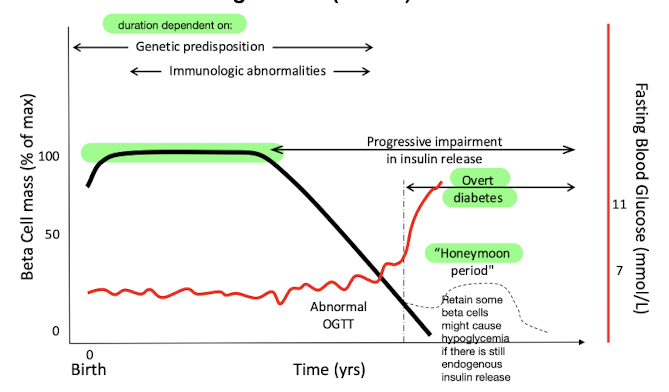
what is the honeymoon period of type 1 diabetes
retain some beta cell function
this may cause hypoglycemia if there is still endogenous insulin release in patients taking insulin
what are environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes
recent stressful event
irregular vaccination schedule
fetal infections
nitrosamine-containing products
is screening recommended for type 1 diabetes
no
what are the long term goals of therapy for type 1 diabetes
prevent onset or delay progression of microvascular and macrovascular complications
what are the short term goals of therapy for type 1 diabetes
alleviate symptoms of hyperglycemias and minimize the risk of hypoglycemia
how are the goals of therapy for type 1 diabetes accomplished
maintaining glycemic treatment targets
A1c
fasting pre-meal blood glucose
2-hour post-prandial blood glucose
physiologic replacement of insulin
what is the target A1c for most people
<7.0%
what is the target A1c for children and adolescents
<7.5%
what is the target fasting pre-meal blood glucose for most people
4-7 mmol/L
what is the target fasting pre-meal blood glucose for children and adolescents
4-8 mmol/L
what is the target 2-hour post-prandial blood glucose for most people
5-10 mmol/L
how does the hexamer formation of insulin affect its absorption
insulin in hexamer form is released slowly into the body
insulin in single subunits is absorbed rapidly
what kind of insulin is NPH
basal intermediate acting
cloudy
e.g. Humulin N, Novolin ge NPH
what kind of insulin is glaragine
basal long-acting
clear
e.g. Basaglar, Lantus, Toujeo, Semglee
what kind of insulin is detemir
basal long-acting
clear
e.g. Levemir
what kind of insulin is degludec
basal ultra-long-acting
clear
e.g. Tresiba
what kind of insulin is icodec
once-weekly basal
clear
e.g. Awiqli
what kind of insulin is lispro
bolus rapid-acting
clear
e.g. Humalog (100 & 200), Admelog
what kind of insulin is aspart
bolus rapid-acting
clear
e.g. Fiasp, NovoRapid, Turapi, Kirsty
what kind of insulin is glulisine
bolus rapid-acting
clear
e.g. Apidra
what kind of insulin is regular
bolus short-acting
clear
e.g. Humulin R, Novolin ge Toronto
what is the recommended insulin regimen for type 1 diabetes
basal-bolus (intensive glycemic control)
basal = long-acting or intermediate acting
bolus (meal related) = rapid acting or short acting
increased risk of hypoglycemia
what are other insulin regimens for type 1 diabetes that are not recommended
split-mixed → combination of rapid/short acting plus intermediate acting administered before breakfast and supper
sliding-scale → AVOID
what is the important evidence from the DCCT and EDIC studies of type 1 diabetes
multidose intensive insulin regimen is recommended (basal-bolus)
statistically significant and clinically important reduction in microvascular complications and macrovascular complications
statistically significant and clinically important increase in risk of hypoglycemia