DENT Fun. I - Type II, III, and IV Hypersensitivity
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Type II Hypersensitivity
- "Transfusion Reactions": Antibodies attack wrong blood types in the body
- NON-IgE Ab-Mediated destruction of cells
Type II Hypersensitivity Reactions are mainly ____ mediated.
IgG
Antibodies of Type II Hypersensitivity bind F(c) Receptors that induce ____ or ____.
ADCC/Phagocytosis
ADCC
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
Type II Hypersensitivity Reactions activate Complement Proteins (T/F)
True
Type II Hypersensitivity Reactions lead to Inflammation (T/F)
True; Cellular Destruction induces Inflammation
Blood Transfusion Reaction
An improper Blood Transfusion involving a blood type different from the Host; Causes Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN)
Autoimmune disease where maternal antibodies are directed against the fetus due to the presence of Rh-Antigen on the fetus
A mother has a 2 year-old and is pregnant. The mother is Rh-. The first child is also Rh-. The fetus, however, is Rh+. Will Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN) occur?
No
HDFN requires a sensitization phase, so the second child will not be affected by the maternal antibodies. However, if the mother has another child that is Rh+, then HDFN would occur if there is no intervention.
What causes maternal antibodies of an Rh- mother to attack an Rh+ fetus?
Initial exposure to Rh+ antigen will produce Anti Rh Memory B-Cells. This causes Isotype Switching of IgM to IgG. IgG can cross the Placenta, causing hemolysis of Fetal RBCs.
RhoGAM
Anti-Rh antibodies that combat HDFN
Drug-Induced Hemolytic Anemia
RBC destruction due to compounds adsorbing to RBCs and antibodies binding these new "foreign" proteins called neoantigens
Myasthenia Gravis
Auto-Antibodies attack ACh-Receptors on muscle cells in the NMJ
- Muscle Weakness
Type III Hypersensitivity
- IgG/IgM mediated reactions that bind SOLUBLE antigen, creating immune complexes that are inefficiently removed
- Highly stable
- In bad situations, can deposit into tissues and blood vessels; Leads to autoimmunity/hypersensitivity
Type III Hypersensitivity Manifestations
- Arthus Reaction
- Serum Sickness
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Arthus Reaction
Local reaction seen in the skin after subcutaneous injection of an Antigen that has already generated IgG antibodies
- Inflammation
- Large, diffuse Erythema and Edema
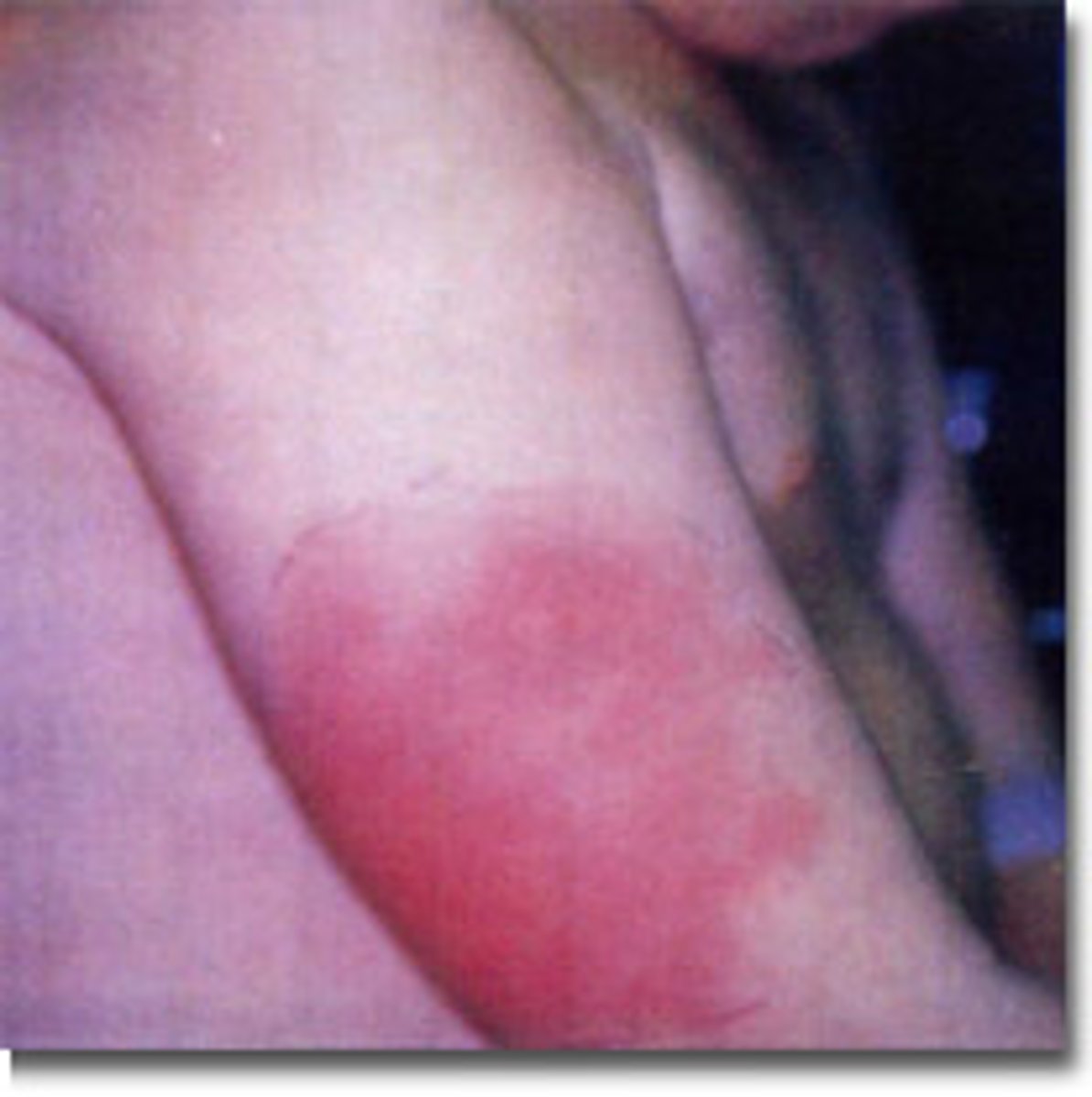
Serum Sickness
Immunization produces Antigen-Antibody complexes that are stored in tissues and cause a harmful reaction to the body's tissues
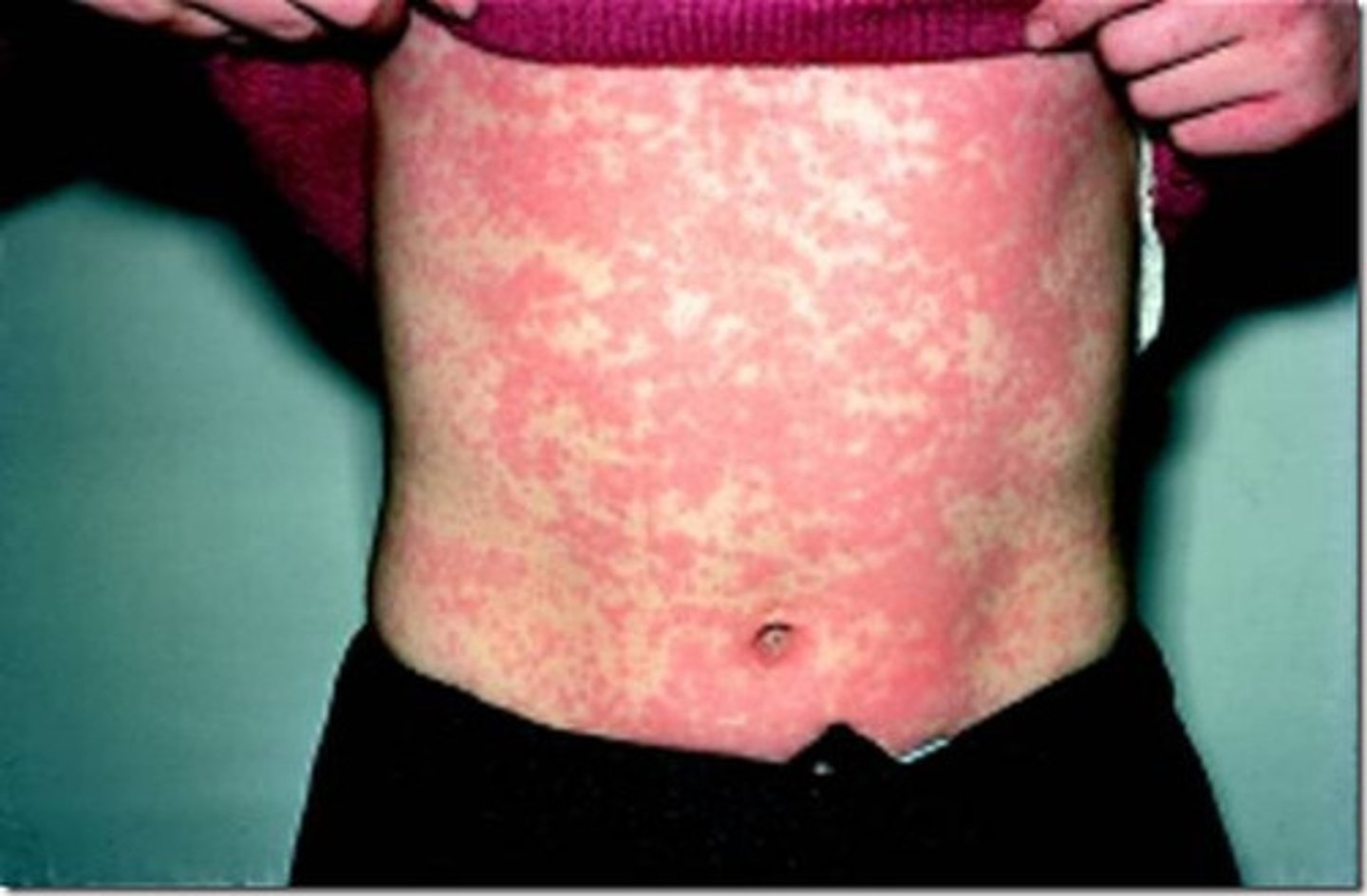
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Autoantibodies attack DNA and histones (Antinuclear Antibodies); Form immune complexes in tissue (Kidney) and blood vessels, destroying them
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANAs)
- Autoantibodies directed against antigens in cell nuclei
- Generated by defective apoptotic mechanisms
Type IV Hypersensitivity
- "Delayed-Type (DTH)"
- T-Cell mediated reaction that takes 1-2 weeks
Type IV Hypersensitivity Sensitization Phase
Development of Antigen-Specific T-Cell Population that takes around 7 days
Type IV Hypersensitivity Effector Phase
T-Cell and Macrophage Activation that occurs 1-3 days after subsequent exposure
____-Cells are the predominant drivers of Type IV Hypersensitivity.
Th1
How can sensitized T-Cells be detected?
via a Skin Test (Tuberculin Reaction)
A positive test produces a solid, red lump
Type IV Hypersensitivity Manifestations
- Granulomatous Inflammation
- Contact Hypersensitivity
- Celiac Disease
- Type I Diabetes
Granulomatous Inflammation
Continuous activation of Macrophages causes them to adhere to one another, fusing to form multinucleated giant cells that can cause damage
Contact Hypersensitivity
Caused by contact of the skin with an offending substance that creates a neoantigen that T-Cells respond to
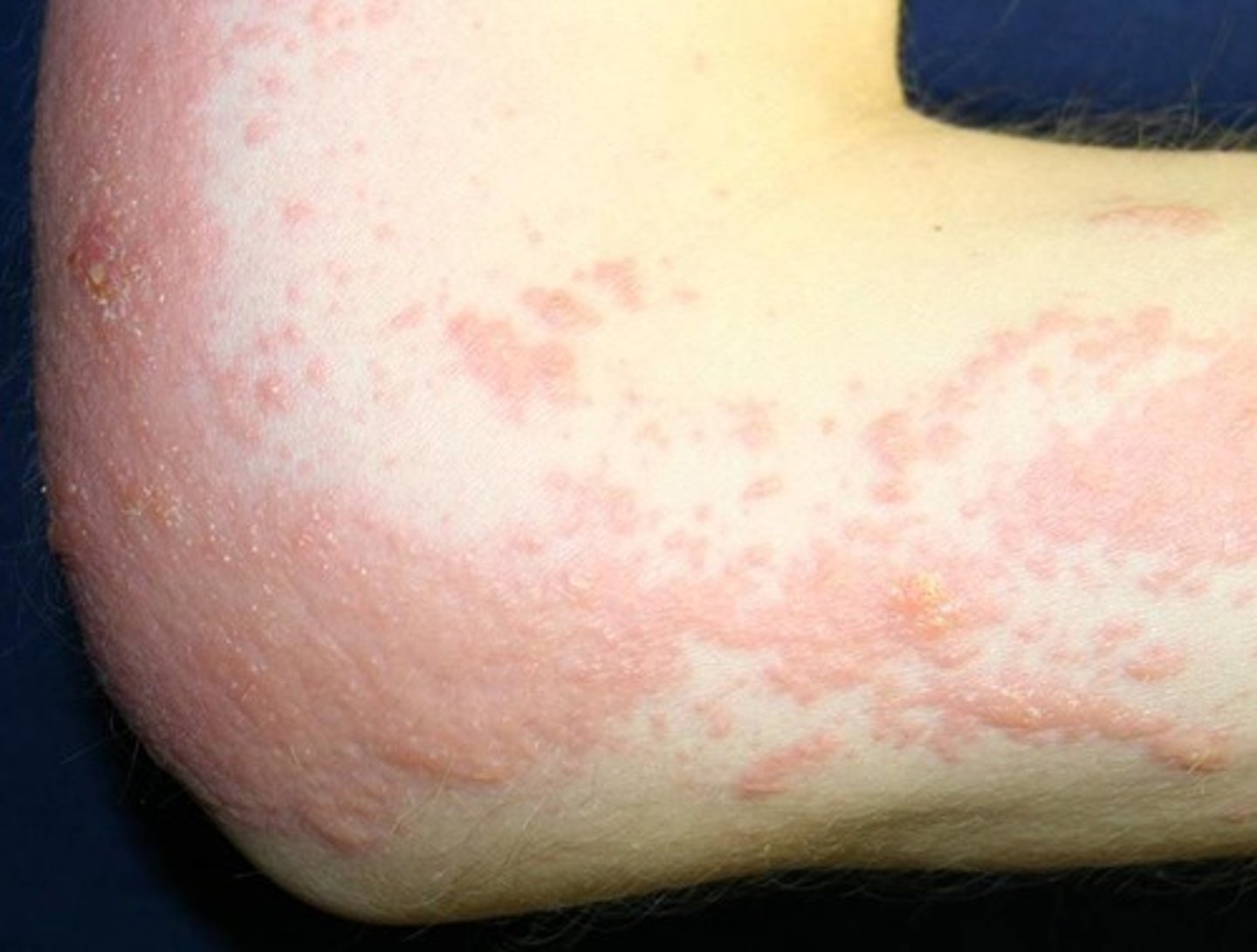
Celiac Disease
Autoimmune disease in which CD4+ T-Cells respond to gluten-derived peptides presented by Macrophages in the GALT. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines are secreted, causing inflammation and destruction of Intestinal Epithelia.
Type I Diabetes
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes caused by activation of CD8+ T-Cells that are sensitive to β-Cells of the Pancreas
____ is the most common Type IV Hypersensitivity.
Contact Hypersensitivity
____ can induce all 4 hypersensitivity reactions.
Penicillin