Topic 3 networks
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/286
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:03 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
287 Terms
1
New cards
Define bus topology.
The computer network in which a "bus” connects all the devices cable together through a common cable.
2
New cards
Define cable.
Copper wire (usually coaxial and twisted pair) and fibre (fibre optic cable-made from glass). Cables allow for the connection of computers over a network. \n
3
New cards
Define check digit
Extra digit added to numerical data that is used to check data integrity after input, transmission, storage and processing.
4
New cards
Define Data integrity
The accuracy of data after input, transmission, storage or processing.
5
New cards
Define Check Sum
Error—detecting procedure that generates a sum from the digits of a number.
6
New cards
Define data packet
Portion of a message that is transmitted through a network. Contains data such as check digits and destination address.
7
New cards
Define gateway
Link that resides between computer networks and is responsible for converting data passing through into the appropriate format so it can be understood by the receiving network.
8
New cards
Define handshaking
Exchange of predetermined signals to signify that a connection has been established between two systems.
9
New cards
Define hub
Network connection point for devices. Data arriving at a hub is copied and send to all the devices on the network.
10
New cards
Define ISDN (integrated service digital network)
International communications standard that allows for the transmission of audio/video and other data over digital telephone lines.
11
New cards
Define local area network (LAN)
Computer network where all the connected computers are within a limited geographical area (ex. a home, school, etc.). Connection between the computers may be through cables and/or microwave transmission.
12
New cards
Define microwave transmission
Electronic communication without the need for cables.
13
New cards
Define modem (abbreviation of modulator/demodulator)
Electronic equipment that converts computer digital signals into audio signals and back. The audio signals are transmitted over telephone lines, which allows for distant communication.
14
New cards
Define network
Computer systems that are interconnected and can share resources and data.
15
New cards
Define packet
Group of bits. May include control signals, error control bits, coded information, as well as the destination for the data.
16
New cards
define packet switching
Network communication method that creates and transmits small units of data, called packets, through a network, independently of the overall message.
17
New cards
define networking
Making use of a network.
18
New cards
Define parity bit
Error-detecting procedure that appends a binary digit to a group of binary digits. The sum of all the digits, including the appended binary digit, establishes the accuracy of the data after input, transmission, storage or processing.
19
New cards
Define protocol
International rules that ensure the transfer of data between systems. A protocol that is recognized as the standard for a specific type of transfer is called standard protocol. For example: TCP/IP is a standard protocol.
20
New cards
Define TCP/IP (transmission contro protocol/internet protocol)
Communications protocols used to connect hosts on the Internet.
21
New cards
Define wide area network (WAN)
Computer network where all the connected computers are in a larger geographic area than that served by a LAN or a MAN (metropolitan area network).
22
New cards
What a computer network compromised off?
Compromise of 2 or more computer systems that are connected and able to communicate and exchange data.
23
New cards
Wha is a server?
A server can either be a computer system or a software application that provides a service to the other computer systems connected to the same network.
24
New cards
What is a client?
A client can either be a computer system or a software application that requests a service from a server connected to the same network.
25
New cards
What a Hubs a connection for?
is a connection point for devices on a single network
26
New cards
How do computer systems connect to a hub?U
using ethernet cables that attach to a port
27
New cards
What does a hub consists off?
Multiple ports
28
New cards
"When a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the ____. The ____ then ____ the data and sends it to all devices connected to its ____. The device waiting to receive the data ____ the data. All the other devices just ____ ____."
When a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the hub. The hub then copies the data and sends it to all devices connected to its ports. The device waiting to receive the data accepts the data. All the other devices just ignore it.
29
New cards
What slows down the network when using a hub?
When passing the data along to every port as a lot of traffic is generated on the network, since all the other ports that just ignore the data have to nevertheless receive it.
30
New cards
What is a switch?
connection point for multiple devices on a single network.
31
New cards
unlike a hub, the switch can ____ which network device is ____to which part. This allows the switch to ____data to the exact port and network device for which it is intended. This means that when a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the switch and the switch sends the data to the appropriate receiver rather than____the ports and devices connected to those ports. As such, networks connected with a switch are ____than networks connected with a hub.
unlike a hub, the switch can identify which network device is connected to which part. This allows the switch to transmit data to the exact port and network device for which it is intended. This means that when a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the switch and the switch sends the data to the appropriate receiver rather than all the ports and devices connected to those ports. As such, networks connected with a switch are faster than networks connected with a hub.
32
New cards
What is the use of a router?
Its use is to join multiple networks and serve as an intermediary between these networks so that data can be exchanged effectively and efficiently between network devices of those networks.
33
New cards
"As stated, a ________ or a switch and a router are commonly integrated into a single ________, allowing the creation of a wired or wireless network, as well as connection of that network to other networks, such as the Internet."
As stated, a hub or a switch and a router are commonly integrated into a single box, allowing the creation of a wired or wireless network, as well as connection of that network to other networks, such as the Internet.
34
New cards
What is Local Area Network (LAN)
computer network that connects computer systems that are within a limited geographical area such as a room, a home, an office building or a school. Computer systems interconnected with a LAN usually have high data-transfer rates between them.
35
New cards
What type of mode is commonly used for LAN
A client-server mode of operation is commonly used. This allows for a single computer system to act as the server and be responsible for supplying various services to the clients in the network.
36
New cards
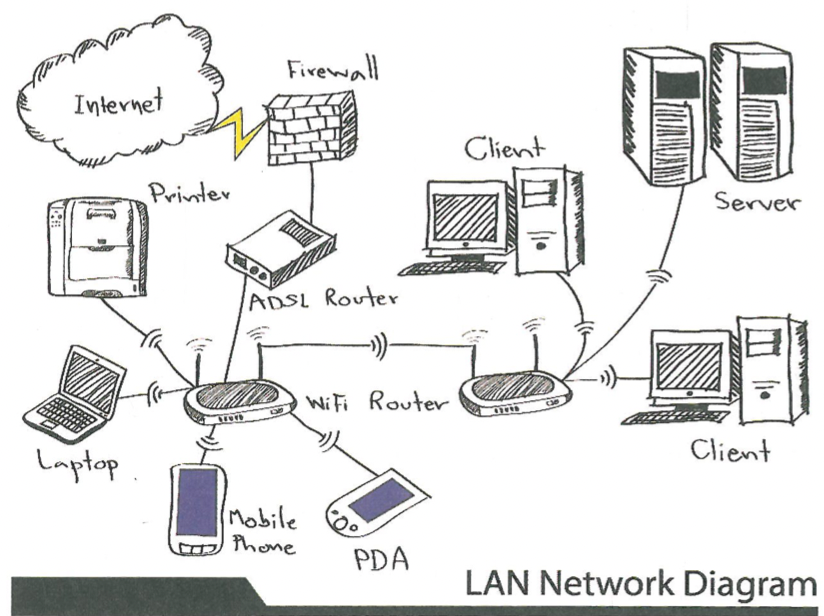
What does LAN allow and does this eliminate the need off?
allow the sharing of peripheral devices between the connected computer networks. This eliminates the need to buy certain peripheral devices for every computer system used.
37
New cards
Give an example of LAN being used with a peripheral device.
For exampleI instead of having to buy a number of printers, one printer can be bought and connected to the server of the LAN, with the rest of the computer systems, the clients, accessing and sharing the printer through the server.
38
New cards
Apart from peripheral devices what is another benefit of LAN?
data can also be shared. This allows for the exchange of data between clients, thus eliminating the need to physically send data using other means, such as by exchanging CDs or memory sticks. This increases flexibility and reduces wasted time.
39
New cards
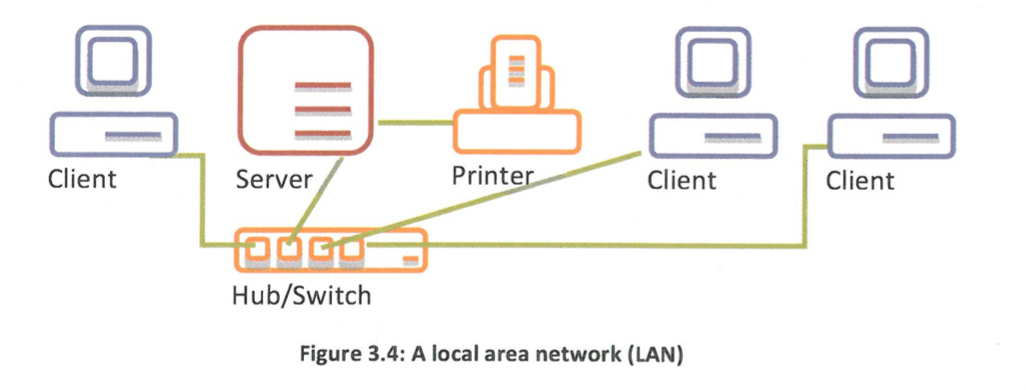
What is the most common technology used to build wired LAN’s?
a hub or a switch using Ethernet cabling.
40
New cards
What is a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)?
links two or more computer systems within a limited geographical area, similar to LAN.
41
New cards
What is the difference between LAN and WLAN?
The difference from a LAN is that WLAN devices are connected using some sort of wireless connection method which allows users to have mobile devices and laptops connected to the network and be able to move around.
42
New cards
What are the benefits of WLAN?
WLANs have all the benefits of LANs, as well as the ease of wireless connection that allows the use of mobile devices on the move.
43
New cards
What is a disadvantage of WLAN compared to LANWha
can be less secure than wired LANs since a potential intruder does not require having a physical connection to the network.
44
New cards
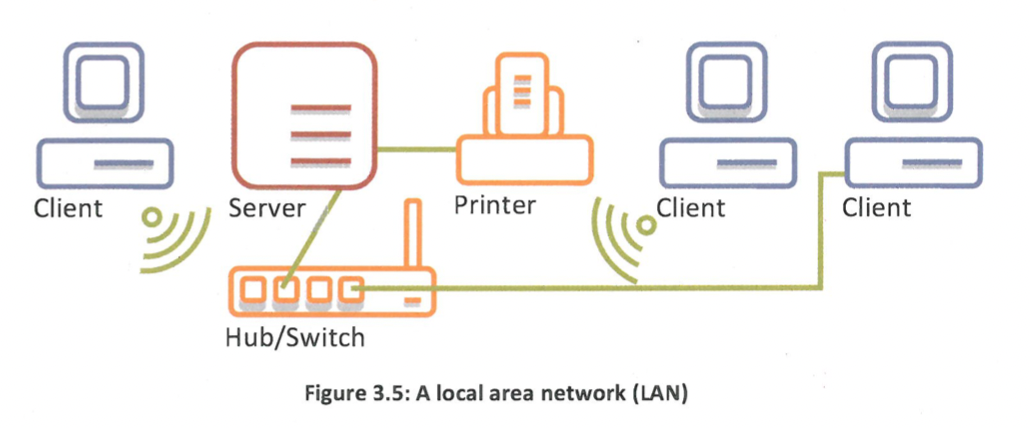
What is the most common technology to build WLAN?
is Wi-Fi, which allows the exchange of data between computer systems using radio waves/
45
New cards
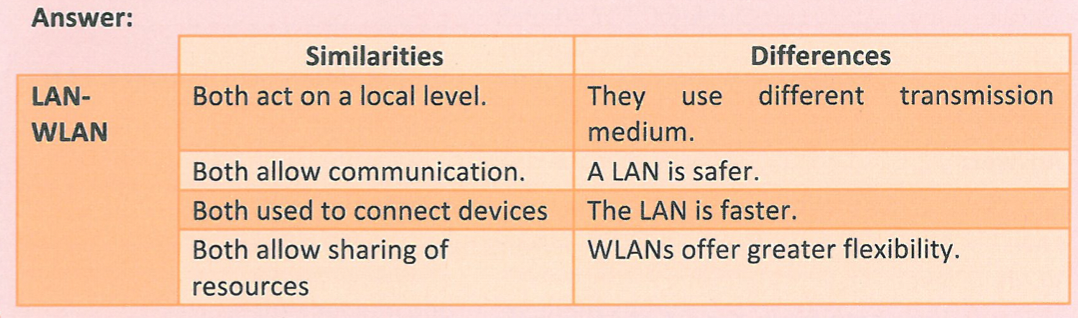
Compare and contrast the similarities and differences between LAN and WLAN
46
New cards
What is a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)?
LAN for every department, so each department will have its own isolated network that cannot be accessed from the outside. Instead of having to set up switches and cabling in order to create separate LANs for every department, a VLAN can be used to partition the initial LAN, where every department is connected, into logical separate networks. Each logical separate network cannot see the computer systems or the shared resources of other such logical separate networks, without specific set up that allows it to see them.
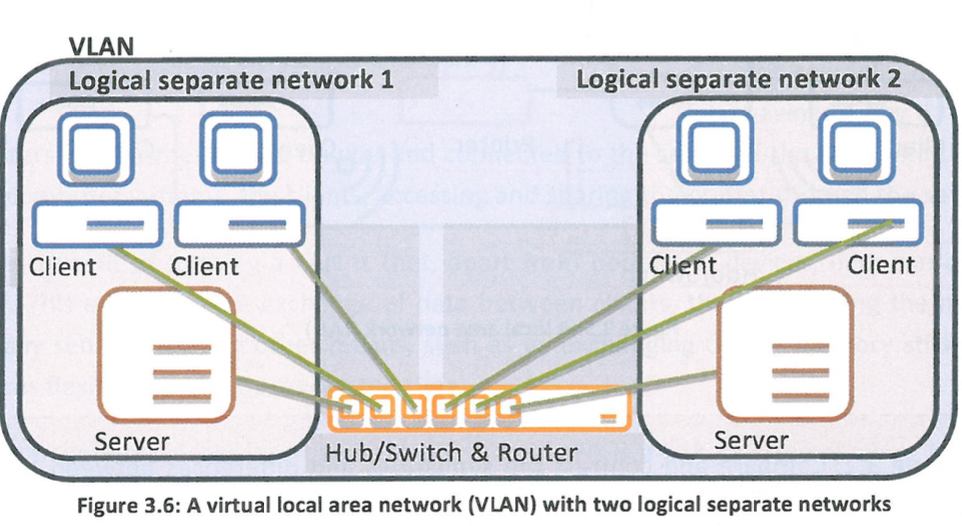
47
New cards
Compare and contrast the similarities and differences between LAN and VLAN.
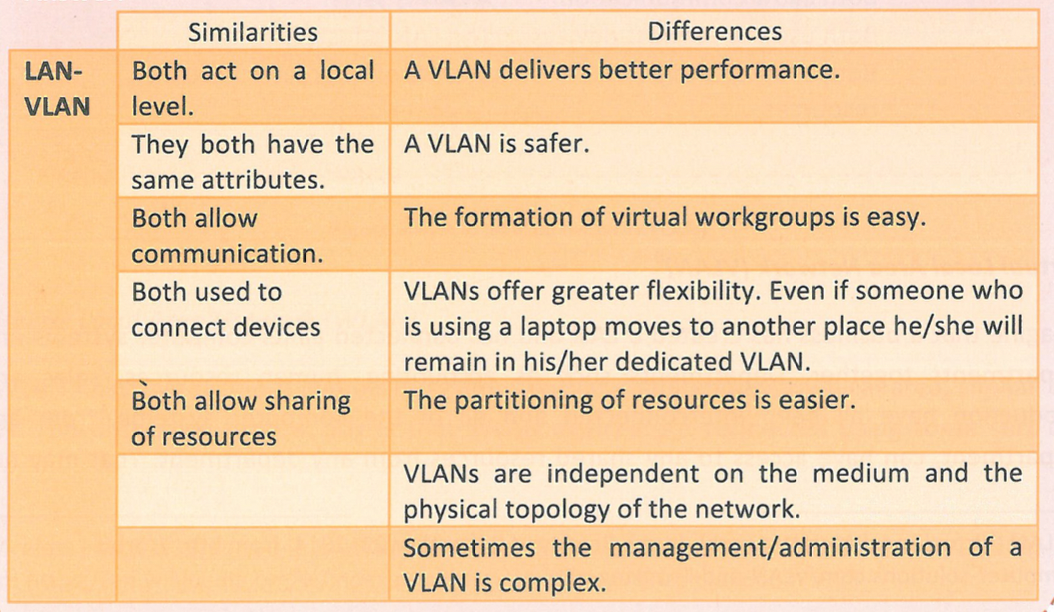
48
New cards
Compare and contrast LAN and VLAN.
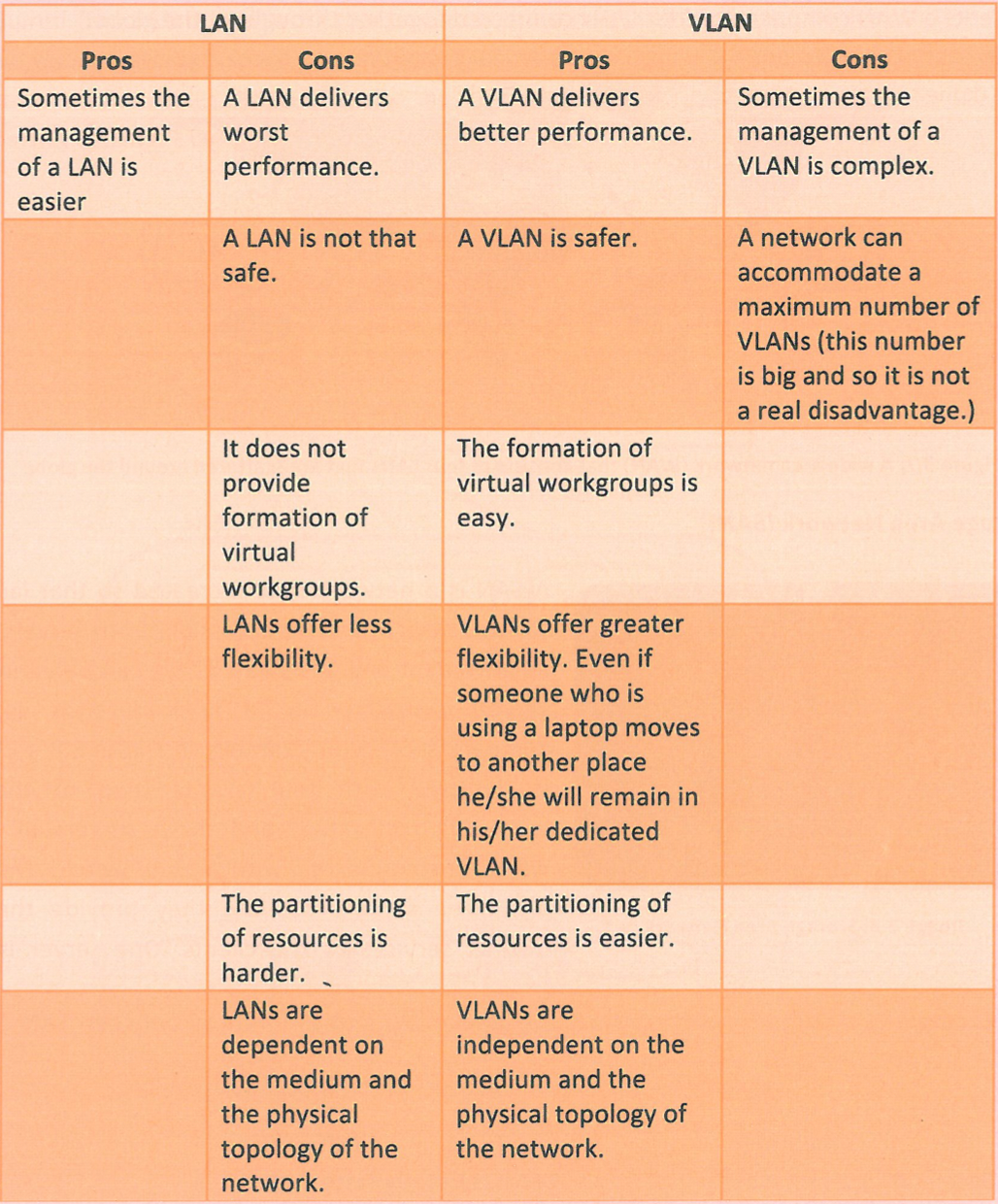
49
New cards
What is Wide Area Network (WAN)?
a computer network that connects computer systems that are within a large geographical area.
50
New cards
Give an example of WAN
The internet
51
New cards
What does WAN cover?
covers a broad area, such as a city, a country or even a network of countries allowing individuals, businesses and governments to carry out their daily business regardless of location.
52
New cards
What does WAN typically consist of?
LANs connected together over a broad geographical area.
53
New cards
Compare and contrast the similarities and differences between LAN and WAN

54
New cards
What is Storage Area Network (SAN)?
A network that is created so that large storage devices can be accessible from servers in a convenient and easy way. There can be various servers connected to a network such as a company’s LAN.
55
New cards
When is SAN required?
ervers require storage space in order to store their data and create backups to prevent data loss, if any storage space fails. The SAN is a network that connects the servers to the storage devices so that they have enough storage space to complete their tasks.
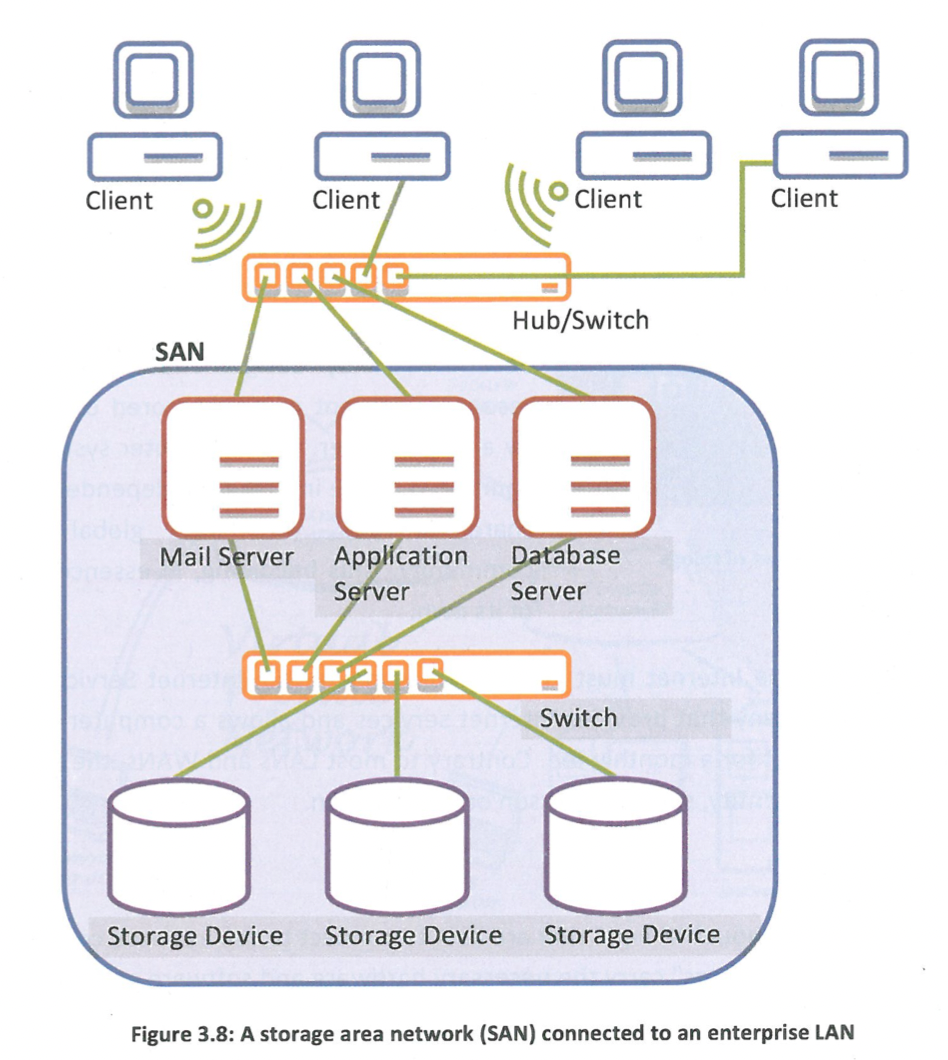
56
New cards
What is Intranet?
is the broad term for a collection of private computer networks within a company, a school or an organization that utilizes standard network protocols like TCP/IP. Considered as a private analogy of the Internet.
57
New cards
What is the main purpose of Intranet?
facilitate communication between individuals or work groups and to improve data sharing.
58
New cards
An _______ is a private network that is only accessible to authorized personnel within an organization. It is not accessible to the public internet. To protect the intranet from external threats, a _______ is used as a security barrier.
1. Intranet
2. Firewall
59
New cards
What is the Internet?
a global WAN connecting millions of computer systems. Since it is a WAN, the Internet connects a large number of smaller networks together, thereby creating the largest WAN network used by billions of users worldwide.
60
New cards
What dies the internet provide?
an extensive number of services to users such as the World Wide Web (WWW), which consists of websites and webpages, as well as support for email, file transfer and other services. As such the Internet is not the same as the WWW but rather the WWW is a service of the internet.
61
New cards
"Unlike other networks, the Internet is __________ by design. That means that its resources are not centrally stored or controlled by a single server."
Unlike other networks, the Internet is decentralized by design. That means that its resources are not centrally stored or controlled by a single server.
62
New cards
Each ________ that is connected to the Internet is independent and can share services with the global Internet community, thus becoming, in essence, a ________ of its own.
Each computer system that is connected to the Internet is independent and can share services with the global Internet community, thus becoming, in essence, a server of its own.
63
New cards
For most, access to the internet must go through what?
a commercial Internet Service Provider (ISP),
64
New cards
What is a commercial Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
a company that provides Internet services and allows a computer system to connect to the Internet for a monthly fee.
65
New cards
Contrary to most LANs and WANs, the Internet is not _____________ by a single entity, such as a person or organization.
Contrary to most LANs and WANs, the Internet is not owned by a single entity, such as a person or organization.
66
New cards
What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
It is the network of individual "things" that are able to connect to the Internet, communicate and exchange data.
67
New cards
In IoT what do ALL “things“ carry?
All "things" carry the necessary hardware and software and are assigned an IP-address
68
New cards
In IoT what is a “things“?
a physical object such as a patient with an implant, a car with an emergency system, an alarm system with advanced warning, a wild animal with a tracking system, etc. Each physical object has a unique embedded system that uniquely identifies it.
69
New cards
What are thee ways to access the internet?
1. **Broadband acces**s via DSL or cable modem, 3 T1 or T3 line.
2. **Wi-Fi access** via Wi-Fi router or Wi-Fi hot spots.
3. **Dial-up access** via modem. Used where broadband access is not available or too expensive, or no Wi-Fi available.
4. **Mobile networks via 36, 4G networks, etc.**
70
New cards
What is Extranet?
An extranet is a computer network that utilizes the Internet to allow controlled access by specific users to a specific LAN or WAN. The specific business may wish to securely share part of its network (and information) with suppliers, partners, customers or other businesses without making its whole network available to them or the public. This part of the network that is extended to users outside the company is termed as extranet.
71
New cards
Extranets could be considered as __________ that are partially accessible to authorized outsiders. A __________ controls the access rights and allows access to the intranet only to people who are authorized.
1. Intranets
2. firewall
72
New cards
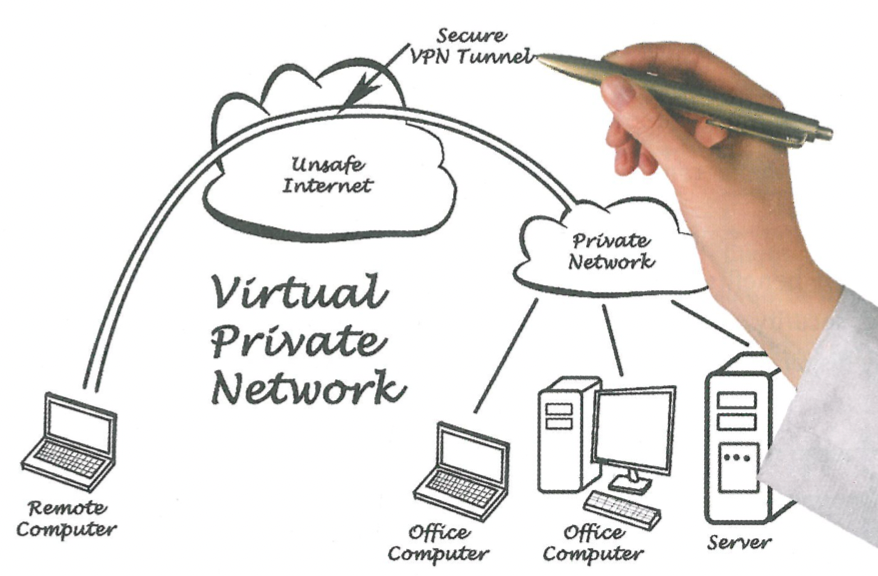
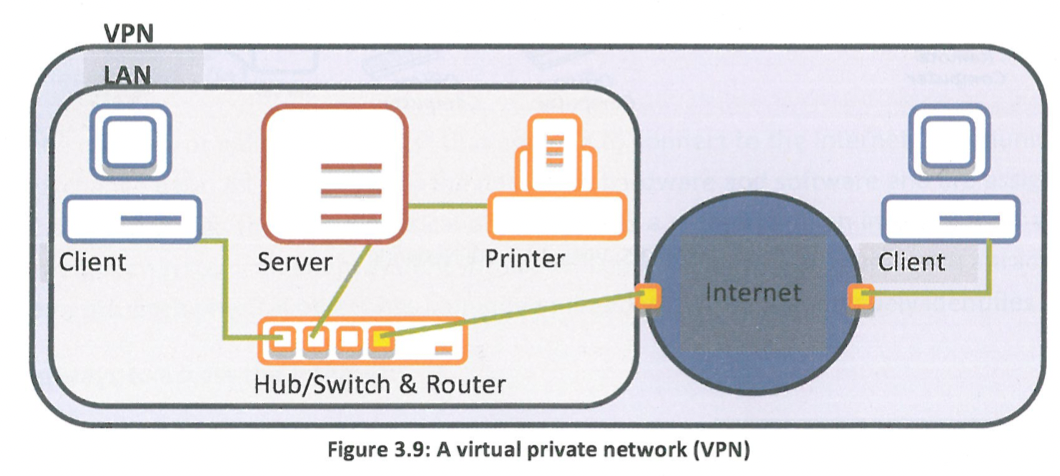
What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
connects two or more computer systems, similar to a LAN or a WLAN, but also allows clients from remote locations to connect to the network and appear to be inside the LAN as if they were physically present.
73
New cards
What does the VPN allow?
The creation of a LAN that is managed through a server software application, to which clients can also connect from a remote location, even through a different network (e.g. the Internet).
74
New cards
What are the benefits of a VPN?
has all the benefits of a LAN, allowing users to share data and resources without compromising security. Furthermore, aVPN can securely and cost—effectively connect geographically disparate offices of a business within a network with all the functionalities of a single LAN.
75
New cards
Compare and contrast the similarities and differences between VPN and EXTRANET.

76
New cards
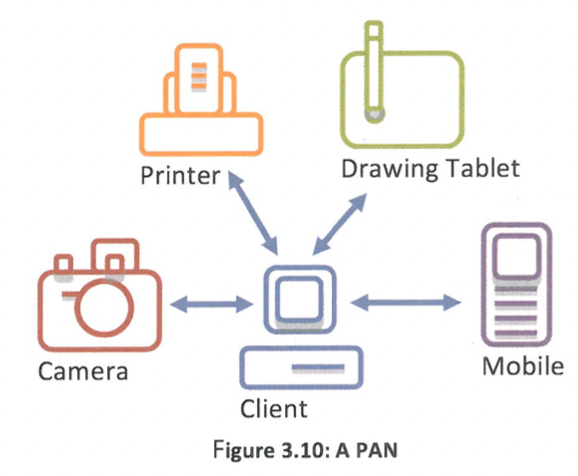
What is personal Area Network (PAN)?
PAN is a network that interconnects devices that are centered around an individual person's workspace. It can be understood as a LAN that supports only one person, instead of a group of people, and covers a very short range, a maximum of 10 meters.
77
New cards
How can devices on PAN connect?
both wired (typically through USB) and wirelessly (typically through Bluetooth) depending on the technologies used.
78
New cards
What is a piconet?
A PAN using a wireless group of devices using Bluetooth technology in order to interconnect
79
New cards
What is Peer-To-Peer (P2P)
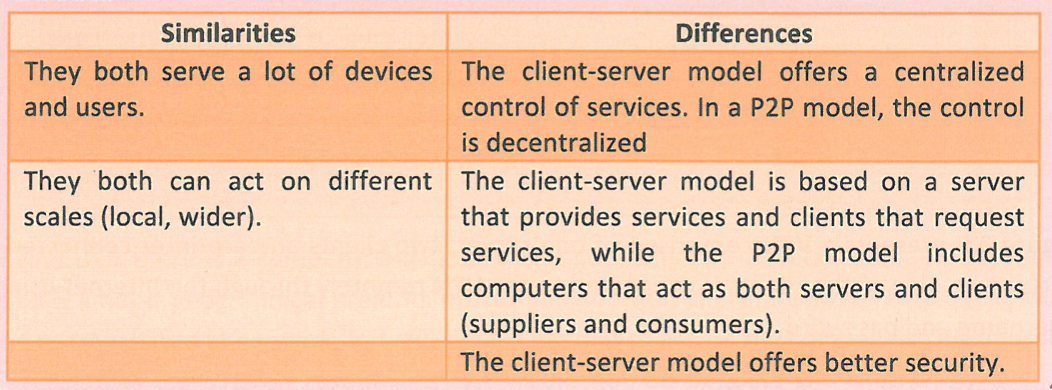
uses a distributed network architecture where all the computer systems (called nodes or peers) in the network are decentralized and are both clients and servers at the same time, consuming and supplying resources from and to the other computer systems connected to the network.
80
New cards
What does P2P remove the need off?
The need for centralized servers is removed, in order to avoid bottlenecks, while each computer system makes part of its resources available for other network computer systems to use.
81
New cards
Compare and contrast the similarities and differences between the client-server model and P2P.
82
New cards
What are the two organizations standardize networking protocols?
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
83
New cards
What would happen if many standards with hardware or software ?
incompatible hardware and software
84
New cards
What do standards describe?
the common ground on which hardware and software manufacturers (Apple, Microsoft, Linux etc.) can depend on in order to build systems that are able to communicate with each other.
85
New cards
Organizing a network design in layers makes the process __________ complex because any problem is broken down into distinct modules. The protocol of a __________ carries out a sequence of operations.
Organizing a network design in layers makes the process less complex because any problem is broken down into distinct modules. The protocol of a layer carries out a sequence of operations.
86
New cards
What are packets?
contains a small amount of data, as well as other important information such as the destination of the packet.
87
New cards
What are three advantages of layers?
1. Easy to manage.
2. Greater understanding of each layer.
3. Common language for each layer.
4. Makes protocol design easier.
5. A manufacturer can focus on technologies of a particular layer.
6. Products of different manufacturers can work together.
7. Technology advances of a layer are independent of technology advancements of other layers (wireless technology advances are not dependent on advances of media format compression (GIF))
88
New cards
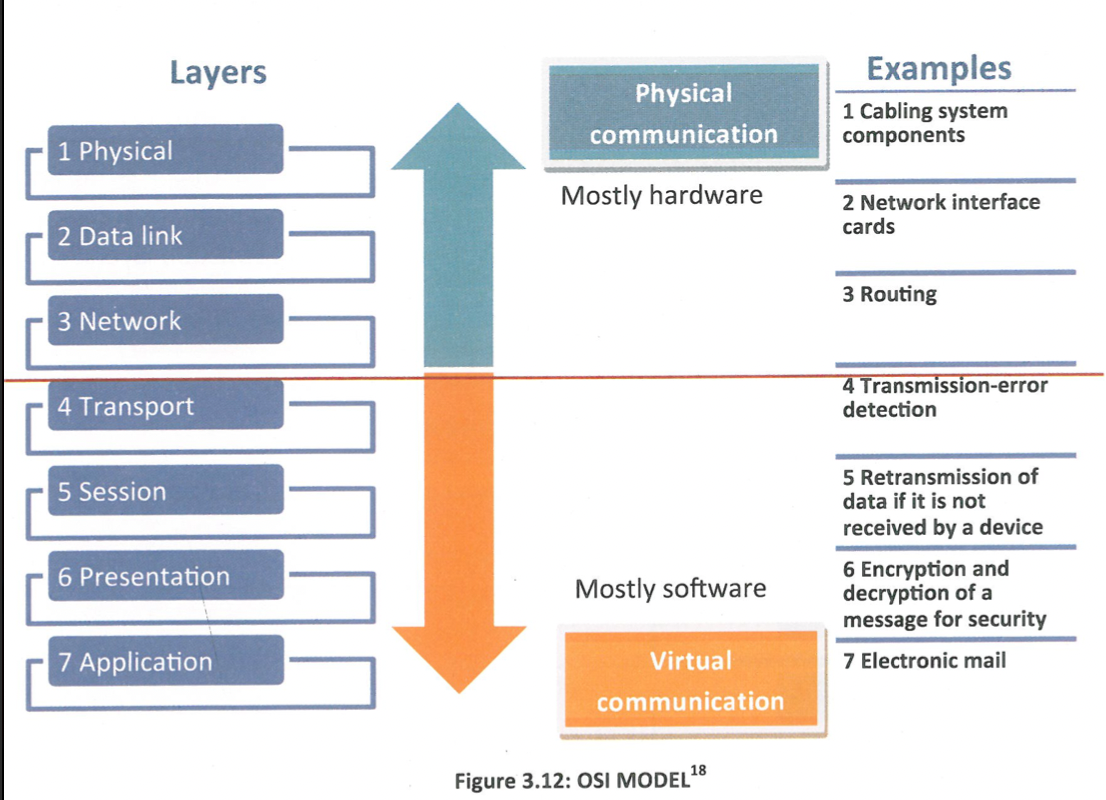
What is the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection model)(Reference model)?
The most widely used networking standard aims to facilitate communication across a variety of systems. It contains seven layers.
89
New cards
OSI model give description of Application Layer used
Performs various services for the applications used by the end users. Example protocol: HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
90
New cards
OSI model give description of Presentation Layer used
Provides data format information, data compression information and data encryption information to the application. Example protocol: Portable Network Graphics (PNG).
91
New cards
OSI model give description of Session Layer used
Manages sessions between two users. Example protocol: UNIX X Window system core protocol.
92
New cards
OSI model give description of Transport Layer used
End to end connections (hosts). Definition of data segments →assignment of numbers → data transfer→ reassemblage of data at the destination. Example protocol: TCP.
93
New cards
OSI model give description of Network Layer used
Handles routing of packets across a network through intermediary ' devices. Example protocol: IP.
94
New cards
OSI model give description of Data Link Layer used
Error handling of physical transmission. Builds frames and amends transmission rate according the buffer of the receiver (flow control). Example protocol: Ethernet, HDLC.
95
New cards
OSI model give description of Physical Layer used
Transmits 0s and 1s over media between devices. Definition of media specifications. Voltage levels. Example protocol: R8232-C (serial port).
96
New cards
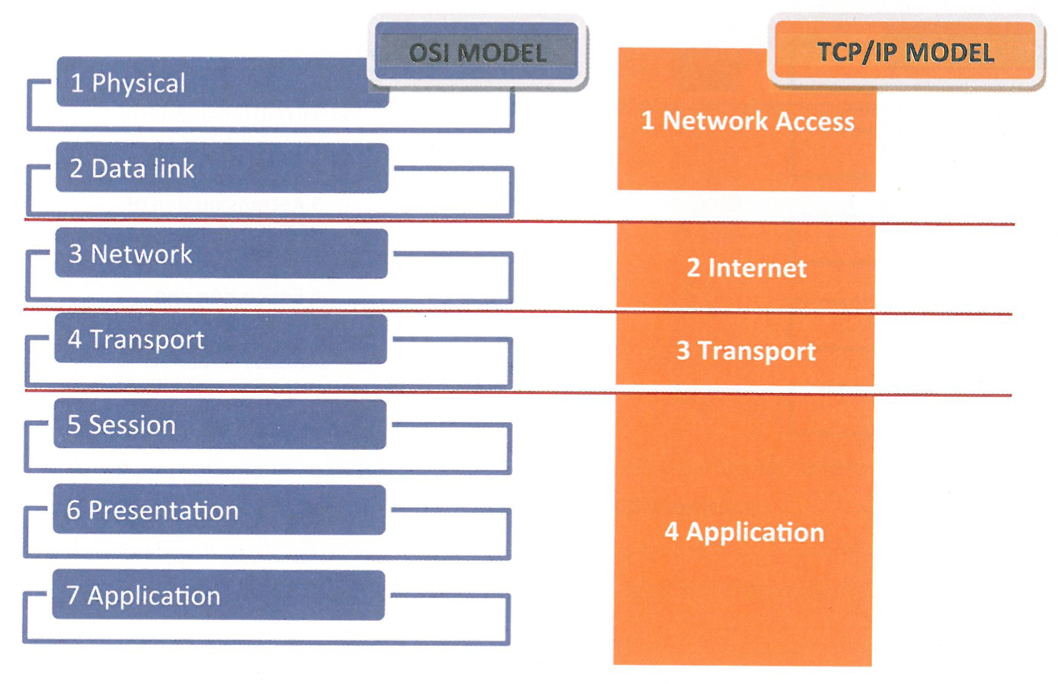
What does the TCP/IP (Transfer Control / Internet protocol model) describe?
describes all the functions that take place at each layer of protocols within the TCP/IP suite.
97
New cards
What type of model is the TCP/IP (protocol model)
a hierarchical model protocol that models and represents all the functionality required for successful communication between users.
98
New cards
The TCP/IP (protocol model) functionality into how many layers is it structured?
into four abstraction layers.
99
New cards
Referring to the TCP/IP (protocol model) what is the description of the Application Layer
Performs various services for the software applications used by the end user. Example protocol: HyperText Transfer Protocol
100
New cards
Referring to the TCP/IP (protocol model) what is the description of the Transport Layer
End to end connections (hosts). Definition of data segments → assignment of numbers → data transfer→ reassemblage of data at the destination. Example protocol: TCP.