Physics M3C4 Forces in Action
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Define the Newton
Force required to accelerate a mass of 1kg by 1ms-2
How can I measure the weight?
Use a Newtonmeter
Define centre of mass
Define centre of gravity
Where are they?
Point where any externally applied force produces straight-line motion but no rotation
Point at which we consider the entire weight of a body to act
Same place
How do find centre of mass/gravity?
“Freely suspended object will come to rest with its centre of mass/gravity vertically below the point of suspension”
Plumbline method:
Make small holes along edges
Insert pin connected to clamp into hole, with plumbline tied to the end of the pin
Allow object to come to rest
Draw a line along vertical string of the plumbline
Repeat for other holes
Center of mass/gravity is at the intersection of the lines
Can check by balancing on finger
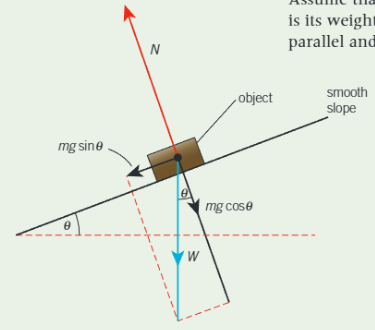
Find acceleration and time taken
Resolve W into F parallel to slope (mgsinθ)
a = F/m
Use s = u t + ½ a t2
What affects drag?
Relationship between drag and speed?
Speed, cross-sectional area of object. Density of fluid.
Drag ∝ Speed2
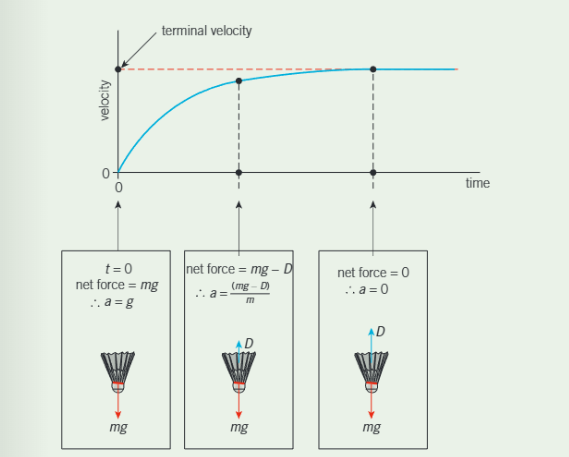
Terminal velocity
At t=0, no drag and a = 9.81
As t increases, speed increases and drag increases
Net force decreases so acceleration decreases
Eventually, drag = weight, 0 acceleration - ‘Terminal velocity’
Experiment to determine terminal velocity
Mark cylinder at regular length intevals (e.g. 10cm)
Fill cylinder with viscous liquid
Release ball bearing from rest at top of cylinder
Start timer, record time at every marked inteval
Record time and calculate the speed of the ball at each inteval
Repeat a total of 3 times, find the average time at each inteval
Terminal velocity when time difference between each inteval is the same
Plot graph os distance (y-axis) agianst time (x-axis)
Terminal velocity when gradient is constant
Gradient = velocity
Define moment
Product of force and perpendicular distance to line of actioin to pivot
What is equilibrium?
What is the principle of moments?
When a body is in equilibrium, net force and net moment is 0.
Principle of moments - for a body in rotational equilibrium, the sum of anticlockwise moments about any point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about the same point
What is torque?
Product of one of the equal forces applied and the perpendicular distance between the forces
Moment of a couple
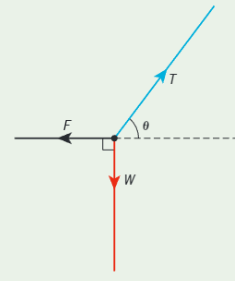
How to appraoch this triangle of forces in equilibirum?
Use trig to resolve into vertical and horizontal components
Vertical resultant force = 0
Horizontal resultant force = 0
Define density
How to determine density?
Mass per unit volume
Find mass by weighing on digital balance. Find volume by displacing liquid in eureka can
Define pressure
Normal force exerted per unit cross-sectional area
Properties of pressure?
Pressure increases with depth (p ∝ h)
Denser fluids exert greater pressure
Fluid pressure at any particular depth is the same in all directions
Fluid pressure does not depend on cross-sectional area
What is Archimedes’ principle?
What happens if upthrust:
> weight of fluid displaced
< weight of fluid displaced
Upthrust of a body immersed in fluid = weight of fluid displaced
Applies to fully or partially submerged objects
If u > weight of fluid displaced, it ascends
If u < weight of fluid displaced, it sinks
Floating objects - upthrust = weight of fluid