audition
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
1
New cards
fundamental frequency
lowest frequency component of a sound (1st harmonic)
lowest frequency component of the harmonic spectrum
ex - 262, 542, 786, 1048 Hz
lowest frequency component of the harmonic spectrum
ex - 262, 542, 786, 1048 Hz
2
New cards
missing fundamental effect
perception of fundamental frequency when it is not present due to harmonics adding at the fundamental frequencies period
3
New cards
timbre
when sounds with same loudness and pitch sound different
due to harmonics and high frequencies
due to harmonics and high frequencies
4
New cards
timbre contrast
enhanced perception of differences when distinct sounds are played together
5
New cards
timbre after effect
perception of full harmonic spectrum is skewed when played after a harmonic with missing elements
6
New cards
attack
part of sound where amplitude increases
onset
onset
7
New cards
decay
part of sound where amplitude decreases
offset
offset
8
New cards
auditory scene
entirely of sounds audible in a given moment
conveys information about evens happening in that moment
conveys information about evens happening in that moment
9
New cards
auditory stream segregation
perceptual organization of a complex acoustic signal into separate auditory events for which each stream is heard as a separate event
grouping by timbre
uses Gestalt law of similarity
grouping by timbre
uses Gestalt law of similarity
10
New cards
ventriloquist effect
audio-visual illusion where sound is misperceives as coming from a source that is moving appropriately when it is actually coming from an invisible source
visual > auditory for location of a sound
visual > auditory for location of a sound
11
New cards
restoration
in spite of interruptions, one can still “hear” sound
based on Gestalt law of good continuation
higher-order sources can help fill in the blanks
based on Gestalt law of good continuation
higher-order sources can help fill in the blanks
12
New cards
Pythagoras
numbers and music intervals
13
New cards
musical range
25 - 4500 Hz
14
New cards
pitch
psychological aspect of sound related mainly to fundamental frequency
15
New cards
octave
interval between two sound frequencies that have a 2:1 ratio
16
New cards
tone height
sound quality corresponding to the level of pitch
monotonically related to frequency
monotonically related to frequency
17
New cards
tone chroma
sound quality shared by tones that have the same octave interval
18
New cards
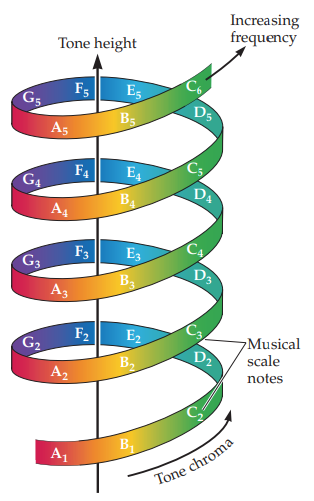
musical helix
visualized pitch
19
New cards
instruments
produce notes < 4000 Hz
20
New cards
chords
2+ notes played simultaneously
constant or dissonant
constant or dissonant
21
New cards
consonant
chord with simple ratios of note frequencies
ex - 3:2, 4:3
ex - 3:2, 4:3
22
New cards
dissonant
chords with complex ratios of note frequencies
ex - 16:15, 45:32
ex - 16:15, 45:32
23
New cards
pelog
Javanese scale with fewer notes than western scale
24
New cards
melody
arrangement of notes/chords in succession (chroma and rhythm) forming a gestalt
25
New cards
tempo
perceived speed of presented sounds
26
New cards
fugue
2+ voices build on a theme introduced at the beginning and repeat it in different pitches
classical music composition technique
classical music composition technique
27
New cards
Bayesian inference
we actively predict that is likely to happen next in music
28
New cards
vocal tract
airway above larynx used for production of speech sounds
29
New cards
respiration
inhaling during speech pushes air out of lungs, through trachea, to the larynx
30
New cards
larynx
two vocal folds air passes through to make speech sounds
larger in men, smaller in children
larger in men, smaller in children
31
New cards
phonation
occurs at the larynx
air passes between the two vocal folds
air passes between the two vocal folds
32
New cards
articulation
occurs in vocal tract
manipulation of jaws, lips, tongue body, tongue tip, and velum/soft palate
manipulation of jaws, lips, tongue body, tongue tip, and velum/soft palate
33
New cards
resonance characteristics
created by changing size and shape of vocal tracts to affect sound frequency produced
34
New cards
formants
peaks in speech spectrum
concentrations in energy occur at difference frequencies depending on length of vocal tract
concentrations in energy occur at difference frequencies depending on length of vocal tract
35
New cards
spectrogram
pattern for sound analysis that provides 3D display plotting time, frequency and intensity
36
New cards
vowels
open vocal tract
37
New cards
consonants
obstructed vocal tract
38
New cards
voicing
whether vocal cords are vibrating or not
39
New cards
coarticulation
successive speech units overlap in articulatory patterns
occurs in fast speech production
occurs in fast speech production
40
New cards
spectral contrast
we perceive syllables on the basis of the relative change in the spectrum
41
New cards
pressure
vibrations of objects cause surrounding molecules to vibrate which causes ________ change in medium
42
New cards
amplitude
magnitude of displacement of a sound pressure wave
43
New cards
intensity
amount of energy falling on a unit area
44
New cards
decibels
ratio between pressure of some sound and the pressure of the reference sound p0
= 20log(p/p0)
= 20log(p/p0)
45
New cards
loudness
psychological aspect of sound related to perceived intensity/magnitude
46
New cards
frequency
number of times per second that a pattern of pressure change repeats
47
New cards
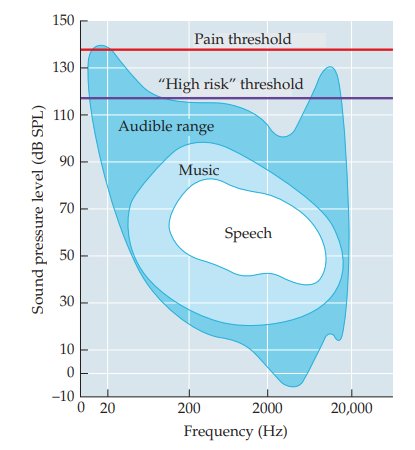
human hearing range
20 - 20 000 Hz
48
New cards
sine waves
all sound can be describe as a combination of _____ _______
49
New cards
spectrum
representation of relative energy present at each frequency
50
New cards
Fourier analysis
any signal (sound) can be separated into component sine waves at different frequencies, adding these sine waves produces the original signal
51
New cards
harmonic spectrum
frequencies of its components are integer multiples of lowest frequency
52
New cards
pinna
outside of ear that collects sounds and funnels them into the ear canal
53
New cards
tympanic membrane
vibrates in response to sound
at end of ear canal
at end of ear canal
54
New cards
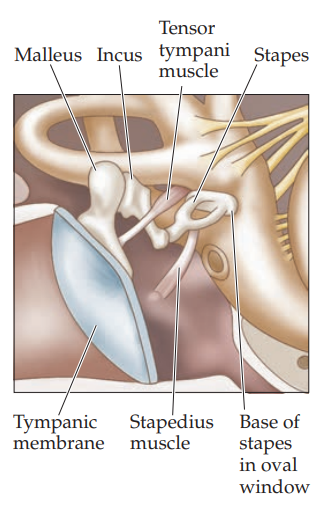
middle ear
3 ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes) which are the smallest ponds in the body
transmit tympanic membrane vibrations to the oval window
transmit tympanic membrane vibrations to the oval window
55
New cards
inner ear
translates changes in sound pressure into neural signals
cochlea which contains oval/round window and 3 canals
cochlea which contains oval/round window and 3 canals
56
New cards
cochlea
spiral structure of the inner ear containing the organ of Corti
filled with water fluids in 3 parallel canals
vestibular canal and tympanic canal are separated by membranes
filled with water fluids in 3 parallel canals
vestibular canal and tympanic canal are separated by membranes
57
New cards
organ of Corti
in cochlea, sits on top of basilar membrane, covered by tectorial membrane
made of hair cells, dendrites of auditory nerve fibers, and scaffold
inner hair cells send afferent information
outer hair cells are efferent/feedback system
made of hair cells, dendrites of auditory nerve fibers, and scaffold
inner hair cells send afferent information
outer hair cells are efferent/feedback system
58
New cards
vibration pathway
ear canal → tympanic membrane → middle ear bones → oval window → vestibular canal
59
New cards
round window
absorbs extremely intense sounds/pressures
60
New cards
intense sound pathway
helicotrema → cochlea → tympanic membrane → round window
61
New cards
tectorial membrane
extends atop organ of Corti
gelatinous structure
gelatinous structure
62
New cards
place code
different parts of cochlea tuned to different frequencies
information about frequency is coded by place along cochlear partition
\
information about frequency is coded by place along cochlear partition
\
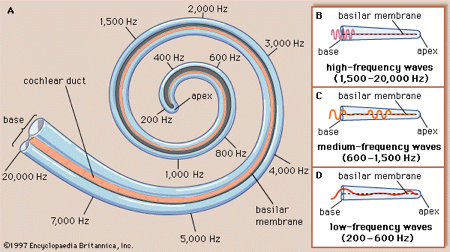
63
New cards
threshold tuning curve
map plotting thresholds of neuron in response to sine wave in varying frequencies at lowest intensity that will give rise to a response
64
New cards
rate saturation
point where nerve fiber is firing as rapidly as possible, incapable of further stimulation
65
New cards
insointensity curves
measures 1 nerve fiber’s firing rate to a wide range of frequencies at the same intensity level
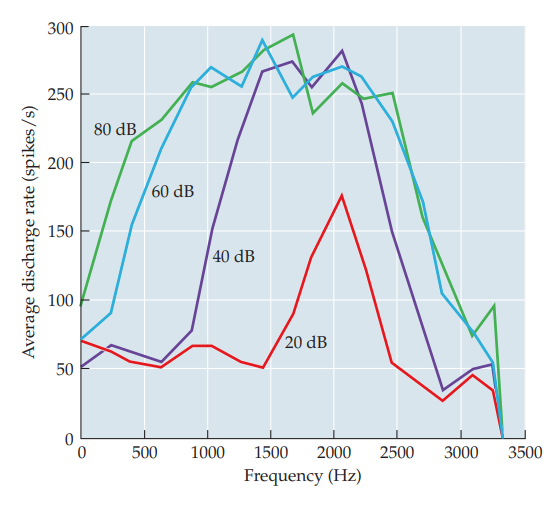
66
New cards
phase locking
firing of a single neuron at one distinct point in the period of a sound wave at a given frequency
67
New cards
temporal code
tuning of different parts of the cochlea to different frequencies
information about sound wave is coded by timing of neural firing
information about sound wave is coded by timing of neural firing
68
New cards
volley principle
multiple neurons can provide temporal code for frequency if each neuron fires at a distinct point in the period but does not fire every period
69
New cards
vestibulocochlear nerve
cranial nerve VIII, one for each ear
synapses in cochlear nucleus
synapses in cochlear nucleus
70
New cards
superior olive
early brainstem region that receives inputs from both ears
71
New cards
inferior colliculus
midbrain nucleus in auditory pathway
72
New cards
medial geniculate nucleus
part of the thalamus that relays auditory signals to the temporal cortex and receives input from the auditory cortex
73
New cards
tonotopic organization
neurons responding to different frequencies are organized anatomically in order of frequency
74
New cards
primary auditory cortex (A1)
first area in temporal lobe where brain processes acoustic information
75
New cards
belt area
adjacent to A1, responds to more complex characteristics of sound
76
New cards
parabelt area
lateral and adjacent to belt area, responds to more complex sounds and input from other senses
77
New cards
psychoacoustics
study of psychological correlation to physical dimensions of acoustics
branch of psychophysics
branch of psychophysics
78
New cards
auditory threshold
map of just barely audible tones of varying frequencies
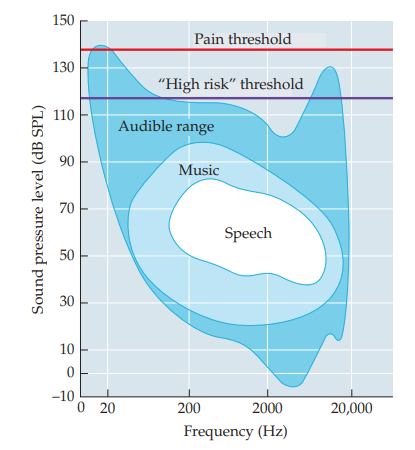
79
New cards
equal loudness curves
sound played at constant level is perceived as louder when played for a greater duration
indicative of temporal integration
indicative of temporal integration
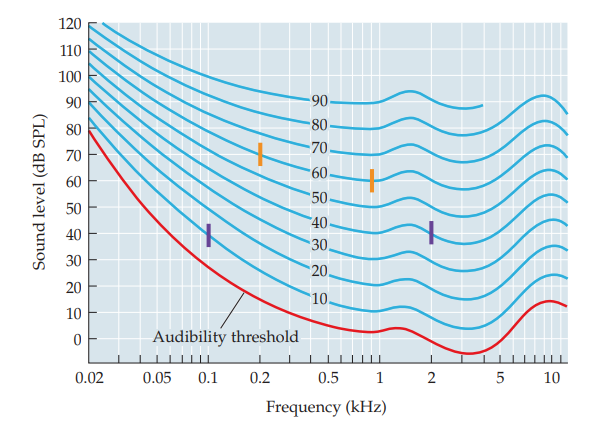
80
New cards
otosclerosis
abnormal growth of ossicles (3 small bones in inner ear)
81
New cards
sensorineural hearing loss
common auditory impairment due to defects in the cochlea or auditory nerve when hair cells are injured
82
New cards
common hearing loss
damage to hair cells due to excessive exposure to noise
young range = 20 - 20 000 Hz
old range = 20 - 15 000 Hz
young range = 20 - 20 000 Hz
old range = 20 - 15 000 Hz
83
New cards
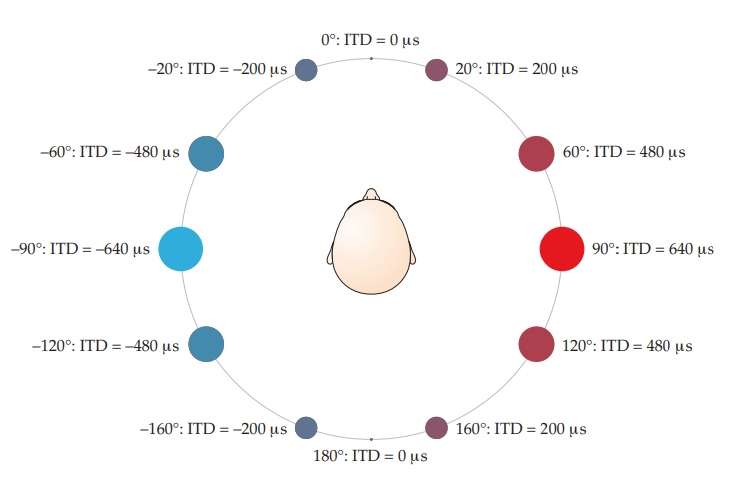
interaural time difference (ITD)
difference in time between a sound arriving at one ear vs the other
84
New cards
azimuth
used to describe locations on imaginary circle that extends around us in a horizontal plane
85
New cards
interaural level difference (ILD)
difference in intensity between a sound arriving at one ear vs the other
largest at +/- 90 degrees & related to angle to source
largest at +/- 90 degrees & related to angle to source
86
New cards
cone of confusion
regions in space where all sound produce the same time and level differences
87
New cards
head related transfer function (HRTF)
pinnae, ear canal, head and torso change intensity of sounds with difference frequencies that arrive at each ear from different locations in space
varies with elevation and azimuth
varies with elevation and azimuth
88
New cards
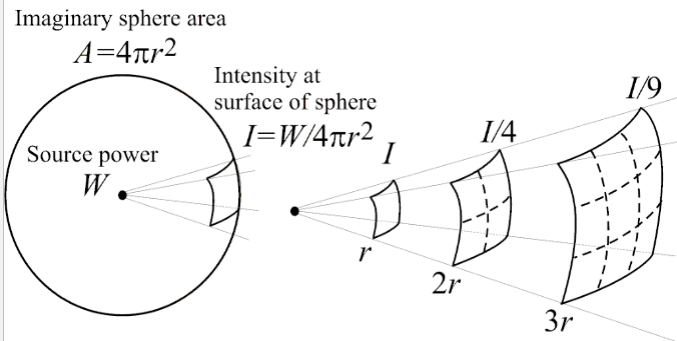
inverse square law
intensity of sound decreases with distance
relative intensity cue
relative intensity cue
89
New cards
spectral composition of sounds
higher frequencies decrease the energy more than lower frequencies as sound waves travel from source to ear
90
New cards
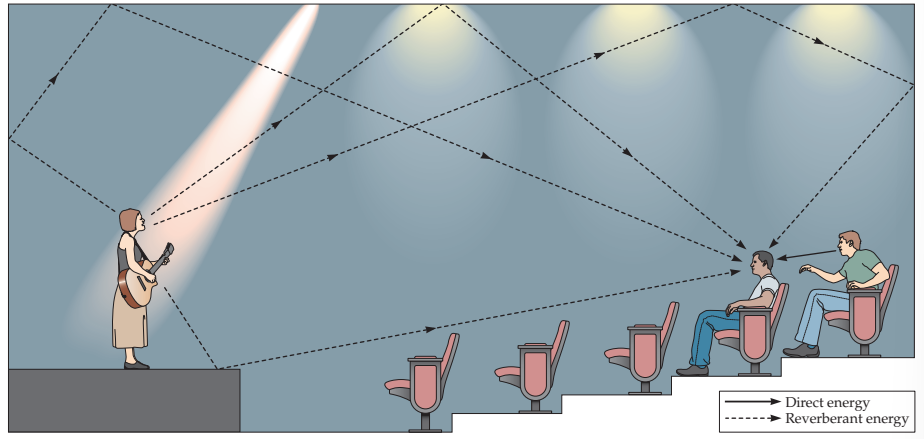
direct/reverberant energy
sound distance cue based on how much direct/indirect sound waves are hitting your ears
more indirect (bouncing off other objects) the further away
more indirect (bouncing off other objects) the further away