Profit
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
So far, we know that to calculate profit:
Profit = TR − TC
What does total cost also include?
Opportunity cost
So we now know that in economics, profit =
Profit = TR − TC (including opportunity cost)
What if a business is making less than normal profit?
It will leave the market, because it’s no longer covering its opportunity cost
So when a firm is making normal profit:
they will stay in the market, because their opportunity cost is just covered
What is the formula for normal profit?
TR=TC
So, in summary, when TR = TC, a firm is making:
Normal profit
When TR is less than TC, a firm is making:
a loss, it’s no longer covering its opportunity cost so will leave the market
And finally, when TR is greater than TC, a firm is making:
Supernormal profit, it is making an extra profit above opp cost
Write the definition of: Total Cost includes opportunity cost
In economics, Total Cost doesn’t just include actual physical costs (e.g. raw materials, wages), it also includes opportunity cost (e.g. the opportunity cost of the manager’s time).
Write the definition of: Normal profit
Normal profit is when TR = TC. The firm will just cover its opportunity cost, so it will stay in the market.
Write the definition of: Losses
Losses are when TR is less than TC. The firm will make less than normal profit, so it will leave the market because it can’t cover its opportunity cost.
Write the definition of: Supernormal profit (also known as abnormal profit)
Supernormal profit is when TR is greater than TC. The firm will make more than normal profit.
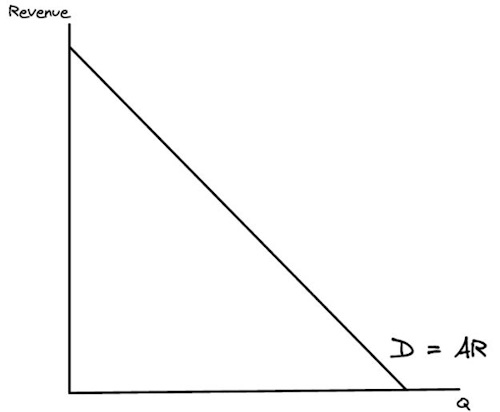
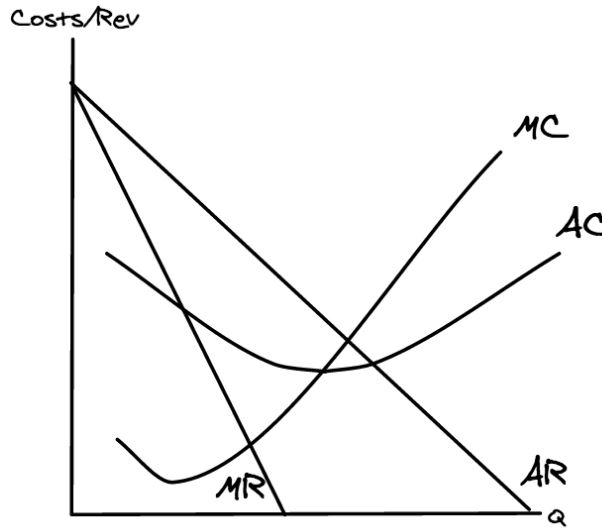
What does an average revenue curve look like?
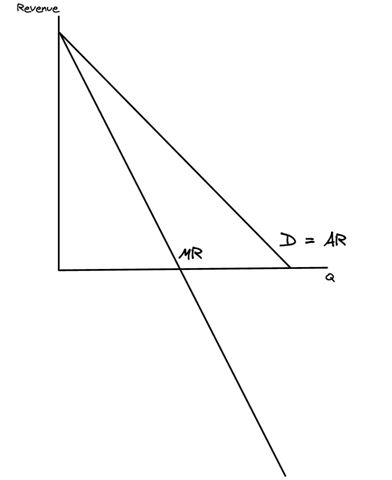
Sketch a marginal revenue curve
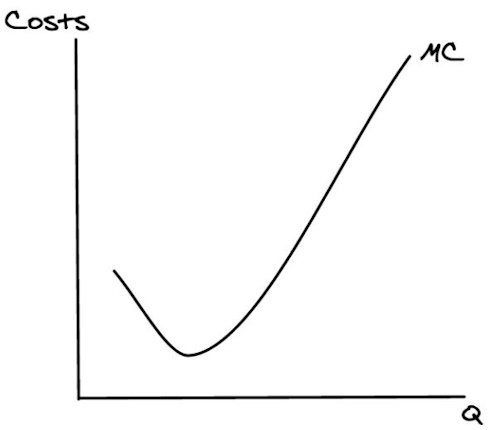
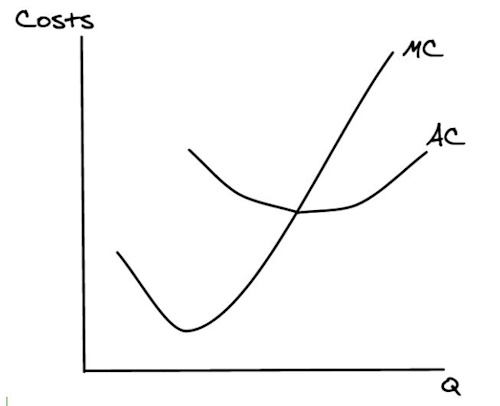
First, we have our marginal cost curve. What did that look like?
Average total cost =
AVC + AFC
So what does our ATC curve look like?
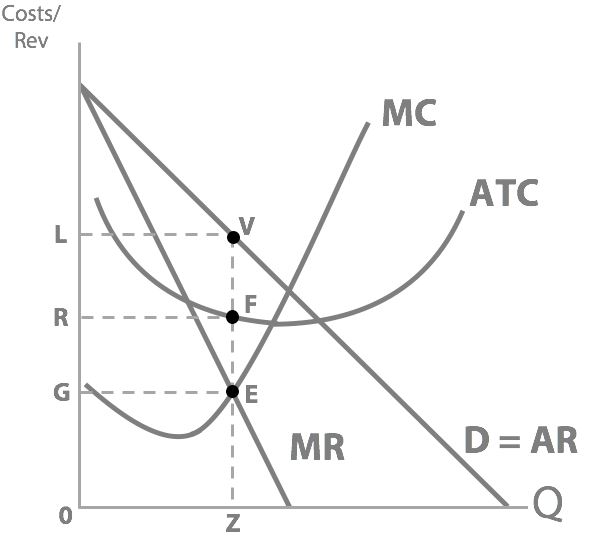
Can you sketch a costs and revenue diagram?
So...what price will Dr Dre sell his beats headphones for!?
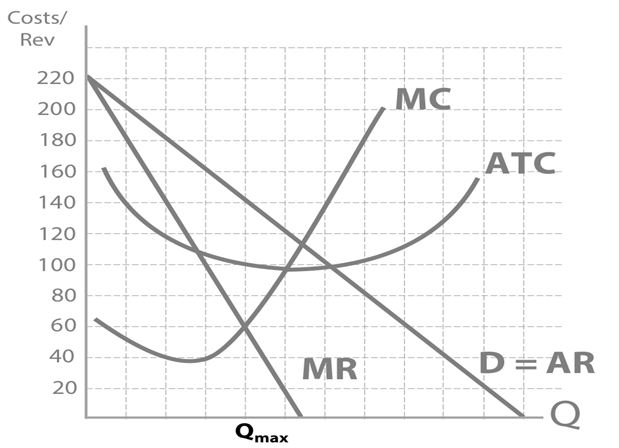
£140
So we’ve now seen that to maximise profits, a firm will set their price to:
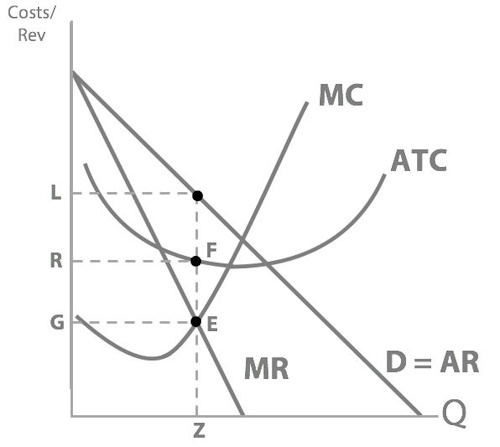
L
So at profit-maximising quantity Z, what is Dre’s total revenue? (Use the letters to draw around the corresponding area.)
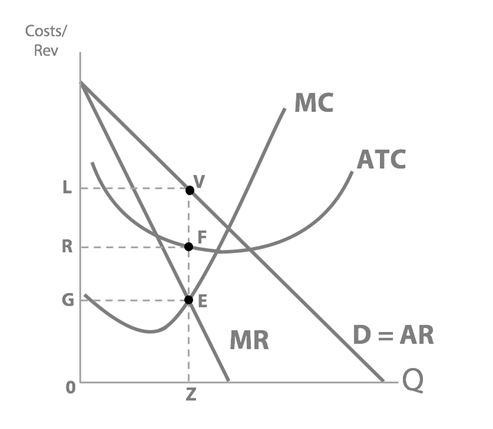
OZVL
Next we have total cost to think about...so, at profit-maximising quantity Z, what is the Dre’s total cost?
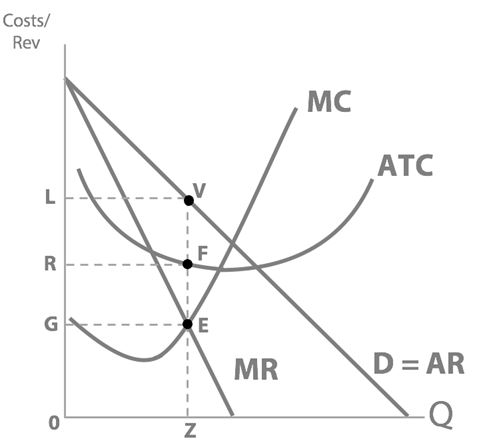
OZFR - Total Cost = Average Total Cost (ATC) × Quantity (Q).
So his total revenue is this green area, price x quantity...his total cost is this red area, ATC x quantity...so what’s Dr Dre’s profit?
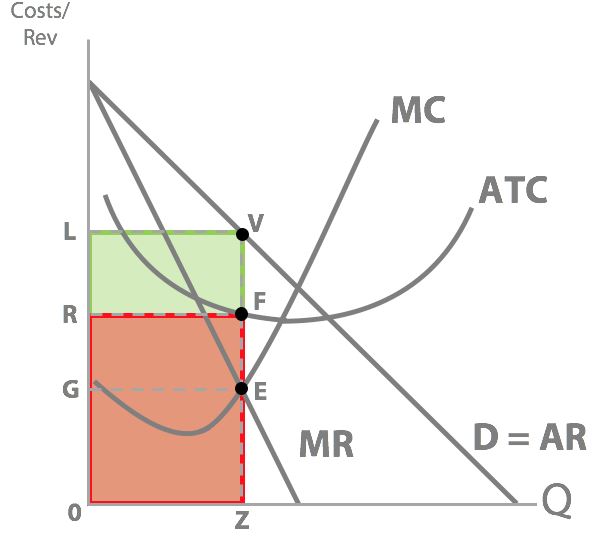
LVFR
Our supernormal profit is represented with:
LVFR
So how much was Branson making at Pmax?
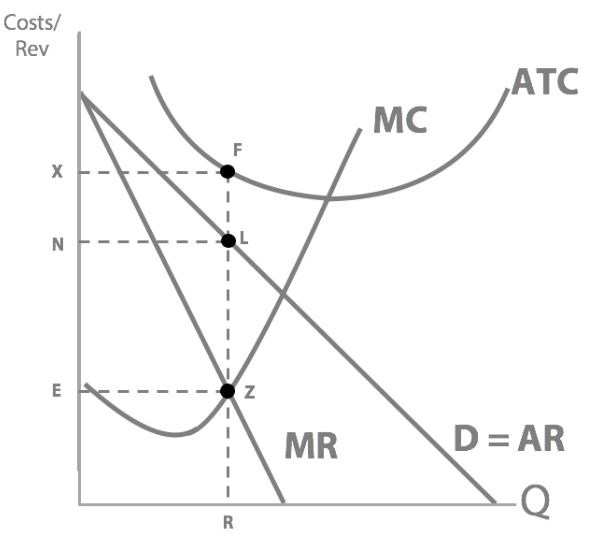
A loss of XFLN
When will firms make a loss? (on graph)
When ATC>Pmax
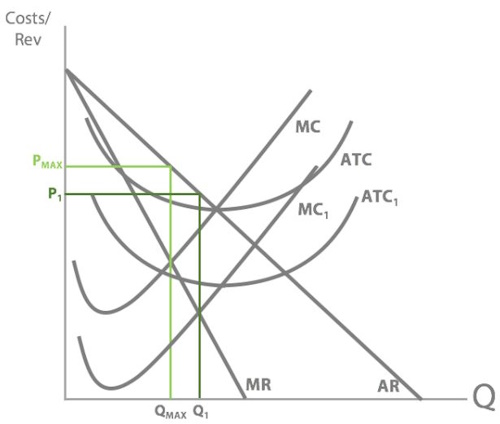
So can you draw Dre’s old revenue and costs + his new AR and MR curves ( increased advertisement of headphones by celebs)
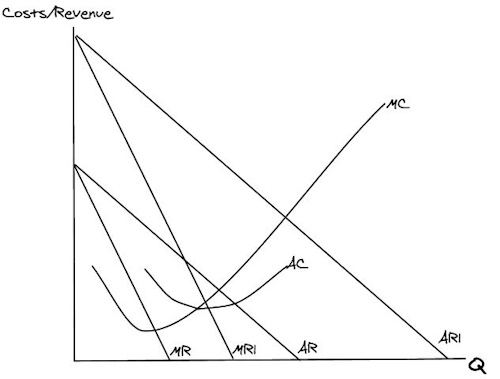
So what’s happened to Dr Dre’s price and quantity when his revenue increased?
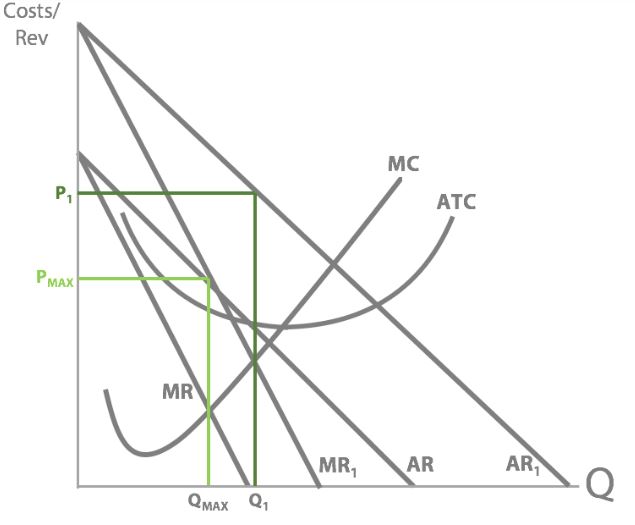
Price increased and quantity increased
So can you draw Blockbuster’s old revenue and costs + their new AR and MR curves after Netflix steal their customers?
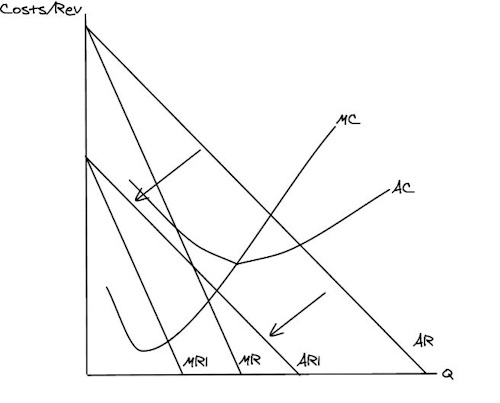
When revenue decreases what effect does this have on price, quantity and profit?
Profit, Prices and Quantity decrease
So when profit maximising, what is Concorde’s actual profit?
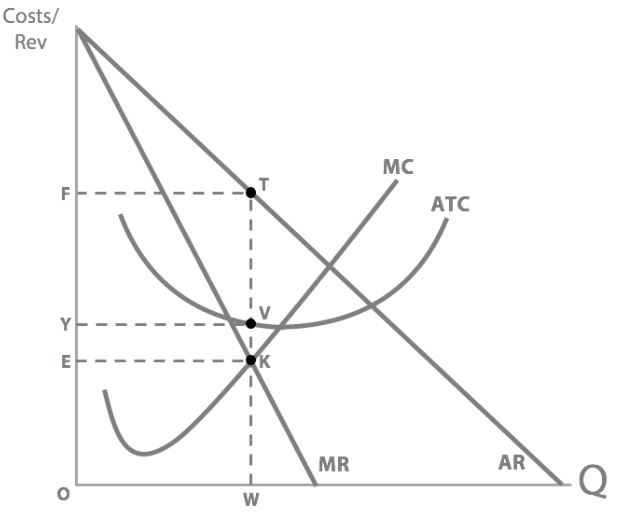
FTVY
So now what would happen if fuel prices suddenly rose?
Concorde’s MC and AC would increase
So can you draw Concorde’s old revenue and costs + their new AC and MC curves after fuel prices rise?
So what's our new profit maximising quantity?
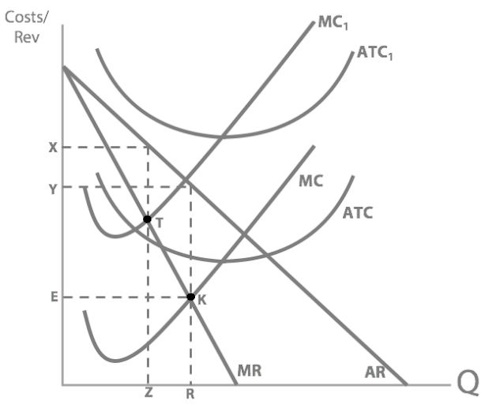
And so our new profit maximising price will be:
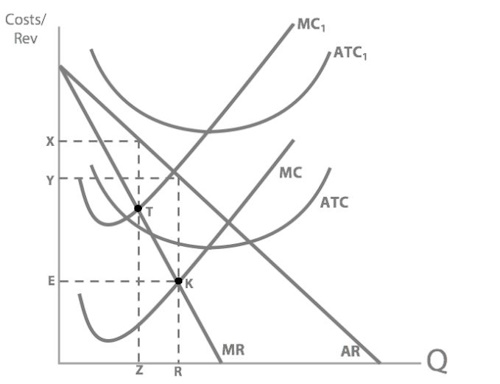
x
So what’s happened to Concorde’s price and quantity when their fuel costs increase?
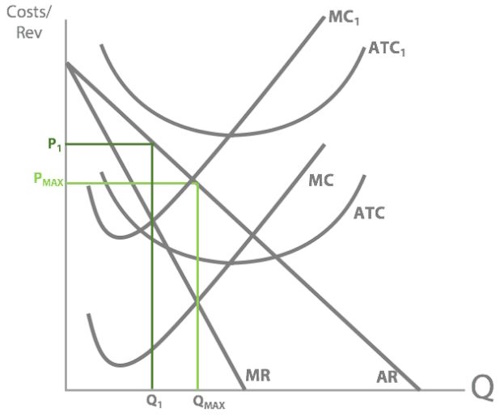
Price increased and quantity decreased
What happens to profit when there is an increase in variable costs?
Profit decreases
So can you draw Pizza Hut’s old revenue and costs + their new AC and MC curves after the robots take over?
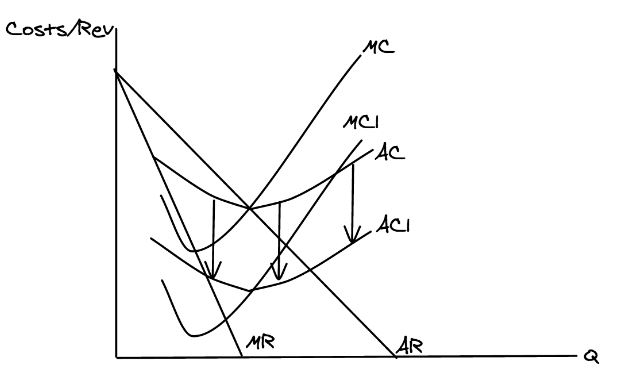
So what’s happened to Pizza Hut’s price and quantity when their robots increased efficiency and replaced workers?
Price decreased and quantity increased
So can you draw Ramsay’s old revenue and costs + his new ATC curves after his rent increases?
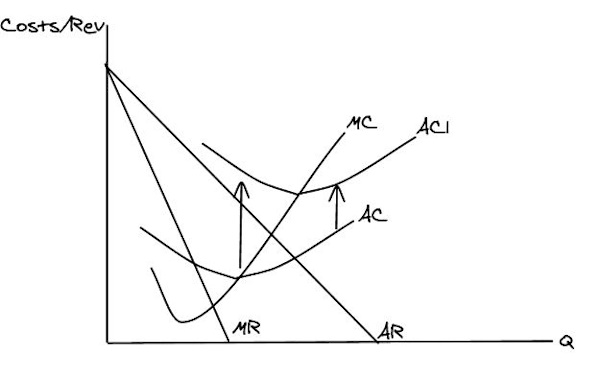
So what's our new profit maximising quantity?
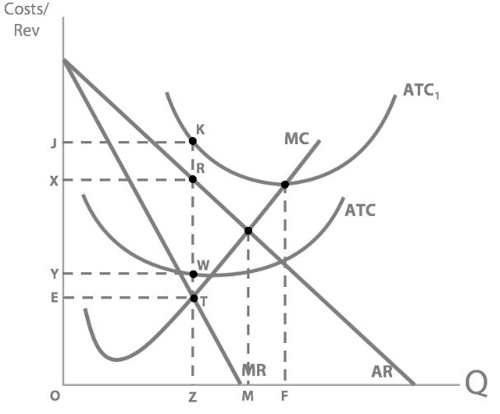
Z
But what about Ramsay’s profit after his rent costs increased?
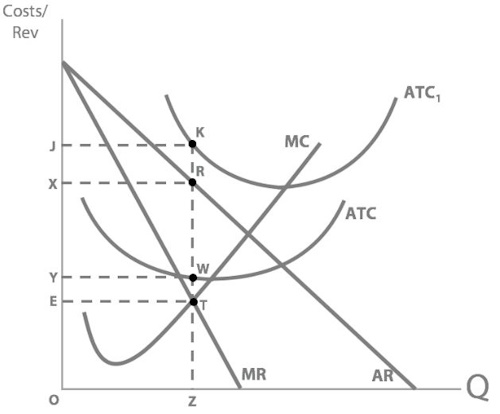
loss of RXJK
So, in the short run, even if a firm is making a LOSS, it will stay in the market if:
Price > AVC
But, if in the short run, AR < AVC:
the firm will leave the market because it’s not covering its average variable costs
We now know that our short run shutdown point is where:
Price = AVC
The gap between AVC and ATC represents:
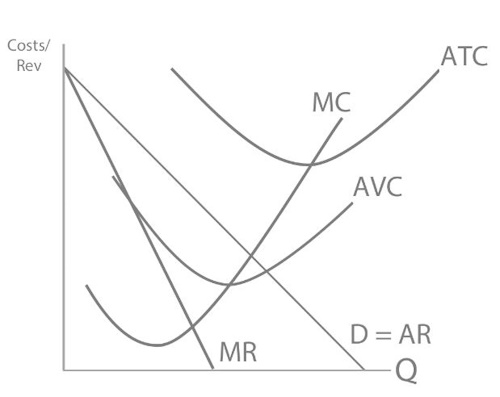
Average fixed costs
So when profit maximising, what is Apple’s profit?
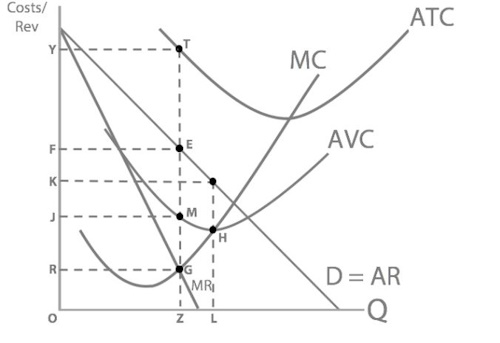
A loss of YTEF
So what will Apple do? (Hint: remember this is the short run for Apple)
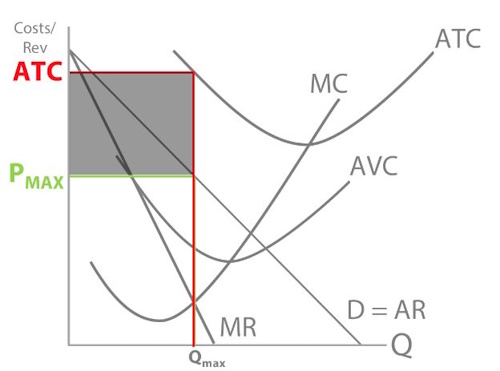
Apple will stay in the market because Price > AVC so it’s covering its variable costs. They are above their short run shut down point, they are making some money on each unit they sell, in the long run they will break even and eventually make profits.
So what will Trump do? (Hint: remember this is the short run for Trump)
\newline
Note: answer this like a 3-mark question in your exam.
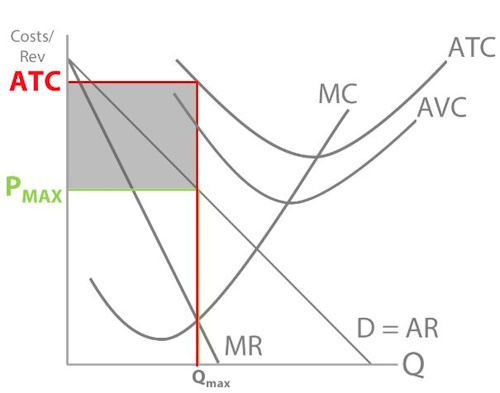
The diagram shows that Trump is below his short run shutdown point - price is now below AVC. So Trump will shutdown and leave the market.
This is because if price (AR) is below AVC, he is selling for a price below the variable cost of producing each unit. So he’s losing money on each unit sold, so he should shut his company down to avoid further losses.
Both firms were making losses...
\newline
But Apple stayed in the market whereas Trump shut down - and this is because:
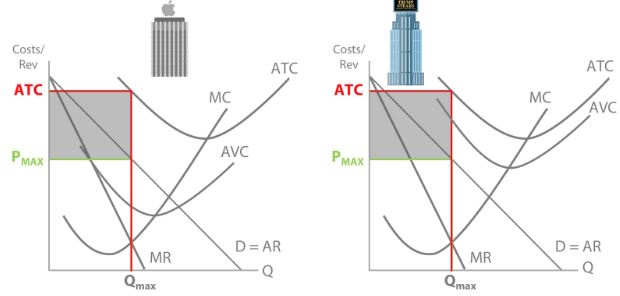
Trump’s price is below AVC, and Apple’s price is above AVC