module 5.1.1 communication and homeostasis
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What are the 2 systems of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
what is the CNS composed off
brain
spinal cord
what is the PNS composed off
neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
structure of the nervous system ( image)
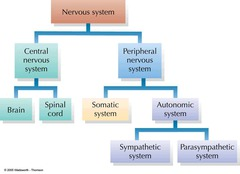
what are the two systems of the PNS
somatic nervous systems
autonomic nervous systems
function of somatic nervous system
consciously controls voluntary muscle movement
Function of the autonomic nervous system
unconsciously controls involuntary activities such as heartbeat and digestion
what systems can the autonomic nervous system be split into?
parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
what is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Activates your flight or fight response
what is the neurotransmitter involved in the sympathetic nervous system?
noradrenaline
adrenaline
what is the neurotransmitter involved in the parasympathetic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
what is the sympathetic system affect on activity levels
Increases
what is the parasympathetic system affect on activity levels
Decreases
what are the 5 structures of the brain
Cerebrum
cerebellum
Hypothalamus
Medulla oblongata
Pituitary gland
function of cerebrum
control Higher brain function ( decision making)
function of Hypothalamus
maintain homeostasis
maintains temperature, control Ψ of blood and hormone production
what is the pituitary gland controlled by
hypothalamus
function of the pituitary gland
produces hormones and stimulates other glands
function of cerebellum
Coordinate muscular movement and maintain balance
function of medulla oblongata
controls involuntary functions
heart rate, breathing rate and blood pressure
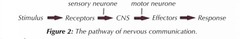
what are the three types of neurones?
Sensory,
relay
motor
what is the function of the Sensory neurones?
Transmit nerve impulses from receptors to the CNS
what is the function of the Motor neurones?
Transmit nerve impulse from the CNS to effectors
what is the function of the Relay neurones?
Transmit nerve impulse between sensory neurons and motor
Pathway of Nervous communication (image)
structure of neurons ( image)
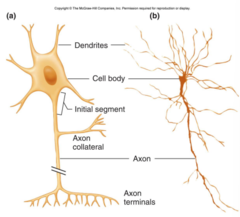
Do neurones have all the normal cell organelles ?
YES
Functions of dendrites and dendrons ?
carry nerve impulses towards the cell body
functions of Axon
carry the nerve impulse away from the cell body
how to remember the functions of Axons and Dendrites
Axons → Away cell body
Dendrites → towarDs cell body
what type of impulses does the nervous system use?
electrical impulses
What is meant by resting potential?
Potential difference ( P.D) when a cell is at rest ( no stimulus)
what is the charges of a nervous system receptor at resting potential?
The inside is more negatively charged relative to the outside --> creates a P.D
what generates resting potential
ion pumps and ion channels
what is a generator potential?
Change in potential difference due to a stimulus
What happens to the membrane when a stimulus is detected ?
Cell membrane becomes more permeable
allows more ions to move in /out of cell
altering the P.D
creates a generator potential
Stimulus and generator potential relationship
Bigger the stimulus → Greater generator potential produced.
what is P.D measured in
millivolts (mV)
what is a action potential
nerve impulse along a neuron
what happens when the generator potential doesn't reach the threshold level ( value)
No Action potential ( stimulus is too weak)
what happens when the generator potential does reach the threshold level
Action potential is triggered
Describe the stimulation of the Pacinian corpuscle
gets stimulated ( tap on arm), lamellae is deformed and press on sensory nerve ending
deforms the stretch mediated Na channels in neurone cell membrane
Na⁺ channels open → Na⁺ diffuses into cell → creating a generator potential
if it reaches threshold level → triggers action potential
Where is the Pacinian corpuscle located?
Skin
What does the pacinian corpuscle detect?
mechanical stimuli ( vibrations and pressure)
Why is it important that organisms respond to stimuli
increase their chance of survival
how do sensory receptors act as transducer ?
convert the energy of a stimulus into electrical energy
Function of the cell body
releases neurotransmitters
structure of mylein sheath
layers of plasma membrane ( lipids)
function of mylein sheath
acts as a insultating layer helps speed up rate of transmission
what maintains and creates the resting potential in n
sodium-potassium pumps
potassium ion channels
in neurones membrane
is the membrane polarised and how?
yes
inside membrane is more negatively charged then outside ( more cations outside)
Resting potential maintenance ( image)
SOPI → sodium out potassium in
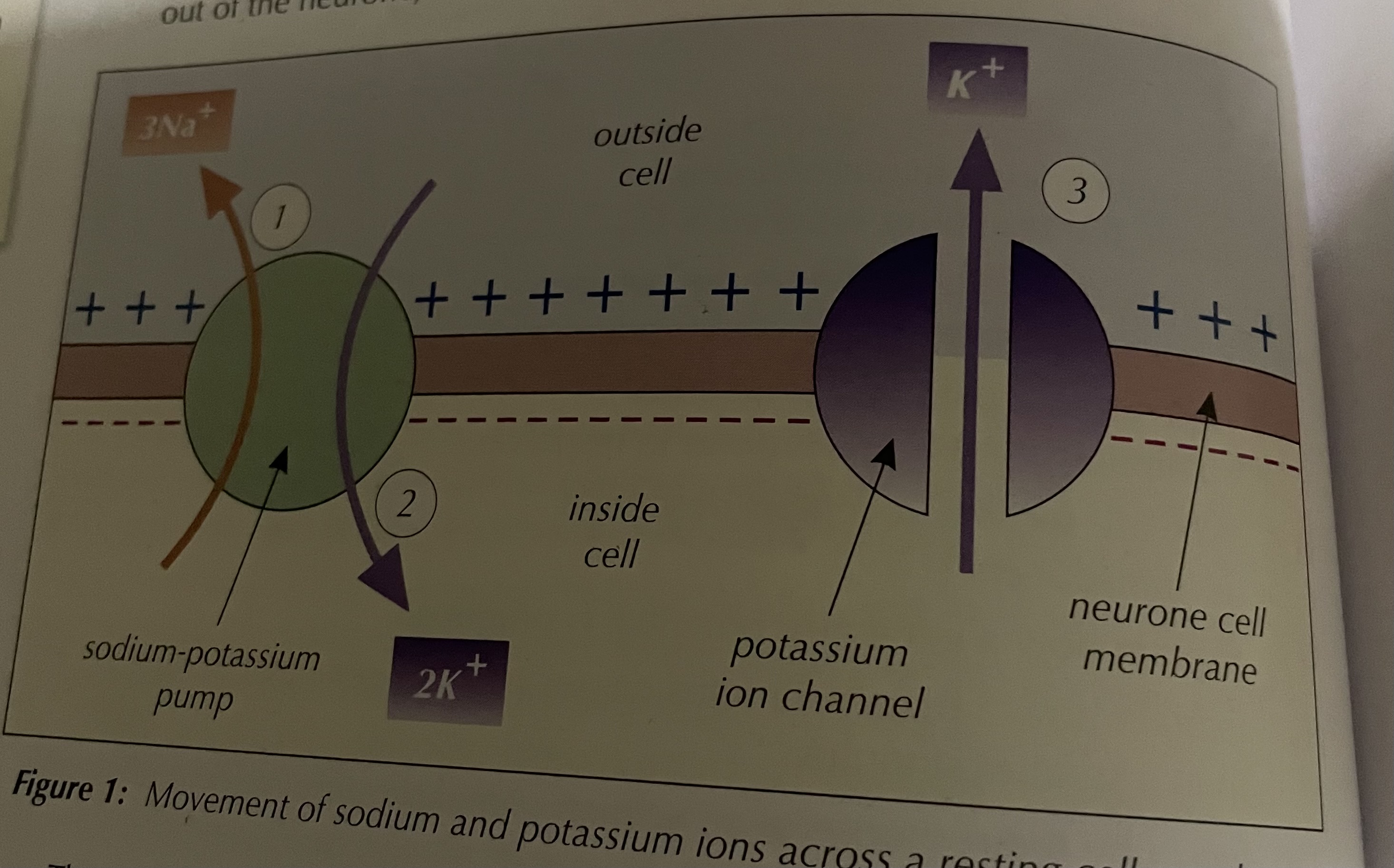
How is the resting potential maintained
Sodium potassium pumps actively ( ATP) move 3 Na⁺ out of neurone for every 2K⁺ moved in
potassium ion channels allow facilitated diffusion of K⁺ out of neurone
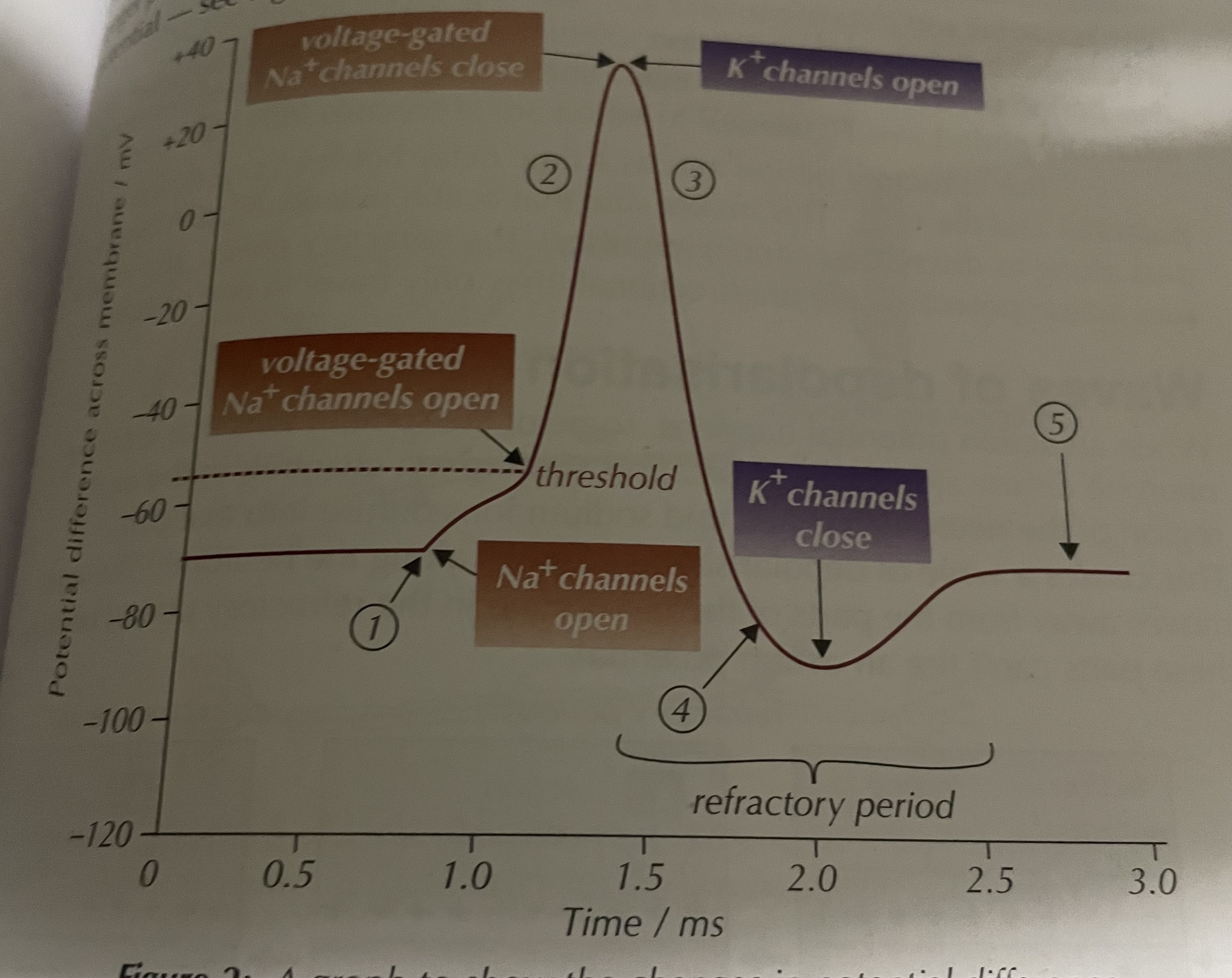
at rest which channels are open
potassium channels are open
sodium are closed
when do action potentials happen
when the neurone is stimulated
what is the voltage value of a neurone at resting potential
-70 mv
Action potential graph
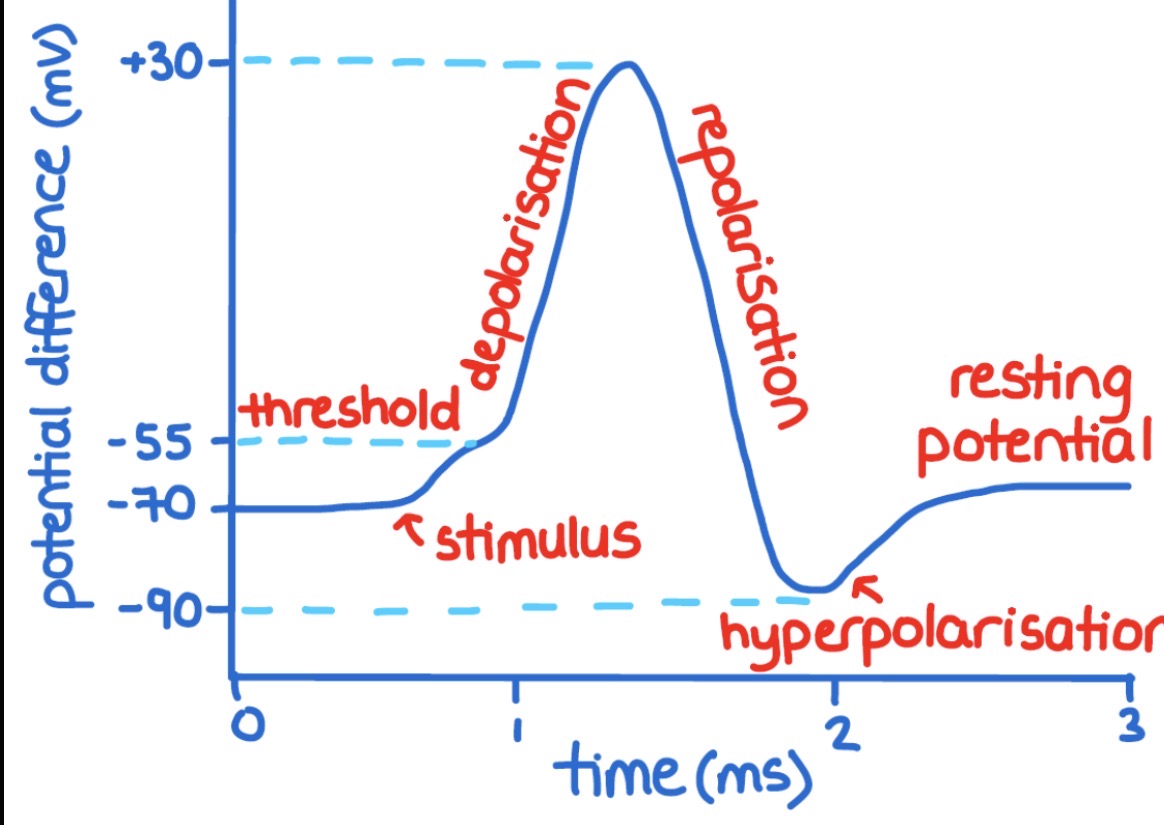
Action potential graph
what are the 5 stages of a action potential
stimulus
depolarisation
repolarisation
hyperpolarisation
resting potential
action potential ( stimulus)
stimulus causes sodium ion channels to open
membrane becomes more permeable → Na⁺ diffuses into neurone
neurone membrane becomes less negative
action potential ( Depolarisation )
P.D reaches Threshold → voltage- gated sodium ion channels open → more Na⁺ diffuse into the neurone ( postive feedback)
action potential ( Repolarisation)
sodium ion channel closes, voltage-gated potassium ion channels open
K⁺ diffuses out of the neuron → membrane starts to go back to resting potential ( negative feedback)
action potential ( Hyperpolarisation)
potassium ion channels are slow to close → many K⁺ ions to diffuse out of the neurone
P.D becomes more negative then resting potential ( less then -70 mv)
action potential ( Resting potential)
ion channels are reset
sodium-potassium pump moves 3Na⁺ out and 2K⁺ in returning membrane to resting potential.
what is the retractory period?
time delay between action potentials as the ion channels are recovering.
neurone cell membrane cant be stimulated
what is the function of the retractory period
ensures action potentials dont overlap
action potentials travel in one direction
what is the result of a bigger stimulus
larger stimulus = more frequent action potentials
factors that affect the rate of conduction of action potentials
Myelination
Axon diameter
Temperature
myelination effect on rate of conduction of action potential
myelination leads to faster rate as depolarisation only happens at the nodes of Ranvier
impulse transmitted from node to node ( this is called saltarory conduction)
non myleinated → impulse travels as a wave along length of axon membrane
Axon diameter effect on rate of conduction of action potential
larger diameter = faster
less resistance to flow of ions than in cytoplasm of smaller axon
depolarisation reaches other parts of neurone membrane faster
Temperature effect on rate of conduction of action potential
temperature increases = rate increases
ions diffuse faster
past 40°C protein pumps and channels denature and speed decreases
what is the cholinergic synapse neurotransmitter ?
acetylcholine (ACh)
what does ACh bind to
cholinergic receptors
How are neurotransmitters removed from the cleft
Broken down by enzymes
Take back into the presynaptic neurone
Which neurotransmitter uses cholinergic synapses
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Cholinergic synaptic transmission process?
Action potential arrives at the synaptic knob of the presynaptic neurone → calcium ion channel open Ca²⁺ diffuses in to synaptic knob
Influx of Ca²⁺ → vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane and exocytosis ( releases ACh)
ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft binds to Cholinergic receptors on post synaptic membrane → Na⁺ channels to open
Influx of Na⁺ → depolarisation
Creates a action potential in post synaptic membrane if threshold is met
How is ACh removed from synaptic cleft
Broken down by enzyme ( acetylcholinesterase)
Products are re-absorbed by the presynpatic neurone
What are agonists
Chemicals with the same shape of neurotransmitter that bind to the same receptors
Example of a agonist
Nicotine (mimics acetylcholine) binds to Cholinergic receptors in the brain
Function/ action of curare
Curare → blocks the effects acetylcholine by blocking certain cholinergic receptors
Muscles can’t be stimulated
Function/ action of nerve gases
Prevents acetylcholine from being broken down in synaptic cleft
Leads to loss of muscle control
Function/ action of Opioids
Blocks calcium ion channels in presynpatic neurone → fewer vesicles → less neurotransmitters released
What are the two types of synapses
Excitatory
Inhibitory
What is a excitatory synapse
A synapse where excitatory neurotransmitters are released
What is a inhibitory synapse
A synapse whre inhibitory neurotransmitters are released
What is meant by a excitatory neurotransmitters
result in the Depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane → action potential
What is meant by inhibitory synapse
Where a inhibitory neurotransmitters are released is an inhibitory synpase
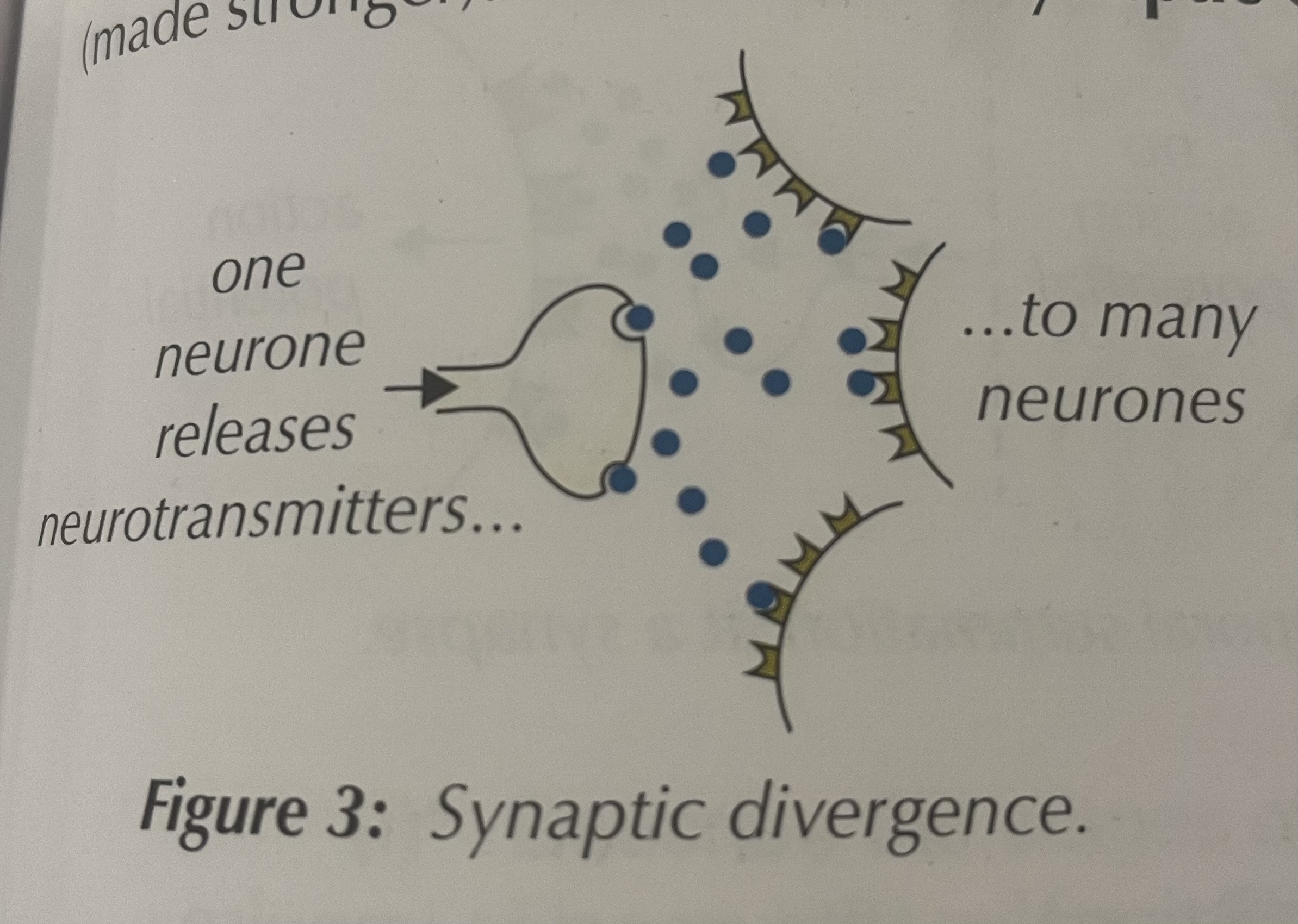
What is synaptic divergence
One neurone connects ( releases neurotransmitters) to many neurones
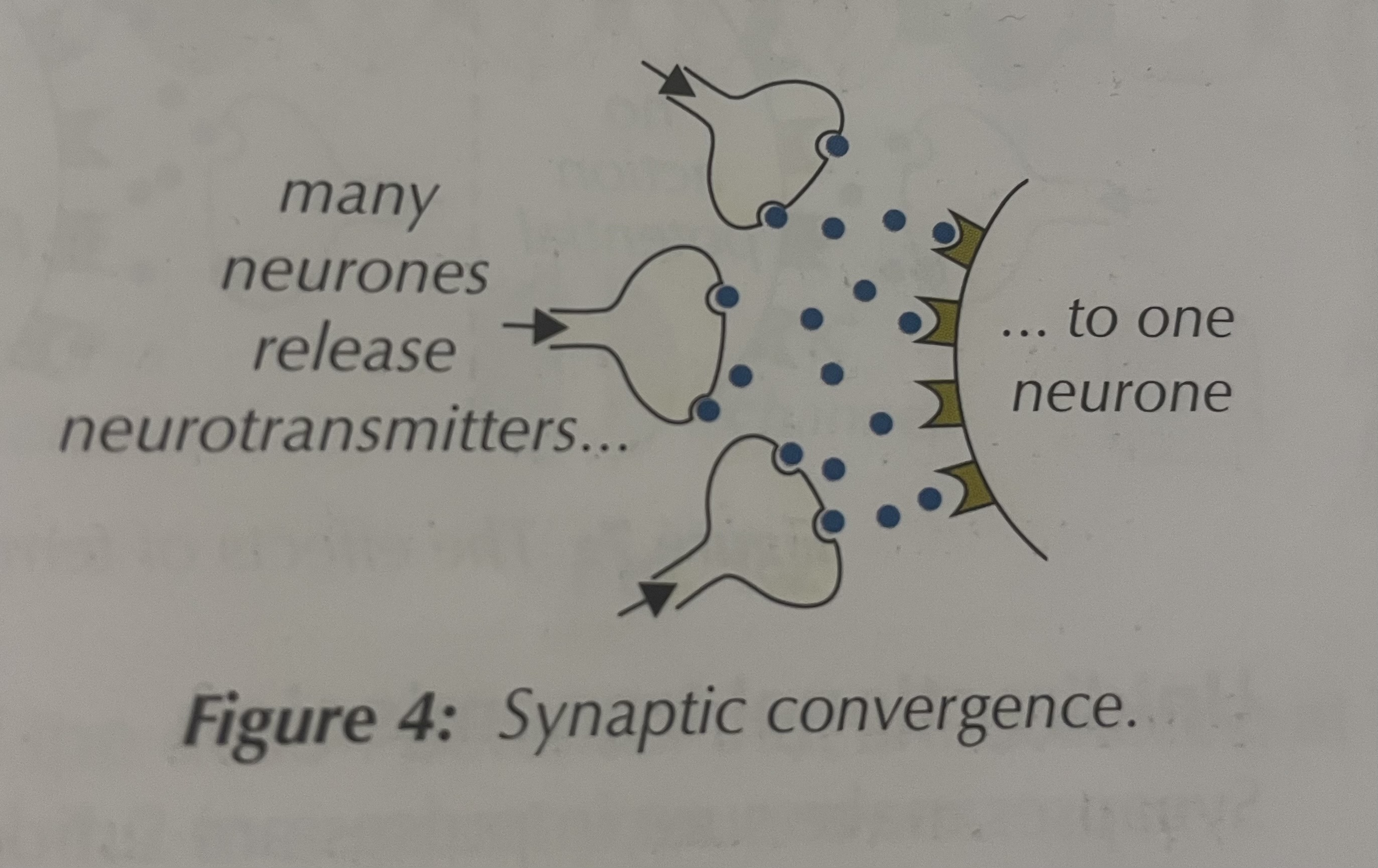
What is synaptic convergence?
Many neurones connect to one neurone
Difference between synaptic convergence and divergence
Convergence → many neurones connect to one neurone / information is stronger ( Con = neurones come together)
Divergence → one neurone connects to many neurones
Synaptic divergence ( image)
Synaptic convergence ( image)
Wha are the two types of summation
Spatial summation
Temporal summation
What is summation
Stimulus is too weak
Total sum of lots of smaller impulses trigger an action potential
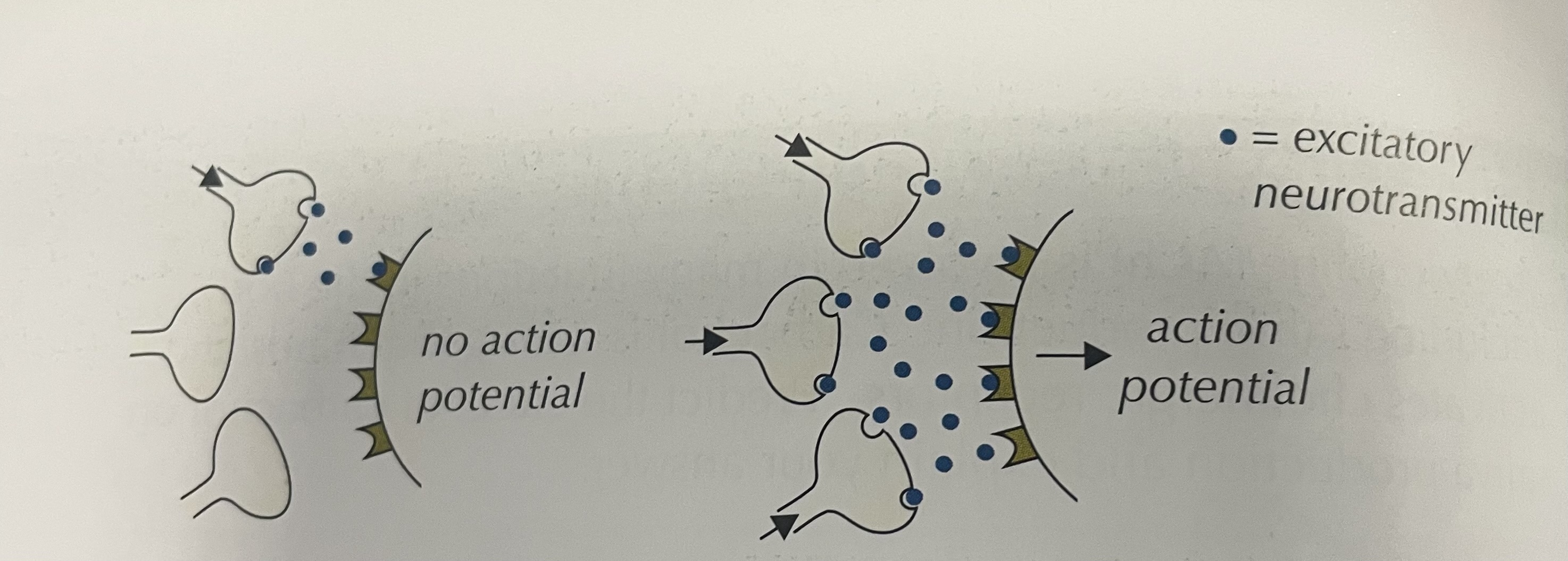
What is spatial summation
Two or more presynaptic neurones converge and release their neurotransmitters simultaneously on same postsynaptic membranes
Effect on inhibitory neurotransmitters on action potential
No action potential
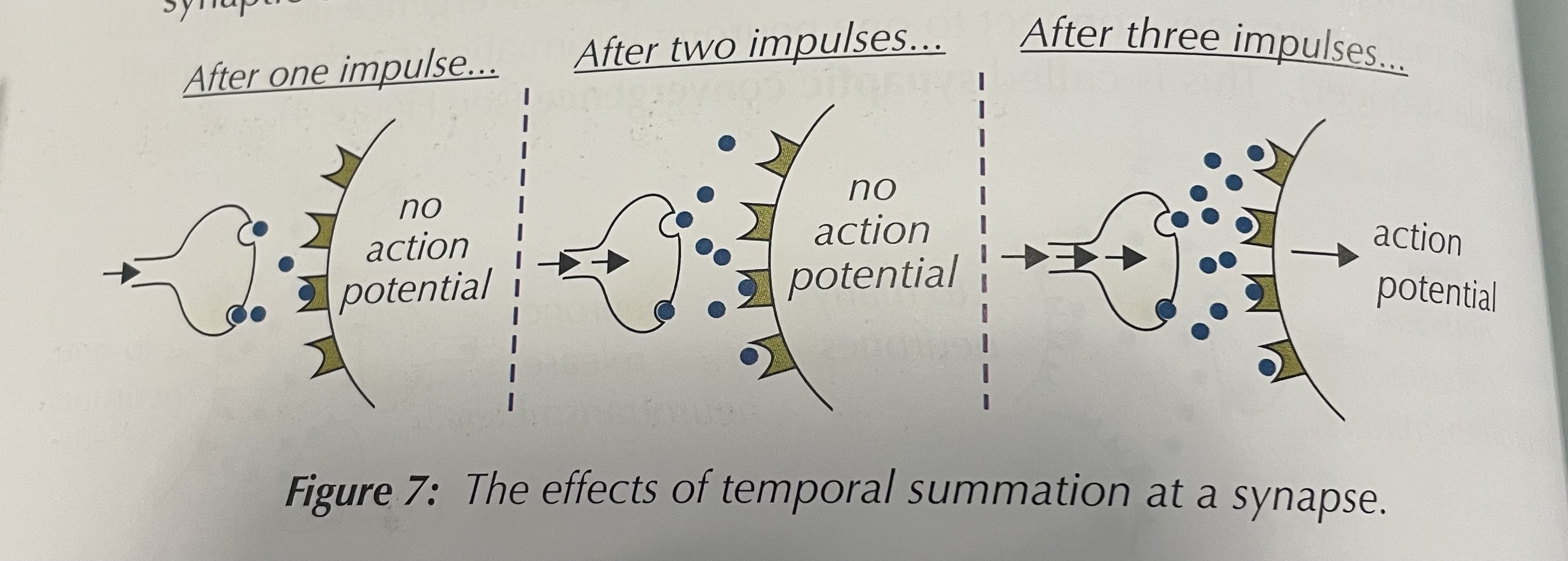
What is temporal summation
Neurone impulse arrives in quick succession from same presynaptic neurone
Higher chance of action potential
Temporal summation ( image)
Spatial summation ( image)
What is the direction of a synapse impulse
Unidirectional ( travel in one direction)