Chapter 26 Phylogeny
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:41 AM on 1/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
Phylogeny
evolutionary history of an organisms; where things originated; ancestry
2
New cards
Biodiversity
All of the diversity/variety of life on Earth
3
New cards
Systematics
study of evolutionary relationships between organisms
4
New cards
Taxonomy
Science of naming organisms
5
New cards
Taxon
a named group of organisms
6
New cards
Classification
assigning organisms to meaningful, hierarchical groups
7
New cards
Homology
Phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry
8
New cards
Analogy
Phenotypic and genetic similarities due to convergent evolution
9
New cards
Convergent evolution
When similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar adaptations in organisms found in different evolutionary lineages
10
New cards
Divergent evolution
Species sharing a common ancestor become more distinct due to a differential selection pressure which gradual leads to speciation
11
New cards
Homologous structures
similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve completely different functions
12
New cards
Cladistics
A systematic approach using common ancestry as the primary criteria for classifying organisms
13
New cards
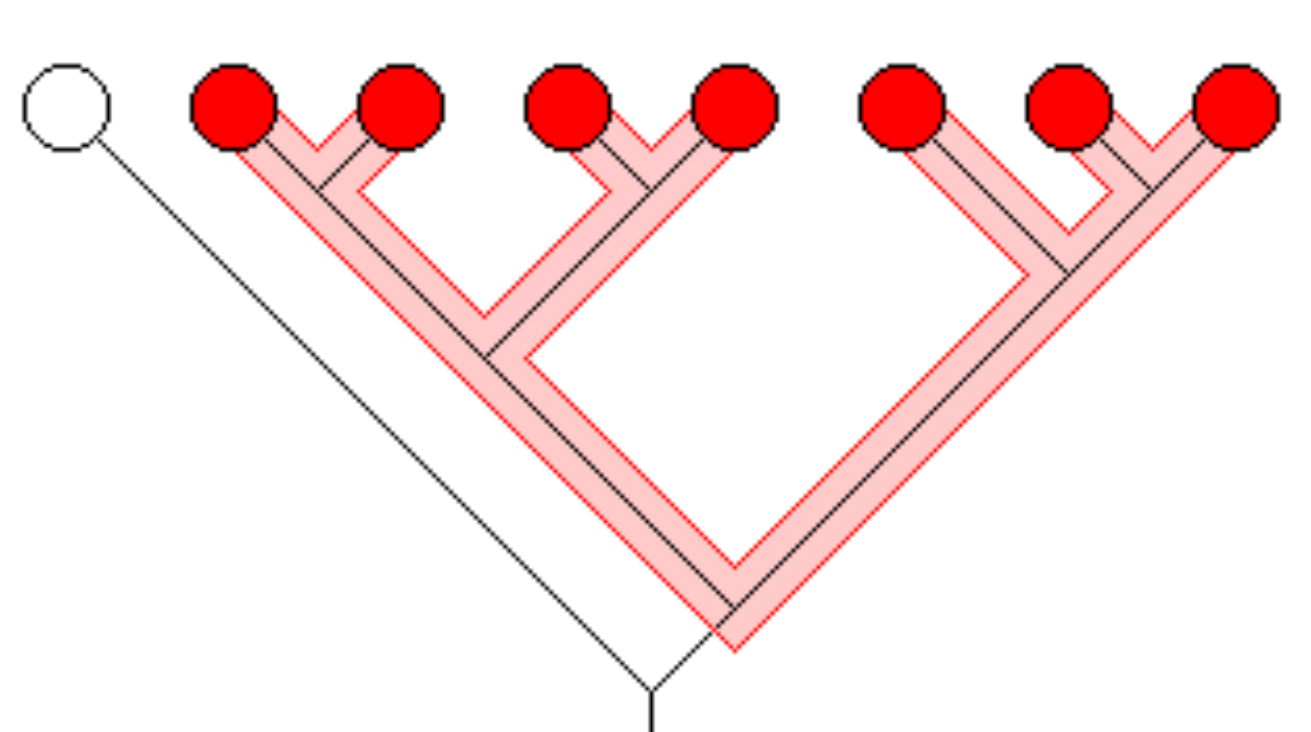
Monophyletic
Ancestral species and all its descendants
14
New cards
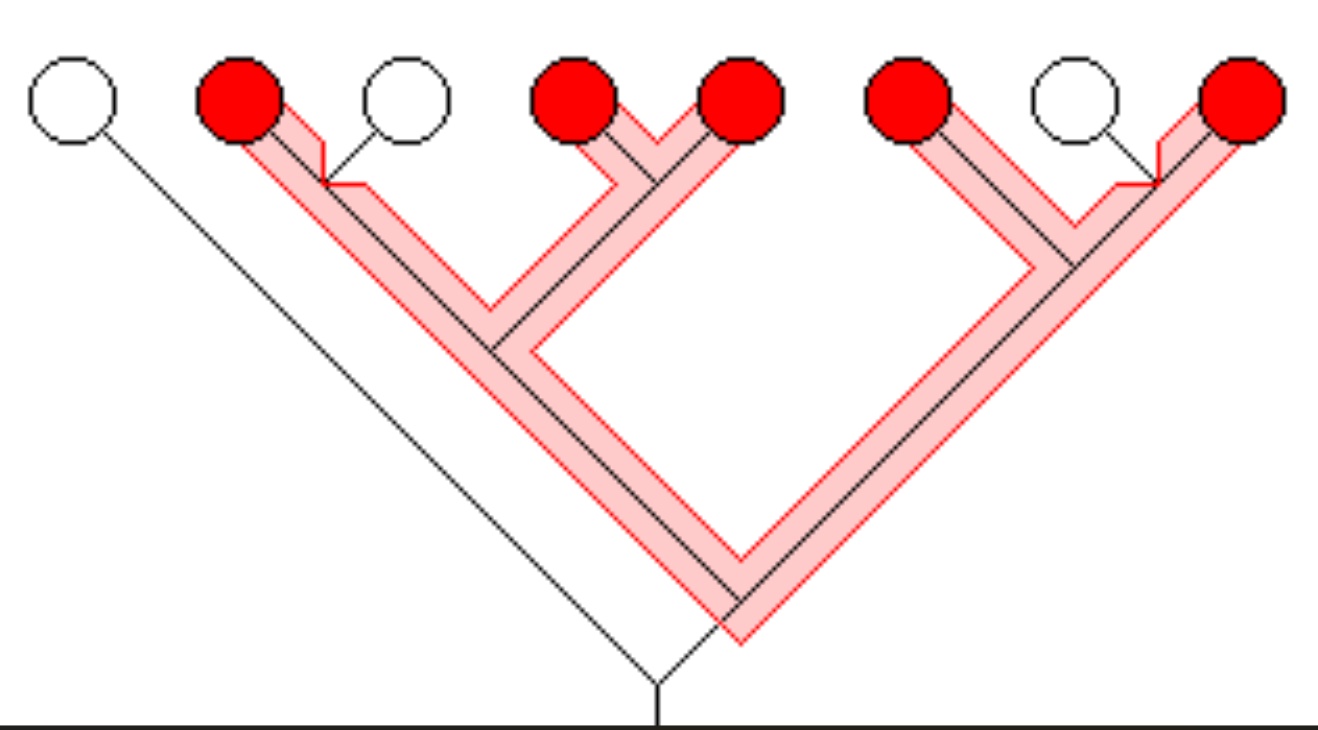
Paraphyletic
Ancestral species and some of its descendants
15
New cards
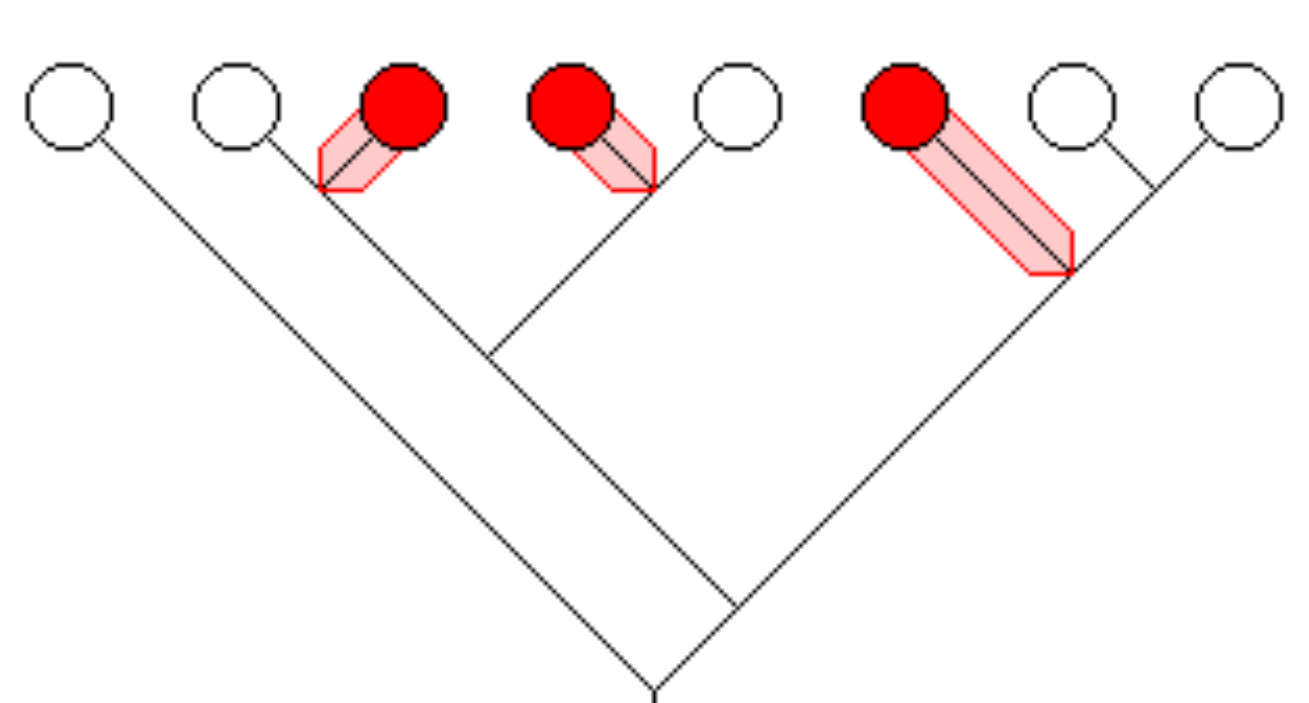
Polyphyletic
Includes distinct related species but not the common ancestor
16
New cards
Apomorphy/Autapomorphy
A specialized trait/character that is unique to a group or species; changed from initial ancestor to something different overtime
17
New cards
Plesiomorphy
An ancestral or primitive character state; present in an ancestor
18
New cards
Synapomorphy
Share, derived characteristics
19
New cards
Symplesiomorphy
Shared and ancestral characteristics
20
New cards
Homoplasy
When 2 of the same characteristics show up randomly
21
New cards
Gene families
Groups of related genes within an organism's genome
22
New cards
Orthologous genes
Homology is the result of a speciation event and hence occurs between genes found in different species
23
New cards
Paralogous genes
Results from a gene duplication where multiple copies of genes have diverged from one another within species
24
New cards
Molecular clocks
Method of estimating the time required for a given amount of evolutionary change based on the observation that some regions of genomes evolve at constant rates
25
New cards
**phylogenetic tree**
used to depict the relationships of organisms
26
New cards
What do phylogenetic trees show
Organisms’ closest relatives, ancestors, and where some of their traits may have originated
27
New cards
**What are the components of a phylogenetic tree**
branching lines that represent divergent evolution, it can be based on DNA, morphology, or biochemistry
28
New cards
What is binomial nomenclature
the scientific naming of organisms using a genus and species that is latin based
29
New cards
Why do we use binomial nomenclature
used to limit confusion when studying organisms due to many having multiple common names
30
New cards
Who introduced nomenclature
Carolus Linnaeus
31
New cards
What is the mnemonic used to remember taxonomic classifications
Dear- Domain
King- Kingdom
Phillip- Phylum
Came- Class
Over- Order
For- Family
Great- Genus
Sex- Species
King- Kingdom
Phillip- Phylum
Came- Class
Over- Order
For- Family
Great- Genus
Sex- Species
32
New cards
Why do Linnaean classification and phylogenetics/systematics sometimes disagree
Organisms can look similar and be distantly related and vice versa, depending on what system you use is who the organism might be related to
33
New cards
What are the three domains of life
Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
34
New cards
Who proposed the third domain
Carl Woese
35
New cards
Why was a third domain proposed
Due to Archaea and Bacteria having too much diversity between each other to be grouped together