Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 6: Fermentation & Anaerobic Alternatives
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
Biochemistry
A-Level Chemistry
AQA
Organic Chemistry
Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 6: Fermentation & Anaerobic Alternatives
Section 6: Fermentation & Anaerobic Alternatives
Section 6
Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section 6
Cellular Respiration: P&P
Fermentation & Anaerobic Alternatives
Fermentation
Anaerobic Alternatives
Module 8: Cellular Respiration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Hibernation Adaptation
Lowered metabolism in mammals conserving energy during winter.

Chloroplast Chemiosmosis
Light-driven ATP synthesis in plant cells.
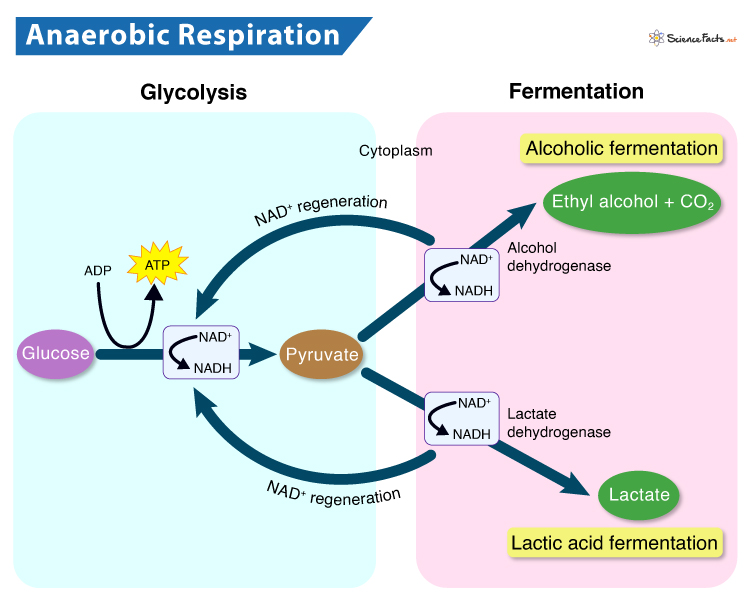
Fermentation
Anaerobic process breaking down sugars without oxygen.
Anaerobic process
Metabolic process occurring without the presence of oxygen.
ATP production without oxygen or electron transport chain
Energy generation in the absence of O2, using substrate-level phosphorylation.
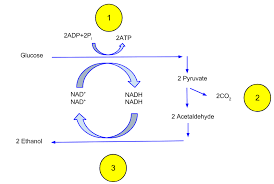
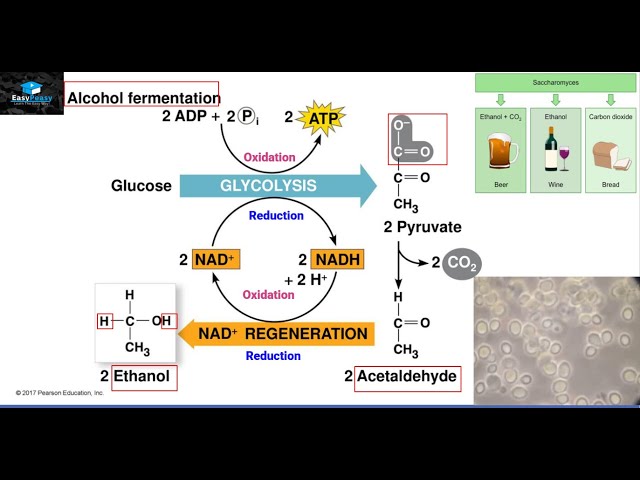
Alcohol Fermentation
Anaerobic conversion of pyruvate to ethanol, releasing CO2 and regenerating NAD+.
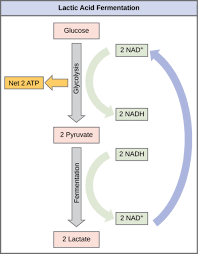
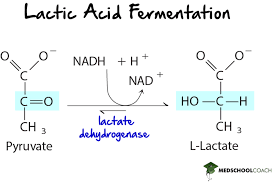
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Anaerobic conversion of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+.
NAD+
Coenzyme recycled for glycolysis continuation during anaerobic fermentation.
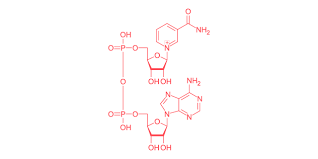
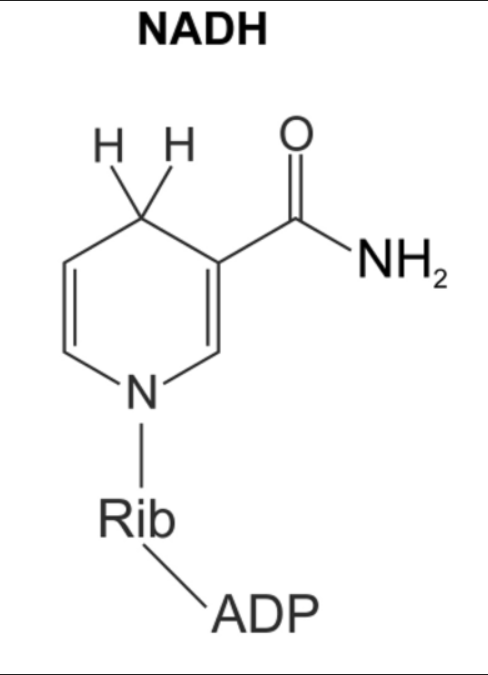
NADH
Electron carrier donates electrons, reducing pyruvate and regenerating NAD+.
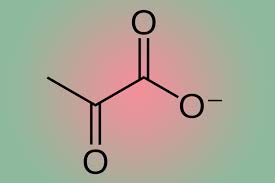
Pyruvate
Glycolysis end product used in fermentation and gluconeogenesis processes.
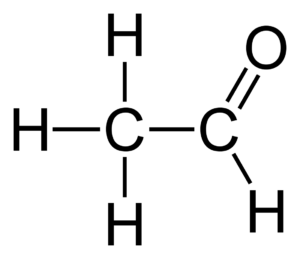
Acetaldehyde
Intermediate in alcohol fermentation, reduced to ethanol.
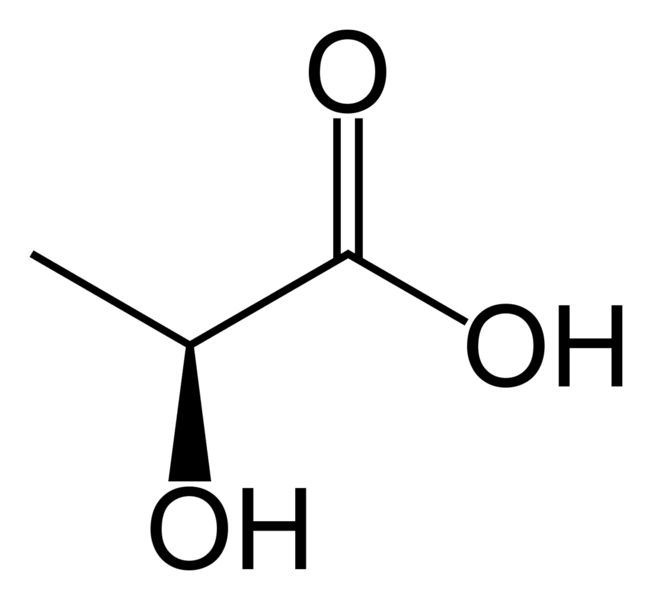
Lactate
End product of lactic acid fermentation.
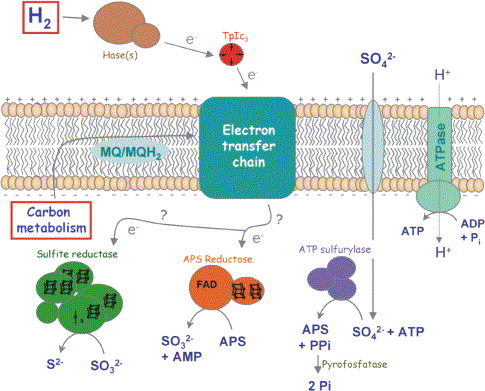
Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria
Microorganisms that use sulfate as the final electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration.
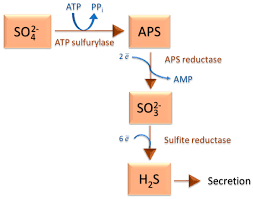
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Product of sulfate reduction during anaerobic respiration.

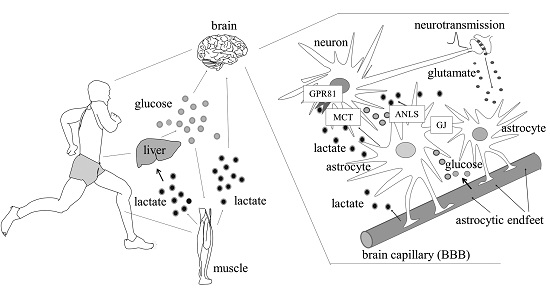
Strenuous Exercise
Strenuous Exercise
Oxygen limitation in muscles causes lactate production via fermentation.
Potassium Ions (K+)
Ions imbalance affects muscle function and fatigue, contrasting with lactate accumulation effects.

Liver Metabolism
Lactate is converted to pyruvate or glucose (Cori cycle).
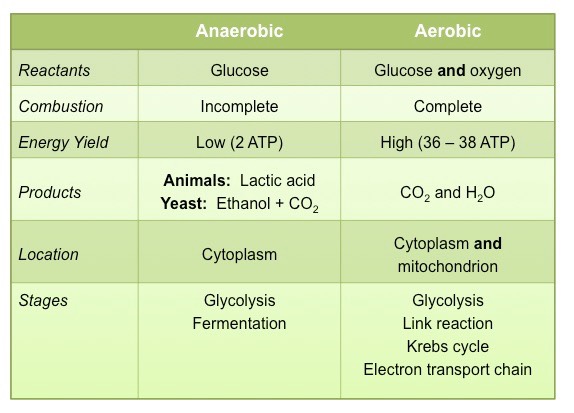
Comparison of Pathway
ATP yield differences in fermentation: anaerobic vs. aerobic.
Obligate Anaerobes
Organisms that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen

Facultative Anaerobes
Organisms switch between aerobic respiration and fermentation/anaerobic respiration based on oxygen availability.
Anaerobic Respiration
ATP generation via electron transport chain, excluding oxygen as acceptor.
Sulfate as final electron acceptor
Molecule replaces oxygen in anaerobic bacteria's electron transport chain.
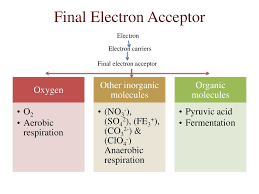
Final electron acceptor
Substrate accepting electrons in anaerobic respiration, like sulfate.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria released oxygen, enabling aerobic respiration evolution.

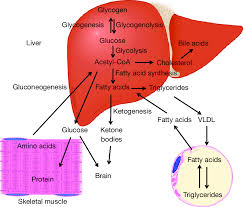
Evolutionary Basis of Glycolysis
Different metabolic routes connect carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism.
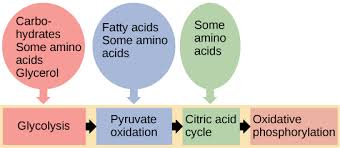
Metabolic Pathways Interconnection
Different metabolic routes connect carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism.
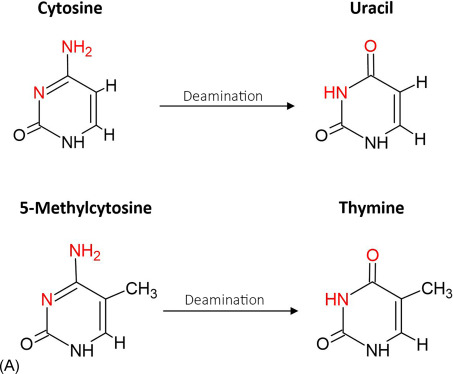
Deamination
Amino group removal enables amino acid conversion for respiration.
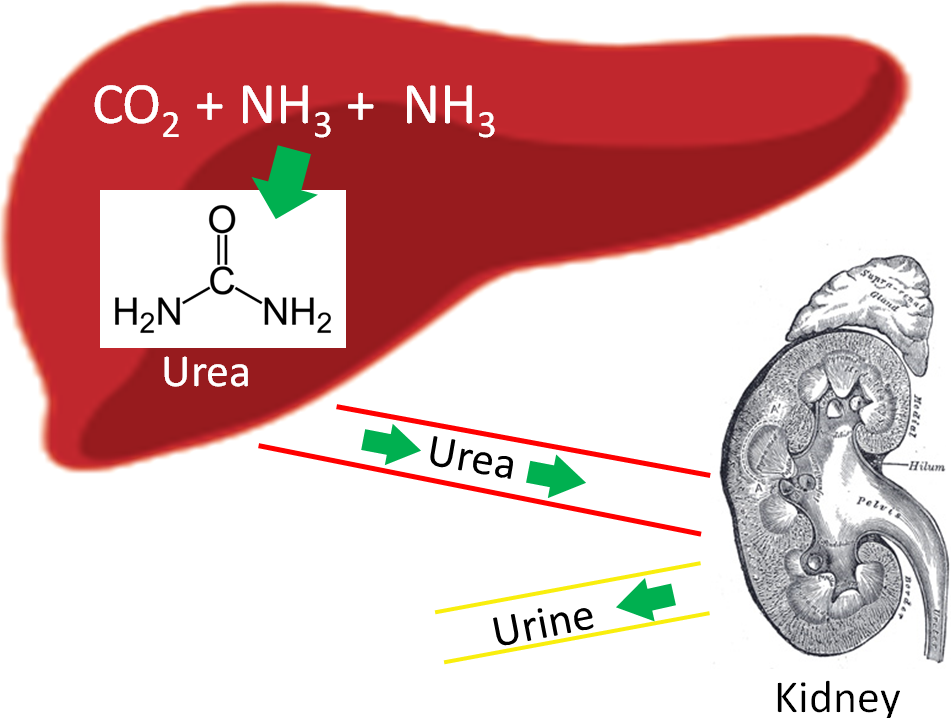
Nitrogenous Waste
Nitrogenous Waste
Ammonia, urea, or uric acid from deamination process.
Carbon Skeletons
Carbon chains from broken amino acids or fats enter glycolysis or citric acid cycle.
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways degrade complex molecules, releasing energy during fermentation.
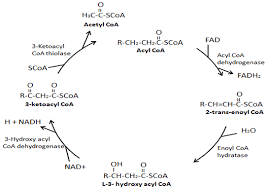
Beta Oxidation
Fatty acids convert to acetyl CoA, entering the citric acid cycle, alternative to glucose metabolism.
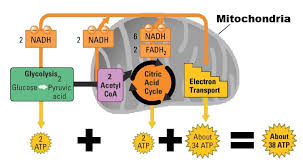
ATP Yield
Fermentation produces 2 ATP anaerobically; aerobic processes yield more ATP using oxygen, highlighting differences in energy production methods.
Anabolic Pathways
Anabolism builds complex molecules, consuming energy, unlike catabolism.
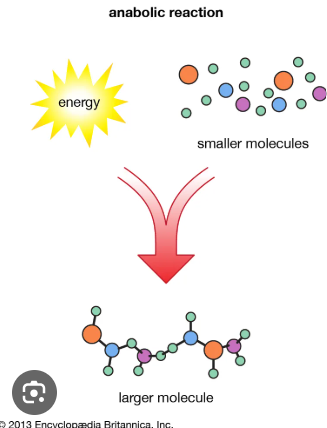
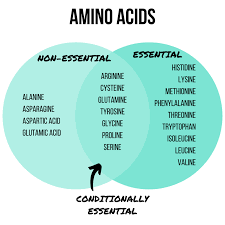
Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids, required from diet, affect metabolic fuel availability for respiration.
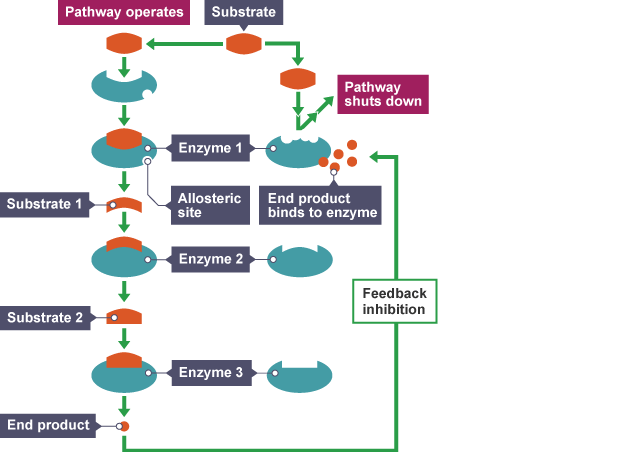
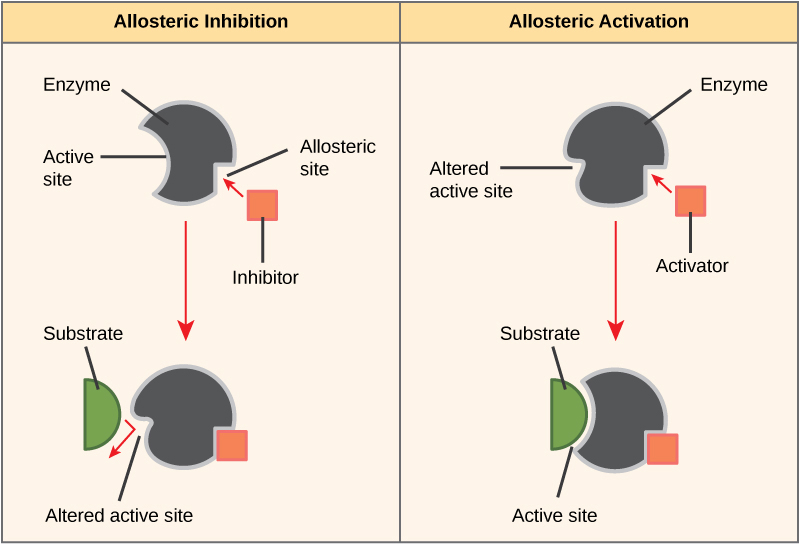
Feedback Inhibition
End product inhibits earlier step, controlling respiration and fermentation rates.
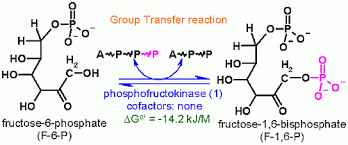
Phosphofructokinase
ATP and citrate regulate glycolysis, linking glucose breakdown to energy.
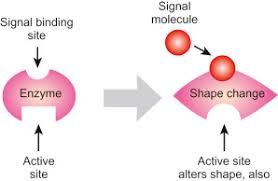
Allosteric Enzyme
Enzymes regulated by non-active site binding control metabolic pathways and are crucial for metabolic flow.
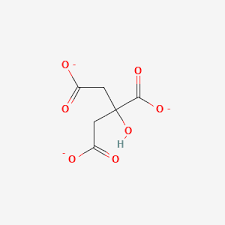
Citrate
Intermediate inhibits phosphofructokinase, connecting glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
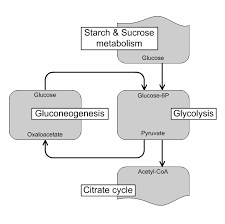
Metabolic Interchanges
Cells convert molecules, impacting respiration's fuel sources and efficiency.
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
Intermediate of glycolysis linked to various other metabolic pathways.

Energy Flow
Metabolism involves energy movement and transformation through biochemical reactions in organisms.
Metabolic Balance
The maintenance of homeostasis in metabolic processes, ensuring energy supply meets demand.
Ecosystem Cycling (role of respiration)
The role of decomposition and respiration in returning carbon to the atmosphere and nutrients to the soil