Unit14-3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the order of colors in the visible spectrum (low to high frequency)?
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet (ROYGBV; ~400–700 nm).
How are wavelength and frequency related for EM waves?
λf = c. Higher f → shorter λ (e.g., violet light has higher f than red).
Classify EM radiation with λ = 1 cm.
Microwaves (range: ~1 mm to 1 m).
What causes constructive interference?
Path difference Δℓ = mλ (waves in phase).
What causes destructive interference?
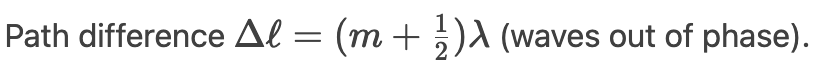
Define diffraction.
Bending/spreading of waves when passing through an aperture or around obstacles.
How does single-slit diffraction differ from double-slit interference?
Single slit: Wide central max with dimmer side fringes. Double slit: Evenly spaced bright/dark fringes.

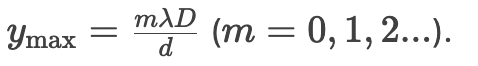
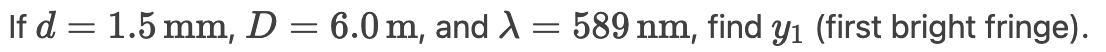
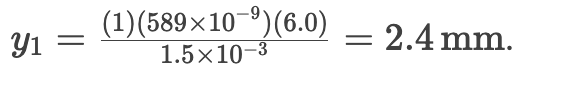
How does decreasing slit separation (d) affect the fringe pattern?

What is the path difference for the 3rd dark fringe?
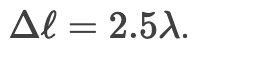
Why does the central maximum in single-slit diffraction have the highest intensity?
All wavelets interfere constructively at θ = 0.
What happens to the central max width if slit width decreases?
It widens (diffraction increases).
Pitfall: "Light travels faster in denser media."
Correction: Light slows down in denser media (v = c / n).
Write the double-slit bright fringe formula.
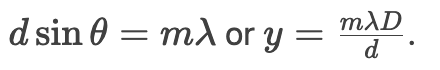
What is the condition for destructive interference?
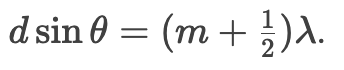
How is the EM spectrum ordered (long to short λλ)?
