The History of Life on Earth
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Macroevolution
Major changes in life above the species level in earth’s history

Origin of First Cells
When earth was hot, mostly ocean with volcanic gases & low O2 (3.5 bya)
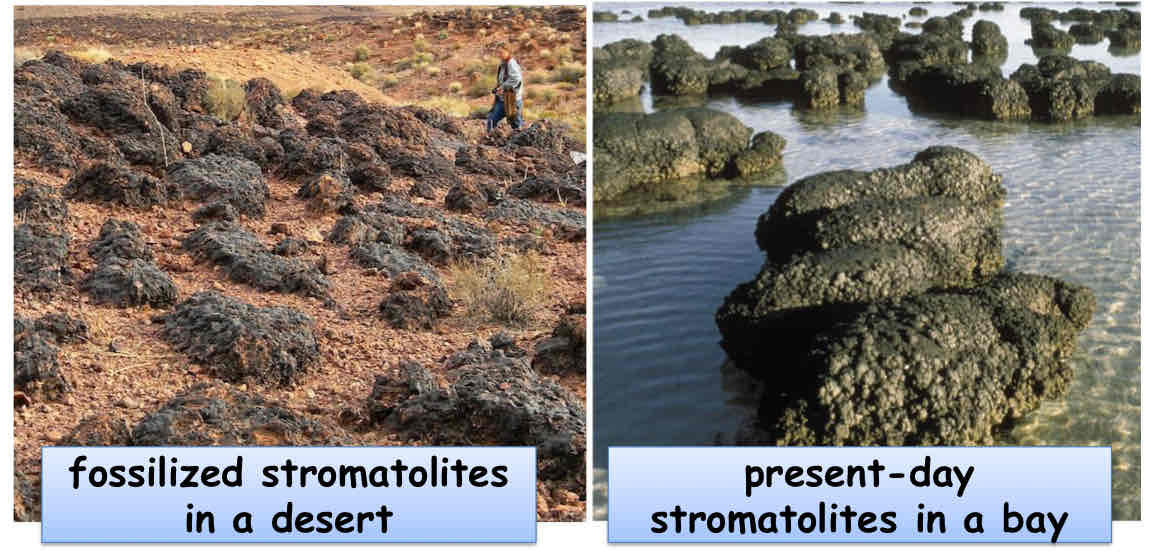

Earliest Evidence of Life
Oldest cell fossils are prokaryotes
in stromatolite formation (3.5 bya)
Layered mates of prokaryotes & minerals
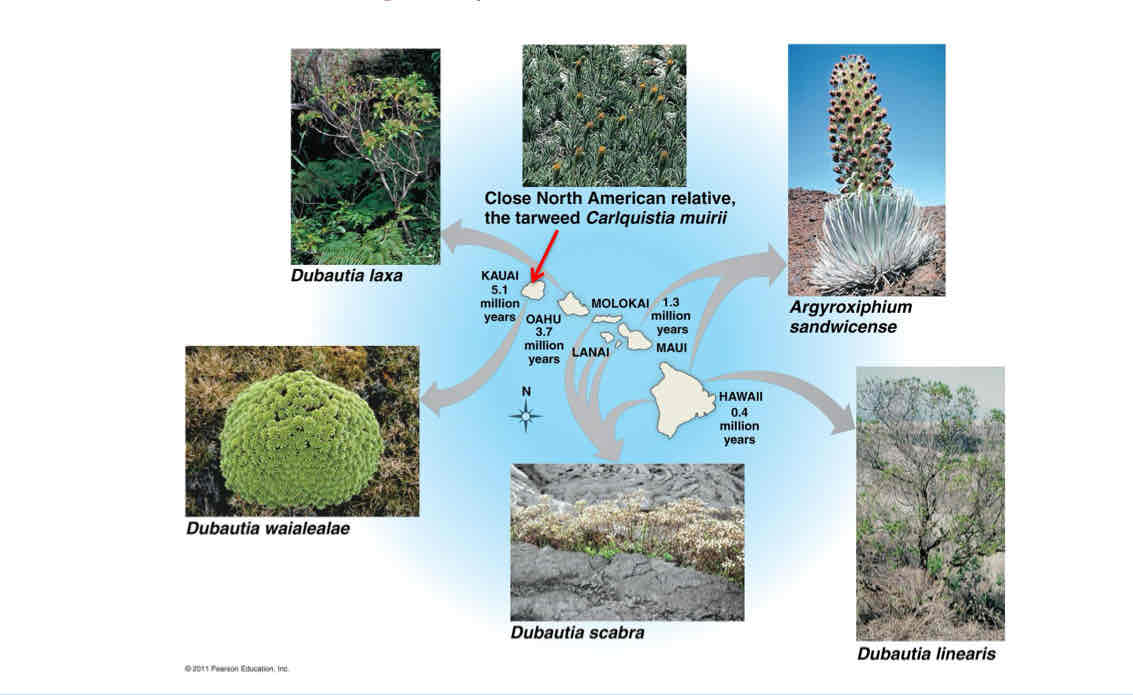
Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive radiation has occurred small-scale in isolated island groups
Historically, major radiations followed with mass extinctions
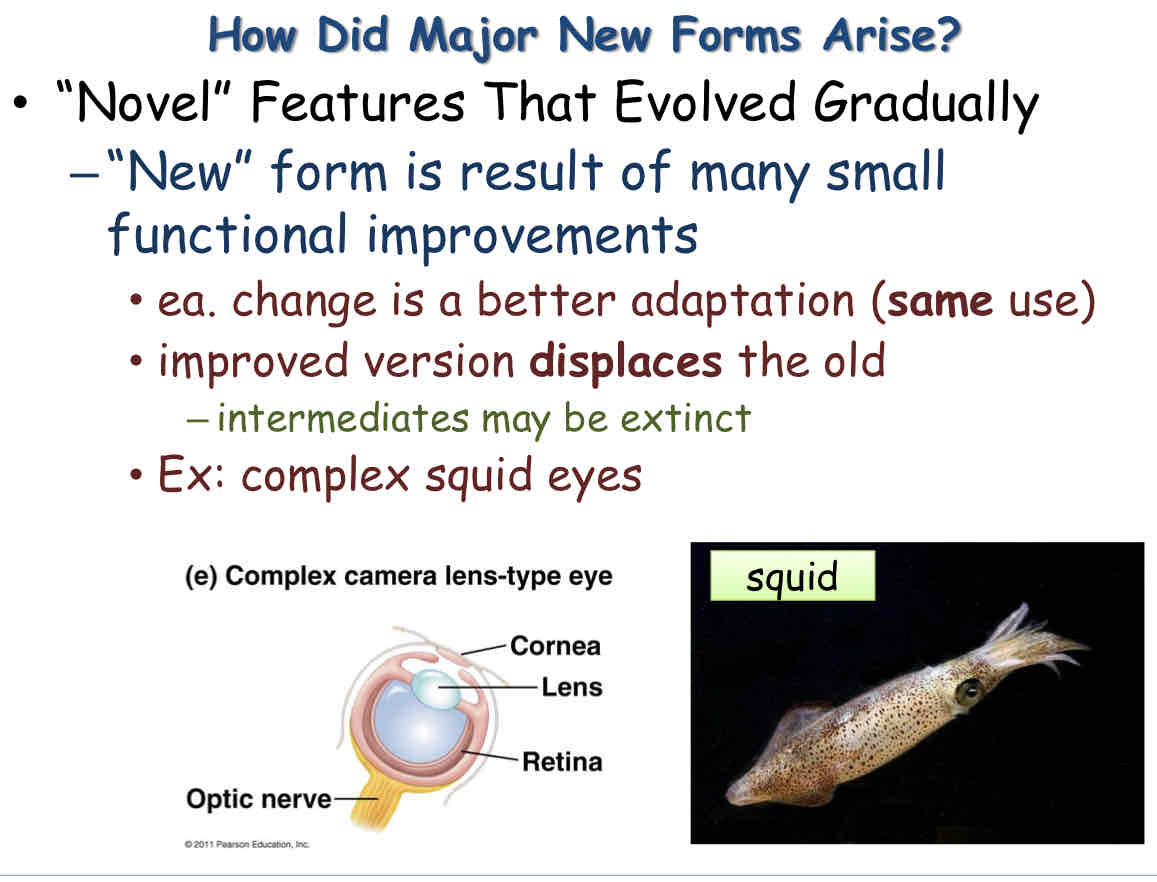
Novel Features
Novel features are features that evolved gradually
Novel features is result of many small function improvements
change = better adaptation but for same use
Ex: complex squid eyes
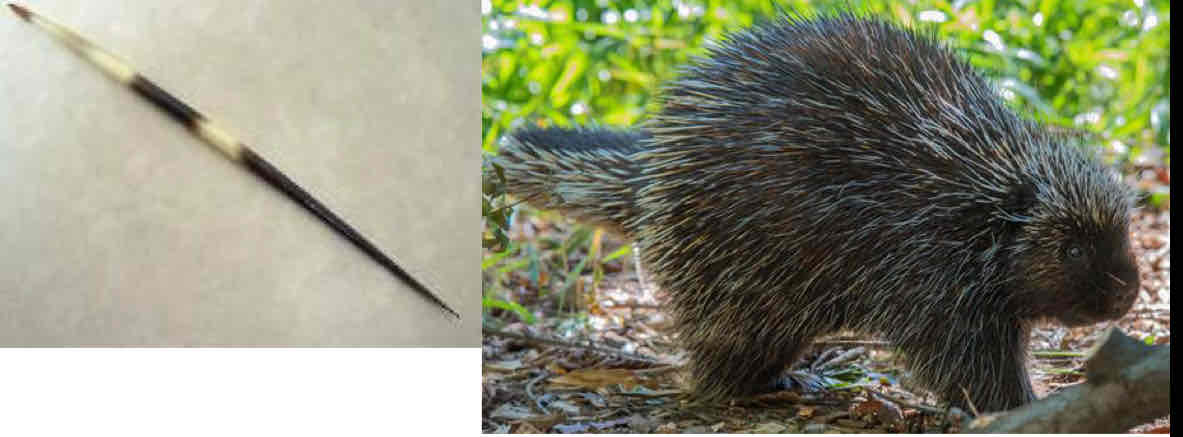
Exaptation
adaptations to different uses
Ex: Hair (insulation) —>porcupine quills (defense)

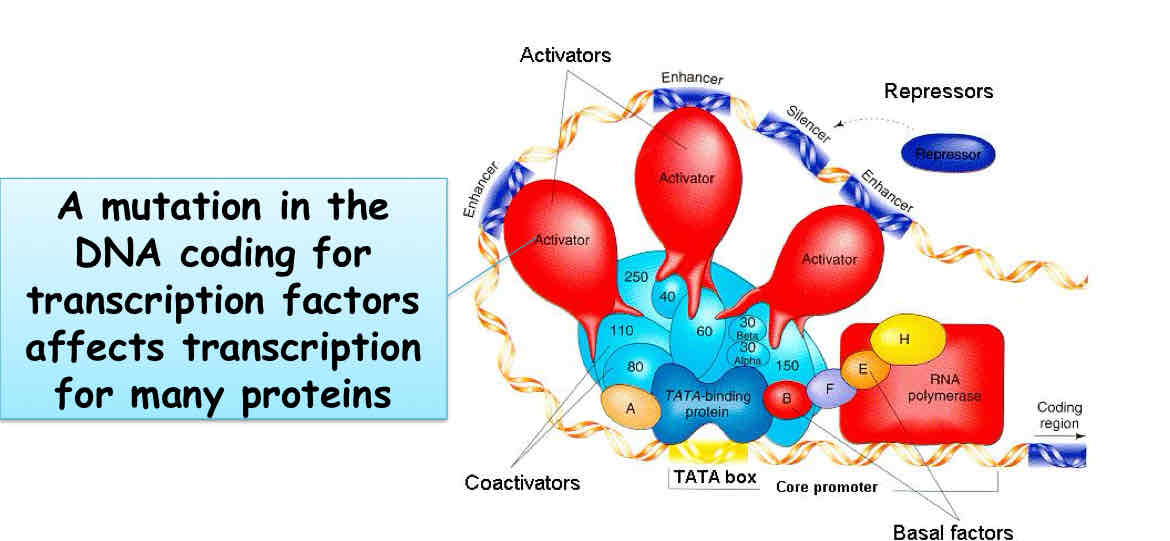
Regulatory Genes
Regulatory Genes control when, where, & which expressed
single mutations may affect expression of many genes during development
Ex: DNA Coding for Transcription factors affects transcriptions for many proteins.
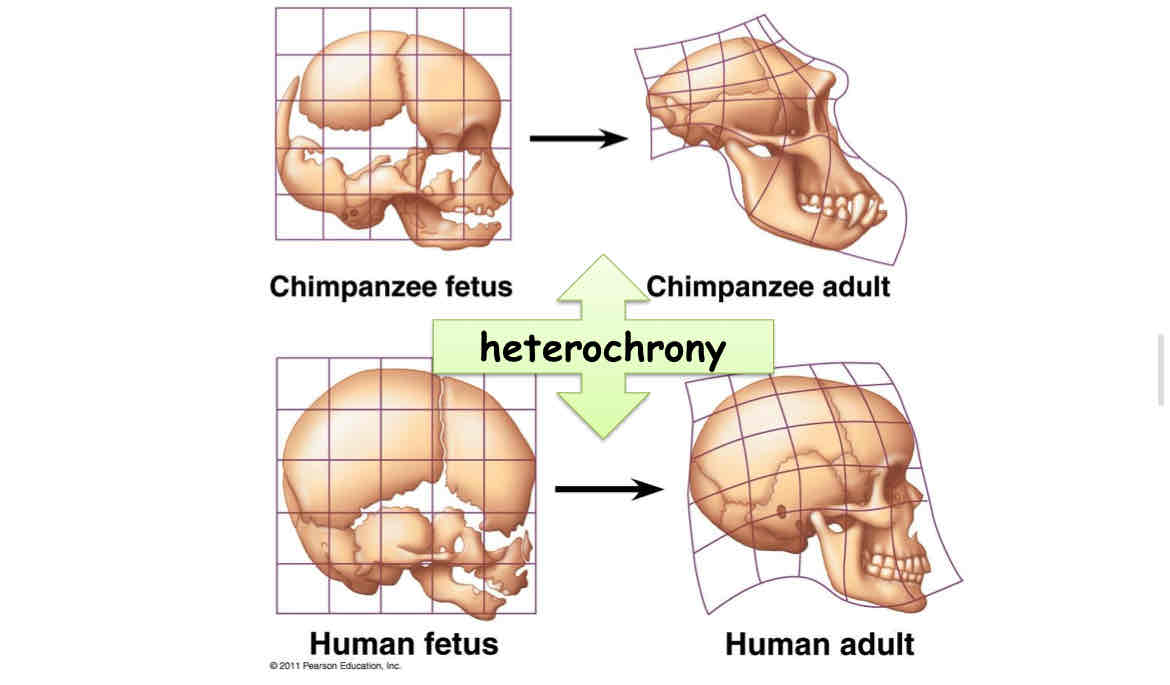
Heterochrony
Heterochrony is evolutionary change in form due to change in rate or timing of developmental events
a change in growth rate of parts can produce a new final shape
Ex: Premature children
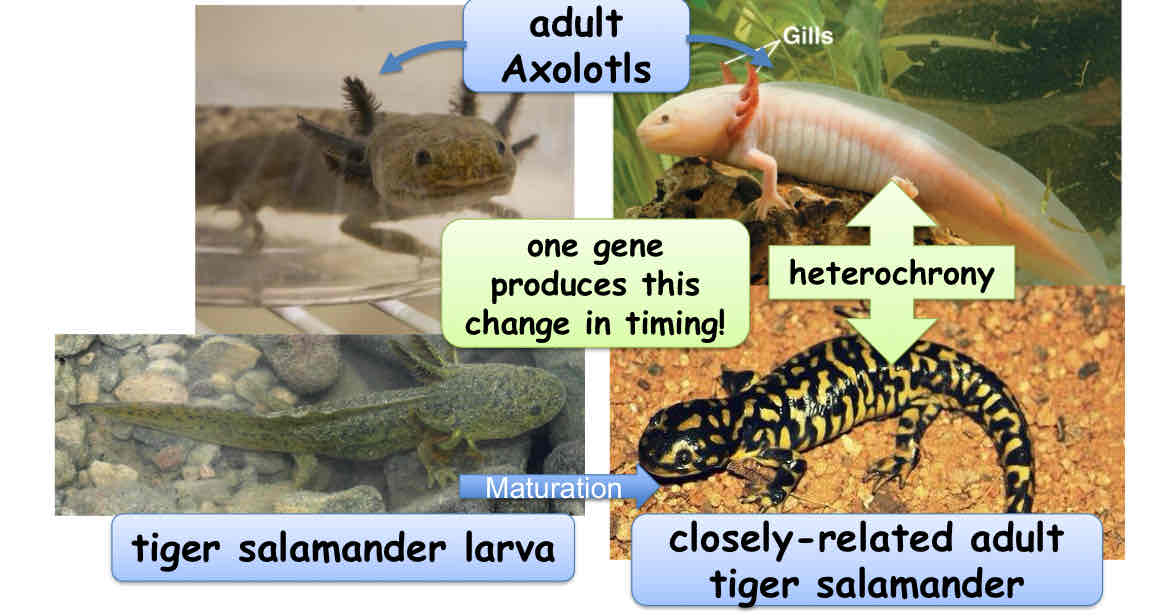
Paedomorphosis
Paedomorphosis is a change of timing produces a sexually mature adult with juvenile features
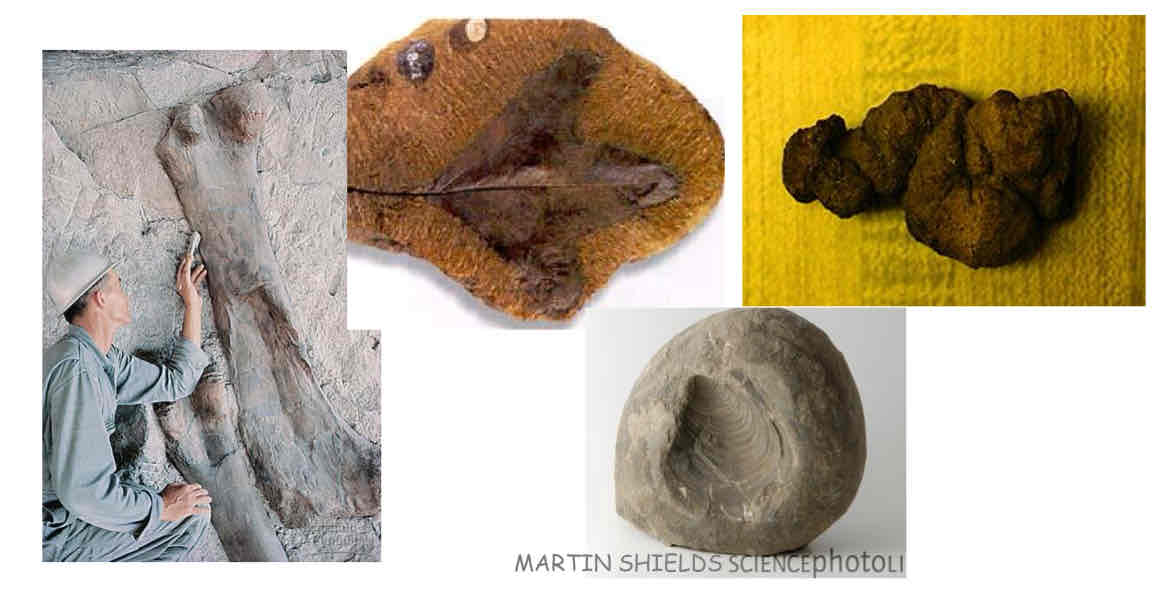

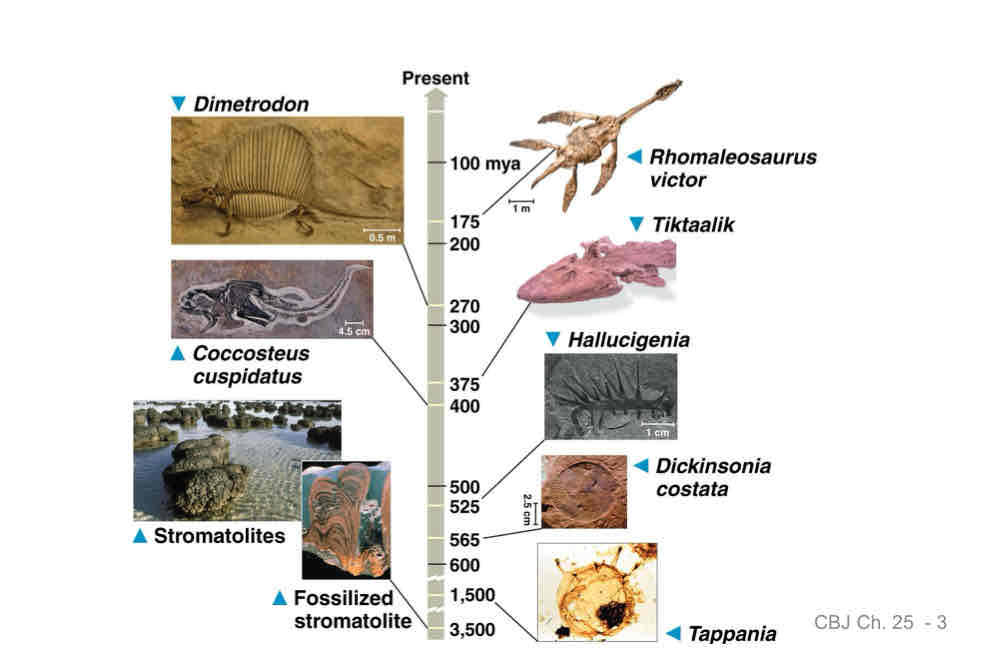
The Fossil Record
Fossils are remnants, casts, or traces of organisms
What do fossils tell us ?
anatomy, habitats, diet, lifestyle, activity, genetic info (DNA)

Hadean Eon
Planet formed 4.6 bya
molten rock surface, no liquid water
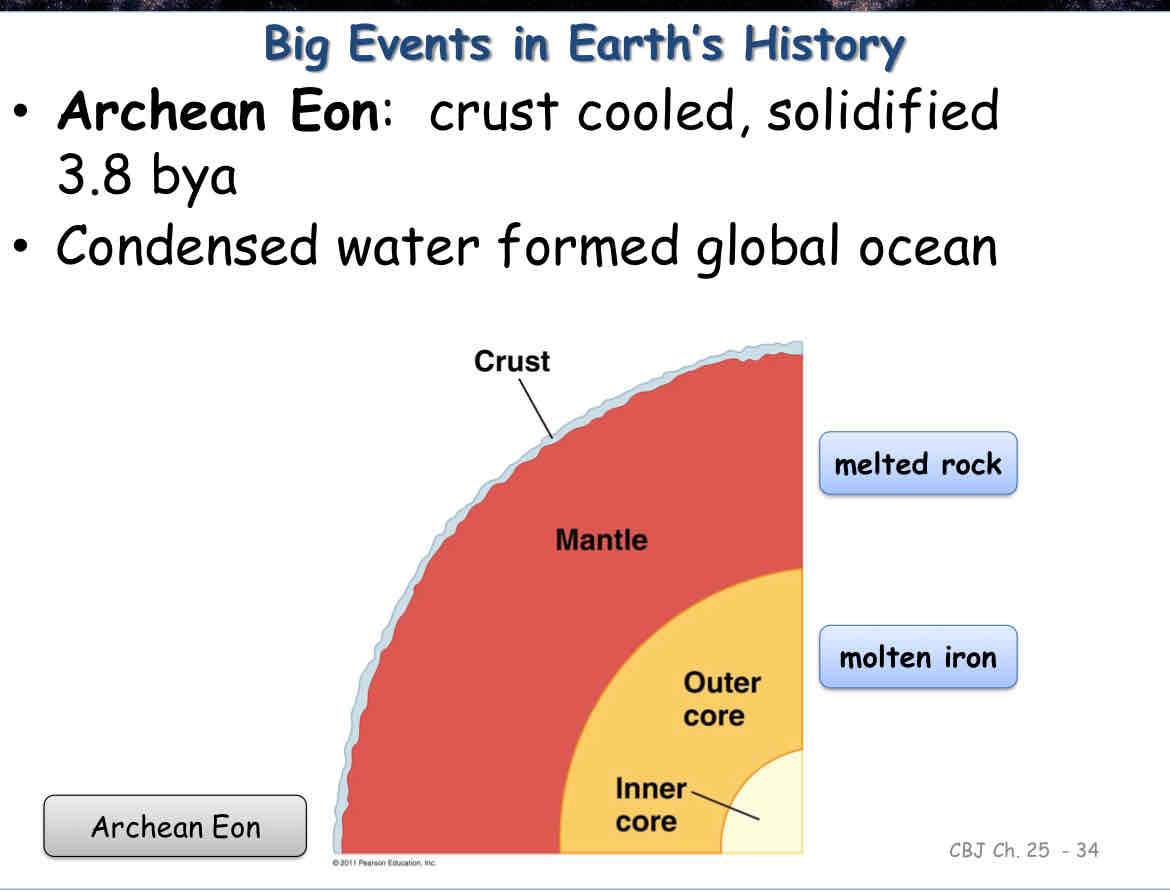
Archean Eon
crust cooled, solidified, 3.8 bya
Condensed water formed global ocean
Tectonic plates shift
First life ! Prokaryotic cells

Proterozoic Eon
eukaryotic life began 2.1 bya
Continents form as islands merge
First multicellular life
Paleozoic Era
Cambrian explosion of animal diversity
Ex. Age of Fishes, First land vertebrates
Ends with Permian Mass Extinction (Volcano) THE BIG ONE
Mesozoic Era
Age of Dinosaurs & reptiles
Cone bearing seed plants dominate
First mammals & birds
Breakup of Pangaea ( climate change, allopathic speciation, species distribution)
Cretaceous Mass Extinction
Mesozoic Era ends (meter, Yucatán peninsula)
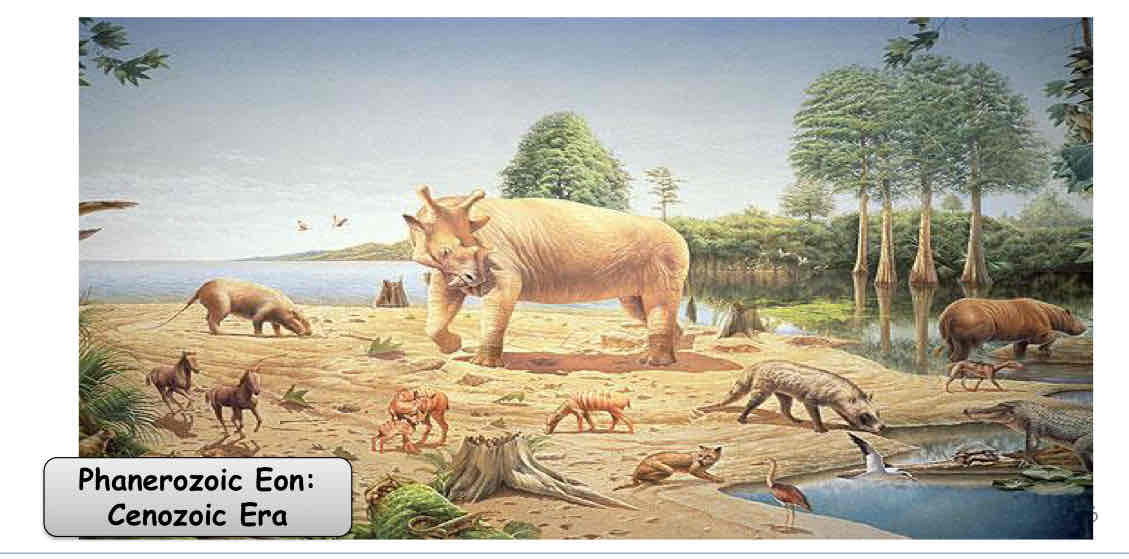

Cenozoic Era
major diversification of mammals, flowering plants, insects, birds
First humans