Exam 3 Thinking, Language, and Thought
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Cognition
All mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating information.

Metacognition
Cognition about our cognition; Keeping track of and evaluating our mental processes.

Concepts
Mental groupings of similar objects, events, ideas, or people.

Prototype
Mental image or best example of a category or concept.
Trial and Error
Attempt various solutions to a problem until they find one that works; systematically or otherwise.

Algorithms
Methodical, logical rule, or procedure that guarantees a solution to a problem; slow process
Heuristics
Simpler thinking strategies that are usually speedier than an algorithm, but more prone to error.

Insight
Abrupt, true-seeming, and often satisfying solution (eureka moment).

Confirmation Bias
Searching for information that supports our ideas and ignoring or distorting contradictory evidence.

Fixation
Inability to see a problem from a new perspective.

Mental Set
The tendency to approach a problem with previously successful mindset.

Intuition
Effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought; Implicit/unconscious knowledge gained from experience.

Representativeness Heuristic
Judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent or match particular prototypes.

Availability Heuristic
Judging the likelihood of events based on their mental availability in memory.

Motivated Reasoning
Rather than using evidence to draw conclusions, conclusions are used to assess evidence.

Framing
Changing the perception of an idea or issue through deliberate presentation.

Creativity
Divergent Thinking
Expanding the number of possible problem solutions.

Convergent Thinking
Narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution.

Components of Creativity
Expertise, Imaginative Thinking, Venturesome Personality, Intrinsic Motivation, Creative Environment

Language
A dynamic system of symbols used for thought and communication.

Phoneme
Smallest distinctive sound unit in language.
Morpheme
Smallest language unit that carries meaning.

Grammar
System of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand each other.

Semantics
Deriving meaning from sounds.

Syntax
Rules for ordering words.

Noam Chomsky
Father of modern linguistics; Humans predisposed to learn grammar; All languages share basic grammar rules.

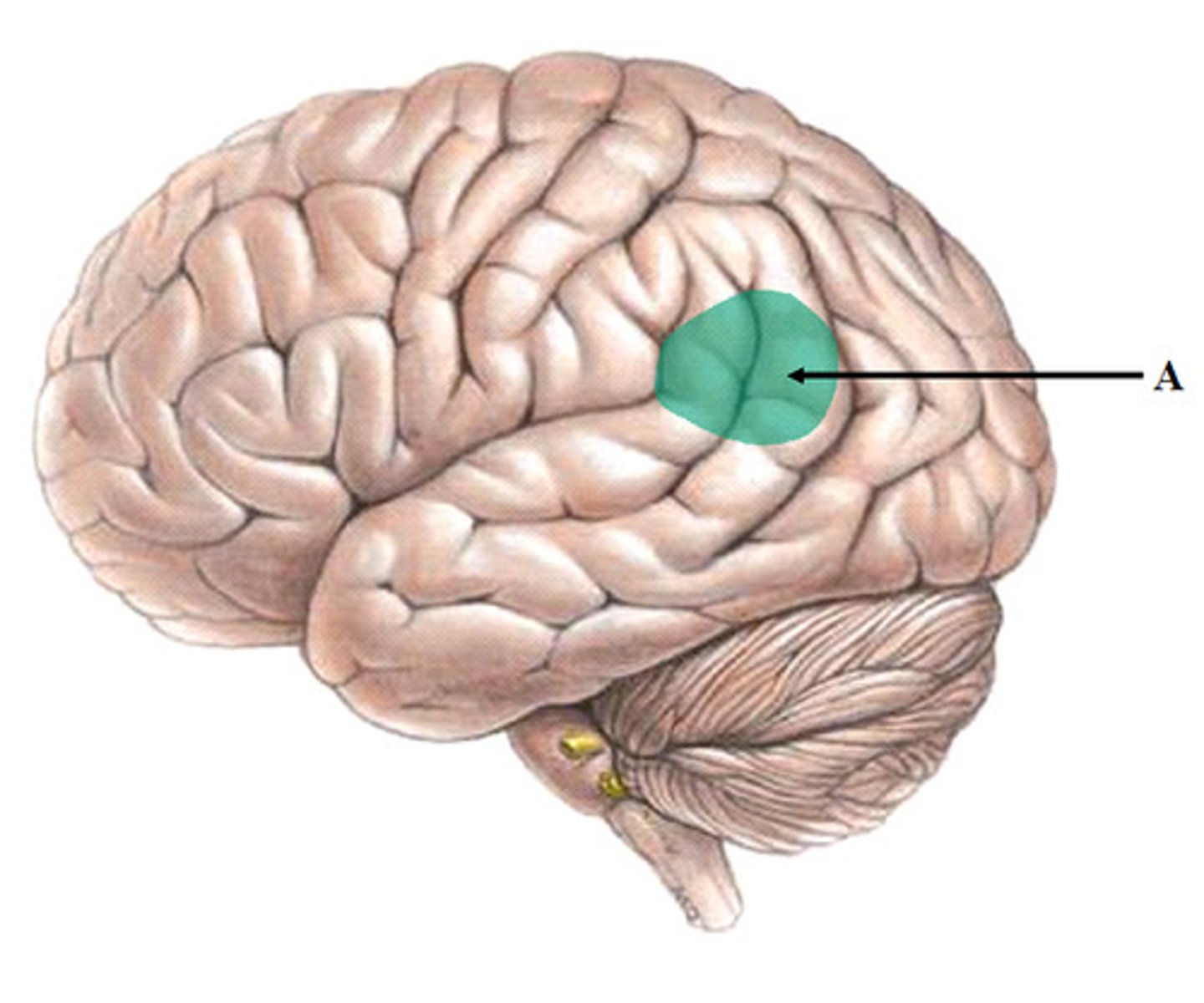
Broca's Area
Frontal lobe brain area, usually in the left hemisphere; Helps control language expression by directing the muscle movements involved in speech.
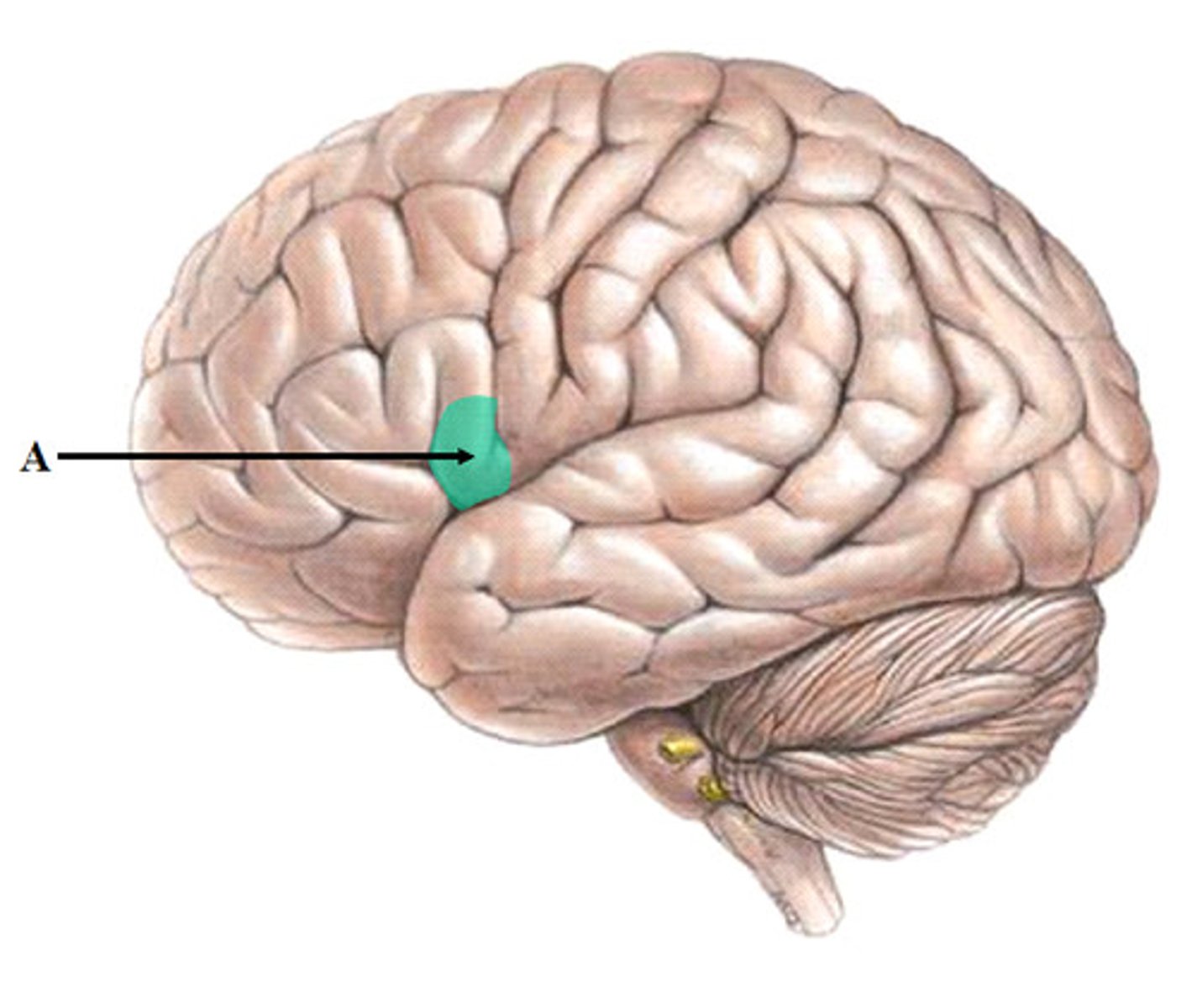
Wernicke's Area
Brain area in the left temporal lobe; Involved in language comprehension and expression.
Linguistic Relativism
Our words influence our thinking (mental categories. preferred pronouns).

Linguistic Determination
We can think about things that we don't have words for.