Toxicology Lecture 2
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dose Responses and Bioassays
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Define “Hazard.”
the intrinsic dangerous property of a toxin.
Define “Risk“ in toxicology
The probability of having a bad outcome when exposed to a hazardous material.
How can toxicants be managed?
either by reducing the hazards, or decreasing the risk.
How are chemical/industrial hazards determined when it comes to humans?
“epidemiology“ - studying patterns in populations. For example you can look at data and determine that neighbourhoods near coal plants get sick more often.
What’s the issue with epidemiology studies?
Correlation ≠ causation.
You can say that neighbourhoods near coal plants get sick more often, but without experiments you can’t definitively say that coal is what makes them sick.
Other ways to determine hazards -
Test on human cell cultures. Called in vitro. Often Henrietta Lack’s cells.
Compare to a known toxin. Is the structure similar to another?
Animal testing. called in vivo.
What is the name we give animal testing to make ourselves feel better about what we’re doing?
Bioassays.
Besides the obvious, what do we use animal testing for? Hint: to find out the amount of toxins that can be put in the en_________________.
How many toxins can be present in the environment without causing biology damage.
The three R’s of animal testing?
Replacement, Reduction, Refinement.
Use computer models if you can.
Reduce the amount of lives you make miserable.
If you must force an animal to live through hell on earth, refine the experiment so that minimal hell must be experienced.
What are ‘carriers‘ in toxicology?
substances used to dissolve hydrophobic toxins so that they can be properly taken in by the animal.
What does ‘dose-response relationship‘ mean?
data that quantifies exposure and response. Or, dose to an ‘endpoint.’ Usually defined as death. Death is easy.
dose-response curve?
the shape that dose response relationships take when graphed.
How is ‘dose‘ measured?
we use mg/kg to ensure every animal is getting an equivalent amount of toxin for their body. Great!
What does ‘acute exposure‘ mean to a toxicologist?
hours to days. (often 96hr/4 days)
What does ‘chronic exposure‘ mean to a toxicologist?
months or years.
what is a “Graded dose-response“ graph?
Graphing out an individuals response. Can graph out two separate effects, if you want.
what is a “Quantal dose-response“ graph?
testing a population. In this population, an individual is either a “responder“ or a “non-responder.“
Rank 4 routes of exposure, based off of how fast it takes to get to the bloodstream.
Injection, (directly into the blood).
Inhalation
Eating
Applied to the skin.
What other types of concentration are there, besides LC50?
NOEC: No Observation Effect Concentration - Highest dose you can have where nothing happens.
LEOC: Lowest Observable Effect - Lowest dose where you get responses.
Nominal vs Measured Concentrations?
Nominal: The amount you applied.
Measured: How much the animal actually metabolized.
How can we use dose response curves for medication?
ED50: The dose that has the intended effect in 50% of the population
TD50: The dose that starts to do bad things to 50% of the population.
What is ‘TI‘?
Therapeutic index: TD50/ED50.
If you get a high number, the drug is safe.
Low number, maybe don’t add this drug to the market.
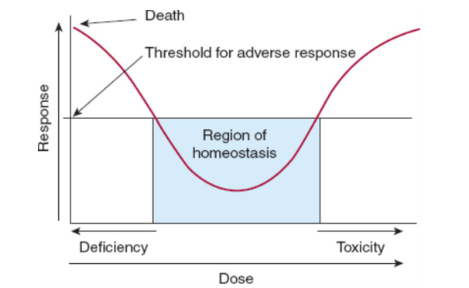
What would a ‘U‘ shape mean in a dose-response curve graph?
it means that the substance is necessary in the body - in the right amount.
Low amounts = death
High amounts = death.
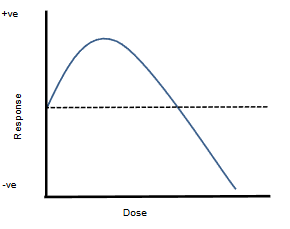
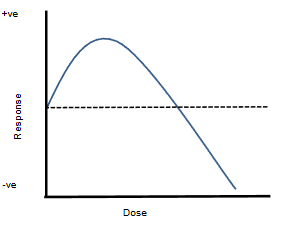
What would a this shaped graph mean in a dose-response curve graph?
that the substance is beneficial in small amounts, but then becomes toxic.
Note: Not compatible with xenobiotics. Nobody wants those.
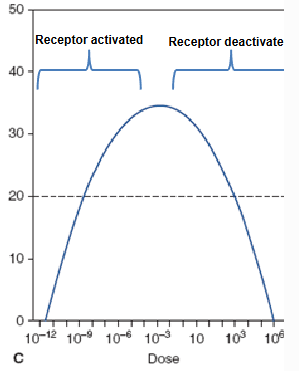
What would a this shaped graph mean in a dose-response curve graph?
At low responses, they interact with the stuffs,
At high responses, they overload the stuffs and they don’t even pay attention to it and nothing happens.
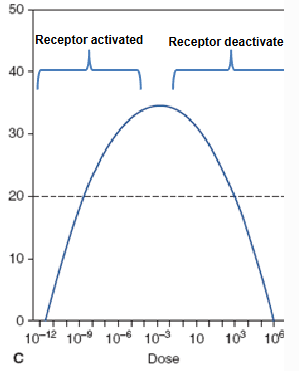
‘Subchronic???‘
This means that a lot of the important stuff that happens is NOT death, but, you know, living in misery.
BRO St. Agatha Catholic School!!! it’S A REAL PLACEIN TOREONTRO TORONTA TORONTO HE WASN’T JOKING HE ACTUALLY DID GET FLASHBACKS OMG THAT’S SO FUNNY WTF
St. Agatha’s Catholic School.
Wow so um, what do we do to the animals if they live??
Euthanize them and uhhh…. yeah see what’s up. NO SURVIVORS ARE ALLOWED.
What is a Biomarker?
A measurable biological response that, if you find, tells you that an animal has undergone a certain toxin.